Applications of Molecular Imaging & Hyperpolarized MRI
Electronic Poster
Molecular Imaging
Monday, 24 April 2017
| Exhibition Hall |
16:15 - 17:15 |
| |
|
Computer # |
|
3591.
 |
25 |
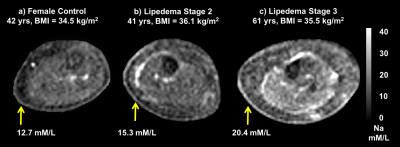
A novel application of quantitative sodium MRI for distinguishing lipedema from obesity 
Rachelle Crescenzi, Adriana Marton, Paula Donahue, Helen Mahany, Ping Wang, Joshua Beckman, Manus Donahue, Jens Titze
Sodium MRI is a molecular imaging tool that may be sensitive to the impact of lymphatic impairment on tissue homeostasis, yet has not been evaluated in a clinical population with a lymphatic disorder. Lipedema is a lymphatic fat-disorder that is under-recognized due to a need for further advanced MR imaging to diagnosis and assess treatment efficacy of the condition. Here, we apply quantitative 3T sodium imaging for the first time in a lipedema cohort to quantify tissue sodium levels and found elevated sodium concentration in the skin and muscle of patients with lipedema compared to BMI- and age-matched controls.
|
|
3592.
 |
26 |
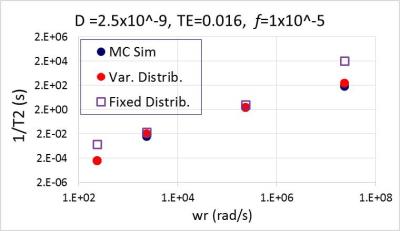
The verification of the T2 distributed relaxation model (DRM) for a polydisperse nanoparticle system 
Bashar Issa
Theories describing T2 enhancement due to the presence of superparamagnetic particles agree well with experimental and Monte Carlo simulation data under the condition that the particles are monodisperse both in size and magnetization. We present a T2 distributed model that takes into account the particle size and magnetization distributions. The results shown confirm the ability of the distributed relaxation model to correctly predict T2 values for a mixed MAR and SDR sample of MNP under a wide range of values of size, magnetization, volume fraction, etc. The new model will reduce the error in calculating T2 values using the mean size and mean magnetization values when a distribution of MNP exists.
|
|
3593.
 |
27 |
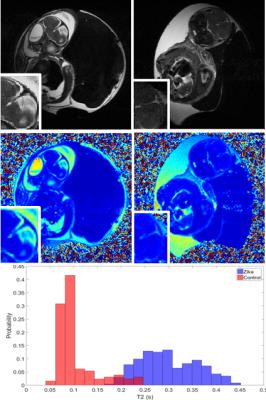
Chicken Embryo: An Excellent Platform for Monitoring Zika Virus Induced Microcephaly and Tracking Stem Cells - permission withheld
Qun Zhao, Forrest Goodfellow, Gregory Simchick, Thomas Hodge, Melinda Brindley, Steven Stice
A chicken embryo is the developmental biology’s oldest model organism. In ovo development of the chicken embryo closely mirrors human embryo development. The relatively large size, ease of access, and lack of maternal motion generated in pregnant mammals are distinct advantages the chicken embryo model provides. The chicken embryo provides an excellent platform for monitoring morphology and metabolism of central neural system (CNS) by using MRI or NMR spectroscopy over the course of development. In this presentation our recent work on monitoring Zika virus induced microcephaly and tracking stem cells are presented.
|
|
3594.
 |
28 |
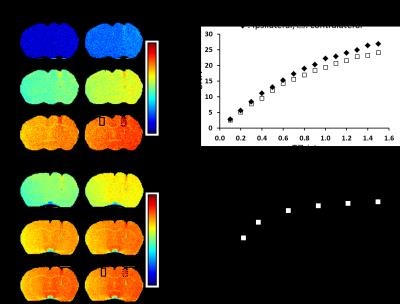
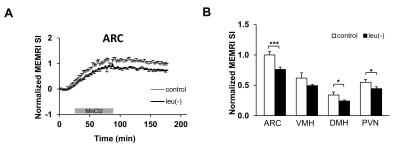
Leucine deprivation causes hypothalamic neuronal inhibition accompanied by systemic metabolic changes. 
Anna Ulyanova, Jadegoud Yaligar, Anantharaj Rengaraj, Tian Xianfeng, Venkatesh Gopalan, Sanjay K Verma, Christiani Jeyakumar Henry, S Sendhil Velan
The lack of dietary essential amino acid leucine influences energy metabolism via hypothalamic leptin signaling pathway. However, these neural circuits and its relationship with pathogenesis of obesity still remain unclear. In this work we investigated the hypothalamic neural pathway, abdominal fat and liver fat by multi-parametric imaging in leucine deficient diet fed mice. MEMRI results indicated that leu deficiency triggers neuronal inhibition in certain hypothalamic regions suggesting POMC neuronal pathway involvement in enhanced energy expenditure through leptin signaling pathway. Combined with systemic metabolic changes this may facilitate in understanding of amino acid sensing and metabolic regulatory network of energy homeostasis.
|
|
3595.
 |
29 |
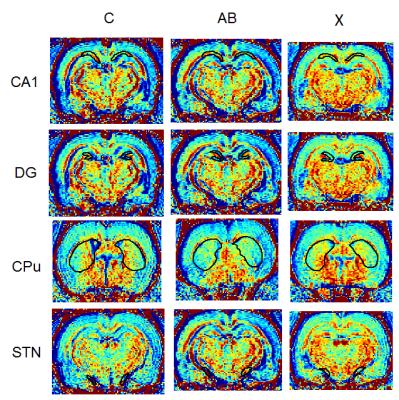
Detecting neuronal activity in rat model of dementia with Lewy bodies by using MEMRI 
Meng-Syuan Lin, Ying-Jui Ho, Jun-Cheng Weng
Dementia with Lewy bodies (DLB) is thought to be the second commonest cause of neurodegenerative dementia in older people, accounting 15 to 25% cases at autopsy. However, to date there are no reliable methods of instrumental and laboratory diagnosis of this disease while its treatment is based on reducing the symptoms. The drug X has been shown to have neuroprotective effects in neurodegenerative diseases. Therefore, we aimed to clarify the medicinal effectiveness of drug X through manganese-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging (MEMRI). Our results indicated that drug X may have clinical potential in the treatment of DLB.
|
|
3596.
 |
30 |
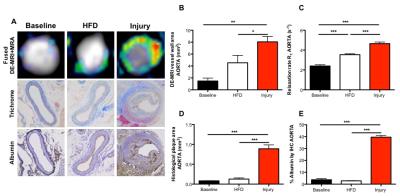
Aortic endothelial injury modifies plaque composition at a distally located site through increased monocyte extravasation 
Begona Lavin Plaza, Alkystis Phinikaridou, Marcelo Andia Kohnenkampf, Rene Botnar
The deleterious impact of atherosclerosis on other cardiovascular diseases has recently been shown, but the effect of vascular alterations on plaque formation at a distal site, including the underlying mechanisms of this systemic response, has not been elucidated. In this study, we used an albumin-binding contrast agent to assess whether (1) endothelial injury in the abdominal aorta accelerates plaque progression in the brachiocephalic artery located distally to the site of injury and (2) whether monocytes can be the link between acute and systemic response.
|
|
3598.
 |
32 |
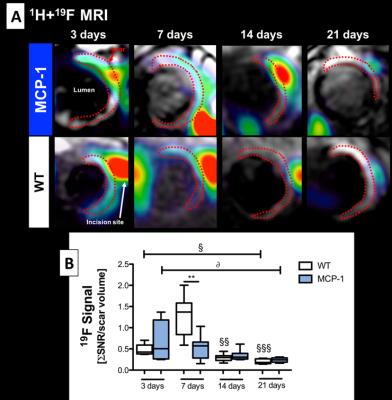
Molecular Imaging of the effects of monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 (MCP-1) on extracellular matrix remodeling following myocardial infarction - permission withheld
Isabel Ramos, Markus Henningsson, Maryam Nezafat, Begoña Lavin, Silvia Lorrio, Alkystis Phinikaridou, Ulrich Flögel, Ajay Shah, René Botnar
After a myocardial infarction (MI) the degree of inflammation and its timely resolution, together with the degradation and deposition of extracellular matrix proteins are key processes in post-MI healing. Monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 (MCP1) plays an important role in the recruitment of monocytes/macrophages and its absence has revealed a significant reduction of inflammatory cell recruitment and subsequent ECM protein production in the infarcted area. Here, we explored the merits of multinuclear 1H/19F MRI for the simultaneous assessment of myocardial inflammation and remodelling in a murine model of MI. 19F containing nanoparticle that is avidly taken up by macrophages was used to investigate inflammatory cell recruitment into injured myocardium2, and a small molecular weight gadolinium-based elastin-specific MR contrast agent was used to evaluate changes of elastin content post-MI3.
|
|
3597.
 |
31 |
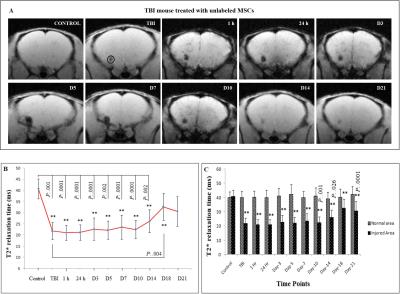
Precise longitudinal MRI tracking of systemically infused dual labelled mesenchymal stem cells and their regenerative potential in traumatic brain injury mice - video not available
Sushanta Mishra, Subash Khushu, Gurudutta Gangenahalli
Stem cells transplantation has emerged as a promising alternative therapeutic due to its potency at injury site. Thus, tracking of stem cells is very essential. Here, we have described a serial in vivo tracking of implanted stem cells through 7T MRI and its differentiation potential into neuronal precursors. T2*-weighted images and relaxation study demonstrated a significant signal loss and effective decrease in T2* relaxation time on day-3 at injury site. Expression of neuronal markers like GFAP, MAP2 and NeuN were observed in transplanted MSCs. The proposed procedure could be extrapolated for stem cell tracking and therapies in various neurodegenerative diseases.
|
|
3600.
 |
34 |
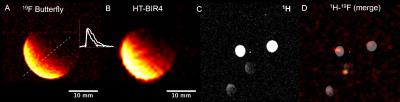
Post-mortem Cardiac and Skeletal Muscle 19F MRI of PFCE-labeled and FuGENE-transfected Cardiac Progenitor Stem Cells in the C57BL/6 Mouse 
Christakis Constantinides, Ricardo Carnicer, Ayman Al Haj Zen, Mahon Maguire, Eileen McNeil, Edyta Swider, Mangala Srinivas, Carolyn Carr, Jurgen Schneider
Stem cell (SC) technologies constitute a potential new therapeutic approach aiming to achieve tissue regeneration. Despite advances in the visualization of pre-labeled SCs with SPIOs (1H MRI), and of nanoparticles (NPs) containing perfluoro-crown-ethers (PFCE) [2-4] in 19F MRI, there have been no prior reports on cardiac 19F imaging with direct SC injections. We report herein the implementation of a fast acquisition protocol for cardiac and skeletal muscle 19F imaging of the C57BL/6 mouse post-mortem, and identify the minimum cellular load for PFCE labels to achieve visualization following direct SC cell injections.
|
|
3601.
 |
35 |
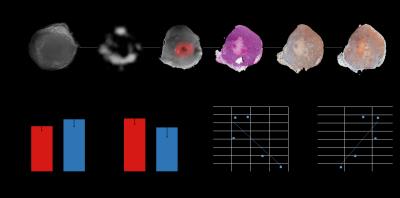
Characterizing the Tumor Microenvironment 
Samata Kakkad, Balaji Krishnamachary, Marie-France Penet, Yelena Mironchik, Flonne Wildes, Zaver Bhujwalla
Total choline in tumors is associated with increased aggressiveness. Since the distribution of total choline in tumors is usually heterogenous, here we have examined the relationship between high and low total choline, obtained with 1H MRSI, with hypoxia and necrosis in a human breast cancer xenograft model engineered to express red fluorescence protein under hypoxic conditions. We found that the highest total choline regions were associated with hypoxia. We also observed that overall total choline in tumors inversely correlated with the necrotic fraction, suggesting that reduced total choline may reflect increased cell death in tumors.
|
|
3599.
 |
33 |
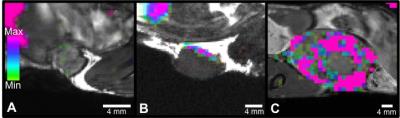
19F-based MRI cell tracking shows that the density of tumour associated macrophages in breast tumours corresponds to tumour aggressiveness and metastatic potential 
Ashley Makela, Jeffrey Gaudet, Paula Foster
Tumour associated macrophages (TAMs) have been associated with tumour aggressiveness, including tumour growth and metastatic potential. 19F-based MRI is used in this study to track these cells in vivo, revealing the ability to differentiate TAM content between 3 murine models of breast cancer. Highly aggressive tumours had significantly higher 19F signal when compared to the low and non aggressive variants. This information may be of use as a biomarker, to differentiate between tumours with high infiltration of TAMs, which have the propensity to metastasize and progress quicker, versus tumours with less TAMs, which may not advance as quickly.
|
|
3609.
 |
43 |
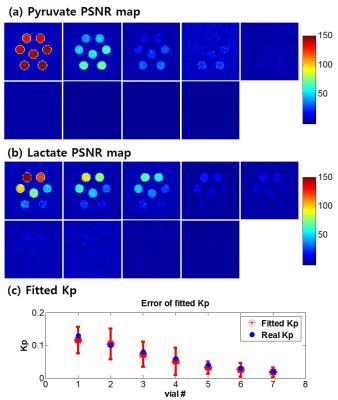
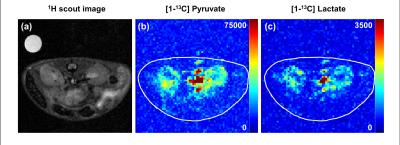
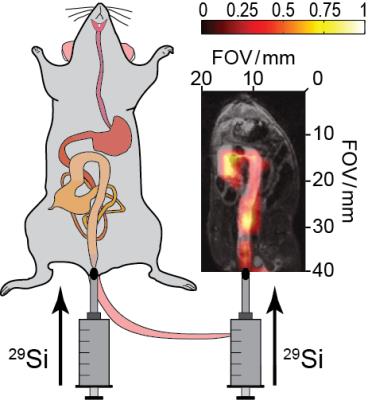
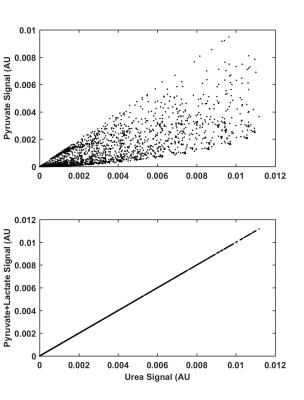
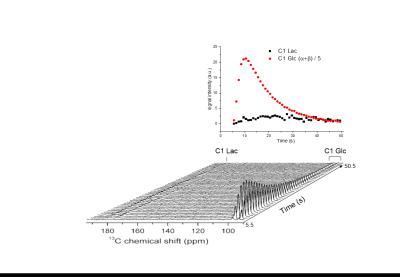
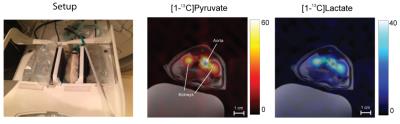
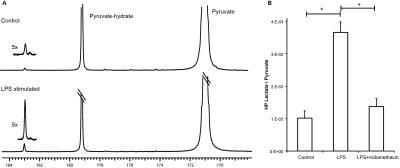
Molecular Detection of Inflammation in a Macrophage Cell Model Using Hyperpolarized 13C-Pyruvate 
Renuka Sriram, Justin DeLos Santos, Julia Nguyen, Mark Van Criekinge, Seth Vigneron, John Kurhanewicz, John MacKenzie
Carbon-13 magnetic resonance with dynamic nuclear polarization is a potential molecular imaging strategy to detect and monitor inflammation. In this study we investigated hyperpolarized 13C-pyruvate and alterations in its conversion to 13C-lactate as an imaging biomarker for disease severity and monitoring treatment response in inflammatory disorders.
|
|
3604.
 |
38 |
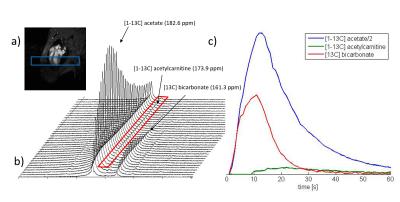
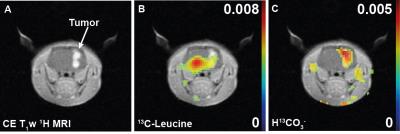
Imaging branched-chain amino acid metabolism in glioma using hyperpolarized [1-13C] alpha-ketoisocaproate 
Eul Hyun Suh, Weijun Ou, Ian Corbin, Dean Sherry, Jae Mo Park
Upregulated branched-chain amino transaminase 1 (BCAT1) expression is a common metabolic feature of most primary cancers with wild-type isocitrate dehydrogenase (IDH), including glioblastoma. In this study, 13C-labeled a-ketoisocaproate (KIC) metabolism was investigated in a brain tumor-bearing rat to assess BCAT1 and branched-chain α-ketoacid dehydrogenase (BCKDH) activities in the tumor. Following an intravenous bolus injection of hyperpolarized [1-13C]KIC, both [1-13C]leucine and 13C-bicarbonate were observed in the brain. We observed less [1-13C]leucine but greater bicarbonate production in the tumor compared to normal, healthy brain tissue, suggesting downregulated chemical exchange of [1-13C]KIC with leucine catalyzed by BCAT1 and upregulated BCKDH activity, respectively.
|
|
3606.
 |
40 |
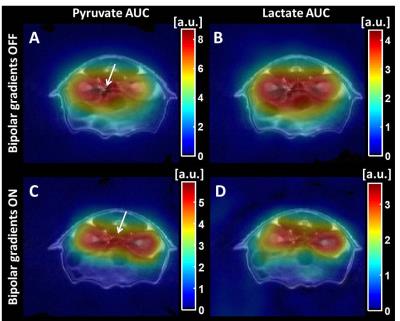
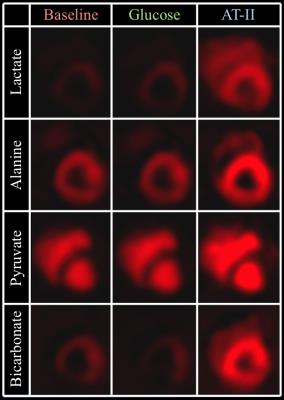
Acute afterload-imposed change in porcine cardiac metabolism imaged by hyperpolarized [1-13C]Pyruvate 
Rasmus Tougaard, Esben Hansen, Christoffer Laustsen, Jakob Lindhardt, Marie Schroeder, Hans Erik Bøtker, Won Yong Kim, Henrik Wiggers, Hans Stødkilde-Jørgensen
Deranged metabolism is now considered a key causal factor in heart failure and has therefore gained considerable scientific interest. The novel technique hyperpolarized MR has emerged as a leading methodological candidate to study these derangements. We employed a clinically relevant, large animal model of angiotensin-II-mediated acute hypertension to study cardiac metabolism in the setting of elevated afterload using hyperpolarized [1-13C]Pyruvate MR. The method was able to detect acute increases in both anaerobic and aerobic cardiac metabolism, which, in the future could mean a useful way of monitoring a possible treatment response to afterload reduction by using hyperpolarized MR.
|
|
3605.
 |
39 |
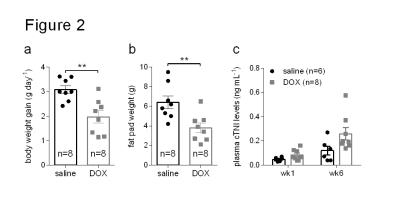
Metabolic changes in the heart precede functional changes in a rat model of doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity 
Kerstin Timm, Jack Miller, Dragana Savic, Vicky Ball, Lucia Giles, Cher-Rin Chong, Michael Dodd, Damian Tyler
Chemotherapeutic agents such as doxorubicin can cause serious adverse effects on the heart, leading to decreased left ventricular function and heart failure. The biochemical mechanisms for this are not fully understood, however, increased oxidative stress in cardiomyocytes as well as bioenergetic changes to the heart have been suggested as primary triggers for the functional decline. Here we show that hyperpolarized 13C magnetic resonance spectroscopy and CINE magnetic resonance imaging of the heart can detect metabolic as well as functional changes in a clinically relevant rat model of doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity, and that metabolic changes may precede functional abnormalities.
|
|
3607.
 |
41 |
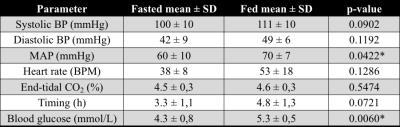
Hyperpolarized [1-13C]Pyruvate MRI identifies metabolic differences pertaining to the fasted and fed state in porcine cardiac metabolism 
Rasmus Tougaard, Esben Hansen, Christoffer Laustsen, Thomas Nørlinger, Emmeli Mikkelsen, Jakob Lindhardt, Marie Schroeder, Per Nielsen, Lotte Bertelsen, Hans Erik Bøtker, Won Yong Kim, Henrik Wiggers, Hans Stødkilde-Jørgensen
Standardized large animal models for cardiac hyperpolarized MR metabolic studies are becoming increasingly important as translation into human trials progresses. We employed a porcine (n=17) model of fasting/feeding to study these two states and to examine normal feeding as a standardized model for increasing hyperpolarized [1-13C]Pyruvate signal in the heart. All metabolic ratios were higher in fed animals with no additional variance. This indicates the role of pyruvate uptake to be more important in pigs than in rodents, underlining the need for large animals in metabolic research, and also suggests feeding to be a feasible, standardized model for increasing signal.
|
|
3608.
 |
42 |
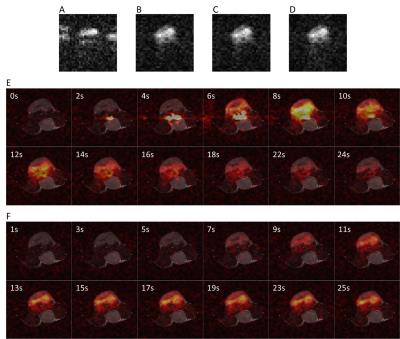
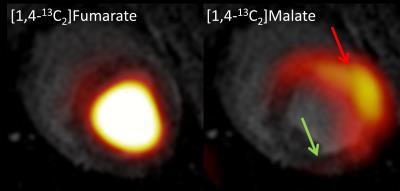
Fumarate to Malate Conversion in Infarcted Porcine Heart – a Pilot Study 
Esben Hansen, Rasmus Tougaard, Per Nielsen, Jakob Lindhardt, Hans Jørgensen, Christoffer Laustsen
Hyperpolarized MR may be a key tool for investigation cardiac metabolism and cardiac treatment response. [1,4-13C2]Fumarate is an emerging and interesting candidate for measuring and visualizing cardiac injury after ischemia. In this study we showed an initial step for imaging cardiac cell death in a large animal model with [1,4-13C2]malate. The [1,4-13C2]malate signal correlated well with increased 13C-lactate signal and 13C-alanine absence. Overall, this shows increased metabolism in the infarcted area and ongoing necrosis.
|
|
3602.
 |
36 |
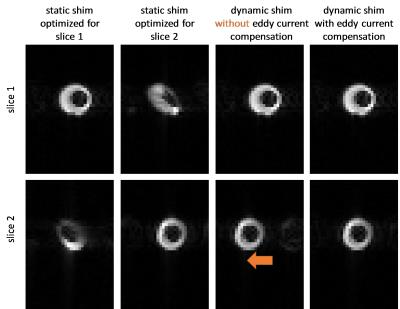
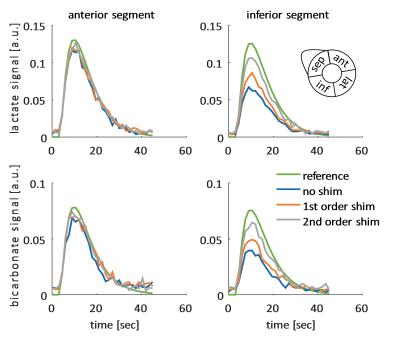
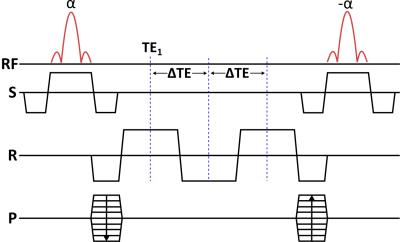
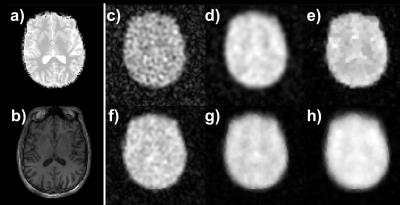
3D CMRO2 Mapping in Human Brain with Direct 17O-MRI: Comparison of Methods for Image Reconstruction and Partial Volume Correction 
Dmitry Kurzhunov, Robert Borowiak, Marco Reisert, Axel Krafft, Ali Özen, Michael Bock
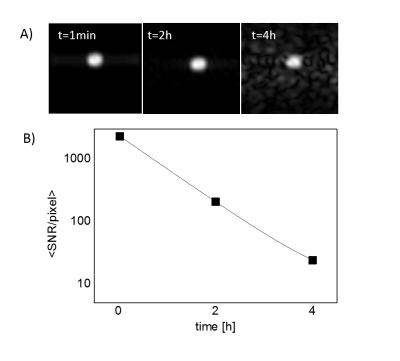
This study presents a comparative analysis of different reconstruction techniques for quantification of 3D maps of the cerebral metabolic rate of oxygen consumption (CMRO2) in human brain. CMRO2 maps were calculated from a direct 17O-MRI experiment at 3T in which 17O gas was inhaled. Conventional Kaiser-Bessel reconstruction of 17O MR images was compared to two iterative reconstruction methods using total variation (TV) and anisotropic diffusion (AD) of coregistered proton data as constraints. AD-constraint reconstruction, which acts as a non-homogeneous edge-preserving smoothing filter, enabled CMRO2 mapping at clinical field strengths by increasing the SNR, and reducing partial volume effects.
|
|
3613.
 |
47 |
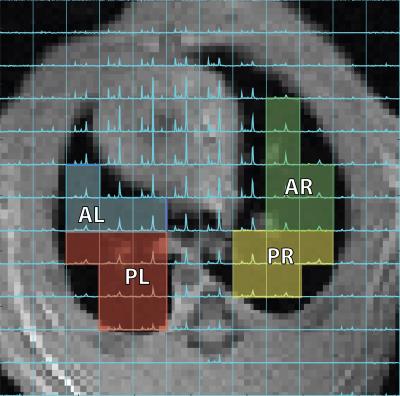
Regional Analysis of Hyperpolarized Lactate-to-Pyruvate Ratio Can Improve Sensitivity to Monitor Progression of Acute Pulmonary inflammation 
Mehrdad Pourfathi, Hooman Hamedani, Yi Xin, Stephen Kadlecek, Maurizio Cereda, Harrilla Profka, Ian Duncan, Nicholas Drachman, Sarmad Siddiqui, Kai Ruppert, Joe Naji, Rahim Rizi
In this hyperpolarized pyruvate imaging study of acute lung injury, we assessed alterations of regional lactate-to-pyruvate ratio during the progression of lung inflammation caused by acid aspiration. The study shows that posterior lactate-to-pyruvate ratio changes more significantly after injury compared to the anterior ratio. This is consistent with the pattern observed with proton MRI. We report good correlation between increased lactate-to-pyruvate ratio due to inflammation and increased proton image intensity as a result of formation of edema, especially in the posterior regions.
|
|
3603.
 |
37 |
Multiparametric tumor characterization using simultaneous 1H-MRI, [18F]FDG PET and hyperpolarized [1-13C]pyruvate MRSI 
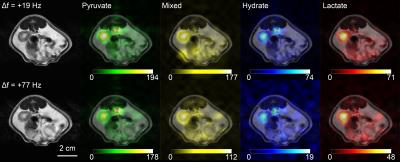
Christian Hundshammer, Miriam Braeuer, Müller Christoph, Adam Hansen, Jorge Cabello, Mathias Schillmaier, Benedikt Feuerecker, Stephan Duewel, Schachoff Sylvia, Birgit Blechert, Michael Michalik, Jan-Bernd Hövener, Steffen Glaser, Axel Haase, Franz Schilling, Andreas Kjaer, Stephan Nekolla, Schwaiger Markus
In order to understand complex mechanisms of the tumor biology, multimodal imaging approaches are useful. Here we present a workflow to characterize subcutaneous MAT-B-III tumors in rats on a clinical 3T PET/MR. Proton imaging was used for tumor localization and to characterize tumor cellularity by diffusion-weighted imaging. Glucose uptake and downstream glucose metabolism of pyruvate by lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) was addressed by [18F]FDG-PET and hyperpolarized [13C]pyruvate metabolic imaging. The [18F]FDG standard uptake values and the LDH activity were consistently and reproducibly higher compared to normal tissue.
|
|
3610.
 |
44 |
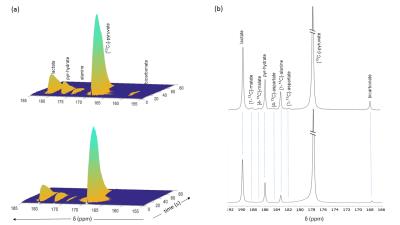
Metabolism of Hyperpolarized Pyruvate detects Knockout of Pyruvate Dehydrogenase Kinase 
Gaurav Sharma, Cheng Yang Wu, R. Max Wynn, David Chuang, Craig R. Malloy, Chalermchai Khemtong, A. Dean Sherry
The Pyruvate Dehydrogenase Complex (PDC) plays a critical role in the regulation of carbohydrate metabolism. Pyruvate Dehydrogenase Kinase (PDK) inhibits PDC via phosphorylation making it a novel therapeutic target for metabolic diseases. The present study aimed to evaluate whether the metabolism of HP-13C pyruvate is sensitive to PDK inhibition. Our results showed that higher production of HP-bicarbonate via PDC in PDK deficient livers. 13C NMR isotopomer analysis of tissue extracts confirms higher 13C-enrichment of AcCo-A in the DKO livers than the control group. The result suggested that the appearance of HP-bicarbonate is a sensitive biomarker for monitoring the consequences of PDK inhibition.
|
|
3614.
 |
48 |
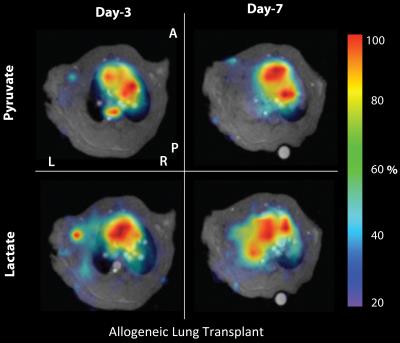
Metabolic characterization of rat lung transplantation using HP [1-13C]-pyruvate MRI 
Sarmad Siddiqui, Mehrdad Pourfathi, Andreas Habertheuer, Yi Xin, Harrilla Profka, Hooman Hamedani, Stephen Kadlecek, Ali Naji, Prashanth Vallabhajosyula, Rahim Rizi
Orthotopic rat lung transplantation is a well-established animal model used for elucidating the mechanics of lung transplant surgery. However, most lung function assessment is conducted via invasive techniques. In this study, we demonstrated that hyperpolarized pyruvate MRI can be used to generate metabolic biomarkers that can be used for non-invasive lung function assessment after transplantation. In successful syngeneic lung transplants, the lactate-to-pyruvate ratio remains low in both lungs after transplant. However, in allogeneic or failed syngeneic lung transplantation, the native lung returns to baseline one week after surgery, whereas the transplanted lung shows a significant(~3-fold) increase in the lactate-to-pyruvate ratio.
|
|
3612.
 |
46 |
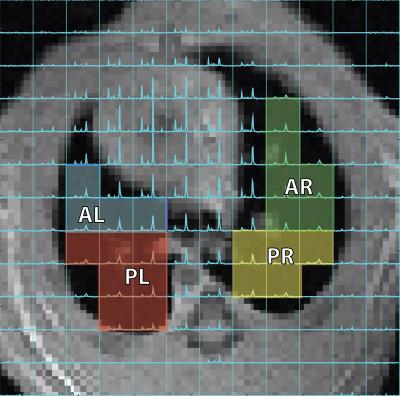
A Multi-Variate Regional Study of Acute Lung Injury Using Hyperpolarized [1-13C] Pyruvate 
Hooman Hamedani, Mehrdad Pourfathi, Yi Xin, Stephen Kadlecek, Maurizio Cereda, Harrilla Profka, Ian Duncan, Sarmad Siddiqui, Nicholas Drachman, Kai Ruppert, Rahim Rizi
In this study we seek to investigate the dependency of the changes of lactate-to-pyruvate ratio on various covariates in the settings of experimental acute lung injury using a random-effect model.
|
|
3611.
 |
45 |
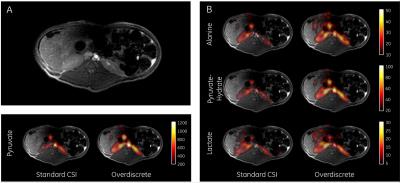
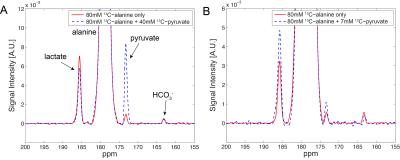
Optimization of redox-state assessment in rat liver using hyperpolarized [1-13C]alanine 
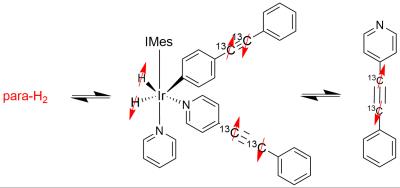
Jae Mo Park, Ralph Hurd, Daniel Spielman
In this study, we demonstrated the strategies of increasing signal sensitivities of 13C-pyruvate and 13C-lactate generated from an injection of hyperpolarized 13C-alanine by (1) adjusting the alanine dose and (2) co-injecting unlabeled pyruvate. 120-mM alanine produced larger amount of labeled pyruvate and lactate as compared to when 80-mM or 40-mM alanine was injected. The co-injection of 7-mM unlabeled pyruvate showed up to 49% SNR increase in pyruvate and lactate peaks.
|
|