|
Electronic Poster Session
Body: Breast, Chest, Abdomen, Pelvis |
Tuesday, 19 June 2018
Electronic PosterBody: Breast, Chest, Abdomen, Pelvis
4319 -4342 Breast 1
4343 -4365 Lung MRI
4366 -4389 Prostate 1: Clinical
4438 -4461 Breast 2
4462 -4485 Hyperpolarised Compound Imaging
4486 -4509 Prostate 2: Technical |
| |
Breast 1
Electronic Poster
Body: Breast, Chest, Abdomen, Pelvis
Tuesday, 19 June 2018
| Exhibition Hall |
16:15 - 17:15 |
| |
|
Computer # |
|
4319.
 |
49 |
 Development of single-sided portable NMR methods for the sensing of mammographic density Development of single-sided portable NMR methods for the sensing of mammographic density
Patricia O'Gorman, Monique Tourell, Tonima Ali , Honor Hugo , Thomas Lloyd , Erik Thompson , Konstantin Momot
Single-sided NMR was used to investigate the ability of spin-relaxation time constants to distinguish between regions of low and high mammographic density in human breast tissue. Measurements were performed on breast slices obtained from women undergoing breast reduction surgery or prophylactic mastectomy. T1 values in regions of high mammographic density were found to be significantly different to those measured in regions of low mammographic density. The findings suggest that portable NMR may be suitable for quantification of mammographic density in the breast tissue, presenting a promising and low-cost means of MD assessment in vivo without the use of ionising radiation.
|
|
4320.
 |
50 |
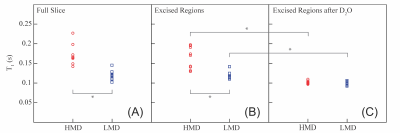
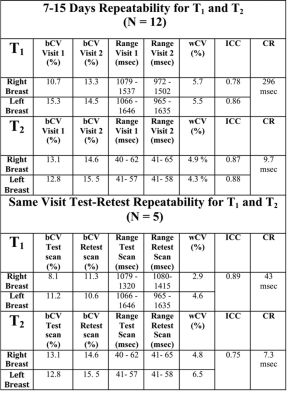
 Repeatability of 3D MR Fingerprinting Measurements in Normal Breast Tissue Repeatability of 3D MR Fingerprinting Measurements in Normal Breast Tissue
Ananya Panda, Yong Chen, Satyam Ghodasara, Katherine Wright, Nicole Seiberlich, Mark Griswold, Vikas Gulani
3D Breast Magnetic Resonance Fingerprinting (MRF) allows simultaneous breast tissue T1 and T2 mapping. In this study, same session repeatability of 3D MRF technique in normal breast tissue was evaluated (test/retest 10 minutes apart) and in two consecutive visits. The within subject coefficient of variance (wCV) for two visit scans was < 6% for T1 and < 5% for T2. The wCV for test-retest scan for T1 was <5% and for T2 was 6.5%. One-week repeatability of 3D MRF was good for both T1 and T2 (ICC T1: 0.81 T2: 0.88 at second visit). These variations are smaller than observed inter-subject variability. Thus breast MRF may be useful for longitudinal patient follow-up.
|
|
4321.
 |
51 |
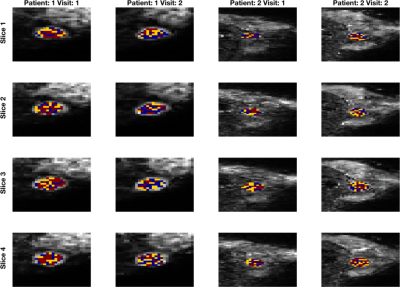
 Repeatability of Diffusion-Weighted Imaging Model Parameters within a Benign Breast Cancer Cohort Influences Optimal Model Choice Repeatability of Diffusion-Weighted Imaging Model Parameters within a Benign Breast Cancer Cohort Influences Optimal Model Choice
Neil Jerome, Igor Vidic, Liv Egnell, Torill Sjøbakk, Agnes Østlie, Hans Fjøsne, Pål Erik Goa, Tone Bathen
Diffusion-weighted MR imaging (DWI) is an essential tool in oncology. Diffusion models beyond monoexponential fitting attempt to capture non-Gaussian decay using additional data acquisition. Model repeatability and suitability is critical, but often neglected. We report findings from fitting multiple diffusion models in a benign breast cancer repeatability cohort, and show no clear dominance of diffusion models across voxels, patients, or scans. Repeatability of ADC, IVIM, and stretched exponential parameters are reported, and highlight the complexity of making inferences from DWI parameters.The potential of DWI in oncology is tempered by a need for critical appraisal of the model and parameter applicability.
|
|
4322.
 |
52 |
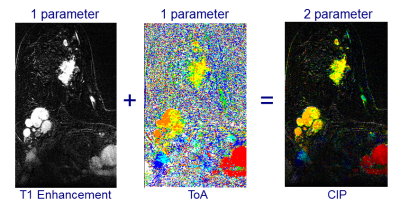
 Are the thousands of images generated by each ultrafast dynamic contrast enhancement (DCE) MRI of breast cancer effectively summarized by color intensity projection (CIP) images? Are the thousands of images generated by each ultrafast dynamic contrast enhancement (DCE) MRI of breast cancer effectively summarized by color intensity projection (CIP) images?
Keith S Cover, Katya M Duvivier, Pim de Graaf, Rianne Wittenberg, Ruth Smit, Joost PA Kuijer, Mark MB Hofman, Ben J Slotman, Ruud M Verdaasdonk
Ultrafast dynamic contrast enhancement (DCE) is a MRI sequence that, when used standalone, can serially screen for breast cancer in 2 minutes. However, each acquisition generates thousands of 2D images in a 4D stack. Color intensity projections (CIP) images are 2 parameter color images that encode the time of arrival (ToA) of contrast agent in the hue (red, orange, yellow, green, cyan, blue) and the amount of contrast enhancement in the brightness. A CIP image of each ultrafast slice provides an informative summary to radiologists with the same sensitivity and specificity to malignancies as the ultrafast 4D stack.
|
|
4323.
 |
53 |
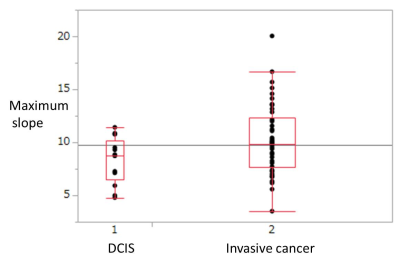
 Ultrafast dynamic contrast-enhanced MRI of the breast: Correlations with prognostic factors of breast cancer. Ultrafast dynamic contrast-enhanced MRI of the breast: Correlations with prognostic factors of breast cancer.
Ken Yamaguchi, Takahiko Nakazono, Ryoko Egashira, Hiroyuki Irie
- The purpose of our study is to determine the correlation between the parameters obtained from ultrafast dynamic contrast-enhanced (ultrafast DCE) MRI and prognostic factors of breast cancer.
- Fifty five breast cancers were included in this study. Ultrafast DCE sequence was performed using higher than usual parallel imaging factor and obtained with 8.3 second temporal resolution. Kinetic parameters obtained from ultrafast DCE were compared with prognostic factors.
- Mean maximum slope of invasive cancer (10.2) was significantly higher than that of DCIS (8.2).
- Ultrafast DCE MRI is useful for differentiating DCIS and invasive breast cancer.
|
|
4324.
 |
54 |
 3D MRI for Quantitative Analysis of Quadrant Percent Density (QPD): Correlation with Location of Breast Cancer Growing in Different Quadrants 3D MRI for Quantitative Analysis of Quadrant Percent Density (QPD): Correlation with Location of Breast Cancer Growing in Different Quadrants
Jeon-Hor Chen, Siwa Chan, Yang Zhang, Dah-Cherng Yeh, Min-Ying Su
We applied an MR-based quadrant percent density (QPD) method to investigate the association between the occurrence of cancer and the amount of dense tissue. Computer-aided method was applied to segment the breast and dense tissue, and then a breast was divided into four quadrants using nipple, centroid, and chestwall as the anatomic landmarks. In a total of 206 women, 88 (42.7%) had cancer growing in the upper-outer quadrant. Only 42 (20.4%) women had cancer growing in the quadrant with the highest QPD, suggesting that the amount of dense tissue cannot explain the disproportional occurrence of breast cancer in different quadrants.
|
|
4325.
 |
55 |
 Correlation of Breast Stiffness Measured by Ultrasound with Breast Density Measured on MRI Matched by Using a Prone-Supine Deformation Model Correlation of Breast Stiffness Measured by Ultrasound with Breast Density Measured on MRI Matched by Using a Prone-Supine Deformation Model
Jeon-Hor Chen, Siwa Chan, Yang Zhang, Dah-Cherng Yeh, Min-Ying Su
We correlated breast tissue stiffness measured by US elastography with the MR-measured density from the whole breast and the tissue in the US stiffness measurement window. Twenty women were studied, and only the normal breast was analyzed. A finite element model was applied to deform the prone MRI to match with supine US images by using the inversed gravity loaded transformation to locate the corresponding tissue region. There were no correlation between breast stiffness and the whole breast percent density (r=-0.09) and the local percent density (r=-0.12), suggesting that breast density and stiffness may be independent cancer risk factors.
|
|
4326.
 |
56 |
 The Added Utility of Diffusion Tensor Imaging for Differentiating Malignant and Benign Breast Lesions on 3T MRI: A Machine Learning Based Approach The Added Utility of Diffusion Tensor Imaging for Differentiating Malignant and Benign Breast Lesions on 3T MRI: A Machine Learning Based Approach
Jing Luo, Daniel Hippe, Habib Rahbar, Sana Parsian, Savannah Partridge
Diffusion tensor imaging (DTI) may provide additional information on tissue characteristics over dynamic contrast enhanced (DCE) MRI, however there are conflicting results regarding its utility. Our study evaluated DCE and DTI features of histologically proven breast lesions on 3T MRI. Using a machine learning-based LASSO approach for multivariate regression and bootstrap-based internal validation, the model incorporating DCE and DTI parameters demonstrated significantly better performance in differentiating malignant and benign lesions compared to models using DCE or DTI parameters alone. These findings suggest that the addition of DTI sequences to DCE MRI may improve diagnostic performance.
|
|
4327.
 |
57 |
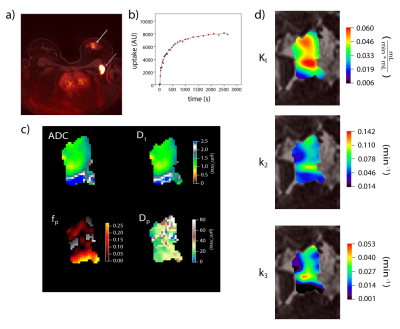
 Diffusion-weighted Intravoxel incoherent motion (IVIM) MRI and dynamic 18F-FDG-PET imaging in breast cancer patients via simultaneous PET/MR Diffusion-weighted Intravoxel incoherent motion (IVIM) MRI and dynamic 18F-FDG-PET imaging in breast cancer patients via simultaneous PET/MR
Andrea Liu, Artem Mikheev, Eric Kim, David Rigie, Sylvia Adams, Deborah Axelrod, Henry Rusinek, Alto Stemmer, Kimberly Jackson, Jean Logan, Linda Moy, Amy Melsaether, Sungheon Kim, Eric Sigmund
Aggressive breast tumors possess heterogeneity that impacts successful diagnosis and treatment. Mapping this complexity with imaging biomarkers of different biologic specificity supports patient-specific management. We compare biomarkers from diffusion-weighted MRI (intravoxel incoherent motion (IVIM)) and 18F-fluorodeoxyglucose (FDG) PET (dynamic pharmacokinetic modeling) in 10 breast cancer patients in a simultaneous PET/MR system. Voxelwise correlations were performed to study intralesion relationships between biomarkers. Intralesion correlations were observed, such as between PET plasma transfer rate K1 and tissue diffusivity Dt, that also showed potential diagnostic value in tumor classification. This feasibility study establishes a workflow that enables more detailed investigation in larger cohorts.
|
|
4328.
 |
58 |
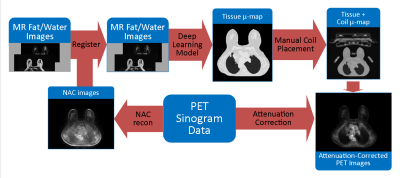
 Attenuation Correction Map Calculation and Truncation Completion for Breast PET/MR Imaging using Deep Learning Attenuation Correction Map Calculation and Truncation Completion for Breast PET/MR Imaging using Deep Learning
Jacob Johnson, Roberta Strigel, Leah Henze Bancroft, Amy Fowler, Alan McMillan
While Positron Emission Tomography (PET) used jointly with Magnetic Resonance (MR) Imaging shows promise in breast imaging, unique constraints require novel solutions to achieve attenuation-corrected images. We propose an algorithm for producing a linear attenuation coefficient map and truncation completion created from MR images using deep learning.
|
|
4329.
 |
59 |
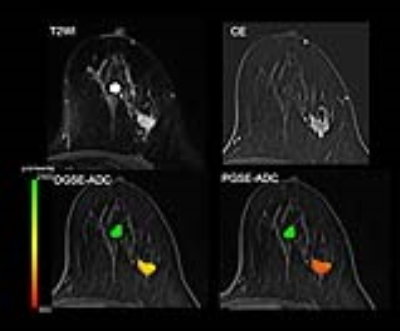
 Time makes the difference: Comparison of ADC values obtained with OGSE and PGSE sequences for differentiation of human breast tumors Time makes the difference: Comparison of ADC values obtained with OGSE and PGSE sequences for differentiation of human breast tumors
Mami Iima, Masako Kataoka, Kanae Kawai Miyake, Maya Honda, Rena Sakaguchi, Ayami Ohno Kishimoto, Mizue Suzuki, Katsutoshi Murata, Thorsten Feiweier, Masakazu Toi, Kaori Togashi
The diffusion time dependence of ADC measurements has been investigated using OGSE and PGSE sequences in human breast tumors. Relative changes in ADC values corresponding to two diffusion times, in addition to ADC values for each diffusion time were calculated in malignant and benign breast lesions as well as in normal breast tissues. Significant differences of ADC changes, in addition to ADC values for each diffusion time, have been found among malignant and benign lesions and normal breast tissue. No ADC changes have been identified in a dedicated breast phantom. ADC maps corresponding to different diffusion times indicate that ADC changes might provide insight in revealing new tissue features like, for instance, intracellular structure of breast tumors.
|
|
4330.
 |
60 |
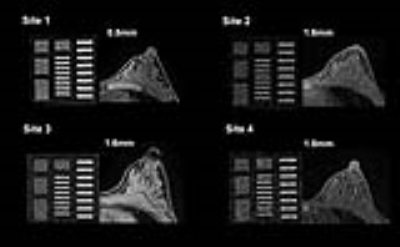
 Quality assessment with a breast phantom and a volunteer for multi-institutional MRI trials including DWI Quality assessment with a breast phantom and a volunteer for multi-institutional MRI trials including DWI
Mami Iima, Masako Kataoka, Maya Honda, Yuta Urushibata, Ryosuke Okumura, Takashi Koyama, Kenji Uwakubo, Katsutoshi Murata, Mitsuyo Matsumoto, Yu Ueda, Kaori Togashi
The novel method for quality control applicable for commonly used breast MR images (T1WI, T2WI and DWI) in terms of semi-quantitative and quantitative analysis was proposed. The scan was performed across multiple sites on both a breast phantom and a volunteer. The provided scores and apparent spatial resolution were comparable between a phantom and a volunteer. Quality of breast MR images across sites were variable, and standardization using a dedicated breast phantom is considered necessary to assure good diagnostic performance of breast MRI.
|
|
4331.
 |
61 |
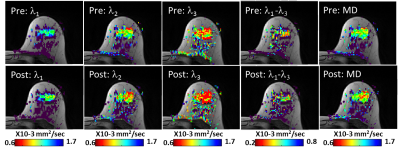
 The Effect of Intravenous Administration of a Gadolinium-Based Contrast Agent on Breast Diffusion Tensor Imaging: Qualitative and Quantitative Evaluation. The Effect of Intravenous Administration of a Gadolinium-Based Contrast Agent on Breast Diffusion Tensor Imaging: Qualitative and Quantitative Evaluation.
Anabel Scaranelo, Hadassa Degani, Dov Grobgeld, Nancy Talbot, Karen Bodolai, Edna Furman-Haran
We have investigated whether the values of the diffusion tensor imaging (DTI) parameters of breast normal tissue, as well as of benign and cancer lesions are affected by gadolinium-based contrast administration. Changes in the DTI parameters and consequently in DTI-based lesion size were evaluated pre and post dynamic contrast enhanced (DCE) MRI. Results indicated that scanning with DTI post DCE did not impact the diffusion parameters in breast normal tissue and benign lesions and the lesions’ size but revealed a significant reduction of the diffusion coefficients in breast cancers, suggesting potential improvement of DTI diagnostic specificity post-contrast.
|
|
4332.
 |
62 |
 Lactate concentration measured by multiple quantum coherence (MQC) MRS in whole human breast tumour is associated with tumour grading Lactate concentration measured by multiple quantum coherence (MQC) MRS in whole human breast tumour is associated with tumour grading
Sai Man Cheung, Ehab Husain, Yazan Masannat, Klaus Wahle, Steven Heys, Jiabao He
High level of aerobic glycolysis and an elevated lactate accumulation have been linked to tumour aggressiveness. However, current evidence, mainly based on small animal models or biopsy sections, remains controversial. Since lactate and lipid share the same spectral frequency, conventional MRS is inadequate in measuring lactate under overwhelming lipid signal. Multiple quantum coherence (MQC) MRS allows excellent suppression of lipid even in breast tissues. We applied MQC MRS to measure lactate concentration in grade II and III freshly excised whole human breast tumours to assess if there was a difference between the two groups.
|
|
4333.
 |
63 |
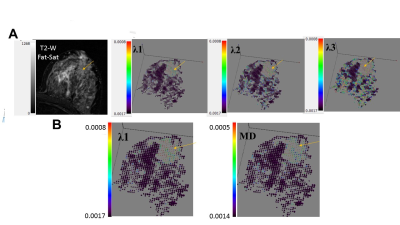
 Enhanced Ellipsoid Mapping of Diffusion Tensor Breast MRI for Improved Lesion Conspicuity Enhanced Ellipsoid Mapping of Diffusion Tensor Breast MRI for Improved Lesion Conspicuity
Myra Shapiro-Feinberg, Edna Furma-Haran, Dov Grobgeld, Hadassa Degani
Ellipsoid mapping of the breast with a specific colorization mode has been developed as a visualization means for evaluating the entire information embedded in breast Diffusion Tensor Imaging (DTI) and improve breast cancer detection. The 3D ellipsoid maps were displayed at voxel resolution with their shape and orientation determined by a respective eigenvalue-eigenvector pair of the associated diffusion tensor, followed by colorizing the ellipsoids according to the values of each diffusion tensor parameter. The results show that the enhanced ellipsoid mapping with λ1 colorization accentuating breast malignancy, may allow efficient differentiation of breast malignancy from normal breast tissue.
|
|
4334.
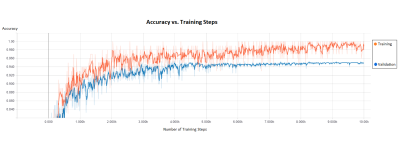 |
64 |
 Diagnostic Assessment of Breast Cancer in Non-Contrast MRI Images Through an Artificial Intelligence Machine Learning Algorithm Diagnostic Assessment of Breast Cancer in Non-Contrast MRI Images Through an Artificial Intelligence Machine Learning Algorithm
Craig Detheridge, Philip Saponara, Jaspreet Bhangu, Boris Bloch, Kevin Thomas
Contrast-Enhanced Breast MRI is a common method for diagnosis of Breast Cancer. An Artificial Intelligence Machine Learning Algorithm was developed to analyze Non-Contrast Breast MRI scans and predict diagnoses. The algorithm was trained using MRI data that had pathological specimens to validate diagnoses, obtained from The Cancer Imaging Archive. The AI was found to be 95% accurate in classifying tissue as cancerous or benign. This algorithm could be used to assist diagnoses in clinical practice. Future work will assess the generalizability of the algorithm on data from other scan sites, and the potential for classifying specific subtypes of Breast Cancer.
|
|
4335.
 |
65 |
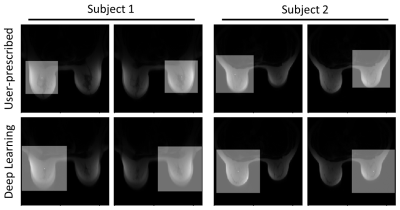
 Towards Fully Automated Breast MR Exams using Deep Learning Towards Fully Automated Breast MR Exams using Deep Learning
Kang Wang, Dawei Gui, James Holmes, Alan McMillan, Leah Henze Bancroft, Roberta Strigel, Frank Korosec, Ersin Bayram
Breast MR exams can be challenging for inexperienced MR technologists. For example, breast MRI typically requires the prescription of two carefully positioned and sized shim volumes, one for each breast, to improve the local B0 homogeneity and fat suppression. Normally, this procedure is performed manually, which requires an experienced MR technologist and can be challenging for new technologists. The goal of this project is to use deep learning to automate breast MR prescription, including placing the two shim volumes and imaging volumes automatically, to improve breast MR prescription consistency, quality, and to shorten the exam time.
|
|
4336.
 |
66 |
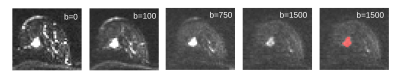
 Complementary value of End-to-end Deep Learning and Radiomics in Breast Cancer Classification on Diffusion-Weighted MRI Complementary value of End-to-end Deep Learning and Radiomics in Breast Cancer Classification on Diffusion-Weighted MRI
Paul Jaeger, Sebastian Bickelhaupt, Frederik Laun, Wolfgang Lederer, Heidi Daniel, Tristan Kuder, Stefan Delorme, Heinz-Peter Schlemmer, Franziska Steudle, Klaus Maier-Hein
Two fundamentally different approaches have been proposed recently for the classification of breast lesions on diffusion-weighted MRI Images: “Radiomics” extracts quantitative parameters by fitting a biophysical model to the q-space signal and subsequently computes handcrafted features to feed a classifier. Convolutional neural networks on the other hand autonomously learn all processing components in an end-to-end training. To date it is unclear how the two methods compare with respect to overall performance, complementary value of features and combinability. We address these open research questions and propose a combined model that significantly outperforms the two standalone approaches.
|
|
4337.
 |
67 |
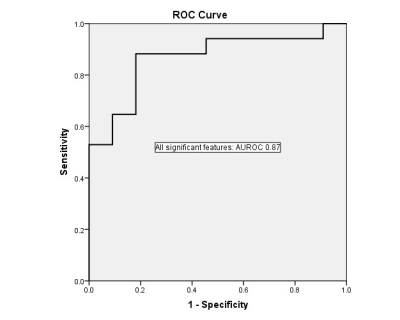
Whole-Tumor Histogram Analysis of Multiparametric MRI for Subtype Classification of Breast Cancer
Did Not Present
Tianwen Xie, Qiufeng Zhao, Robert Grimm, Caixia Fu, Yajia Gu, Weijun Peng
Recently, several studies have shown the value of Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) radiomics in non-invasive lesion subtype classification. In this study, we proposed the use of histogram texture features of multiparametric maps to differentiate subtypes of breast cancer. 34 different whole-tumor histogram features were analyzed. Classification was performed between ER-positive and Triple-negative groups resulted in AUROC of 0.94, while classification between ER-positive and HER2-positive groups, and classification between HER2-positive and Triple-negative yielded AUROC of 0.79, and 0.86, respectively.
|
|
4338.
 |
68 |
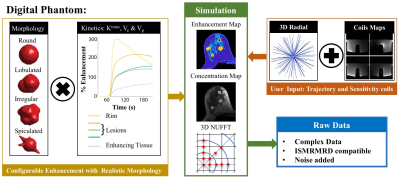
 In silico Platform for Evaluation of Constrained Reconstruction in DCE-MRI In silico Platform for Evaluation of Constrained Reconstruction in DCE-MRI
Jorge Jimenez, Leah Henze Bancroft, Roberta Strigel, Kevin Johnson, Scott Reeder, Walter Block
In this work, we show the value of a digital phantom to evaluate a dynamic reconstruction. We evaluated the fidelity of the reconstruction using SSIM measurements from simulations and three patients to support conclusions derived from the digital phantom. The highly configurative characteristics of the in-silico platform provide a tool for other researchers to test, evaluate and compare their own acquisition and reconstruction techniques.
|
|
4339.
 |
69 |
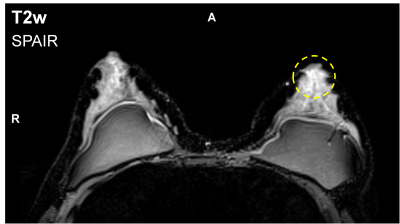
 RF-Induced Potential False-Negative Lesion in Breast T2-weighted MRI at 3T: Exploration of a Single-Channel kT-Points Solution RF-Induced Potential False-Negative Lesion in Breast T2-weighted MRI at 3T: Exploration of a Single-Channel kT-Points Solution
Raphael Tomi-Tricot, Vincent Gras, Thu Ha Dao, Antoine Perrot, Franck Mauconduit, Nicolas Boulant, Pierre Zerbib, Alain Rahmouni, Alexandre Vignaud, Alain Luciani, Alexis Amadon
Breast MRI can benefit from the improved signal-to-noise ratio brought by high-field systems to achieve finer spatial or temporal resolutions. However, dielectric resonance associated with the shorter RF wavelength provokes inhomogeneous excitation in the tissues. In this work, it was shown that such artefacts can induce hyperintensity in T2-weighted images, thus potentially misleading clinicians into excluding malignancy in a lesion. A solution is proposed to reduce the RF artefact on 3D T2w acquisitions using single-transmit-channel kT-points, which could be used on any 3T scanner.
|
|
4340.
 |
70 |
 Development and Validation of MR Radiomics Nomogram for Preoperative Prediction of Axillary Lymph Node Metastasis in Patients With Breast Cancer Development and Validation of MR Radiomics Nomogram for Preoperative Prediction of Axillary Lymph Node Metastasis in Patients With Breast Cancer
Mei Xue, Jing Li, Shunan Che, Liyun Zhao, Yuan Tian, Lizhi Xie, Bing Wu, Xiangfei Chai, Panli Zuo, Chencui Huang
Axillary lymph node (ALN) status is an important prognostic factor for overall breast cancer survival. The number of axillary lymph node metastases is closely related to the risk of distant metastasis1. Accurate identi?cation of axillary lymph node involvement in patients with breast cancer is crucial for prognosis and treatment strategy decisions. Axillary lymph node dissection (ALND) is currently the standard procedure for determining ALN status. Sentinel lymph node biopsy was used to determine whether axillary lymph node dissection was needed, which is invasive2. Image based non-invasive predictors of axillary lymph nodes are highly desirable, and currently face challenges. The aim of this study was to develop and validate a radiomics nomogram that incorporates both the radiomics signature and clinicopathologic risk factors for individual preoperative prediction of axillary lymph node metastasis in patients with breast cancer.
|
|
4341.
 |
71 |
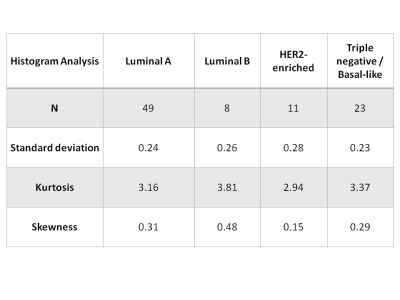
 Qualitative and Quantitative Assessment of Tumor Heterogeneity for the Differentiation of Molecular Subtypes in Breast Cancer Qualitative and Quantitative Assessment of Tumor Heterogeneity for the Differentiation of Molecular Subtypes in Breast Cancer
Sunitha Thakur, Joao Horvat, Dilip Giri, Aditi Iyer, Manuela Durando, Elizabeth Morris, Katja Pinker
Heterogeneity in breast cancer is related to aggressiveness and poor prognosis. In this study, we evaluated if qualitative visual evaluation and quantitative assessment with histogram analysis of tumor heterogeneity on diffusion weighted imaging (DWI) could be used to predict molecular subtype in invasive breast cancer. We retrospectively evaluated 91 patients with invasive ductal carcinoma. Two radiologists classified the imaging appearance of tumors on DWI according to heterogeneity. The lesions were also evaluated with histogram analysis on apparent diffusion coefficient maps. There was no statistically significant difference on heterogeneity among molecular subtypes on visual evaluation or histogram analysis.
|
|
4342.
 |
72 |
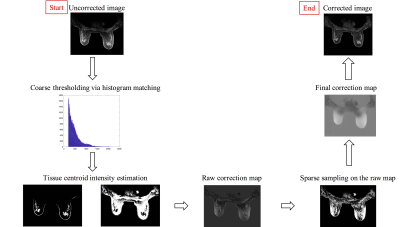
 Fast intensity non-uniformity correction for breast MRI using sparse samples Fast intensity non-uniformity correction for breast MRI using sparse samples
Linxi Shi , Steffi Perkins, Catherine Moran, Brian Hargreaves, Bruce Daniel
The quantitative application of breast MRI is hindered by image non-uniformity artifact due to B0 and B1 variations. In this work, we developed an effective intensity non-uniformity correction algorithm for breast MRI with high computational efficiency. Compare to existing methods, the proposed method is readily implementable clinically as a software plug-in without modification of existing imaging protocols or hardware, and can potentially be applied to MR images of other anatomical sites.
|
|
Lung MRI
Electronic Poster
Body: Breast, Chest, Abdomen, Pelvis
Tuesday, 19 June 2018
| Exhibition Hall |
16:15 - 17:15 |
| |
|
Computer # |
|
4343.
 |
73 |
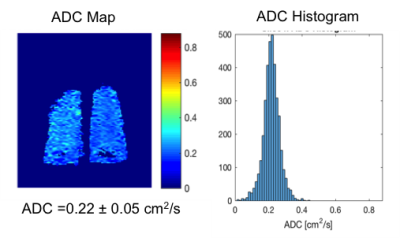
 Examination of Lung Function among Older Smokers with and without COPD by Apparent Diffusion Coefficient (ADC) of 3He MRI Examination of Lung Function among Older Smokers with and without COPD by Apparent Diffusion Coefficient (ADC) of 3He MRI
Yanping Sun, Jia Guo, Pallavi Balte, Stephen Dashnaw, Martin Prince, Elizabeth Oelsner, Christian Lo Cascio, Mitchell Albert, Jim Wild, Emlyn Hughes, R. Graham Barr
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) is defined as persistent airflow limitation by spirometry. However, some smokers with normal spriometry have significant respiratory symptoms. We used 3He apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) to examine the lungs in older smokers with and without COPD (n=50). This study showed high ADC in both smokers with and without COPD. The difference in ADC between COPD and non-COPD was significant. ADC was correlated positively with percent emphysema and %FVC, and negatively with FEV1 to FVC ratio and, non-significantly with FEV1. 3He ADC may provide different information of lung microarchitecture from spirometry in smoking related pulmonary diseases.
|
|
4344.
 |
74 |
Lung cancer screening with MRI: characterization of nodules with different non-enhanced MRI sequences.
Video Permission Withheld
Michael Meier-Schroers, Rami Homsi, Hans Schild, Daniel Thomas
Due to increased interest in pulmonary MRI as a radiation free alternative to CT for lung cancer screening, we analyzed MRI characteristics of pulmonary nodules with different non-enhanced sequences.
|
|
4345.
 |
75 |
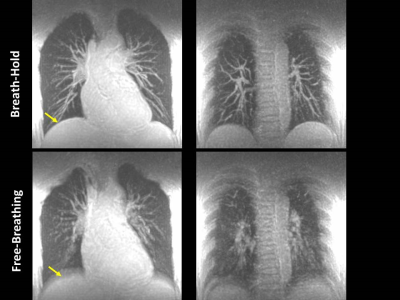
 Clinical Feasible Breath-Hold Lung Imaging Using Zero Echo Time MRI Clinical Feasible Breath-Hold Lung Imaging Using Zero Echo Time MRI
Chien-Yuan Lin, Hsiao-Ling Lin, Charng-Chyi Shieh, Chia-Wei Li, Wing P. Chan
A high resolution, rapid scanning in one breath-hold and three-dimensional zero-echo time protocol for lung imaging was established in this study. It successfully captured rapid-decaying lung signal and eliminated the motion artifact and consequently exhibit high quality of pulmonary anatomy, including the tortuous vessels architecture and bronchial wall in exceptional clarity and detail. Additionally, it provides the volume estimation of pulmonary tissue and shows somewhat comparable with the calculation result from computed tomography.
|
|
4346.
 |
76 |
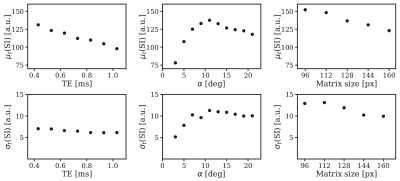
Functional lung imaging with partially spoiled ultra-fast steady-state free precession at 1.5T and 3T
Video Permission Withheld
Grzegorz Bauman, Orso Pusterla, Oliver Bieri
In this work we propose an alternative acquisition framework for functional lung imaging using matrix pencil (MP) decomposition (a derivative of Fourier decomposition method) based on partially spoiled ultra-fast steady-state free-precession (ps-ufSSFP) imaging. We showed that MP decomposition is feasible in healthy volunteers using ps-ufSSFP at 1.5T and 3T. Hence, ps-ufSSFP can be a viable solution for the application of MP MRI at 3T where imaging with balanced ufSSFP can be problematic due to the occurrence of off-resonance artifacts.
|
|
4347.
 |
77 |
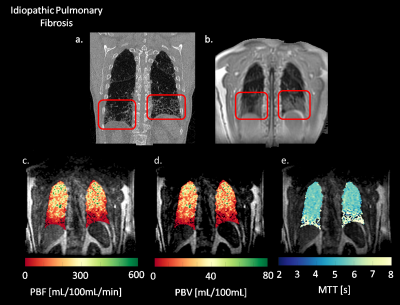
 Quantification of Pulmonary Perfusion in Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis: Preliminary Results Quantification of Pulmonary Perfusion in Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis: Preliminary Results
Luis Torres, Wei Zha, Mu He, Bastiaan Driehuys, Sean Fain
IPF is a pulmonary disease with no validated biomarkers in current clinical use. Here, we compared pulmonary perfusion in an IPF subject versus healthy subject using Dynamic Contrast-Enhanced MRI (DCE-MRI). A decrease in PBF, PBV and an increase in MTT was seen in IPF compared to the healthy control. High spatial correlation of perfusion defects and fibrosis is seen when compared to the morphological images, suggesting DCE-MRI may prove to be a useful technique for evaluating IPF.
|
|
4348.
 |
78 |
 Diffusion kurtosis imaging in solitary pulmonary nodules: comparison with quantitative dynamic contrast enhanced MR imaging in malignant and benign pulmonary nodule differentiation Diffusion kurtosis imaging in solitary pulmonary nodules: comparison with quantitative dynamic contrast enhanced MR imaging in malignant and benign pulmonary nodule differentiation
Shuchang Zhou, Liming Xia, Xu Yan
Theoretically, DKI and quantitative DCE-MRI can provide more precise microstructure and perfusion information of tissues. However, the two methods had rarely been reported in solitary pulmonary nodules (SPNs) to date, so we collected 37 patients with SPNs underwent both DKI and DCE-MRI and measured relative parameters. The Kapp, Ktrans, Ve and iAUC values were significantly higher in lung cancer than in benignity. Kapp had best sensitivity and accuracy, and iAUC had best specificity. The combination of both methods can provide a robust way to discriminate SPNs before clinical management.
|
|
4349.
 |
79 |
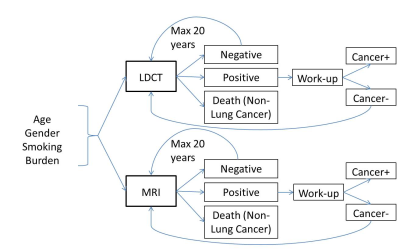
 Markov Model of Lung Cancer Screening Demonstrates Equivalent Lung Cancer Detection using either Lung MRI or Low-Dose CT Screening Strategies Markov Model of Lung Cancer Screening Demonstrates Equivalent Lung Cancer Detection using either Lung MRI or Low-Dose CT Screening Strategies
Bradley Allen, Mark Schiebler, Hans-Ulrich Kauczor, Jürgen Biederer, Timothy Kruser, Nisha Mohindra, David Odell, James Carr, Gorden Hazen
Lung cancer screening with low dose CT (LDCT) has been shown to result in a 20% mortality reduction, but has relatively low specificity for lung cancer diagnosis, as well as concerns related to radiation dose and overdiagnosis. Lung MRI has similar sensitivity and improved specificity for lung cancer detection. In this study, we developed a Markov model of lung cancer screening to compare performance of LDCT and MRI. Based on our analysis, lung cancer screening with MRI could provide an equivalent number of lung cancer diagnoses, while dramatically reducing the number of false positive findings relative to LDCT.
|
|
4350.
 |
80 |
 Robust Retrospective Respiratory Gating for Detection of Small Pulmonary Nodules with UTE MRI Robust Retrospective Respiratory Gating for Detection of Small Pulmonary Nodules with UTE MRI
Naoharu Kobayashi, Abbie Begnaud, Tadashi Allen, Gregory Metzger, Robert Kratzke, Michael Garwood
Retrospective respiratory gating using a 3D time series lung image reconstructed with sub-second temporal resolution is introduced to achieve accurate small pulmonary nodule detection with ultrashort echo time (UTE) MRI. Changes of the diaphragmatic level during free breathing were tracked using the 3D time series lung image. With the extracted respiratory motion, the data in exhalation were reconstructed to a high resolution image. The feasibility and robustness of the proposed retrospective gating method were tested by surveilling incident lung nodules in two UTE MRI examinations: a baseline scan and a follow-up scan in 10 weeks.
|
|
4351.
 |
81 |
A new diagnostic method for Pneumothorax:3D-UTE MRI
Did Not Present
Can HUANG, Yang FAN, Tao JIANG
Radiation may has great impact on teenagers who are the high risk population for pneumothorax. Compared to X-ray and CT, MRI is a imaging modality without radiation. The purpose of this study is to examine the feasibility of using UTE MRI to diagnose the pneumothorax.
|
|
4352.
 |
82 |
 Dynamic contrast-enhanced MRI for the evaluation of perfusion heterogeneity in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis Dynamic contrast-enhanced MRI for the evaluation of perfusion heterogeneity in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis
Nicholas Weatherley, Helen Marshall, Paul Hughes, Jody Bray, David Capener, Matthew Austin, Laurie Smith, Stephen Renshaw, Stephen Bianchi, Jim Wild
Dynamic contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging (DCE-MRI) produces metrics of lung perfusion at the capillary level. To date, little assessment of patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF) has been reported with DCE-MRI. In fourteen patients with IPF, we found that regions of low flow and high transit times were associated with anatomical disease. Whole lung metrics of transit time and heterogeneity of blood volume demonstrated a relationship with pulmonary function tests. Such functional imaging strategies may be useful in quantifying functional changes in the pulmonary vasculature in IPF.
|
|
4353.
 |
83 |
 Longitudinal assessment of changes in lung microstructure in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis with hyperpolarized gas diffusion-weighted MRI Longitudinal assessment of changes in lung microstructure in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis with hyperpolarized gas diffusion-weighted MRI
Ho-Fung Chan, Nicholas Weatherley, Neil Stewart, Guilhem Collier, Stephen Bianchi, Jim Wild
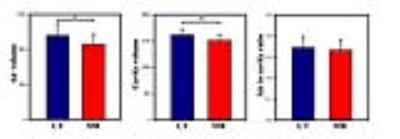
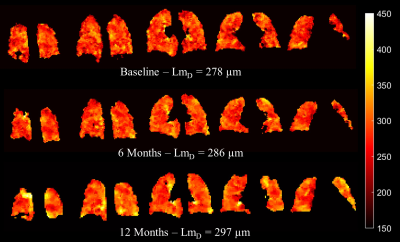
Apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) calculated from hyperpolarized gas diffusion-weighted (DW)-MRI has been shown to be elevated in lungs afflicted with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF). This work assesses the sensitivity of 3He DW-MRI metrics to longitudinal changes in IPF patients by evaluating 3He ADC and mean diffusive length scale (LmD) from the stretched exponential model at baseline, 6 and 12 months. ADC was not significantly different between visits, but a statistically significant increase of 13 µm in LmD was observed after 12 months suggesting multiple b-value DW-MRI is sensitive to progressive microstructural changes in the lungs in IPF.
|
|
4354.
 |
84 |
 A Comparison of Hyperpolarized Helium-3 and Xenon-129 MR Fractional Ventilation Imaging A Comparison of Hyperpolarized Helium-3 and Xenon-129 MR Fractional Ventilation Imaging
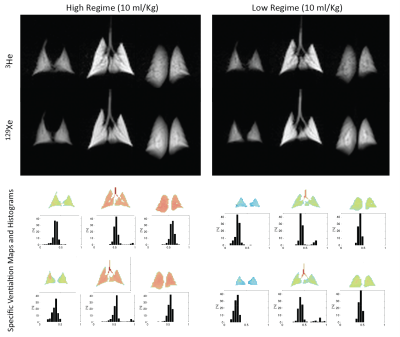
Hooman Hamedani, Kai Ruppert, Yi Xin, Stephen Kadlecek, Faraz Amzajerdian, Ryan Baron, Ian Duncan, Luis Loza, Mehrdad Pourfathi, Sarmad Siddiqui, Harrilla Profka, Mary Spencer, Tahmina Achekzai, Maurizio Cereda, Rahim Rizi
In response to the global shortage of 3He, we studied the feasibility and safety of performing a multi-breath wash-in MR imaging technique to measure fractional ventilation using hyperpolarized (HP) 129Xe in the same manner as with 3He.
|
|
4355.
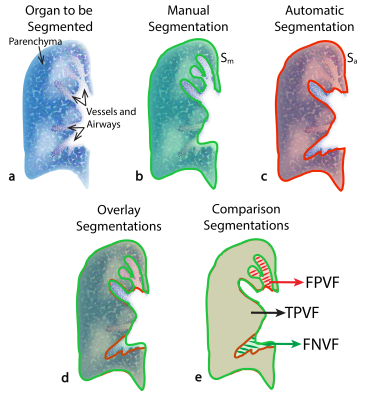 |
85 |
 Deep Learning Lung Segmentation in Paediatric Patients Deep Learning Lung Segmentation in Paediatric Patients
Orso Pusterla, Simon Andermatt, Grzegorz Bauman, Sylvia Nyilas, Philipp Madörin, Tanja Haas, Simon Pezold, Francesco Santini, Philipp Latzin, Philippe Cattin, Oliver Bieri
Automatic lung segmentation of MR images is challenging; especially in the presence of pathologies. In this work, we tackle lung segmentation of 2D and 3D ultra-fast steady-state free precession MRI in cystic fibrosis patients by using deep learning based on a neural network of multi-dimensional gated recurrent units.
|
|
4356.
 |
86 |
 3D T1 mapping in the lungs during free breathing using asymmetrical cylindrical encoding 3D T1 mapping in the lungs during free breathing using asymmetrical cylindrical encoding
Simon Triphan, Mark Wielpütz, Hans-Ulrich Kauczor, Bertram Jobst
T1 in the lungs has been found to be interesting both for oxygen enhanced imaging and as a biomarker in COPD. In this work, T1 mapping in human lungs was implemented using a cylindrically encoded 3D measurement using asymmetric radial encoding in an inversion recovery experiment. Breathing was compensated by employing DC-gating with the MR signal, using a correction to cancel the influence of the inversion recovery. It is shown that using a segmented scheme for 3D phase encoding steps that spreads steps over k-space while minimizing leaps in T1-weighting improves gating performance and thus the resulting T1 maps.
|
|
4357.
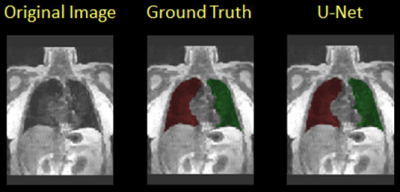 |
87 |
 Automatic Segmentation of Lung Anatomy from Proton MRI based on a Deep Convolutional Neural Network Automatic Segmentation of Lung Anatomy from Proton MRI based on a Deep Convolutional Neural Network
Xue Feng, Nicholas Tustison, Renkun Ni, Zixuan Lin, John Mugler, III, Craig Meyer, Talissa Altes, Joanne Cassani, Y. Michael Shim, Kun Qing
With rapid development of pulmonary MRI techniques, increasingly useful morphological and functional information can be obtained, such as pulmonary perfusion, ventilation and gas uptake through hyperpolarized-gas MRI. Identification of lung anatomy is usually the first step for quantitative analysis. In the work, we proposed and validated a new approach for automatic segmentation of lung anatomy from proton MRI based on 3D U-Net structure. The new method had a relatively consistent performance in all subjects (dice overlap 0.90-0.97). Its future application for anatomical based analysis of structural and/or functional pulmonary MRI data needs further validation in larger number of data.
|
|
4358.
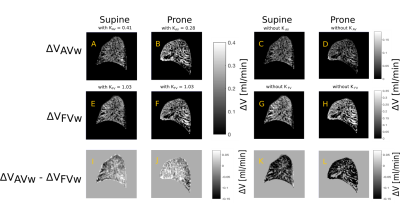 |
88 |
 Correction for Ventilation Quantification Errors due to Registration in Pulmonary Lung MRI Fourier Decomposition Correction for Ventilation Quantification Errors due to Registration in Pulmonary Lung MRI Fourier Decomposition
Filip Klimeš, Andreas Voskrebenzev, Marcel Gutberlet, Agilo Kern, Lea Behrendt, Till Kaireit, Alexander Rotärmel, Julius Renne, Christian Schönfeld, Frank Wacker, Jens Vogel-Claussen
Ventilation-perfusion (V/Q) scan plays an important role in the assessment of lung function. Currently, Fourier Decomposition (FD), a method for simultaneous ventilation and perfusion measurement, uses fractional ventilation (FV) as a semi-quantitative measurement of lung ventilation. Just recently, a multi-echo spoiled gradient echo sequence method for regional alveolar ventilation (AV) measurement with FD was presented. This study demonstrates that both methods suffer from an artificial proton amount change during registration, which affects quantification. Correction factors are derived for both methods and used to compare AV and FV measurement. Additionally, the regional influence of T2* correction is assessed.
|
|
4359.
 |
89 |
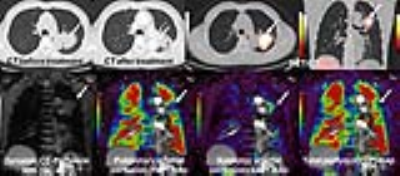
Multiparametric Approach by Quantitatively Assessed Dynamic First-Pass Contrast-Enhanced Perfusion MRI with FDG-PET/CT: Capability for Therapeutic Response Prediction in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer After Conservative Therapy
Video Permission Withheld
Yoshiharu Ohno, Masao Yui, Shigeharu Ohyu, Yuji Kishida, Shinichiro Seki, Katsusuke Kyotani, Takeshi Yoshikawa
To the best of our knowledge, no studies have been reported of a direct comparison of dynamic CE-perfusion MRI with PET/CT for therapeutic effect prediction for NSCLC patients treated with chemoradiotherapy. We hypothesized that multiparametric approach of quantitatively assessed dynamic CE-perfusion MRI with PET/CT have potential for better therapeutic effect prediction than single parametric methods by both modalities in NSCLC patients treated with chemoradiotherapy. The purpose of this study was therefore to directly compare the capability for therapeutic response prediction by among quantitatively assessed dynamic CE-perfusion MRI, FDG-PET/CT and multiparametric approach by both modalities in NSCLC patients treated with chemoradiotherapy.
|
|
4360.
 |
90 |
Multi- and Sigle Parametric Approaches using Chemical Exchange Saturation Transfer (CEST) Imaging, Diffusion-Weighted Imaging and FDG-PET/CT for Pulmonary Nodule Diagnosis
Video Permission Withheld
Yoshiharu Ohno, Masao Yui, Mitsue Miyazaki, Yuji Kishida, Shinichiro Seki, Katsusuke Kyotani, Takeshi Yoshikawa
No major reports have been reported the capability for differentiating malignant and benign pulmonary lesions among multi- and single parametric approaches by CEST imaging, DWI and PET/CT. We hypothesized that multi parametric approach by all three techniques had better potential for diagnosis of pulmonary nodule than single parametric approach, when applied with CEST imaging, DWI and FDG-PET/CT. The purpose of this study was to directly and prospectively compare the capability for differentiating of malignant from benign pulmonary nodules between multi- and single-parametric approaches by CEST, DWI, and FDG-PET/CT.
|
|
4361.
 |
91 |
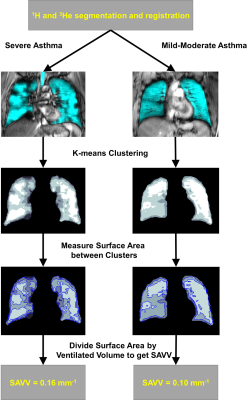
 Quantification of Hyperpolarized 3He MRI Ventilation Heterogeneity in Asthmatics: Surface Area of Ventilation Clusters Quantification of Hyperpolarized 3He MRI Ventilation Heterogeneity in Asthmatics: Surface Area of Ventilation Clusters
Andrew Westcott, Rachel Eddy, Dante Capaldi, Heather Young, David McCormack, Grace Parraga
Ventilation heterogeneity measured using hyperpolarized noble-gas magnetic-resonance imaging (MRI), presents a significant challenge in terms of the need for imaging processing tools to generate rapid, reproducible, intuitive and clinically relevant biomarkers. In particular, new tools are needed to differentiate ventilation defects and patchy ventilation that likely represent different functional phenotypes. Therefore, here we developed a new way to quantify MRI ventilation heterogeneity using the surface area between ventilation clusters – the ratio of surface area to ventilation volume (SAVV) measured in units of mm-1. MRI SAVV was significantly greater in severe asthmatics (n=24), as compared to mild-to-moderate asthmatics (n=16).
|
|
4362.
 |
92 |
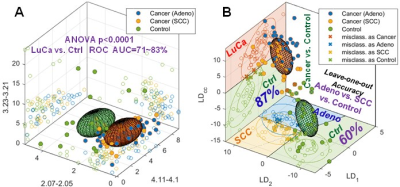
 Discovery and Verification of Lung Cancer Serum Biomarkers using Paired Tissue and Serum Discovery and Verification of Lung Cancer Serum Biomarkers using Paired Tissue and Serum
Leo Cheng, Isabella Dittmann, Li Su, Johannes Kurth, Andreas Schuler, Yannick Berker, Lindsey Vandergrift, Sarah Dinges, Piet Habbel, Eugene Mark, David Christiani
A widespread, minimally-invasive method for early detection of lung cancer is urgently needed in the lung cancer clinic. Using high resolution magic angle spinning magnetic resonance spectroscopy, we measured paired tissue and serum samples from the same patients. We correlated serum and tissue results to discover and verify serum markers for lung cancer types and stages and predicted overall survival for early Stage I lung cancer. Measured from serum, prolonged survival is associated with relative overexpression of glutamine, valine, glycine, and relative suppression of glucose and lipids.
|
|
4363.
 |
93 |
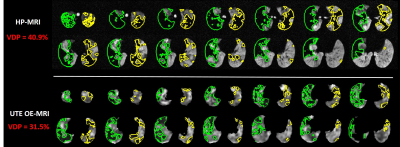
 Pulmonary Ventilation Imaging in Cystic Fibrosis Using Oxygen-enhanced MRI: Comparison with Hyperpolarized Helium-3 MRI Pulmonary Ventilation Imaging in Cystic Fibrosis Using Oxygen-enhanced MRI: Comparison with Hyperpolarized Helium-3 MRI
Wei Zha, Robert Cadman, Scott Nagle, Sean Fain
Recent technical advances in oxygen-enhanced (OE) MRI using 3D radial UTE sequence support quantitative differentiation of diseased vs healthy lungs using ventilation defect percent (VDP). A cohort of cystic fibrosis (CF) subjects with different disease severities underwent spirometry, hyperpolarized (HP) 3He and OE-MRI and a subset of those returned for a repeat visit 1-2 weeks later. The results suggest global VDP measures from HP- and OE-MRI were correlated (ρ=0.80, p<0.0001) with comparable test-retest repeatability, showed similar correlation with spirometry. Moreover, UTE OE-MRI with isotropic spatial resolution provides both structural and functional evaluations of obstructed lungs.
|
|
4364.
 |
94 |
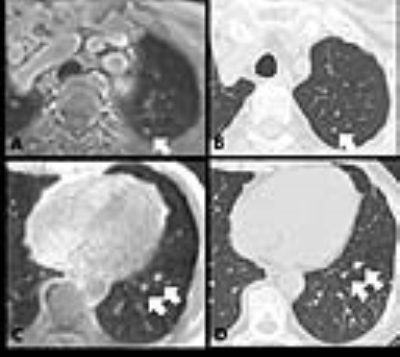
 Pulmonary nodule detection using ultra-short TE (UTE) with a 3D variable-TE stack-of-spirals sequence Pulmonary nodule detection using ultra-short TE (UTE) with a 3D variable-TE stack-of-spirals sequence
Yu-Sen Huang, Emi Niisato, Mao-Yuan Su, Alto Stemmer, Jin-Shing Chen, Yeun-Chung Chang
UTE with 3D variable-TE stack-of-spirals sampling has been developed recently and allows shorter scan times by using undersampling in combination with an iterative, self-consistent parallel imaging reconstruction (SPIRiT). The goal of this study was to investigate the feasibility of this new technique in patients for detecting pulmonary nodules. The sequence was optimized for both free-breathing and breath-holding. Compared with CT images, the detection rate for pulmonary nodules in the UTE images was 92% for free-breathing and 75% for breath-holding. Our results suggest that the proposed UTE sequence has the capacity to detect pulmonary nodules under both free-breathing and breath-holding conditions.
|
|
4365.
 |
95 |
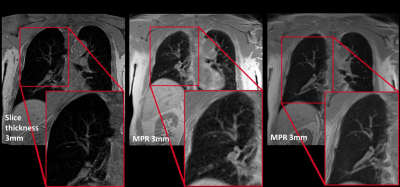
 MR imaging of the lung with a respiratory-gated ultrashort echo time (UTE) sequence with spiral acquisition technique: A feasibility study in oncology patients MR imaging of the lung with a respiratory-gated ultrashort echo time (UTE) sequence with spiral acquisition technique: A feasibility study in oncology patients
Min Jae Cha, Hyun Jeong Park, Eun Sun Lee, Sung Bin Park, Yang Soo Kim, Byung In Choi
We have demonstrated the feasibility of respiratory-gated ultrashort echo time sequence with spiral acquisition technique (spiral UTE; 1.5-mm isotropic resolution; echo time, 0.05 msec) of the lung for pulmonary nodule detection in oncology patients. Overall nodule detection rate was 86% (43 of 50 nodules) and the detection rate for nodules of ≥5 mm was 100 % (20 of 20 nodules). Mean acquisition time for spiral UTE was 327 seconds (range, 300 – 465 seconds). We think that spiral UTE could be a potential alternative to chest CT in oncology patients, who are in the risk of inevitable radiation exposure.
|
|
Prostate 1: Clinical
Electronic Poster
Body: Breast, Chest, Abdomen, Pelvis
Tuesday, 19 June 2018
| Exhibition Hall |
16:15 - 17:15 |
| |
|
Computer # |
|
4366.
 |
97 |
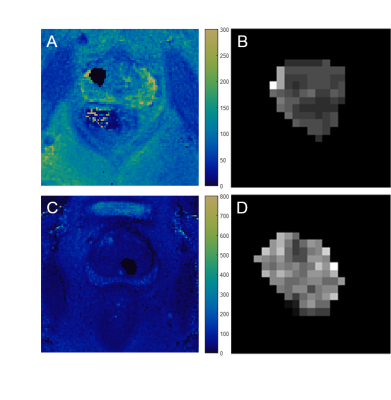
 Texture Analysis in Magnetic Resonance Fingerprinting of the Prostate: Utility for Differentiation of Grade, and Cancer from Non-cancerous tissue. Texture Analysis in Magnetic Resonance Fingerprinting of the Prostate: Utility for Differentiation of Grade, and Cancer from Non-cancerous tissue.
Samuel Frankel, Ananya Panda, Debra McGivney, Gregory O'Connor, Alice Yu, Mark Griswold, Chaitra Badve, Vikas Gulani
Prostate cancer and prostatitis can have considerable overlap on conventional MR imaging. Texture analysis on multiparametric MRI shows promise in characterization of prostate, but has not been used on quantitative prostate maps. Here we utilize texture analysis on magnetic resonance fingerprinting (MRF) maps of prostate for characterization of prostate lesions. Results show that texture features can differentiate cancer and non-cancerous transition zone and between grades of cancer in peripheral zone. This could add value to MRF-based relaxometry and conventional MRI to improve lesion characterization.
|
|
4367.
 |
98 |
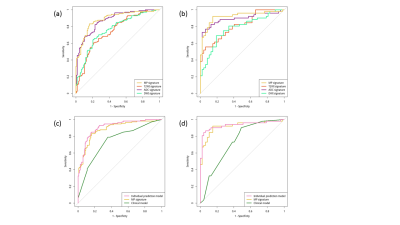
 Multiparametric MRI Radiomic Signatures: Individual Prediction for Prostate Cancer and Benign lesions with same imaging findings Multiparametric MRI Radiomic Signatures: Individual Prediction for Prostate Cancer and Benign lesions with same imaging findings
Min Xu, Xiangming Fang, Mengjie Fang, Di Dong, Jie Tian, Zhongshuai Zhang
Quantitative Radiomic features based on multiparametric Magnetic Resonance Imaging have great clinical value in discriminating prostate cancer and benign lesions with same imaging findings. We extracted Radiomic features and compared the discrimination efficiency of the combined three types of images with each single type of images, then incorporated independent clinical risk factors and further developed an individual prediction model. The experimental results show that the individual prediction model achieved more accurate diagnosis results than only using Radiomic signatures or clinical factors
|
|
4368.
 |
99 |
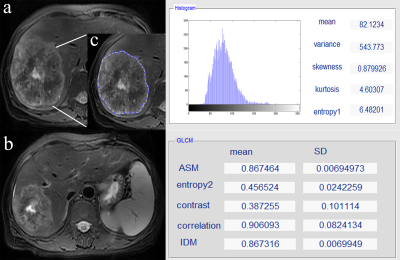
MR texture analysis: potential imaging biomarker for prediction of chemotherapy response in patients with colorectal liver metastases
Did Not Present
Huan Zhang, Wenhua Li, Feixiang Hu, Yiqun Sun, Tingdan Hu, Tong Tong
The aim of this study was to determine if pre-treated MR texture features of colorectal liver metastases (CRLMs) are predictive of chemotherapy response after the first-line chemotherapy. The results indicate that MR texture features on pre-treated T2 images seem to be a promising tool for predicting the chemotherapy response of patients with colorectal liver metastases.
|
|
4369.
 |
100 |
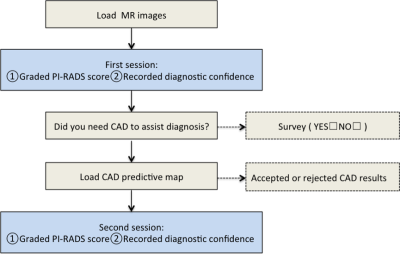
 Evaluation the Feasibility of Integrating Computer-aided Diagnosis as a Second Reader into Prostate Multiparametric MRI Diagnostic Process Evaluation the Feasibility of Integrating Computer-aided Diagnosis as a Second Reader into Prostate Multiparametric MRI Diagnostic Process
Lina Zhu, Ge Gao, Xiaoying Wang, Jing Liu, Rui Wang, Kai Zhao, Yuan Jiang
Computer-aided diagnosis (CAD) for prostate cancer (PCa) detection based on multiparametric MRI (mpMRI) has become an active field of research, which has shown good stand-alone performance. Before its widely use in daily clinical work, further study still should be done for CAD reading paradigm and the interaction between CAD and human reader. In this article, we implemented CAD in the real world practice, aiming to evaluate the feasibility of integrating CAD as a second reader into the clinical diagnostic process. The results showed this reading paradigm was feasible and CAD might help readers detect more patients with PCa.
|
|
4370.
 |
101 |
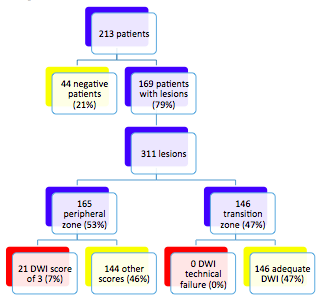
 How often is the Dynamic Contrast Enhanced (DCE) score needed in PI-RADS version 2? How often is the Dynamic Contrast Enhanced (DCE) score needed in PI-RADS version 2?
Albert Roh, Andreas Loening, Richard Fan, Geoffrey Sonn, Shreyas Vasanawala
The value of the Dynamic Contrast Enhanced (DCE) sequence in scoring a prostate lesion using PI-RADS version 2 is unknown. Our retrospective review of 213 patients who underwent prostate MRI and subsequent biopsy determined that the rate at which DCE was needed for obtaining the final PI-RADS score was 9%. This low rate raises the possibility of limiting the initial screening prostate MRI to an abbreviated non-contrast protocol, calling back the patient for the DCE sequence only if the initial exam is equivocal.
|
|
4371.
 |
102 |
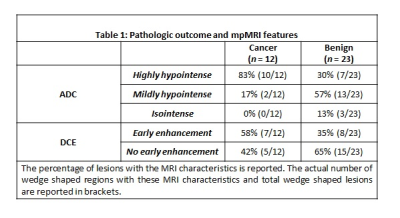
 Multi-parametric MRI features and pathologic outcome of wedge shaped lesions on T2-weighted images Multi-parametric MRI features and pathologic outcome of wedge shaped lesions on T2-weighted images
Aritrick Chatterjee, Sevil Tokdemir, Alexander Gallan, Shiyang Wang, Ambereen Yousuf, Tatjana Antic, Gregory Karczmar, Aytekin Oto
This study investigated the multi-parametric MRI features and pathologic outcome of wedge shaped lesions on T2-weighted images in 76 patients. A greater percentage of wedge shaped features were found to be malignant than shown previously. Malignant wedge shaped regions were primarily highly hypointense on ADC maps and showed early enhancement on DCE-MRI. Benign wedge shaped lesions were predominantly mildly hypointense on ADC maps and showed no early enhancement and pathologically outcome showed prostatitis, hemosiderin-laden macrophages, prominent blood vessels, intraluminal blood and atrophy. Malignant wedge shaped lesions were found to have significantly lower ADC compared to benign wedge shaped regions.
|
|
4372.
 |
103 |
 Differentiating prostate cancer from benign prostatic hyperplasia using multiparametric MRI Differentiating prostate cancer from benign prostatic hyperplasia using multiparametric MRI
Aritrick Chatterjee, Alexander Gallan, Dianning He, Xiaobing Fan, Devkumar Mustafi, Ambereen Yousuf, Tatjana Antic, Gregory Karczmar, Aytekin Oto
This study investigates multiparametric MRI (mpMRI) appearance of different types of BPH and whether quantitative mpMRI is effective in differentiating between PCa and BPH in 60 patients. mpMRI and specifically quantitative ADC values can be used for differentiating PCa and BPH, improving PCa diagnosis in the transition zone. However, DCE-MRI metrics are not effective in distinguishing PCa and BPH. In contrast to previous understanding, glandular BPH has short T2 values (hypointense on T2-weighted images), demonstrates restricted diffusion, and may have similar quantitative mpMRI measurements to stromal BPH. Additionally, glandular and cystic BPH appear differently on mpMRI and are histologically different.
|
|
4373.
 |
104 |
 Diagnosis of Prostate Cancer using MRI derived quantitative Risk Maps Diagnosis of Prostate Cancer using MRI derived quantitative Risk Maps
Aritrick Chatterjee, Dianning He, Xiaobing Fan, Tatjana Antic, Ajit Devaraj, Yulei Jiang , Gregory Karczmar, Aytekin Oto
This study develops a new tool that estimates the risk map for prostate cancer using quantitative mpMRI metrics and investigates the feasibility of this tool in screening for PCa. Quantitative mpMRI parameters: ADC, T2 and DCE signal enchantment values were calculated and subsequently cancer presence was predicted based on estimated risk scores. The sensitivity, specificity, positive predictive value and negative predictive value for PCa detection using a sector based analysis were 75.0%, 88.6%, 84.7% and 80.8% respectively. The area under the curve in ROC analysis was 0.818. Importantly, all the index lesions were identified by the risk map tool.
|
|
4374.
 |
105 |
 The effects of dutasteride on quantitative T2 and T2-weighted imaging in men on active surveillance for prostate cancer: results from a placebo-controlled, randomized clinical trial The effects of dutasteride on quantitative T2 and T2-weighted imaging in men on active surveillance for prostate cancer: results from a placebo-controlled, randomized clinical trial
Francesco Giganti, Giulio Gambarota, Caroline Moore, Neil McCartan, Mark Emberton, Clare Allen, Alex Kirkham
We investigated MRI changes in quantitative T2 parameters in lesions and healthy tissue in men on active surveillance (AS) for prostate cancer (PCa) taking dutasteride or placebo for six months. The protocol included a multi-echo sequence for quantification of the T2 relaxation times. A synthetic signal contrast (T2Q) between lesion and healthy tissue was assessed using quantitative T2 values. Signal contrast was calculated using T2-weighted sequence (T2W contrast). No differences for T2W contrast were observed. A significant correlation between T2Q and T2W contrast was shown. Dutasteride does not influence T2 contrast and relaxation in men on AS for PCa.
|
|
4375.
 |
106 |
Quantitative T2 values for Detection and Grading of Prostate Cancer
Video Permission Withheld
Tobias Franiel, Julia Mai, Mohamed Abubrig, Thomas Lehmann, Felix Güttler, Elisabeth Weiland, Tom Hilbert, René Aschenbach, Friedrich-Carl von Rundstedt, Marc-Oliver Grimm, Ulf Teichgräber
Purpose: Determination of quantitative T2 values in prostate tissue and their evaluation for detection and grading of prostate cancer.Methods: 3T T2 maps and ADC maps of 75 patients with 857 prostate areas (378x normal, 177x cancer, 150x BPH, 119x prostatitis and 33x precancer) were determined.
Results: T2 values differed significantly between cancer and normal (AUC=0.871), between cancer and BPH (AUC=0.827) and between cancer with GleasonScore 6 and ≥ 7 (AUC=0.742). T2 relaxivities decreased with increasing GleasonScore and correlated significantly with ADC-values (r=0.772).
Conclusion: T2 values seem to be adequate for the differentiation between prostate cancer and normal tissue or BPH.
|
|
4376.
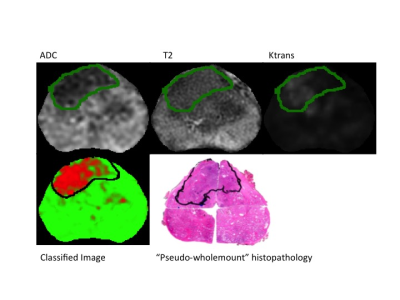 |
107 |
 Does Machine Learning, As An Independent Arbitrator Of MR Contrast-Ranking In Prostate Cancer Exams, Agree With PI-RADS version 2? Does Machine Learning, As An Independent Arbitrator Of MR Contrast-Ranking In Prostate Cancer Exams, Agree With PI-RADS version 2?
Steve Patterson, Peter Lee, Chris Bowen, Jennifer Merrimen, Cheng Wang, Steven Beyea, Sharon Clarke
We show that a simple machine learning algorithm validated most, but not all, aspects of the Prostate Imaging Reporting and Data System (PI-RADS) version 2 formalism derived exclusively from clinical perspectives. Specifically, the value of diffusion-weighted imaging (DWI) and dynamic contrast-enhanced (DCE) sequences in the peripheral zone was confirmed. In contradistinction to PI-RADS, DWI was found to be more valuable in the transition zone than T2 weighted imaging; however, a T2 texture feature afforded a small but significant increase in classifier accuracy in this zone.
|
|
4377.
 |
108 |
 Detection of Clinically Significant Prostate Cancer: Incremental Value of Deep Learning to PI-RADS V2 Detection of Clinically Significant Prostate Cancer: Incremental Value of Deep Learning to PI-RADS V2
Liang Wang
Deep learning has great potential in medical imaging. 168 patients underwent 3T mpMRI of prostate before mpMR-targeted biopsies plus systematic sampling. Two radiologists from two separate institutions, by using the Prostate Imaging Reporting and Data System (PI-RADS) V2 and a multimodal convolutional neural networks (CNN)-based deep learning, independently assessed prostate MRI examinations. Histopathologic findings were used as the reference standard. In detecting csPCa, both reviewers had significantly higher AUCs using CNN-based deep learning. Reviewer 2 benefited much more from CNN-based deep learning than did reviewer 1. Combined PI-RADS with CNN-based deep learning contribute significant incremental value in the detection of csPCa.
|
|
4378.
 |
109 |
 Feasibility of USPIO enhanced 7 Tesla MRI for detecting lymph node metastases in prostate cancer Feasibility of USPIO enhanced 7 Tesla MRI for detecting lymph node metastases in prostate cancer
Bart Philips, Rutger Stijns, Sören Johst, Stephan Orzada, Ansje Fortuin, Jelle Barentsz, Marnix Maas, Tom Scheenen
Ultrahigh field MRI offers opportunities for USPIO enhanced MRI for diagnosing lymph node metastases in prostate cancer, by improving resolution and increasing the sensitivity to USPIO particles. The assessment of lymph nodes based on size, shape and USPIO uptake can improve the differentiation between non-cancer and metastatic lymph nodes and may also lower the detection size limit for metastatic nodes. In this work we show the first results of USPIO enhanced MRI and computed echo time imaging of patients with high risk prostate cancer at 7 Tesla.
|
|
4379.
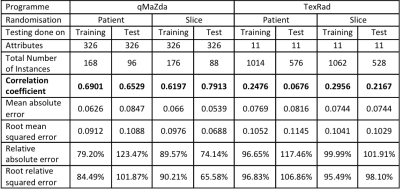 |
110 |
 Use of Texture Analysis to Predict Prostate Artery Embolization Outcomes with MR imaging Use of Texture Analysis to Predict Prostate Artery Embolization Outcomes with MR imaging
Susanna Kallioinen, Terence Jones, James Harding, Manpreet Dhillon, Sachin Modi, Nigel Hacking, Drew Maclean, Charles Hutchinson
Pre-prostate artery embolization (PAE) magnetic resonance images (MRI) from patients with benign prostatic hypertrophy (BPH) were segmented and analysed using two different texture analysis software, qMaZda and TexRad. Percentage reduction in prostate volume and percentage reduction in the International Prostate Symptom Score (IPSS) were used as MRI based outcome measures to build models to be able to predict outcomes from PAE. MRI texture analysis using qMaZda with a linear regression model is able to somewhat predict the percentage prostate volume reduction three months after PAE but not the percentage reduction in IPSS.
|
|
4380.
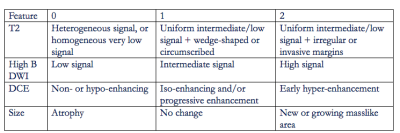 |
111 |
 Utility of Multiparametric Prostate Magnetic Resonance Imaging for Prediction of Treatment Response Following Focal Laser Ablation Utility of Multiparametric Prostate Magnetic Resonance Imaging for Prediction of Treatment Response Following Focal Laser Ablation
Ely Felker, Leonard Marks, Fuad Elkhoury, David Lu, Daniel Margolis, Shyam Natarajan, James Sayre, Steven Raman
We evaluated the utility of multiparametric prostate MRI, including T2-weighted imaging, diffusion-weighted imaging (DWI) and dynamic contrast-enhanced imaging, in predicting treatment response following focal laser ablation of prostate cancer in a multi-reader study. DWI appears to be the most useful sequence in response assessment, but inter-reader agreement was moderate at best.
|
|
4381.
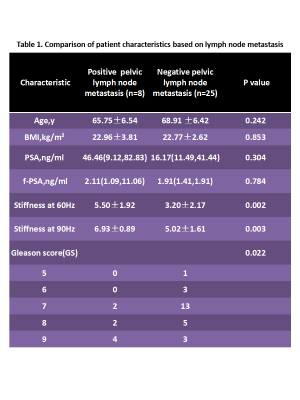 |
112 |
 Preliminary Investigation of MR Elastography to Predict Lymph Node Metastasis in Prostate Cancer Preliminary Investigation of MR Elastography to Predict Lymph Node Metastasis in Prostate Cancer
Jin Wang, TianHui Zhang, Ying Deng, Sichi Kuang, Bingjun He, Qungang Shan, Jun Chen, Phillip Rossman, Arvin Arani, Xin Gao, Ziying Yin, Meng Yin, Kevin Glaser, Richard Ehman
Prostate cancer(PCa) is one of the leading causes of cancer-related deaths in North American men. Nodal metastases occur in 3-42% of men with clinically localized prostate cancer and the presence of nodal metastases has a strong negative impact on survival. Lymph node staging plays an important role in planning initial management in nonmetastatic PCa. Early detection and resection are important for staging and for the prognosis. We evaluated the diagnostic performance of MR elastography (MRE) in patients with PCa. Results from 33 patients with PCa show that MRE at both of 60Hz and 90Hz has the potential to be a useful technique for predicting PCa lymph node metastases and to establish prognosis and treatment planning.
|
|
4382.
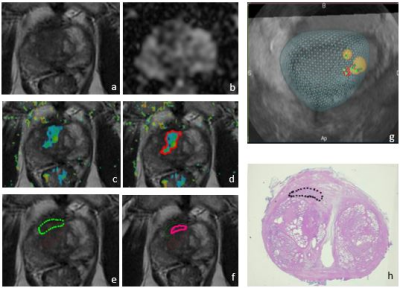 |
113 |
 Improvement of prostate cancer detection combining a computer aided diagnosis system to TRUS-MRI targeted biopsy. Improvement of prostate cancer detection combining a computer aided diagnosis system to TRUS-MRI targeted biopsy.
Martina Pecoraro, Riccardo Campa, Giovanni Barchetti, Isabella Ceravolo, Vincenzo Salvo, Elena Indino, Maurizio Del Monte, Carlo Catalano, Valeria Panebianco
To validate the role of mpMRI combined to CAD system, to increase prostate cancer detection rate using TRUS-MRI guided biopsy. 167 individuals, with elevated PSA level and no previous positive biopsy were enrolled and 63 underwent targeted biopsy. Two radiologists evaluated the exams adopting PIRADSv2 and CAD system. Radiologists’ evaluation proved better diagnostic performance compared to CAD. The highest detection rate for clinically significant cancer was obtained biopsying “target into target” lesions. CAD system proved to be useful in pinpointing the neoplastic area within MRI lesions, representing a valuable tool in identifying biopsy targets to improve CDR.
|
|
4383.
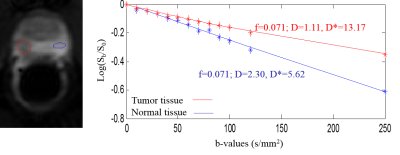 |
114 |
 Intravoxel Incoherent Motion Diffusion Weighted Imaging of Prostate Cancer Intravoxel Incoherent Motion Diffusion Weighted Imaging of Prostate Cancer
Lei Qin, Daniel Glazer, Pelin Ciris, Andriy Fedorov, Thiele Kobus, Fiona Fennessy, Stephan Maier, Robert Mulkern
Intravoxel Incoherent Motion (IVIM) DWI was acquired with 13 b-values, ranging from 0 to 250 s/mm2. With such low b-values, a short TE results in a better signal-to-noise ratio. Monoexponential fitting was performed to obtain ADC, and biexponential fitting was performed to obtain diffusion D, perfusion fraction f, and perfusion related pseudo-diffusion coefficient D*. In a prostate cancer (PCa) patient cohort, we only found a significant difference between normal and tumor tissue for D, which was absent in ADC, f, and D*. This suggests that IVIM biexponential analysis can help remove perfusion component from diffusion, leading to a more accurate measurement in diffusion coefficient.
|
|
4384.
 |
115 |
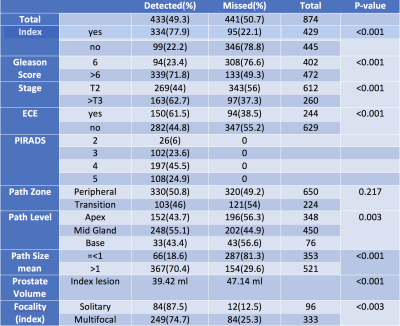
 3T Multiparametric MRI based detection of Prostate Cancer: features of detected and missed tumors base on PIRADS v2 in 429 patients- using whole mount histopathology reference 3T Multiparametric MRI based detection of Prostate Cancer: features of detected and missed tumors base on PIRADS v2 in 429 patients- using whole mount histopathology reference
Amirhossein Mohammadian Bajgiran, Sohrab Afshari Mirak, Ely Felker, Preeti Ahuja, Cleo Maehara, William Hsu, David Lu, Robert Reiter, Anthony Sisk, Steve Raman
We evaluated the performance of the 3 Tesla multiparametric MRI (mp-MRI) for detection of prostate cancer (PCa) based on Prostate Imaging Reporting and Data System (PI-RADS) Version 2 in 429 patients with 874 lesions. The overall and index tumor detection rate of 3T mp-MRI was 49.3% and 77.9% respectively. The tumor detection rate based on PIRADS v2 increased by size, grade, stage, solitariness and smaller prostate volume. Most missed lesions were small and low grade although a small proportion of large and high grade lesions were not detected.
|
|
4385.
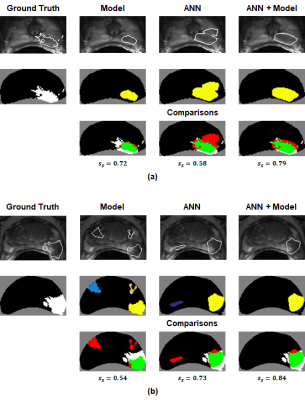 |
116 |
 Clinical usage and impact of predictive models of prostate cancer on multiparametric MRI: a single-observer exploratory evaluation Clinical usage and impact of predictive models of prostate cancer on multiparametric MRI: a single-observer exploratory evaluation
Ethan Leng, Benjamin Spilseth, Gregory Metzger
A single-observer, experiential study was conducted to understand how predictive models of prostate cancer on multiparametric MRI can be used clinically, and to determine whether such models have the potential to improve observer performance. A radiologist experienced in prostate MRI was asked to interpret mpMRIs for 34 patients before and after viewing model-generated predictive maps. Results show that the radiologist generally had low confidence in the accuracy of the predictive maps. However, his performance was significantly improved in the cases where he judged the predictive maps to be helpful. A multi-reader iteration of the study is planned.
|
|
4386.
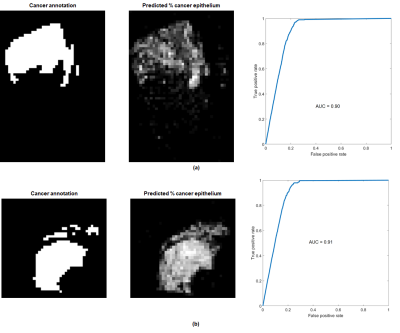 |
117 |
 Estimation of prostate cancer distribution on pathology slides via image analysis of IHC-stained slides. Estimation of prostate cancer distribution on pathology slides via image analysis of IHC-stained slides.
Ethan Leng, Jonathan Hendriksen, Jin Jin, Stephen Schmechel, Gregory Metzger
For the development of CAD systems of prostate cancer, manual annotation of cancer by experienced pathologists is the gold standard for establishing the ground truth. However, the process is tedious and has finite precision. Here, we describe a framework that uses quantitative analysis of IHC-stained slides to derive parameters, which in turn are used by a trained predictive model to estimate the spatial distribution of malignant epithelium. Thresholding of the results provides a reasonable map of cancer that is comparable to manual annotation.
|
|
4387.
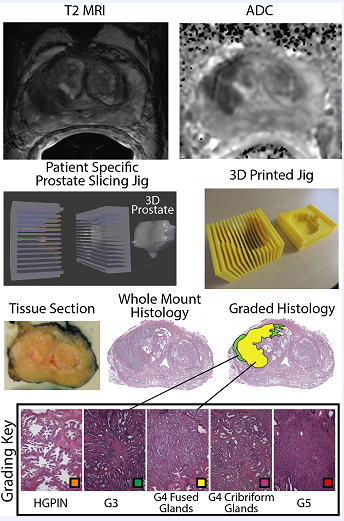 |
118 |
 The RadPath Surfer: A Radiologic-Pathologic tool for visualizing prostate cancer histology The RadPath Surfer: A Radiologic-Pathologic tool for visualizing prostate cancer histology
Sean McGarry, Sarah Hurrell, Kenneth Jacobsohn, Kenneth Iczkowski, Michael Griffin, Petar Duvnjak, Andrew Nencka, Mark Hohenwalter, Peter LaViolette
Prostate cancer is clinically defined by the Gleason Score (GS), based on the pattern of cells and glands. While imaging is useful for localizing prostate cancer, clinical diagnosis is based only on pathology; as such, tools which combine clinical imaging and pathology are highly useful as training tools. This study combines expert annotated histology aligned with clinical imaging to provide a visualization tool, allowing the user to select a region on the MRI and view the underlying pathology and Gleason annotation.
|
|
4388.
 |
119 |
 Diagnostic performance of qualitative and quantitative 3T DCE-MRI parameters of prostate cancer lesions in transition and peripheral zone stratified by pathology Gleason score and PI-RADSv2 score Diagnostic performance of qualitative and quantitative 3T DCE-MRI parameters of prostate cancer lesions in transition and peripheral zone stratified by pathology Gleason score and PI-RADSv2 score
Sohrab Afshari Mirak, Kyung Sung, Amirhossein Mohammadian Bajgiran, Nazanin Asvadi, Ely Felker, Preeti Ahuja, Anthony Sisk, Robert Reiter, Steven Raman
We investigated the diagnostic performance of qualitative and quantitative parameters of dynamic contrast enhanced magnetic resonance imaging (DCE-MRI) of prostate cancer (PCa) in 238 patients with 303 lesions located in transition (TZ) and peripheral zone (PZ) stratified by pathology Gleason score (GS) and PI-RADSv2 score with whole mount histopathology validation. There was a significant difference in qualitative and quantitative values between low and high-grade tumors and PI-RADSv2 scores in PZ PCa lesions. However, for tumors located in TZ, only DCE curve type was significantly different between low and high-grade PCa.
|
|
4389.
 |
120 |
 Diffusion-weighted Imaging and Dynamic Contrast-enhanced Imaging Distinguish Inflammation from Low Grade Cancer and Normal Tissue in the Peripheral Zone of the Prostate Diffusion-weighted Imaging and Dynamic Contrast-enhanced Imaging Distinguish Inflammation from Low Grade Cancer and Normal Tissue in the Peripheral Zone of the Prostate
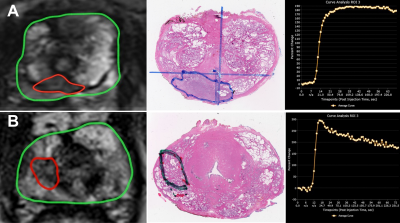
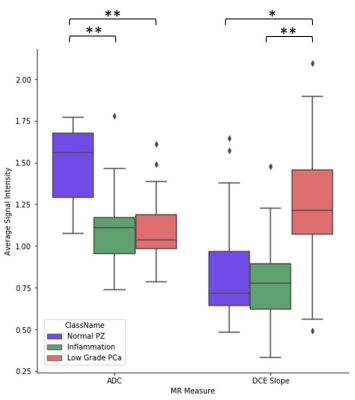
Natalie Korn, Olga Starobinets, Jeffry Simko, John Kurhanewicz, Susan Noworolski
Inflammation can complicate the ability to distinguish normal tissue from cancer in the peripheral zone of the prostate. In this work, we show that a multiparametric MRI including dynamic contrast-enhanced imaging (DCE) and diffusion-weighted imaging can distinguish inflammation in the peripheral zone of the prostate from both low-grade prostate cancer and normal tissue. A depth-restricted decision tree built on the apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) and maximal wash-in slope on DCE correctly classified 79.6% of regions of normal tissue, inflammation, and low-grade cancer in the peripheral zone of the prostate based on pathologist-detailed regions on whole-mount resected glands.
|
|
Breast 2
Electronic Poster
Body: Breast, Chest, Abdomen, Pelvis
Tuesday, 19 June 2018
| Exhibition Hall |
17:15 - 18:15 |
| |
|
Computer # |
|
4438.
 |
49 |
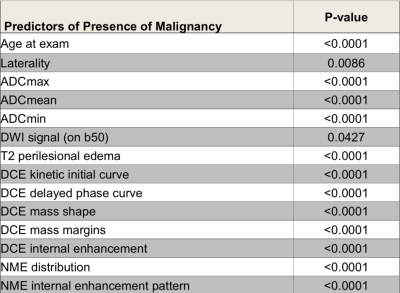
 Breast Cancer Diagnosis: A Multiparametric Magnetic Resonance Imaging Model with Dynamic Contrast Enhanced and Diffusion Weighted Imaging Breast Cancer Diagnosis: A Multiparametric Magnetic Resonance Imaging Model with Dynamic Contrast Enhanced and Diffusion Weighted Imaging
Katja Pinker-Domenig, Michelle Zhang, Joao Horvat, Blanca Bernard-Davila, Rosa Elena Ochoa-Albiztegui, Elisabeth Morris, Sunitha Thakur, Pascal Baltzer, Thomas Helbich
To develop a multiparametric MRI model incorporating the ACR BI-RADS recommended descriptors for DCE-MRI, T2-weighted and DW imaging biomarkers for accurate breast cancer diagnosis. A multivariate logistic regression analysis of multiparametric MRI data from 210 breast tumors was performed to determine parameters that jointly predicted malignancy. A multiparametric MRI model incorporating quantitative and qualitative for DCE-MRI [mass margins (p=0.0012), initial EH (p=0.422) and delayed enhancement (0.0065)] and DW imaging biomarkers [ADCmean (p=0.0031)] enables an accurate breast cancer diagnosis. Results indicate that to maximize diagnostic accuracy a multiparametric MRI approach with DWI and DCE sequences must be considered.
|
|
4439.
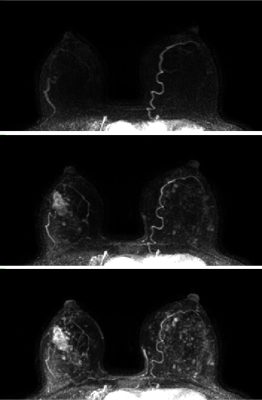 |
50 |
 Initial enhancement in breast ultrafast DCE-MRI as a marker for malignancy Initial enhancement in breast ultrafast DCE-MRI as a marker for malignancy
Federico Pineda, Ty Easley, Hiroyuki Abe, David Schacht, Gregory Karczmar
59 patients with dense breasts and suspicious findings on mammography underwent pre-biopsy DCE-MRI including high-temporal-resolution (‘ultrafast’) imaging during the first minute post-contrast. Parameters descriptive of early enhancement (initial slope and initial area under the gadolinium curve) were significantly different between benign and malignant lesions. Ultrafast imaging allowed for measurement of kinetic parameters with respect to the bolus time-of-arrival in the breast; removing dependence on variables such as cardiac output. High-temporal resolution DCE allows accurate measurements of very early enhancement kinetics, when differences between benign and malignant lesions may be largest; this could aid in the evaluation of suspicious breast lesions.
|
|
4440.
|
51 |
 Lymph Node Multi-parametric MRI Is a Strong Predictor of Pathologic Response to Chemotherapy: ACRIN/I-SPY Trial Lymph Node Multi-parametric MRI Is a Strong Predictor of Pathologic Response to Chemotherapy: ACRIN/I-SPY Trial
Silu Han, Renee Cattell, James Kang, Thomas Ren, Pauline Huang, Haifang Li, Jules Cohen, Paul Fisher, Roxanne Palermo, Tim Duong
MRI primary breast lesion volume has been shown to be a strong predictor in the response to chemotherapy for invasive breast cancer. However, the prediction accuracy remains low. In this study, we investigated the feasibility of using lymph node volume and signal enhancement ratio as predictors of the chemotherapy response. The result shows that the lymph nodes signal-enhancement ratio is a stronger predictor than lymph node volume and primary in-breast lesion volume.
|
|
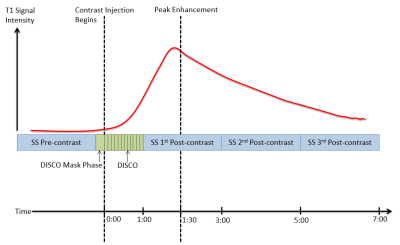
4441.
 |
52 |
 Combined Ultrafast and Steady State DCE-MRI Differentiates Invasive Breast Cancer Types and Is Associated with Pathological Complete Response to Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy Combined Ultrafast and Steady State DCE-MRI Differentiates Invasive Breast Cancer Types and Is Associated with Pathological Complete Response to Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy
Meredith Sadinski, Natsuko Onishi, Katherine Gallagher, Theodore Hunt, Amita Shukla-Dave, Danny Martinez, Brittany Dashevsky, Elizabeth Morris, Elizabeth Sutton
132 patients with invasive breast cancer were imaged with our DCE-MRI protocol incorporating ultrafast, DISCO imaging of early wash-in phase with standard, steady state DCE-MRI. Heuristic and pharmacokinetic metrics were calculated from the DISCO and steady state images and compared between invasive lobular and invasive ductal carcinomas. Bolus Arrival Time was significantly higher in ILC than in IDC. Association of parameters with pathological complete response to neoadjuvant chemotherapy administered after the imaging exam was investigated for a subset of 25 patients. Heterogeneity-related parameters were significantly higher in the pCR group encouraging further investigation into imaging biomarkers predictive of treatment response.
|
|
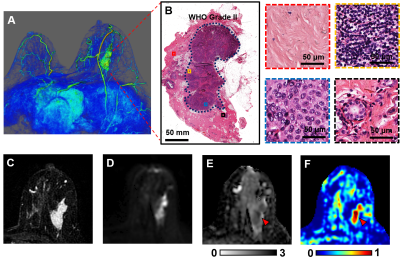
4442.
 |
53 |
 Characterize Tumor Cellularity in Breast Cancer with Diffusion MRI Characterize Tumor Cellularity in Breast Cancer with Diffusion MRI
Zezhong Ye, Na Zhao, Joshua Lin, Qingsong Yang, Jeff Viox, Peng Sun, Jianping Lu, Song-Kwei Song
Recent consensus suggested breast MRI lacks necessary sensitivity or specificity to detect breast cancer. MRI may over-diagnose breast cancer and result in over-treatment. The novel diffusion MRI histology (D-Histo) method demonstrated its ability to accurately locate lesion and quantify cancer cellularity and afforded greater sensitivity and specificity than ADC did in distinguishing between tumor and benign tissues. D-Histo’s improved diagnostic accuracy thus better guides treatment planning, and more accurately measures treatment efficacy.
|
|
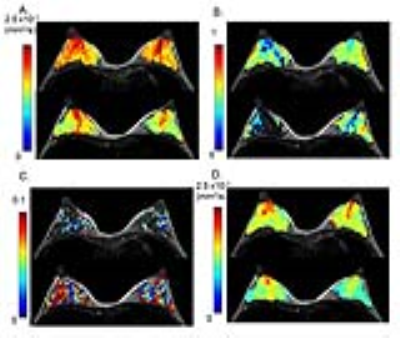
4443.
 |
54 |
 Intravoxel incoherent motion (IVIM) and non-Gaussian diffusion MRI of the lactating breast Intravoxel incoherent motion (IVIM) and non-Gaussian diffusion MRI of the lactating breast
Mami Iima, Masako Kataoka, Rena Sakaguchi, Shotaro Kanao, Natsuko Onishi, Makiko Kawai, Katsutoshi Murata, Kaori Togashi
The effect of breastfeeding on IVIM and non-Gaussian diffusion MRI was investigated. ADC0 and sADC values significantly decreased (P < 0.001 and P < 0.001) while K values significantly increased (P < 0.05) post-breastfeeding. fIVIM values significantly increased after breastfeeding (P < 0.01). No significant difference was found in D* values. There was significant heterogeneity in ADC0 maps post-breastfeeding, both in retroareolar and segmental scores (P < 0.0001 and = 0.0001). IVIM and non-Gaussian diffusion parameters significantly changed between pre- and post-breastfeeding status, and care needs to be taken in interpreting DWI data in lactating breasts.
|
|
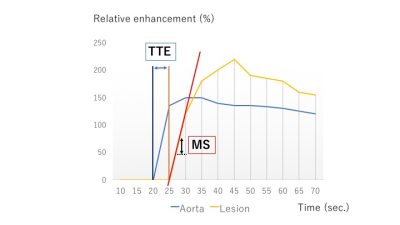
4444.
 |
55 |
 Novel parameters of Ultrafast DCE MRI of the breast using a compressed sensing technique Novel parameters of Ultrafast DCE MRI of the breast using a compressed sensing technique
Maya Honda, Masako Kataoka, Natsuko Onishi, Shotaro Kanao, Hajime Sagawa, Mami Iima, Kanae Miyake, Dominik Nickel, Masakazu Toi, Kaori Togashi
We evaluated new parameters of breast ultrafast dynamic contrast-enhanced (UF-DCE) MRI using compressed sensing technique: the maximum slope (MS), time to enhancement (TTE) and the time interval between arterial and venous visualization (AVI). MS was higher, and TTE and AVI were shorter in malignant lesions compared to benign lesions, although there were discrepancies among these parameters and BI-RADS based delayed phase patterns. There seemed to be some relevance between these parameters and histopathologic findings.
|
|
4445.
 |
56 |
 Effect of Contrast Dose on Diagnostic Performance in DCE-MR Breast Imaging Effect of Contrast Dose on Diagnostic Performance in DCE-MR Breast Imaging
Lawrence Dougherty, Elizabeth McDonald, Gamaliel Isaac, Thuy-My Le, Mark Rosen
A retrospective reader study was performed to assess breast MRI diagnostic performance as a function of contrast dose. There was an increase in sensitivity for malignancy with increasing contrast dose with no significant decrease in specificity. Greater confidence in the lesion assessment was also shown by the inter-observer agreement, which increased at the higher doses. Diagnostic performance of DCE-MR breast imaging was greater when subjects received a higher gadolinium dose than the current standard of 0.10 mmol/kg.
|
|
4446.
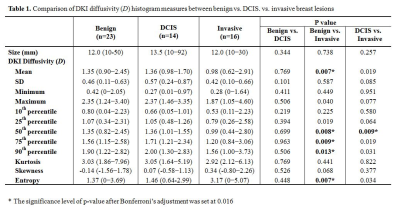 |
57 |
Diffusional Kurtosis Imaging for Differentiation of Additional Suspicious Lesions on Preoperative Breast MRI of Patients with Known Breast Cancer
Video Permission Withheld
Vivian Park, Sungheon Kim, Eun-Kyung Kim, Hee Jung Moon, Jung Hyun Yoon, Min Jung Kim
We investigated the potential of diffusional kurtosis imaging (DKI) and conventional diffusion weighted imaging (DWI) for differentiation of additional suspicious lesions on preoperative breast MRI patients with known breast cancer. This study included 53 pathologically confirmed lesions larger than 10mm in 45 women with known breast cancer. DKI and DWI parameters were compared between lesions. Multiple DKI parameters showed a significant difference between benign vs. invasive breast lesions and a few differed between DCIS vs. invasive breast lesions, with high specificity. However, DKI and DWI could not distinguish DCIS from benign lesions and may have lower potential in this subgroup
|
|
4447.
 |
58 |
 Effectiveness of 6 monthly MRI screening for breast cancer in women with a BRCA mutation – a numerical simulation. Effectiveness of 6 monthly MRI screening for breast cancer in women with a BRCA mutation – a numerical simulation.
Keith S Cover, Joost PA Kuijer, Mark MB Hofman, Jeroen Veltman, Monique D Dorrius, Ritse M Mann, Katya M Duvivier
Currently, MRI screening for breast cancer in women with a BRCA mutation is annually. However, studies on tumour doubling times indicate that some tumours grow faster. To assess the value of more frequent screening we numerically simulated annual and 6 monthly screening based on reported tumour doubling times in women with the BRCA mutation. For annual screening, the simulation predicted 14% of cancers with poor prognosis (diameter > 2 cm), in line with clinical studies. For 6 monthly screening the simulation predicted 3% with poor prognosis. Therefore, 6 monthly screening should yield a substantial reduction in tumours with a poor prognoses .
|
|
4448.
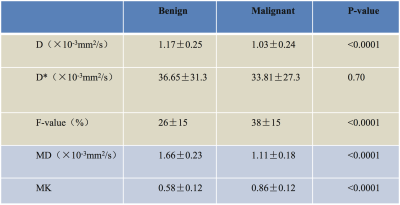 |
59 |
 The Value of DKI and IVIM Quantitative Parameters in Differentiating Breast Lesions and Correlations with Histopathologic Factors: A Preliminary Study The Value of DKI and IVIM Quantitative Parameters in Differentiating Breast Lesions and Correlations with Histopathologic Factors: A Preliminary Study
Chenglu Ke, Shunan Che, Jing Li, Lizhi Xie
The current study aimed to evaluate the application of diffusion kurtosis imaging (DKI) and intravoxel incoherent motion (IVIM) in the differential diagnosis of breast lesions. The association of DKI and IVIM derived parameters were compared with pathological types, histologic grade, and Ki-67 expression of primary breast cancers. The results indicated that MD, MK, D and f are capable of distinguishing benign from malignant breast lesions. Furthermore, significant correlations were observed between MD and different histologic grade and Ki-67 expression, repsectivley.
|
|
4449.
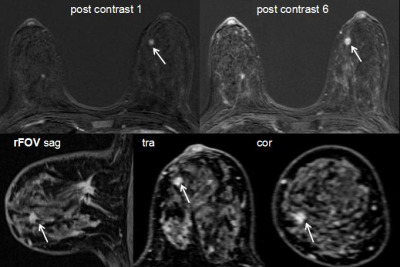 |
60 |
Clinical Value of Reduced field-of-view Sagittal Delayed-Enhanced Breast MRI
Did Not Present
Xiuhua Lv, Feihan Jiao, Junqing Xu, Hong Yin
This study aimed to investigate the clinical value of reduced field-of-view (rFOV) sagittal delayed enhanced MRI in diagnosing of breast tumor. we assessed two groups with and without rFOV sagittal delayed enhanced scanning with a time interval of at least six months.In our study, the detection rate, specificity and positive predictive value of the test group with rFOV were significantly higher than that of the control group without rFOV. rFOV sagittal delayed enhanced scanning indicated clinical value in detecting and differential diagnosis of benign and malignant breast tumors.
|
|
4450.
 |
61 |
Quantitative evaluation of Diffusion tensor and Intravoxel incoherent motion (IVIM) magnetic resonance imaging in cyclic mastalgia in premenopausal young women
Did Not Present
Qiuju Fan, Hui Tan, Nan Yu, Yuxin Lei, Shaoyu Wang, Yong YU
Severe breast pain may significantly affect activities related to life quality, while its aetiology is still poorly understand. DTI and IVIM can provide valuable information on tissue microstructure, microcirculation and pathophysiology that has been extensively used on the breast cancer [1].
|
|
4451.
|
62 |
 Breast Lesion Detection and Characterization with Contrast-Enhanced Magnetic Resonance Imaging: Prospective Randomized Intra-individual Comparison of Gadoterate Meglumine versus Gadobenate Dimeglumine at 3 Tesla Breast Lesion Detection and Characterization with Contrast-Enhanced Magnetic Resonance Imaging: Prospective Randomized Intra-individual Comparison of Gadoterate Meglumine versus Gadobenate Dimeglumine at 3 Tesla
Paola Clauser, Thomas Helbich, Panagiotis Kapetas, Maria Bernathova, Katja Pinker, Pascal Baltzer
The aim of our study was to compare a 0.075 mmol/kg dose of gadobenate dimeglumine, with a 0.15 mmol/kg dose of gadoterate meglumine for breast lesion detection and characterization at 3T-MRI. Patients included underwent two examinations, 24-72h apart, one with gadobenate and one with gadoterate administered in randomized order. Three readers evaluated the examinations and diagnostic performance was calculated and compared. 104 women with 142 histologically verified breast lesions (109 malignant, 33 benign) were included. Detection with gadobenate was comparable to gadoterate (p>0.165). Gadobenate demonstrated significantly higher specificity and accuracy (p<0.007). Multivariate analysis demonstrated reader-independent superior diagnostic accuracy with gadobenate.
|
|
4452.
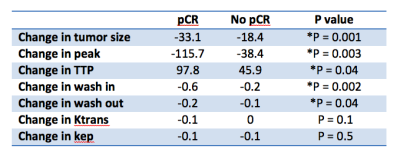 |
63 |
 Quantitative Predictors of Response to Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy on Dynamic Contrast-Enhanced Breast MRI Quantitative Predictors of Response to Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy on Dynamic Contrast-Enhanced Breast MRI
Hyung Won Choi, Melissa Joines, Anne Hoyt, Laura Doepke, Jane Dascalos, Cheryce Fischer, Nanette DeBruhl, Nazanin Yaghmai, Kara Lee Pool, Bo Li, James Sayre, Stephanie Lee-Felker
In this IRB-approved, HIPAA-compliant retrospective study, 63 consecutive women with newly diagnosed breast cancer undergoing neoadjuvant chemotherapy with pre- and post- chemotherapy breast MRI on a 3.0 Tesla scanner prior to surgery at our institution between January 2013 and December 2015 were included for analysis. Decrease in tumor size, decrease in peak enhancement, increase in time to peak, decrease in wash in, and decrease in wash out on post-chemotherapy breast MRIs were predictive of pathologic complete response on surgical pathology, a surrogate for prognosis.
|
|
4453.
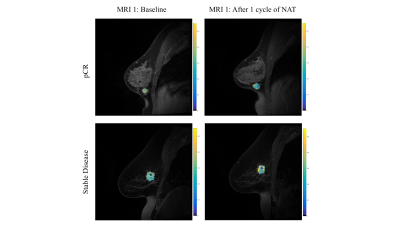 |
64 |
 Magnetization Transfer MRI of Breast Cancer Response to Neoadjuvant Therapy: Preliminary Results Magnetization Transfer MRI of Breast Cancer Response to Neoadjuvant Therapy: Preliminary Results
Jack Virostko, Anna Sorace, Chengyue Wu, Stephanie Barnes, Angela Jarrett, Debra Patt, Boone Goodgame, Sarah Avery, Thomas Yankeelov
Magnetization transfer MRI (MT-MRI) may be sensitive to changes in the macromolecular content of tumors and the extracellular matrix that occur during neoadjuvant therapy for breast cancer. We demonstrate in a pilot population of breast cancer patients that the magnetization transfer ratio declines after the first cycle of chemotherapy in women who achieve response to therapy, while the magnetization transfer ratio increases in tumors that do not respond to therapy.
|
|
4454.
 |
65 |
 Feasibility of multispectral spin echo breast quantitative susceptibility mapping: an alternative to post-biopsy mammogram after MR-guided breast biopsy Feasibility of multispectral spin echo breast quantitative susceptibility mapping: an alternative to post-biopsy mammogram after MR-guided breast biopsy
Sarah Eskreis-Winkler, Katherine Simon, Youngwook Kee, Junghun Cho, Thanh Nguyen, Pascal Spincemaille, Michele Drotman, Yi Wang
During MR-guided breast biopsy, a titanium biopsy marker is deployed in the biopsy cavity to mark the spot. Conventional MR cannot distinguish between these markers and the pockets of air that are often introduced during the biopsy, necessitating a subsequent mammogram to confirm biopsy marker location. Our goal is to replace post-biopsy mammogram with a short MR protocol leveraging the difference in magnetic susceptibility between titanium and air in order to distinguish them as sources of MR signal voids. To this end, we generate quantitative susceptibility maps (QSM) using 3D fast spin echo acquired at four frequency offsets.
|
|
4455.
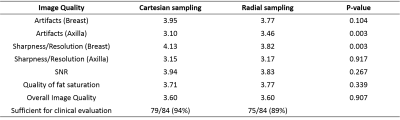 |
66 |
 Comparison of Radial and Cartesian Acquisitions for Visualization of the Axilla in Breast MRI: Reader Study Comparison of Radial and Cartesian Acquisitions for Visualization of the Axilla in Breast MRI: Reader Study
Pingni Wang, Roberta Strigel, Makiko Kawai, Ty Cashen, Julia Velikina, Kang Wang, Frank Korosec, Urvi Tailor, Jillian Karow, Kevin Johnson, Andre Fischer, James Holmes
Dynamic contrast-enhanced (DCE) MRI using conventional Cartesian sampling is used in routine clinical practice due to its high sensitivity for breast cancer. However, ghosting artifacts caused by cardiac motion can obscure the axilla, making interpretation of this area more difficult and potentially obscuring findings. Radial acquisitions are less motion sensitive due to more frequent sampling of the center of k-space and prior work has suggested these methods for breast MRI. In this study, we report results from a reader study to assess image quality of a 3D stack-of-stars radial acquisition compared with Cartesian imaging for breast MRI.
|
|
4456.
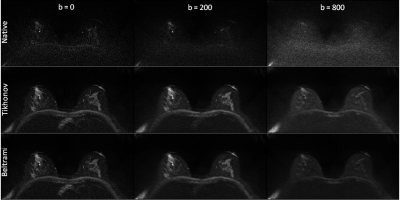 |
67 |
 One millimeter isotropic breast DWI combining readout-segmented EPI and super-resolution One millimeter isotropic breast DWI combining readout-segmented EPI and super-resolution
Maya DELBANY, Julie POUJOL, Aurélien BUSTIN, Isabelle THOMASSIN-NAGGARA, Jacques FELBLINGER, Pierre-André VUISSOZ, Freddy ODILLE
High-resolution diffusion-weighted imaging (DWI) has the potential to improve the specificity of breast MRI. In this work a method is proposed for 3D isotropic DWI of the whole breasts. Three breast DWI datasets were acquired using a readout-segmented DW-EPI sequence (rs-EPI) with thick slices (3 mm) and 1mm-shifts in the slice direction. A high isotropic resolution (1x1x1 mm3) DWI dataset was reconstructed using a super-resolution reconstruction (SRR) on the low-resolution anisotropic acquisiitons, with different regularization schemes (Tikhonov and Beltrami, an edge-preserving constraint). This study shows the benefit of this strategy compared to native acquisitions with 1 mm slice thickness. A quantitative SNR evaluation is presented.
|
|
4457.
 |
68 |
 Addition of in-vivo proton MRS to DCEMRI increases the sensitivity of cancer detection in breast cancer patients especially in cases of indeterminate dynamic MRI findings. Addition of in-vivo proton MRS to DCEMRI increases the sensitivity of cancer detection in breast cancer patients especially in cases of indeterminate dynamic MRI findings.
Naranamangalam Jagannathan, Khusbhu Agarwal, Uma Sharma, Smriti Hari, Vurthaluru Seenu, Sandeep Mathur, Siddhartha Gupta, Rajinder Parshad
Potential of addition of in-vivo proton (1H) MRS to DCEMRI data especially in indeterminate DCE findings was evaluated. MRS and DCEMRI data of 56 breast cancer patients were included in the analysis. 47/56 cases showed type III curve indicating cancer with a sensitivity of 83.9%. MRS showed true positive findings of cancer in 44/47 cases. Among 9 indeterminate DCE cases, MRS was positive for cancer in 6 cases, implying that 50/56 cases were true positive for cancer with 89.3% sensitivity. Addition of MRS to DCEMRI data increases the sensitivity of cancer detection especially in indeterminate DCE findings.
|
|
4458.
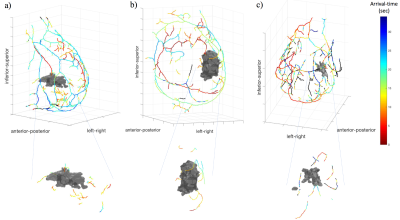 |
69 |
 Quantitative analysis of ultra-fast DCE-MRI to identify vascular inputs and outputs in breast tumors Quantitative analysis of ultra-fast DCE-MRI to identify vascular inputs and outputs in breast tumors
Chengyue Wu, Federico Pineda, Gregory Karczmar, Thomas Yankeelov
Identifying and characterizing vascular inputs and outputs in tumors would be useful in both the diagnostic and prognostic settings. In this contribution, we propose a novel methodology that combines vessel detection with analysis of ultra-fast DCE-MRI data to integrate both morphological and functional information of tumor associated vessels to identify those that serve as inputs and outputs to breast tumors.
|
|
4459.
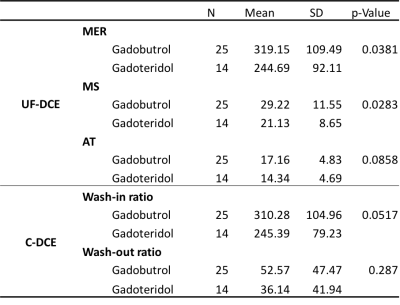 |
70 |
 Comparison of 1.0M Gadobutrol and 0.5M Gadoteridol for Kinetic Parameters on Breast Dynamic Contrast Enhanced Magnetic Resonance Imaging at 3T Comparison of 1.0M Gadobutrol and 0.5M Gadoteridol for Kinetic Parameters on Breast Dynamic Contrast Enhanced Magnetic Resonance Imaging at 3T
Hajime Sagawa, Masako Kataoka, Shotaro Kanao, Natsuko Onishi, Maya Honda, Dominik Nickel, Masakazu Toi, Katsuhiko Ueda, Kaori Togashi
The contrast effects of 1.0M gadobutrol were compared to that of 0.5M gadoteridol in breast cancer at 3T using hybrid MRI protocol which combined conventional DCE (C-DCE) with ultrafast DCE (UF-DCE). The significant differences were observed only in UF-DCE, maximum enhancement ratio (MER) and maximum slope (MS). The slightly higher peak relative enhancement produced by gadobutrol compared with gadoteridol might help in the detection and evaluation of breast lesions in the earlier phases.
|
|
4460.
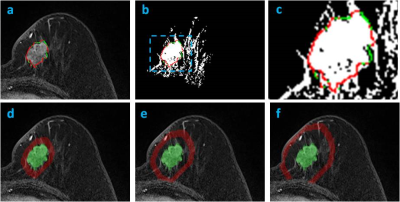 |
71 |
 Quantitative Analysis of Peri-Tumor Interface Fat and the Volumetric Fat Percentage and Contrast Enhancement in Three Peri-Tumoral Shells to Differentiate Molecular Subtypes of Breast Cancer Quantitative Analysis of Peri-Tumor Interface Fat and the Volumetric Fat Percentage and Contrast Enhancement in Three Peri-Tumoral Shells to Differentiate Molecular Subtypes of Breast Cancer
Jeon-Hor Chen, Yang Zhang, Siwa Chan, Dah-Cherng Yeh, Min-Ying Su
A 3D morphological analysis method was developed to analyze the fat content on tumor boundary interface and in different peri-tumoral shells away from the tumor. A total of 114 mass type breast cancers were analyzed, including 87 HR(+), 13 HR(-)HER2(+), and 14 TN. The volumetric fat percentage in three shells surrounding the tumor: 150%-100%, 200%-150%, 250%-200% of the tumor convex hall were measured, also the mean contrast enhancement in fibroglandular tissue contained within three shells were measured. The peri-tumor fat content and contrast enhancement is the highest in the most aggressive TN tumors compared to other subtypes.
|
|
4461.
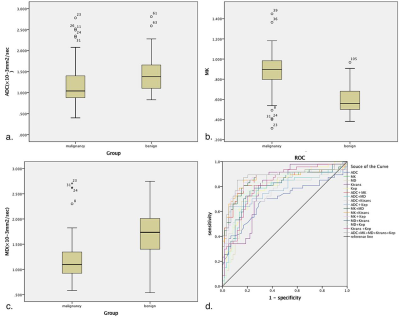 |
72 |
Effectivity and correlation of parameters derived from diffusion kurtosis imaging and quantitative dynamic contrast-enhanced MRI in the breast imaging
Did Not Present
Ting Li, Siying Wang, Yun Xiong, Kangan Li
The aim of this study is to evaluate the diagnostic efficacy of 3.0T MRI diffusion kurtosis imaging and quantitative dynamic contrast enhancement in benign and malignant breast lesions, and to explore the differential diagnosis ability of different pathological types and molecular subtype lesions. The results showed that 3.0T MRI diffusion kurtosis imaging and dynamic contrast-enhanced quantitative hemodynamic parameters are of great value in the differential diagnosis of benign and malignant breast lesions. The combination of both can significantly improve the diagnostic efficiency.
|
|
Hyperpolarised Compound Imaging
Electronic Poster
Body: Breast, Chest, Abdomen, Pelvis
Tuesday, 19 June 2018
| Exhibition Hall |
17:15 - 18:15 |
| |
|
Computer # |
|
4462.
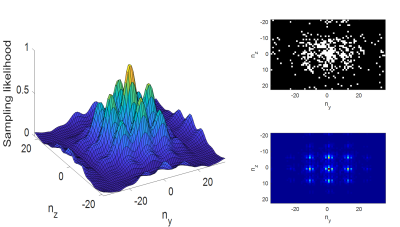 |
73 |
 Highly Accelerated Dynamic Acquisition of 3D Grid-Tagged He-3 Lung Images Using Compressed Sensing Highly Accelerated Dynamic Acquisition of 3D Grid-Tagged He-3 Lung Images Using Compressed Sensing
William Garrison, Kun Qing, Sina Tafti, John Mugler, Y Shim, Jaime Mata, Gordon Cates, Eduard de Lange, Craig Meyer, Jing Cai, G Miller
Radiotherapy in the context of lung cancer can become less effective if lung biomechanics are not well-characterized. MRI of grid-tagged, inhaled hyperpolarized He-3 gas provides images with strong signal at the tag locations, allowing time-resolved tracking of regional lung motion that can be used to inform strategies for precision radiotherapy. The present work demonstrates rapid acquisition of high-quality 3D grid-tagged images obtained with 8-fold under-sampling and reconstructed using compressed sensing. The dramatic imaging acceleration inherent in this technique allows multiple 3D image sets to be acquired during a single breath-hold, effectively permitting 4D-MRI of lung motion during exhalation.
|
|
4463.
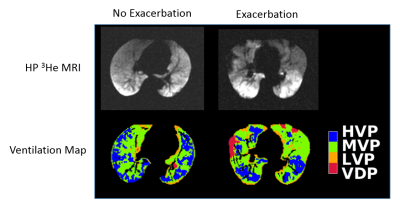 |
74 |
 High Ventilation Percent on Hyperpolarized Helium-3 MRI is Associated with Reduced One-Year Risk of Asthma Exacerbation High Ventilation Percent on Hyperpolarized Helium-3 MRI is Associated with Reduced One-Year Risk of Asthma Exacerbation
David Mummy, Wei Zha, Shannon Kehoe, Guy Olson, Ronald Sorkness, Nizar Jarjour, Mark Schiebler, Loren Denlinger, Michael Evans, Sean Fain
We assessed the high ventilation percent (HVP) as well as the ventilation defect percent (VDP) on hyperpolarized (HP) 3He MRI and found that both measures were associated with exacerbation in the year following imaging, with the HVP exhibiting the stronger association. Both measures were strong predictors relative to other measures of lung function. These findings suggest that HVP is sensitive to one-year risk of asthma exacerbation and is a potential biomarker of asthma instability.
|
|
4464.
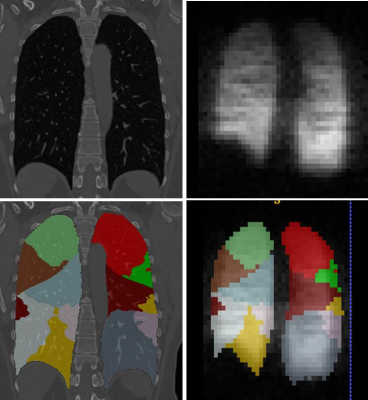 |
75 |
 Bridging the gap between lung small conducting and acinar airways – combined in vivo lung morphometry with hyperpolarized 3He MRI and CT studies. Bridging the gap between lung small conducting and acinar airways – combined in vivo lung morphometry with hyperpolarized 3He MRI and CT studies.
Dmitriy Yablonskiy, Alexander Sukstanskii, James Quirk, Chase Hall, Mario Castro, David Gierada, Vanessa Curtis, Miranda Kirby, Eric Hoffman, Roger Yusen
Air trapping (retention of inspired air during expiration) is usually associated with small conducting airways disease. However, limited information exists on integrity of acinar airways (i.e., alveolar ducts and sacs) in lung regions affected by air trapping. In this study we combine novel CT and MRI metrics to understand the sub-lobar level relationships between MR-derived acinar anatomy and CT-based air trapping metrics. We studied healthy non-smokers, smokers and COPD subjects and found significant associations between air trapping and acinar airways shallowing in upper and middle lungs in all groups but very little association in lower lung, except for COPD patients.
|
 |
4465.
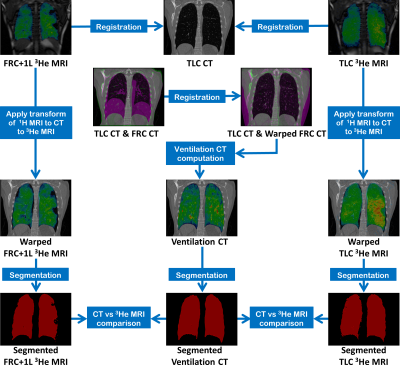 |
76 |
 Comparison of CT ventilation and Hyperpolarised Gas MRI: Effects of breathing manoeuvre Comparison of CT ventilation and Hyperpolarised Gas MRI: Effects of breathing manoeuvre
Bilal Tahir, Helen Marshall, Paul Hughes, Guilhem Collier, Rob Ireland, Jim Wild
Image registration of lung CT images acquired at different inflation levels has been proposed as a surrogate method to map lung ‘ventilation’. However, this technique requires validation against established ventilation imaging modalities such as hyperpolarized gas MRI. Variations in lung inflation may affect regional lung function as imaged with the two modalities. Here, we evaluate the impact of the lung inflation level during MRI when comparing gas MRI and CT ventilation for a cohort of 7 patients with asthma.
|
|
4466.
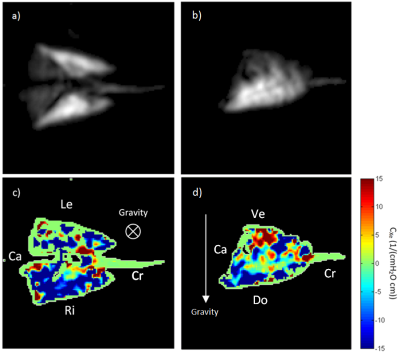 |
77 |
 Mapping of pseudo-compliance using hyperpolarized 129Xe morphometry in the rat lung Mapping of pseudo-compliance using hyperpolarized 129Xe morphometry in the rat lung
Andras Lindenmaier, Brandon Zanette, Elaine Stirrat, Brian Kavanagh, Giles Santyr
Performing 129Xe morphometry at multiple pressures allows for direct mapping of microstructural changes and micromechanical properties of the lung (eg. pseudo-compliance) in both health and disease. In the present study, the effects of posture and gravity on the linear portion of lung pseudo-compliance are investigated using this approach in healthy mechanically-ventilated rats. Spatial gradients in lung pseudo-compliance due to gravity and posture are shown to vary, consistent with the expectations that the lungs are denser dorsally due to the weight above. Scaled regional pseudo-compliance is shown to be in agreement with whole lung compliance measured using 1H MRI.
|
|
4467.
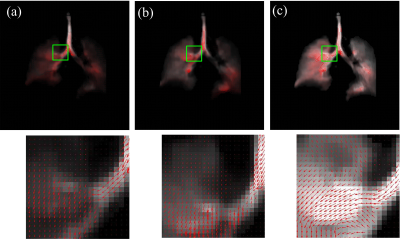 |
78 |
 Depiction of Gas Flow Patterns in Pulmonary Dynamic Hyperpolarized Gas MRI Depiction of Gas Flow Patterns in Pulmonary Dynamic Hyperpolarized Gas MRI
Sa Xiao, He Deng, Caohui Duan, Junshuai Xie, Xianping Sun, Chaohui Ye, Xin Zhou
Dynamic hyperpolarized gas MRI of lung is able to visualize the dynamic changes of pulmonary morphology during the ventilation process, which provides the important information about lung physiology and pathophysiology. However, there is a lack of an effective method to depict the gas flow patterns in the whole lung. In this work, we propose a motion field calculation method based on the pulmonary gas flow properties, which can acquire the velocity and direction of gas flow. The performance of the proposed method is investigated experimentally.
|
|
4468.
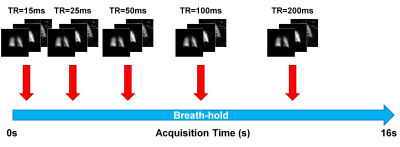 |
79 |
 An Interleaved Spiral-IDEAL Approach for Physiological Gas Exchange Imaging in Humans using a Single Breath-hold of Hyperpolarized 129Xe An Interleaved Spiral-IDEAL Approach for Physiological Gas Exchange Imaging in Humans using a Single Breath-hold of Hyperpolarized 129Xe
Brandon Zanette, Giles Santyr
Pulmonary disease involving lung injury (e.g. ventilator-induced lung injury, radiation-induced lung injury, interstitial lung disease) can lead to pulmonary dysfunction which may not be detectable using proton pulmonary magnetic resonance imaging or ventilation imaging with hyperpolarized noble gases. The solubility of 129Xe in biological tissues and resultant chemical shifts allow for the quantification of physiological gas exchange which hold promise for the clinical evaluation of early pulmonary dysfunction. In this work we demonstrate an approach for dissolved-phase 129Xe gas exchange imaging within a single breath-hold in healthy human volunteers.
|
|
4469.
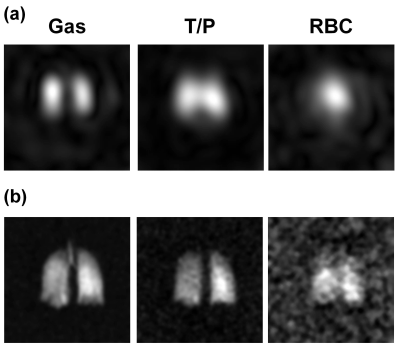 |
80 |
 Clinical Translation of 3D Spiral-IDEAL for Single Breath-hold Imaging of Gas and Dissolved-Phase Hyperpolarized 129Xe in Human Lungs Clinical Translation of 3D Spiral-IDEAL for Single Breath-hold Imaging of Gas and Dissolved-Phase Hyperpolarized 129Xe in Human Lungs
Brandon Zanette, Giles Santyr
Spiral-IDEAL is a fast and efficient technique for imaging dissolved-phase hyperpolarized 129Xe in tissue/blood plasma (T/P) and red blood cell (RBC) compartments of the lung. Previously, spiral-IDEAL has been limited to pre-clinical rodent models using multi-breath techniques not suitable for human subjects. In this work we optimize and demonstrate clinical translation of spiral-IDEAL for single breath-hold 129Xe imaging of human subjects. We compare and contrast several interleaved imaging strategies. Furthermore, we also demonstrate 3D spiral-IDEAL for simultaneous volumetric imaging of gas, T/P, and RBC compartments.
|
|
4470.
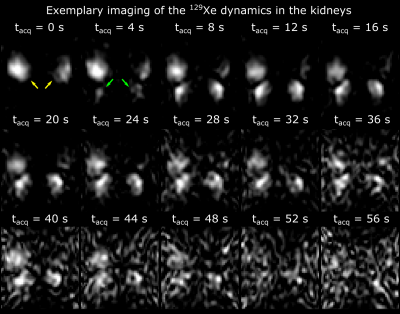 |
81 |
 Dynamic MRI of Hyperpolarized Xenon-129 Uptake in the Human Kidney Using a Dedicated Transmission-Only-Reception-Only Array at 3 Tesla Dynamic MRI of Hyperpolarized Xenon-129 Uptake in the Human Kidney Using a Dedicated Transmission-Only-Reception-Only Array at 3 Tesla
Jorge Chacon-Caldera, Adam Maunder, Madhwesha Rao, Graham Norquay, Oliver Rodgers, Matthew Clemence, Claudio Puddu, Lothar Schad, Jim Wild
Dissolved hyperpolarized 129Xe MRI is an emerging technique. Inhaled xenon dissolves in the blood in the lungs and with a long T1 (8s) has the potential for imaging other organs that are well perfused such as the kidneys. An RF coil array was designed with an anatomically focused transmit field to avoid RF depolarization of dissolved xenon in its transit from the lungs whilst providing local sensitivity over the kidney. Dynamic imaging of dissolved 129Xe in kidneys was performed in 2 healthy volunteers. The signal evolution in the cortex was obtained which might provide novel physiological insight into kidney physiology.
|
|
4471.
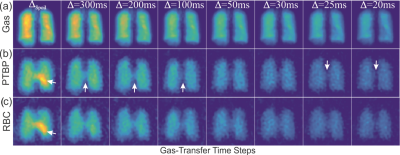 |
82 |
 Hyperpolarized 129Xe Gas Exchange Imaging of the Human Lung using IDEAL with Spiral k-space Sampling Hyperpolarized 129Xe Gas Exchange Imaging of the Human Lung using IDEAL with Spiral k-space Sampling
Ozkan Doganay, Mitchell Chen, Tahreema Matin, Marzia Rigolli, Julie-Ann Phillips, Anthony McIntyre, Fergus Gleeson
This proof of concept study describes implementation and analysis of an IDEAL (Iterative Decomposition of water and fat with Echo Asymmetry and Least-square estimation) based imaging technique for imaging hyperpolarized Xenon-129 (HPX) gas ventilation and dissolved phase compartments in human lungs. The time-series IDEAL imaging approach was tested in a healthy subject corroborating with Bloch equations and a numerical gas-exchange model showing that HPX gas ventilation and dissolved phase compartment images can be obtained, and the gas-transfer dynamics can be measured, in a single breath-hold interval of 8 seconds using 1L of HPX gas with polarization of ~10%.
|
|
4472.
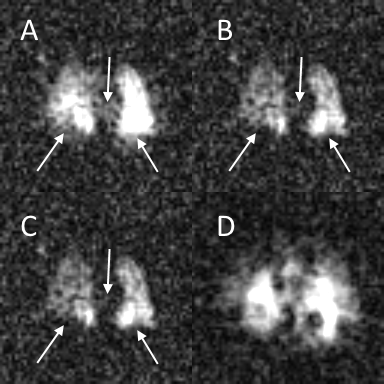 |
83 |
 Retrospective removal of gas-phase signal from pulmonary dissolved-phase Hyperpolarized 129Xe images Retrospective removal of gas-phase signal from pulmonary dissolved-phase Hyperpolarized 129Xe images
Jeff Kammerman, Andrew Hahn, Sean Fain
Dissolved-phase hyperpolarized xenon-129 imaging provides regional information on gas exchange between the lung airspaces, parenchymal tissues, and blood stream. Current spectroscopic techniques require that the dissolved-phase 129Xe signal be acquired with no gas-phase excitation. However, the short T2* of the dissolved-phase requires short RF pulses, limiting the spectral selectivity achievable. This, combined with the high spin density of the gas-phase relative to the dissolved-phase, leads to unwanted gas-phase excitation. In this work, we retrospectively remove contaminant gas-phase signal from both simulated and human subject images using a multi-echo acquisition with iterative estimation of the contaminant gas-phase signal.
|
|
4473.
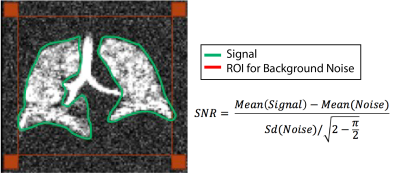 |
84 |
 The Effect of Signal to Noise Ratio on Linear-binning and Adaptive k-means Quantification of Hyperpolarized 129Xe Ventilation MRI The Effect of Signal to Noise Ratio on Linear-binning and Adaptive k-means Quantification of Hyperpolarized 129Xe Ventilation MRI
Mu He, Fei Tan, Wei Zha, Leith Rankine, Sean Fain, Bastiaan Driehuys
129Xe ventilation MRI lacks a reference standard. Here, we circumvent this problem in part by comparing and evaluating the robustness of two independent methods for quantifying ventilation – linear-binning and adaptive k-means - by adding MR noise to the source images until the algorithms fail. Results at different noise levels were compared to that quantified using the original high signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) ventilation image. We found that both methods provide robust quantification until SNR is less than 1.7 ± 0.8 for the linear-binning method, and 2.1 ± 1.2 for the uncorrected adaptive k-means method.
|
|
4474.
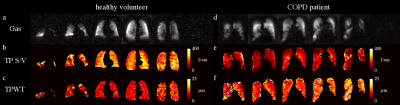 |
85 |
 Voxel-based mapping of lung microstructural parameters using hyperpolarized 129Xe dissolved-phase imaging in healthy volunteers and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease patients Voxel-based mapping of lung microstructural parameters using hyperpolarized 129Xe dissolved-phase imaging in healthy volunteers and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease patients
Agilo Kern, Marcel Gutberlet, Andreas Voskrebenzev, Filip Klimes, Alexander Rotärmel, Frank Wacker, Jens Hohlfeld, Jens Vogel-Claussen
Chemical shift saturation recovery (CSSR) spectroscopy is a method, which is able to assess lung microstructure using 129Xe gas uptake and to discriminate between healthy volunteers and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) patients. However, the absent spatial encoding of standard CSSR spectroscopy poses a limitation of the method for detecting early disease. A method for voxel-based mapping of lung microstructural parameters is proposed. Preliminary data from a study in healthy volunteers and COPD patients employing both CSSR mapping and spectroscopy are presented. Whole-lung median wall thickness and surface-to-volume ratio are highly reproducible and correlate significantly with global values from spectroscopy in COPD patients.
|
|
4475.
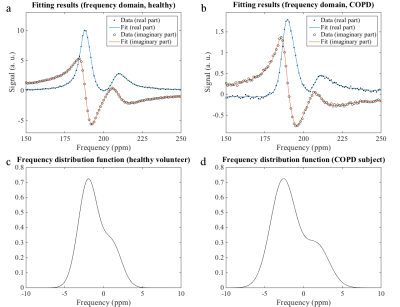 |
86 |
 Hyperpolarized 129Xe MR spectroscopy of the human lung in healthy volunteers and patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD): investigation of lung microstructure Hyperpolarized 129Xe MR spectroscopy of the human lung in healthy volunteers and patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD): investigation of lung microstructure
Agilo Kern, Marcel Gutberlet, Andreas Voskrebenzev, Filip Klimes, Frank Wacker, Jens Hohlfeld, Jens Vogel-Claussen
The NMR line shape in the lung parenchyma exhibits significant broadening due to numerous jumps in magnetic susceptibility. The purpose of this work was to extract this line shape from the 129Xe dissolved-phase spectrum. Free induction decays were acquired in healthy volunteers and COPD patients and a model function including two resonances and a superimposed frequency distribution was fitted to the time-domain data. Both second moment and skewness of the fitted frequency distribution were significantly elevated in COPD patients. The ratio of 129Xe in red blood cells and lung tissue was significantly reduced in COPD patients.
|
|
4476.
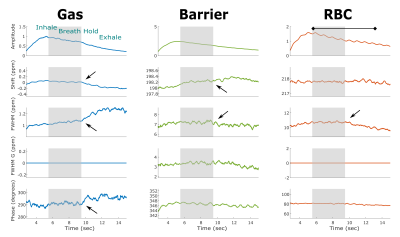 |
87 |
 Quantifying Changes in Time-Resolved Hyperpolarized 129Xe Spectroscopy among Healthy Volunteers, Subjects with Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis, and Subjects with Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension Quantifying Changes in Time-Resolved Hyperpolarized 129Xe Spectroscopy among Healthy Volunteers, Subjects with Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis, and Subjects with Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension
Elianna Bier, Scott Robertson, Geoff Schrank, Craig Rackley, Joseph Mammarappallil, Sudarshan Rajagopal, H. Page McAdams, Bastiaan Driehuys
The temporal dynamics of 129Xe spectroscopy were examined by collecting FIDs during inhalation, breath-hold, and exhalation. These FIDs were fit to a Voigt model to extract four spectral parameters (amplitude, chemical shift, linewidth, and phase) for the airspace, barrier, and RBC 129Xe resonances. The RBC resonance parameters exhibited oscillations at the cardiac frequency which were quantified by peak-to-peak amplitudes. IPF subjects exhibited larger signal amplitude, chemical shift, and phase oscillations than healthy or PAH subjects. This indicates that 129Xe transfer spectroscopy is differentially affected by cardiopulmonary dynamics such that the causes of gas exchange impairment can be distinguished.
|
|
4477.
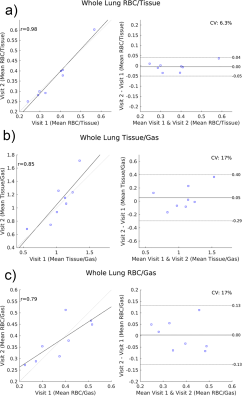 |
88 |
 Repeatability of Pulmonary Functional Metrics of Gas-exchange Measured with Hyperpolarized Xenon-129 MRI Repeatability of Pulmonary Functional Metrics of Gas-exchange Measured with Hyperpolarized Xenon-129 MRI
Andrew Hahn, Jeff Kammerman, Michael Evans, Wei Zha, David Mummy, Robert Cadman, Sean Fain
To advance hyperpolarized Xenon-129 MRI as a robust tool for probing pulmonary gas-exchange in lung diseases, establishing repeatability of quantitative ratios and regional metrics is critical. Repeatability was assessed using Bland-Altman analysis. Average inter-visit tissue-to-gas, red blood cell-to-gas (RBC-to-gas) and RBC-to-tissue ratios were highly repeatable; the primary source of variation was due to lung inflation volume variations, suggesting consistency of breath-hold coaching and dose delivery is important. Regional distribution of measures was also qualitatively well-matched between visits. Demographic factors may also influence these measures; our preliminary data indicate a significant relationship between RBC-to-tissue ratio and subject age.
|
|
4478.
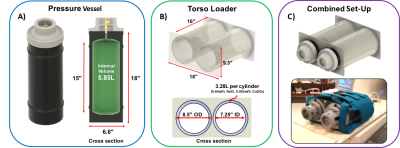 |
89 |
 A Clinical-Scale Thermally Polarized 129Xe Phantom for Quality Assurance in Multi-Center Hyperpolarized Gas MRI Trials A Clinical-Scale Thermally Polarized 129Xe Phantom for Quality Assurance in Multi-Center Hyperpolarized Gas MRI Trials
Naomi Medina, Ziyi Wang, Mu He, Geoffry Schrank, John Nouls, Elianna Bier, Scott Robertson, Ralph Hashoian, John Mugler, Bastiaan Driehuys
Hyperpolarized 129Xe-MRI is emerging as a promising method to quantify pulmonary function, but the transient nature of its signal makes routine quality assurance tasks challenging. With increasing interest in multi-center deployment of this technology, it is critical to develop tools to characterize 129Xe imaging performance across sites and platforms. Here, we demonstrate a robust, portable, clinical-scale thermally-polarized 129Xe phantom and integrated loader shell. Its utility is demonstrated for characterizing human lung imaging coils and enabling routine 2D- QA scans in one-minute. On longer timescales, 3D-imaging is feasible to evaluate 129Xe coil sensitivity profiles.
|
|
4479.
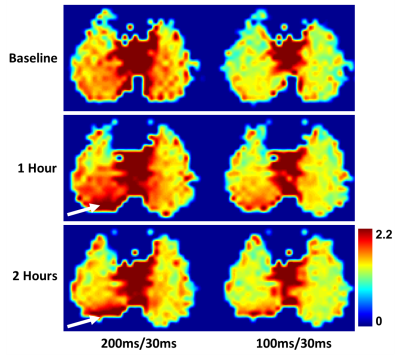 |
90 |
 Assessing the Impact of Acid Aspiration with Hyperpolarized Xenon-129 Dissolved-Phase MRI Assessing the Impact of Acid Aspiration with Hyperpolarized Xenon-129 Dissolved-Phase MRI
Kai Ruppert, Hooman Hamedani, Faraz Amzajerdian, Luis Loza, Yi Xin, Ian Duncan, Harilla Profka, Sarmad Siddiqui, Mehrdad Pourfathi, Maurizio Cereda, Stephen Kadlecek, Rahim Rizi
Acid aspiration frequently occurs in critically ill patients, and can give rise to severe acute lung injury. In this study, we investigated whether hyperpolarized xenon-129 dissolved-phase MRI provides the necessary sensitivity to assess acid aspiration and associated pneumonitis in a rabbit model. We observed changes that most likely corresponded to the formation of interstitial edema as part of an inflammatory response. In particular, perilesional areas of high xenon uptake may reflect tissue at risk of secondary ventilator-induced injury.
|
|
4480.
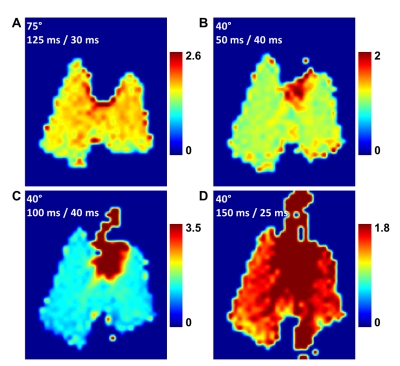 |
91 |
 Investigating Pulmonary Gas Transport Processes with Hyperpolarized Xenon-129 Dissolved-Phase MRI Investigating Pulmonary Gas Transport Processes with Hyperpolarized Xenon-129 Dissolved-Phase MRI
Kai Ruppert, Hooman Hamedani, Faraz Amzajerdian, Luis Loza, Yi Xin, Ian Duncan, Harilla Profka, Sarmad Siddiqui, Mehrdad Pourfathi, Stephen Kadlecek, Rahim Rizi
Several hyperpolarized xenon-129 (HXe) MRI techniques have been developed for characterizing lung function through the observation of parenchymal xenon gas uptake, but these methods tend to provide only a snapshot of a steady-state distribution of the xenon signal within the lung parenchyma. In this study, we investigated the feasibility of extracting gas-transport maps from the relative signal changes between two dissolved-phase images captured with different acquisition parameters. We demonstrated how the acquisition parameters of a suitably-designed HXe MRI pulse sequence can be harnessed for tracing pulmonary gas transport processes, and potentially quantifying them at an unprecedented level.
|
|
4481.
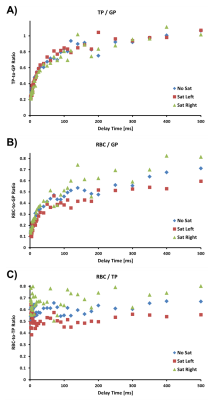 |
92 |
 Using Regional Gas-Phase Saturation to Localize Hyperpolarized Xenon-129 Spectroscopy Measurements Using Regional Gas-Phase Saturation to Localize Hyperpolarized Xenon-129 Spectroscopy Measurements
Kai Ruppert, Hooman Hamedani, Faraz Amzajerdian, Luis Loza, Yi Xin, Ian Duncan, Harilla Profka, Sarmad Siddiqui, Mehrdad Pourfathi, Stephen Kadlecek, Rahim Rizi
Chemical Shift Saturation Recovery MR spectroscopy is becoming a powerful tool for quantifying alveolar gas exchange, but is currently predominantly used for whole-lung assessments. In this study, we investigated the feasibility of regional gas-phase saturation as a tool for coarse spatial localization, testing its utility in a rat model of radiation-induced lung injury. We found a large decrease in the ratio between the red-blood-cell and tissue / plasma peaks in the irradiated lung relative to the lungs in a healthy animal. Our approach might be particularly useful for assessing highly heterogeneous disease patterns (radiation-induced lung injuries, lung transplants, etc.).
|
|
4482.
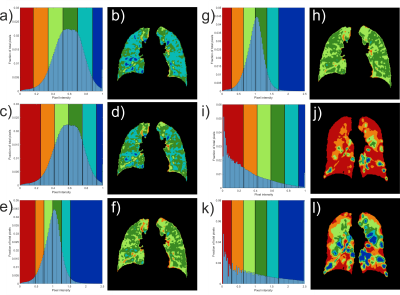 |
93 |
 Linear binning maps for image analysis of pulmonary ventilation with hyperpolarized gas MRI: transferability and clinical applications Linear binning maps for image analysis of pulmonary ventilation with hyperpolarized gas MRI: transferability and clinical applications
Guilhem Collier, Laure Acunzo, Laurie Smith, Paul Hughes, Graham Norquay, Ho-Fung Chan, Alberto Biancardi, Helen Marshall, Jim Wild
This work applies a clustering method developed for image analysis of lung ventilation with hyperpolarized 129Xe to data acquired in a different centre with 129Xe and 3He. Results show that the current method is not readily transferable using published reference values. A different normalization method that increases the reproducibility of ventilation categorization is proposed. After optimization, the technique was applied in groups of patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and cystic fibrosis. Results show significant differences of ventilation distribution indices between patient and healthy control groups.
|
|
4483.
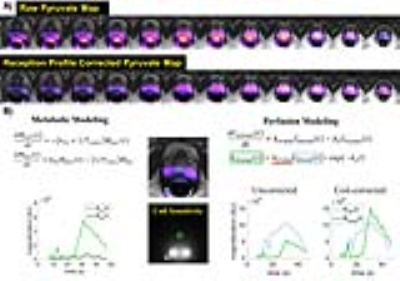 |
94 |
 Dynamic Hyperpolarized 13C CS-EPSI of Human Prostate Cancer – Initial Experience on 17 Patients Testing Acquisition & Quantitative Analysis Methods Dynamic Hyperpolarized 13C CS-EPSI of Human Prostate Cancer – Initial Experience on 17 Patients Testing Acquisition & Quantitative Analysis Methods
Hsin-Yu Chen, Peder Larson, Jeremy Gordon, Robert Bok, Marcus Ferrone, Sue Noworolski, Mark van Criekinge, James Slater, Lucas Carvajal, Natalie Korn, Rahul Aggarwal, Sarah Nelson, Pamela Munster, John Kurhanewicz, Daniel Vigneron
New hyperpolarized-13C MRI instrumentation and methods enabled phase II clinical studies on 17 prostate cancer patients using 3D dynamic CS-EPSI with 0.5cm3 spatial and 2s time resolution. New manufacturing processes for 13C-pyruvate provided more consistent polarization levels, pyruvate concentrations, radical filtrations for reliable and safe patient injections. Improved quantitative methods were designed and implemented for reproducible kinetic modeling, correction for receiver profile, and peak detection, accounting for B0 inhomogeneity and noise characteristics. These studies have shown the ability to detect high pyruvate-to-lactate conversion rates in biopsy confirmed prostate cancer.
|
|
4484.
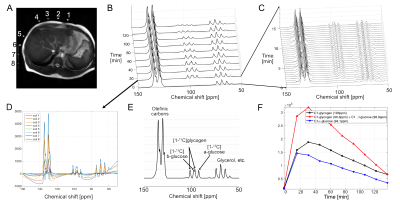 |
95 |
 Rapid hepatic glycogen synthesis in humans using dynamic 13C MR spectroscopy Rapid hepatic glycogen synthesis in humans using dynamic 13C MR spectroscopy
Jae Mo Park, Stefan Stender, Craig Malloy, Jonathan Cohen, Ralph DeBerardinis, Vlad Zaha
The development of hyperpolarized 13C for human patients has refocused interest on radiofrequency (RF) coil design for optimal 13C sensitivity. 13C NMR spectra were acquired from the human liver using a clamshell transmit and 8-channel paddle receive array in a 3T MRI system. Following a baseline 13C liver scan for 15-min, [1-13C]glucose was ingested and 13C MRS data were acquired for 1-3hrs. [1-13C]glucose was observed immediately after ingestion in the stomach, and evolution of [1-13C]glycogen was monitored with < 1min temporal resolution. 13C chemical shift imaging data confirmed that the glycogen signals were localized in the liver.
|
|
4485.
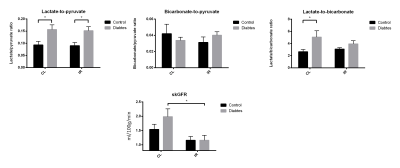 |
96 |
 Acute kidney injury in diabetic rats assessed with hyperpolarized 13C MRI Acute kidney injury in diabetic rats assessed with hyperpolarized 13C MRI
Per Nielsen, Marie Mølmer, Rikke Nørregaard, Christoffer Laustsen
In this study we investigate the metabolic alterations, injury and fibrosis development when combining type 1 diabetes and IRI. We find the anaerobic metabolism is highly upregulated in the diabetic kidney, but this elevation is severely reduced in the reperfusion phase. The reduced injury repair capability of the diabetic kidney leads to high injury induction and fibrosis, which in turn reduces kidney function. Therefore special care should be taken to animals or patients experiencing this combination to avoid renal failure.
|
|
Prostate 2: Technical
Electronic Poster
Body: Breast, Chest, Abdomen, Pelvis
Tuesday, 19 June 2018
| Exhibition Hall |
17:15 - 18:15 |
| |
|
Computer # |
|
4486.
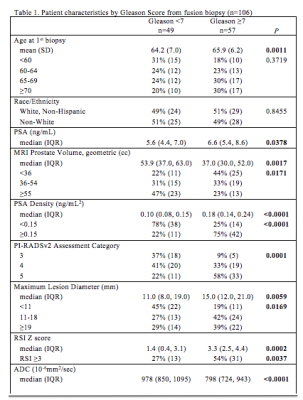 |
97 |
 Restriction Spectrum Imaging-A Novel Diffusion-Based Technique for Detection and Characterization of Prostate Cancer Restriction Spectrum Imaging-A Novel Diffusion-Based Technique for Detection and Characterization of Prostate Cancer
Ely Felker, Leonard Marks, Fuad Elkhoury, David Lu, Daniel Margolis, Sepideh Shakeri, Pooria Khoshnoodi, Lorna Herbert, Nathan White, David Karow, Steven Raman
We evaluated the utility of restriction spectrum imaging (RSI), a novel diffusion-based technique to detect and to characterize prostate cancer among men enrolled in a national cancer institute-funded prospective clinical trial of magnetic resonance ultrasound fusion biopsy. RSI was statistically significantly associated with clinically significant prostate cancer.
|
|
4487.
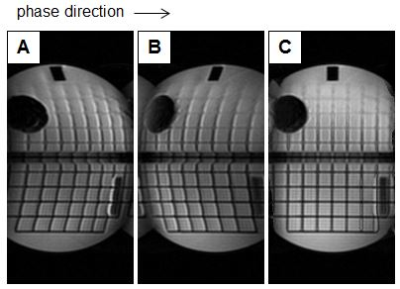 |
98 |
Reduced FOV EPI with Blip-up Blip-down Field Correction for Prostate DWI
Video Permission Withheld
Roger Grimm, Adam Froemming, Stephen Riederer
Geometric distortion in echo planar imaging spin echo images caused by a non-uniform B0 field remains an issue in clinical imaging. The purpose of this work is to combine the reduced-field-of-view echo planar pulse sequence with a blip-up blip-down correction in prostate DWI. We show reduced geometric distortion in prostate imaging and ADC maps with little or no additional acquisition time required over current protocols.
|
|
4488.
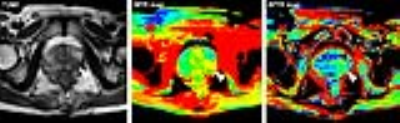 |
99 |
 Amide proton transfer-weighted (APTW) MRI as an in vivo molecular imaging biomarker to detect prostate cancer Amide proton transfer-weighted (APTW) MRI as an in vivo molecular imaging biomarker to detect prostate cancer
Xiaoxi Chen, Lianming Wu, Weibo Chen, Jinyuan Zhou, Jianrong Xu
We explored the capability of using the amide proton transfer-weighted MR imaging as a molecular imaging biomarker to identify prostate cancer. Results showed that both the amide proton transfer ratio (APTR) and magnetization transfer ratio (MTR) in tumors were higher than in non-tumorous regions. APT-MR imaging may have great value in clinical treatment and prognosis of prostate cancer.
|
|
4489.
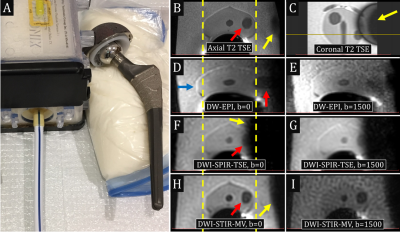 |
100 |
 MultiVane Diffusion-Weighted Imaging for Multiparametric Prostate Magnetic Resonance Imaging in Men with Hip Implants: A Preliminary Report MultiVane Diffusion-Weighted Imaging for Multiparametric Prostate Magnetic Resonance Imaging in Men with Hip Implants: A Preliminary Report
Ali Pirasteh, Brian Johnson, Daniel Costa, Ananth Madhuranthakam, Ivan Pedrosa
Diffusion-weighted echo-planar-imaging (DW-EPI) is the cornerstone of multiparametric MRI in evaluation of prostate cancer in the peripheral zone and can help in the detection of transitional zone tumors. However, DW-EPI suffers from significant image distortion and signal loss in men with hip arthroplasty, a population at risk for development of prostate cancer. We have implemented a DWI sequence with turbo spin-echo readout, MultiVane k-space trajectory, and short-tau inversion recovery fat-suppression that provides images without appreciable distortion and promising preliminary results in evaluation of prostate cancer in men with hip implants.
|
|
4490.
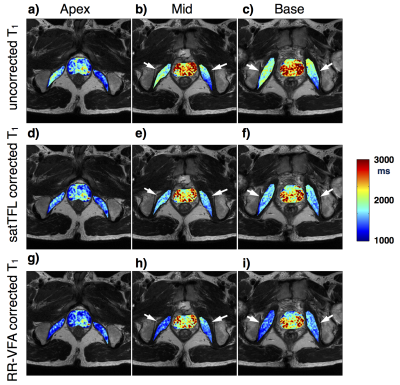 |
101 |
 Intra- and Inter-scanner Variability Evaluation of RR-VFA B1+ and T1 in the Prostate at 3T Intra- and Inter-scanner Variability Evaluation of RR-VFA B1+ and T1 in the Prostate at 3T
Xinran Zhong, Dapeng Liu, James Sayre, Holden Wu, Kyunghyun Sung
Accurate T1 estimation is critical for quantitative prostate DCE MRI. B1+ inhomogeneity can introduce significant error into the T1 quantification, especially for variable flip angle method. Reference region variable flip angle (RR-VFA) method is a promising B1+ and T1 estimation technique, which requires no separate scans for B1+ mapping and can reduce slice profile and position mismatch between B1+ and T1 maps. In this study, we investigated both intra-scanner repeatability and inter-scanner reproducibility regarding B1+ corrected T1 on two 3.0 T scanners to compare RR-VFA to a commercially available B1+ estimation technique. RR-VFA showed comparable intra- and inter-scanner variability to the saturated turbo FLASH based B1+ estimation technique.
|
|
4491.
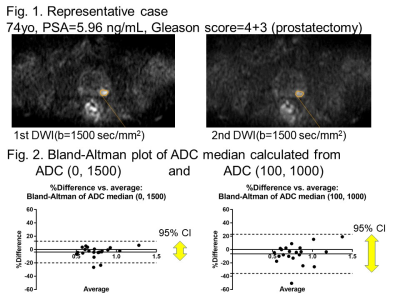 |
102 |
 What combination of b-values is appropriate for ADC calculation in prostate DWI? What combination of b-values is appropriate for ADC calculation in prostate DWI?
Masamitsu Hatakenaka, Naomi Koyama, Naoya Yama, Maki Onodera, Koichi Onodera, Yurina Onuma, Ryo Taguchi, Mitsuhiro Nakanishi
In prostate cancer, although calculating ADC with b-value combination of 50-100 and 800-1000 sec/mm2 is recommended by PI-RADS ver. 2, ADC calculated with b-values of 0 and 1500 sec/mm2 may be superior with respect to repeatability and correlation with cancer aggressiveness.
|
|
4492.
 |
103 |
 Synthetic 3D reconstruction Synthetic 3D reconstruction
Stephen Riederer, Eric Borisch, Adam Froemming, Soudabeh Kargar, Akira Kawashima, Joshua Trzasko
A new method is described in which slice profile in 2D multi-slice acquisition is corrected for with k-space-based processing, restoring resolution along the slice select direction. When used with multiple multi-slice acquisitions the method may allow isotropic 3D resolution. The method is described, and preliminary results from phantom and prostate MRI exams are presented.
|
|
4493.
 |
104 |
 Dynamic Contrast-Enhanced MRI of the Prostate with Single-Echo Dixon Fat Suppression Dynamic Contrast-Enhanced MRI of the Prostate with Single-Echo Dixon Fat Suppression
Eric Stinson, Joshua Trzasko, Soudabeh Kargar, Eric Borisch, Adam Froemming, Akira Kawashima, Phillip Young, Stephen Riederer
The purpose of this work was to adapt our current clinical DCE-MRI protocol to allow for single-echo Dixon fat suppression and maintain image update times <10s. Single-echo Dixon imaging with spatial resolution that matched our current clinical protocol was performed with sub-10s update times and near-optimal Dixon SNR by increasing the readout bandwidth from ±62.5 to ±83.3 kHz. Additionally, pharmacokinetic modelling results look similar to those produced from the standard DCE-MRI protocol. DCE-MRI of the prostate with single-echo Dixon fat suppression provides high spatial and temporal resolution dynamic imaging of contrast uptake without the presence of confounding fat signal.
|
|
4494.
 |
105 |
 The repeatability of fully automated atlas-based prostate segmentation on T2-weighted MR images The repeatability of fully automated atlas-based prostate segmentation on T2-weighted MR images
Mohammed Sunoqrot, Daniel Billdal, Kirsten Selnæs, Mattijs Elschot, Tone Bathen
Computer-aided diagnosis (CADx) systems have been proposed to overcome the limitations of the radiological reading of multiparametric MRI. Fully automated segmentation of the prostate is a crucial step of CADx systems, which can be successfully performed by atlas-based segmentation of T2-weighted (T2W) MR images. For applications like treatment monitoring and active surveillance, the repeatability of automated segmentation method is highly important. In this work, we investigated the repeatability of several fully automated atlas-based prostate segmentation methods. We found that the repeatability of the investigated methods is excellent, which is promising for the further development of CADx systems following patients with multiple measurements over time.
|
|
4495.
 |
106 |
 Multi-echo T2 modelling to predict PIRADS 2.0 score Multi-echo T2 modelling to predict PIRADS 2.0 score
William Devine, Francesco Giganti, Edward Johnston, Eleftheria Panagiotaki, Shonit Punwani, Daniel Alexander, David Atkinson
To investigate if Luminal Water Imaging (LWI), which models multi-compartment T2 decay, can predict the PIRADS 2.0 score of a region of interest (ROI). 52 patients were scanned using both standard mp-MRI and a 32-echo T2 sequence, ROIs were placed in areas of suspected lesion and suspected benign tissue and then these ROIs were each given a PIRADS 2.0 score. The results show that LWI can predict PIRADS 2.0 score as well as the Apparent Diffusion Coefficient (ADC).
|
|
4496.
 |
107 |
 Two compartment fitting for Luminal Water Imaging: multi-echo T2 in Prostate Cancer Two compartment fitting for Luminal Water Imaging: multi-echo T2 in Prostate Cancer
William Devine, Francesco Giganti, Edward Johnston, Eleftheria Panagiotaki, Shonit Punwani, Daniel Alexander, David Atkinson
This work aims both to show that using a constrained fitting method for Luminal Water Imaging with fewer echoes produces accurate parameter estimates and that this fitting method is feasible for detecting and grading Prostate Cancer. Simulated signals were produced and the mean LWF across multiple iterations was calculated for two models. Then 19 patients were imaged and the images were contoured in both cancerous and benign regions. The simulation showed that the proposed constrained method is accurate and the in-vivo imaging reinforced the idea that multi-echo T2 modelling shows promise in detecting and grading PCa.
|
|
4497.
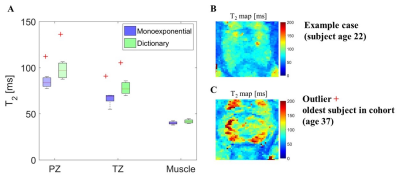 |
108 |
 Accelerated 3D T2 mapping with dictionary-based matching for prostate imaging Accelerated 3D T2 mapping with dictionary-based matching for prostate imaging
Elisa Roccia, Rohini Vidya Shankar, Radhouene Neji, Gastao Cruz, Rene Botnar, Claudia Prieto, Vicky Goh, Isabel Dregely
Quantitative T2 mapping has potential for prostate cancer discrimination. However, current methods are typically 2D, require long scan times and may lead to inaccuracies if using an oversimpli?ed exponential model. We propose rapid 3D T2 mapping based on accelerated 3D multi shot T2-prepared bSSFP acquisition combined with dictionary-based matching. The dictionary of signals was generated using a simulation framework taking into account the specifics of the acquisition, and was then matched to the acquired images to retrieve T2 values. The proposed approach was tested in healthy subjects enabling the acquisition of 3D T2 mapping of the whole prostate in 4min.
|
|
4498.
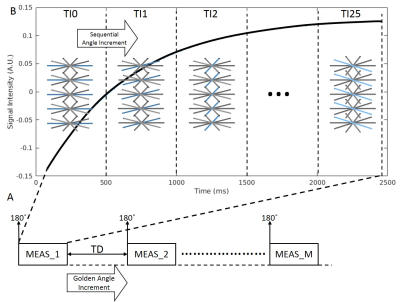 |
109 |
 High-resolution 3D T1 mapping of the prostate with an efficient inversion-recovery radial FLASH pulse sequence High-resolution 3D T1 mapping of the prostate with an efficient inversion-recovery radial FLASH pulse sequence
Zhitao Li, Ali Bilgin, Kevin Johnson, Hina Arif, Diego Martin, Maria Altbach
A 3D IR radial FLASH technique and a model-based iterative algorithm for the reconstruction of undersampled data are demonstrated for efficient high-resolution T1 mapping of the prostate. The method is insensitive to B1 inhomogeneity and provides full coverage of the prostate volume within the time constrains of a clinical examination.
|
|
4499.
 |
110 |
 The Medical College of Wisconsin 39 (MCW39): A Magnetic Resonance Image Template of the Prostate to Facilitate Group Analysis The Medical College of Wisconsin 39 (MCW39): A Magnetic Resonance Image Template of the Prostate to Facilitate Group Analysis
Sean McGarry, Matthew Budde, Sarah Hurrell, Kenneth Ickzowski, Michael Griffin, Petar Duvnjak, Kenneth Jacobsohn, William Hall, Mark Hohenwalter, Andrew Nencka, Peter LaViolette
The Medical College of Wisconsin 39 (MCW39) template provides a common space for the analysis of prostate cancer images. The template was generated through iterative spatial registration of T2-weighted images starting with manually drawn contours as a reference point. Expert annotations of Gleason Grade were transformed into the template space, and maps of tumor probabilities reveal the spatial localization of cancer across the cohort for each grade.
|
|
4500.
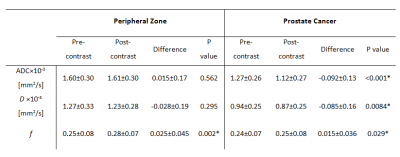 |
111 |
 Effect of Intravascular Contrast Agent on Diffusion and Perfusion Fraction Coefficients in the Peripheral Zone and Prostate Cancer Effect of Intravascular Contrast Agent on Diffusion and Perfusion Fraction Coefficients in the Peripheral Zone and Prostate Cancer
Yousef Mazaheri, Andreas Hötker , Amita Shukla-Dave, Oguz Akin, Hedvig Hricak
We present a systematic approach to characterize differences in pre- and post-contrast diffusion and perfusion parameters. In addition to measuring ADC values before and after contrast injection, we extended the mono-exponential model to incorporate the contribution of pseudo-perfusion to the signal intensity and evaluated the impact of contrast injection on molecular diffusion (D) and perfusion fraction (f). We find in PCa, the coefficient D, like ADC, was significantly lower on post-contrast as compared to pre-contrast DWI, while the perfusion fraction coefficient was significantly higher on post-contrast acquisitions. In PZ, ADC and D did not differ significantly between post- and pre-contrast acquisitions, but f was significantly higher after contrast injection.
|
|
4501.
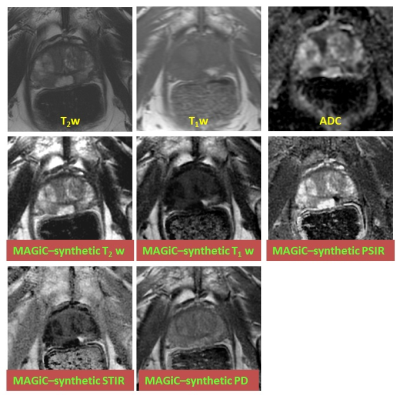 |
112 |
 Synthetic MRI of the Prostate using MAGiC: Clinical Feasibility and Preliminary Results Synthetic MRI of the Prostate using MAGiC: Clinical Feasibility and Preliminary Results
Yousef Mazaheri, Maggie Fung, Duane Nicholson, Amita Shukla-Dave, Hedvig Hricak, Oguz Akin
In this study, we evaluated a 2D combined simultaneous multi-contrast acquisition sequence, referred to MAGiC, which allows simultaneously obtaining images to generate, T1, T2, PD, STIR map with acceptable scan duration within a single acquisition. High quality T1- and T2-w images were synthetically generated using mathematical signal models. Prostate images obtained from patients and volunteers showed that T1 and T2 measured by MAGiC were within 16% of the values measured using conventional mapping techniques with reasonable spatial resolution.
|
|
4502.
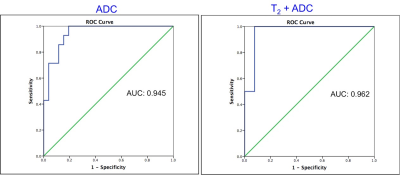 |
113 |
 MR Fingerprinting and ADC Mapping for Characterization of Lesions in Transitional Zone of Prostate MR Fingerprinting and ADC Mapping for Characterization of Lesions in Transitional Zone of Prostate
Ananya Panda, Yun Jiang, Seunghee Margevicius, Wei-Ching Lo, Mark Schluchter, Chaitra Badve, Mark Griswold, Lee Ponsky, Vikas Gulani
This study presents utility of MRF derived relaxometry, and ADC mapping for differentiating transition zone prostate cancers from non-cancerous lesions. Based on targeted biopsy correlation, T1, T2, ADC were compared between cancer, prostatitis and normal transition zone (NTZ). Mean T1, T2 and ADC were significantly different between cancer and NTZ. Mean T1 and ADC were significantly different between prostate cancer and prostatitis. While ADC had an AUC of 0.821 for differentiating cancer and prostatitis, a combination of T1 and T2 mapping had an AUC of 0.875. Thus MRF can add significant value to ADC mapping in characterization of TZ lesions.
|
|
4503.
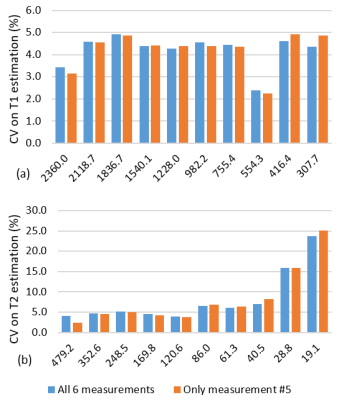 |
114 |
 Multicenter repeatability and reproducibility of MR Fingerprinting Multicenter repeatability and reproducibility of MR Fingerprinting
Wei-Ching Lo, Yun Jiang, Leonardo Bittencourt, Junichi Tokuda, Ravi Seethamraju, Clare Tempany-Afdhal, Ananya Panda, Katherine Wright, Mark Griswold, Nicole Seiberlich, Vikas Gulani
MRF enables rapid collection of multiple tissue properties simultaneously. For clinical applications, the T1 and T2 values must be repeatable over time and on different MRI scanners so that any observed relaxivity difference can be assumed to be due to differences in physiology rather than scanner instability, differences in pulse sequence or map reconstruction implementations. This study evaluated multicenter repeatability and reproducibility of T1 and T2 estimates of MRF in the ISMRM/NIST MRI system phantom and normal prostate regions in patients. The intra-scanner variation was less than 2% for MRF T1 and 4.7% for T2 within the biological range.
|
|
4504.
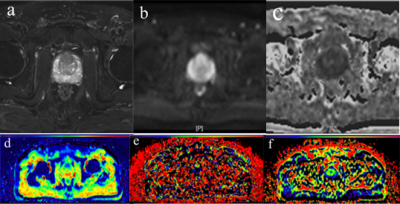 |
115 |
 Histogram Analysis of monoexponential DWI, biexponential IVIM model and PI-RADS V2 for the Differentiation of Prostate Cancer from BPH in the Transition zone Histogram Analysis of monoexponential DWI, biexponential IVIM model and PI-RADS V2 for the Differentiation of Prostate Cancer from BPH in the Transition zone
jie bao, ximing wang, zhongshuai zhang, su hu, xiaoxia ping, chunhong hu
In this study, we propose to evaluate histogram analysis of ADC derived by traditional DWI model, diffusion related parameters calculated by using intravoxel incoherent motion (IVIM) model and PI-RADS V2 for the detection of the prostate cancer (PCa) in the transition zone (TZ). Our results show that the highest classification accuracy was achieved by the mean ADC (0.841) and mean D (0.809, acquired by the IVIM model). Our findings suggest that Monoexponential DWI and biexponential IVIM model could potentially improve the accuracy of the pathological grading of prostate cancer in TZ.
|
|
4505.
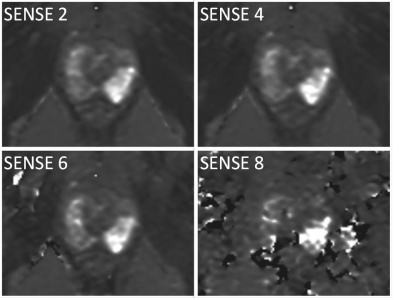 |
116 |
 A study on Compressed SENSE(CSENSE) in prostate T2map at 3T. A study on Compressed SENSE(CSENSE) in prostate T2map at 3T.
seiichiro noda, nobuyuki toyonari, yukari horino, kazuhiro katahira, masami yoneyama, yasutomo katsumata
We study on Compressed SENSE in prostate T2map at 3T The imaging sequence used spin echo type multi echo. In case of SENSE, increase Factor resulted in an artifact peculiar to parallel imaging and an error occurred in T2 value measurement of the prostate. However, in the case of CSENSE, artifacts were reduced and T2 value measurement was also possible. Prostate T2map can reduce imaging time using CSENSE.
|
|
4506.
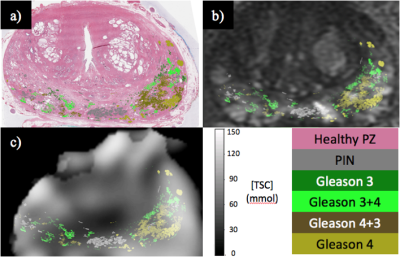 |
117 |
 Characterization of Human Prostate Cancer Using Tissue Sodium Concentration Measured from Sodium MRI Characterization of Human Prostate Cancer Using Tissue Sodium Concentration Measured from Sodium MRI
Nolan Broeke, Justin Peterson, Adam Farag, Aaron Ward, Stephen Pautler, Joseph Chin, Glenn Bauman, Robert Bartha, Timothy Scholl
Over-treatment of prostate cancer is a significant problem in men’s healthcare. Development of non-invasive imaging tools for improved identification of prostate lesions can reduce over-treatment. We have built custom sodium MRI hardware to image and quantify tissue sodium concentration (TSC) in the human prostate. Sodium and multi-parametric MR images are co-registered to Gleason-graded post-prostatectomy histology, the current gold standard for prostate cancer lesion characterization. Our data shows a statistically significant, positive correlation of TSC with Gleason score. These data suggest that TSC measured by sodium MRI, in addition to multi-parametric MRI has utility for non-invasive characterization of prostate cancer.
|
|
4507.
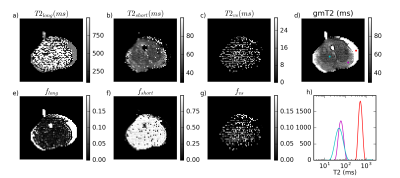 |
118 |
 Quantitative T2 in ex vivo prostate: relationship to microstructure and VERDICT MRI parameters Quantitative T2 in ex vivo prostate: relationship to microstructure and VERDICT MRI parameters
Colleen Bailey, Bernard Siow, Roger Bourne, Edward Johnston, Mrishta Brizmohun Appayya, Hayley Pye, Susan Heavey, Thomy Mertzanidou, Hayley Whitaker, Alex Freeman, Dominic Patel, Greg Shaw, Ashwin Sridhar, David Hawkes, Shonit Punwani, Daniel Alexander, Eleftheria Panagiotaki
Quantitative T2 and VERDICT diffusion MRI data were acquired in ex vivo prostate specimens, using a patient-specific mold to allow comparison with registered prostate images. Analysis indicated differences from in vivo T2 spectra, such as a single T2 component dominating the spectrum in most regions, but with longer T2 values where there was generally more lumen space. A small component with T2 of 10-20 ms was observed in some cancerous regions. The geometric mean of the T2 spectrum was inversely correlated with the intracellular fraction parameter from VERDICT and correlated with the diffusion coefficients of the Tensor component modelling the extracellular space.
|
|
4508.
 |
119 |
 The diagnostic potential and repeatability of Relative Enhanced Diffusivity (RED) as a biomarker for prostate cancer The diagnostic potential and repeatability of Relative Enhanced Diffusivity (RED) as a biomarker for prostate cancer
Daniel Chen Billdal, Mohammed R Sunoqrot, Kirsten Margrete Selnæs, Peter While, Brage Krüger-Stokke, Helena Bertilsson, Tone Bathen, Mattijs Elschot
Relative Enhanced Diffusivity (RED) expresses the relative change in ADC between lower and higher b-value regimes. The purpose of this study was to investigate the diagnostic potential and repeatability of RED as a biomarker for prostate cancer (PCa).
Ten (10) healthy volunteers and 28 high-risk patients diagnosed with PCa underwent diffusion-weighted MRI. For the healthy volunteers, the repeatability of RED was good to acceptable. For the patients, RED was able to discriminate tumors from healthy tissue in the peripheral zone using either b=50 or b=400 mm/s2 as the intermediate b-value (p < 0.001).
|
|
4509.
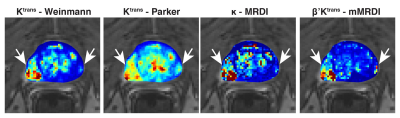 |
120 |
 Evaluation of Fitting Uncertainties and Errors for Dispersion-Based Imaging of Prostate DCE-MRI Evaluation of Fitting Uncertainties and Errors for Dispersion-Based Imaging of Prostate DCE-MRI
KyungHyun Sung
The MR dispersion imaging (MRDI) has shown great promise in prostate DCE-MRI, but there still exist practical limitations due to the complex model fitting. We evaluate fitting uncertainties and errors in parameter estimation for MRDI and recently proposed modified MRDI (mMRDI). We use the time-concentration curves derived from 94 prostate cancer lesions for fitting uncertainties and errors and assess the ability to delineate between cancerous and normal prostate tissues.
|
|
| Back |
| The International Society for Magnetic Resonance in Medicine is accredited by the Accreditation Council for Continuing Medical Education to provide continuing medical education for physicians. |















































































































































