| |
14:15
|
0127.
 |
Texture Feature Analysis of Quantitative and Semi-Quantitative
DCE-MRI Metrics for Early Prediction of Breast Cancer Therapy
Response 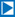
Guillaume Thibault1, Alina Tudorica2,
Aneela Afzal2, Stephen Chui2, Arpana
Naik2, Megan Troxell3, Kathleen Kemmer2,
Karen Oh2, Nicole Roy2, Megan Holtorf2,
Wei Huang2, and Xubo Song2
1BME, OHSU, Portland, OR, United States, 2OHSU,
Portland, OR, United States, 3OHSU,
portland, OR, United States
36 breast cancer patients underwent research DCE-MRI before
and after one cycle of neoadjuvant chemotherapy. 3D tumor
imaging texture features were extracted from parametric maps
of quantitative pharmacokinetic (PK) and semi-quantitative
DCE-MRI parameters, and correlated with pathologically
measured post-therapy residual cancer burden (RCB). Texture
features from quantitative PK parameters were found to be
more useful than those from semi-quantitative metrics for
early prediction of therapy response, while the features
from the SSM PK parameters were superior to the SM
counterparts for prediction of response.
|
| |
14:27
|
0128.
 |
Role of the Intravoxel Incoherent Motion (IVIM) Imaging in the
Pre-treatment Prediction and Early Response Monitoring for
Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy in Locally Advanced Breast Cancer 
Shunan Che1, Chunwu Zhou1, Xinming
Zhao1, Jing Li1, and Bing Wu2
1department of radiology, Cancer Hospital,
Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences, Peking Union Medical
College, Beijing, China, People's Republic of, 2GE
Healthcare MR Research China, Beijing, China, People's
Republic of
Purpose: to explore whether IVIM can determine pre-treatment
differences or monitor early response in breast cancer
patients receiving NAC. Materials and Methods: thirty-six
patients examined with multiple-b DWI were divided into MHR
and NMHR groups. Parameters between MHR and NMHR groups were
compared. Results: the D and f value at the baseline and
mid-treatment of NAC showed significantly differences
between MHR and NMHR. ?D and ?f were significantly higher in
MHR than in NMHR. Conclusion: the D and f value showed
potential value in the pre-treatment prediction and early
response monitoring to NAC in local advanced breast.
|
| |
14:39
 |
0129.
 |
Evaluation of FLAIR maps by PRM provides for glioma response
assessment 
Deborah Sharon Honrado Guest1, Craig Galbán1,
Gary Luker1, Thomas Chenevert1,
Benjamin Lemasson2, Robin Johannes Marius Navest3,
Klaas Nicolaij3, and Brian Ross1
1Radiology, University of Michigan, Ann Arbor,
MI, United States, 2Institut
des Neurosciences, Université Grenoble Alpes, Grenoble,
France, 3Department
of Biomedical Engineering, Technische Universiteit
Eindhoven, EINDHOVEN, Netherlands
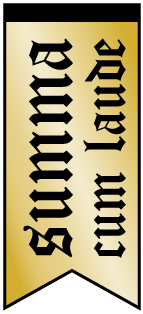
This study investigates the possibility of adapting the PRM
method for use with normalized FLAIR images to predict OS
and TTP for indication of tumor recurrence. Glioma patients
were separated into non-responders and responders to
treatment. Voxels present in the union of the VOIs for the
rFLAIR images were used to evaluate the PRMrFLAIR values
and categorize patients into groups based on changes in
signal intensity. This study shows that predicting TTP and
OS is achievable using PRM with rFLAIR maps for patients
treated with TMZ/IR and provides the first demonstration of
quantifying FLAIR signals in patients over time.
|
| |
14:51
 |
0130.
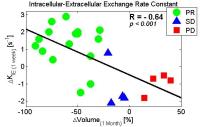 |
Intracellular-extracellular water exchange as a biomarker of
tumor response to stereotactic radiosurgery 
Hatef Mehrabian1,2, Kimberly L Desmond3,
Arjun Sahgal1,4, Hany Soliman1,4, Anne
L Martel1,2, and Greg J Stanisz1,2
1Physical Sciences, Sunnybrook Research
Institute, Toronto, ON, Canada, 2Medical
Biophysics, University of Toronto, Toronto, ON, Canada, 3Medical
Physics and Applied Radiation Sciences, McMaster University,
Hamilton, ON, Canada, 4Radiation
Oncology, Odette Cancer Centre, Toronto, ON, Canada
Targeted radiation treatments are expected to induce DNA
damage in tumor cells which leads to apoptosis. Apoptotic
cells experience an increase in cell membrane permeability
and surface-to-volume ratio, both of which result in
increased water exchange rate between intracellular and
extracellular compartments. Using a three compartment
relaxation model we demonstrate that early changes in
intracellular-extracellular water exchange correlated well
with tumor volume change one-month post-treatment. Moreover,
when the water exchange rate was combined with early tumor
volume change and was employed in a classifier, the patients
with partial response and progressing disease could be
identified with a very high accuracy.
|
| |
15:03
 |
0131.
 |
Multimodality functional imaging in radiation therapy during
treatment: relationship between DW-MRI and 18F FDG PET in head
and neck squamous cell carcinoma 
David Aramburu Nuñez1,2, Antonio Lopez Medina3,
Moises Mera Iglesias4, Francisco Salvador Gomez5,
Vaios Hatzoglou6, Ramesh Paudyal1,
Alfonso Calzado2, Joseph O Deasy1,
Amita Shukla-Dave7, and Victor M Muñoz8
1Medical Physics, Memorial Sloan-Kettering Cancer
Center, New York, NY, United States, 2Department
of Radiology, Complutense University, Madrid, Spain, 3Medical
Physics & Radiological Protection, Galaria - Hospital do
Meixoeiro – Complexo Hospitalario Universitario de Vigo,
Vigo, Spain, 4Medical
Physics, Oncoserv, Santiago de los Caballeros, Dominican
Republic, 5Medical
Physics and Radiological Protection, Galaria - Hospital do
Meixoeiro – Complexo Hospitalario Universitario de Vigo,
Vigo, Spain, 6Radiology,
Memorial Sloan-Kettering Cancer Center, New York, NY, United
States, 7Medical
Physics & Radiology, Memorial Sloan-Kettering Cancer Center,
New York, NY, United States, 8Radiation
Oncology, Galaria - Hospital do Meixoeiro – Complexo
Hospitalario Universitario de Vigo, Vigo, Spain
Biologically guided radiotherapy needs an understanding of
how different functional imaging techniques interact and
link together. DW-MRI and 18F FDG-PET techniques were used
in this study for achieving this objective. 5 HPV-, HNSCC
patients underwent 20 DW-MRI and 10 18F-FDG-PET/CT scans
before and during radiation therapy. ADC maps derived from
DW-MRI and SUV values from 18F-FDG were used for evaluating
tumor response. The initial evaluation of the preliminary
results suggests that in these solid tumors cellularity is
inversely proportional to the glucose metabolic uptake. The
survival status and functional metrics show different trends
for NED, AWD and DOD.
|
| |
15:15
|
0132.
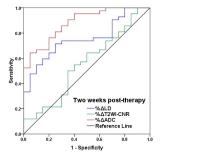 |
MRI in predicting the response of gastrointestinal stromal tumor
to targeted therapy: a patient-based multi-parameter study 
Lei Tang1, Jian Li2, Ying-Shi Sun1,
Xiao-Ting Li1, Zi-Yu Li3, Xiao-Yan
Zhang1, and Lin Shen 2
1Radiology, Peking University Cancer Hospital &
Institute, Beijing, China, People's Republic of, 2GI
medicine, Peking University Cancer Hospital & Institute,
Beijing, China, People's Republic of, 3GI
surgery, Peking University Cancer Hospital & Institute,
Beijing, China, People's Republic of
The percentage changes of the ADC in GIST after two weeks of
targeted therapy exhibited reliable performance in response
prediction, and these variables outperformed T2WI-CNR and
the longest diameter. We suggest that patients continue
their treatment regimens if the percentage increases in the
ADC are no less than 15% after two weeks of therapy. In
contrast, if the ADC decreases or exhibits almost no change,
then a shortening of the follow-up time intervals is highly
recommended to detect possible drug resistance at an early
stage.
|
| |
15:27
 |
0133.
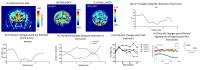 |
Quantitative MRI and optoacoustic imaging tracks treatment
response in tumor 
Prashant Chandrasekharan1, Ghayathri Balasundaram1,
Amalina Binte Ebrahim Attia1, Chris Jun Hui Ho1,
Xuan Vinh To1, Hui Chien Tay1, Kai
Hsiang Chuang1, and Malini Olivo1
1A*STAR, Singapore Bio Imaging Consortium,
Singapore, Singapore
Quantification of oxygenation or hypoxia in a tumor plays a
key role in the treatment response and the overall survival
of glioma patient. This work illustrates a preclinical
study with the use of multimodal imaging technique to
correlate tumor oxygenation and blood perfusion, as well as
to assess the changes involved in the perturbation of the
tumor system using a vascular disruptive agent.
|
| |
15:39
 |
0134.
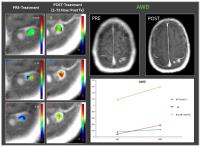 |
Assessment of early treatment response by IVIM DW-MRI and
DCE-MRI in patients with brain metastases treated with
stereotactic radiosurgery. 
David Aramburu Nuñez1,2, Kathryn Beal3,
Vaios Hatzoglou4, Andrei Holodny4,
Ramesh Paudyal1, Yonggang Lu5, Joseph
O Deasy1, and Amita Shukla-Dave6
1Medical Physics, Memorial Sloan-Kettering Cancer
Center, New York, NY, United States, 2Department
of Radiology, Complutense University, Madrid, Spain, 3Radiation
Oncology, Memorial Sloan-Kettering Cancer Center, New York,
NY, United States, 4Radiology,
Memorial Sloan-Kettering Cancer Center, New York, NY, United
States, 5Radiation
Oncology, Washington University, St. Louis, MO, United
States, 6Medical
Physics & Radiology, Memorial Sloan-Kettering Cancer Center,
New York, NY, United States
In clinical settings it is essential to accurately assess,
whether or not a brain metastasis has been successfully
treated or whether the metastasis require additional
treatment. This is the first study that evaluated brain
metastases with IVIM DW-MRI and DCE-MRI data both pre- and
post- stereotactic radiosurgery (SRS). The preliminary
results are promising as it will inform the treating
physicians at an early time point about which patients will
benefit from SRS (or not). The survival status and
functional metrics show different trends for both AWD and
DOD that need to be validated in larger patient population.
|
| |
15:51
|
0135.
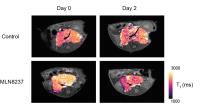 |
T1 is a
biomarker of therapy-induced cell death in the Th-MYCN genetically-engineered
murine model of neuroblastoma. 
Yann Jamin1, Evon S.C. Poon2, Albert
Hallsworth2, Hannah Webber2, Laura S.
Danielson2, Dow-Mu Koh1, Louis Chesler2,
and Simon P. Robinson1
1Division of Radiotherapy & Imaging, The
Institute of Cancer Research, London, United Kingdom, 2Division
of Cancer Therapeutics and Division of Clinical Studies, The
Institute of Cancer Research, London, United Kingdom
In this study we demonstrate that T1 provides a
non-invasive biomarker of response to MLN8237, a potent
Aurora A kinase inhibitor, in the Th-MYCN genetically-engineered
murine model of neuroblastoma, a childhood cancer of the
nervous system. Histopathological characterisation
demonstrates that T1 is
a generic biomarker of cell death in this model. T1 quantification
in pediatric early-phase clinical trials could potentially
help to accelerate the development of urgently needed novel
targeted therapies for children with neuroblastoma.
|
| |
16:03
 |
0136.
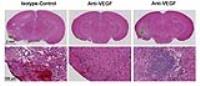 |
Can anti-VEGF Antibody Reverse Radiation Necrosis? A Preclinical
Investigation 
Chong Duan1, Carlos J Perez-Torres2,
Liya Yuan3, John A Engelbach4,
Christina T Tsien5, Keith M Rich3,5,
Robert E Schmidt6, Joseph JH Ackerman1,4,7,8,
and Joel R Garbow4,8
1Chemistry, Washington University in St. Louis,
St. Louis, MO, United States, 2Radiological
Health Sciences, Purdue University, West Lafayette, IN,
United States, 3Neurosurgery,
Washington University in St. Louis, St. Louis, MO, United
States, 4Radiology,
Washington University in St. Louis, St. Louis, MO, United
States, 5Radiation
Oncology, Washington University in St. Louis, St. Louis, MO,
United States, 6Neuropathology,
Washington University in St. Louis, St. Louis, MO, United
States, 7Medicine,
Washington University in St. Louis, St. Louis, MO, United
States, 8Alvin
J Siteman Cancer Center, Washington University in St. Louis,
St. Louis, MO, United States
Recently, radiation necrosis (RN) has been treated
clinically using bevacizumab, an anti-VEGF antibody. While
bevacizumab reduces radiographic RN volume, the treatment
has potentially serious complications and rebound phenomena
after the discontinuation of the therapy. In the present
study, we investigated the anti-VEGF treatment of pure
radiation necrosis in a mouse model. Favorable radiographic
appearance of RN were observed following the anti-VEGF
treatment. However, the lesions were not completely resolved
histologically (e.g., focal mineral deposits were observed
in the treated mice). In addition, despite the treatment,
VEGF and HIF-1α were still upregulated, which presents the
potential risk of recurrence of RN.
|
|










