|
Electronic Poster Session
Body: Breast, Chest, Abdomen, Pelvis |
Wednesday, 20 June 2018
Electronic PosterBody: Breast, Chest, Abdomen, Pelvis
4556 -4579 Body Imaging: Fetal & Placenta
4580 -4603 Body Imaging: Kidney
4604 -4627 Body DWI & Liver Tumour
4676 -4699 Body Imaging: GU (Non-Prostate) & Female Pelvis (Including Placenta)
4700 -4723 Pancreas/GI
4724 -4747 Hepatobiliary 2: Diffuse Liver Disease |
| |
Body Imaging: Fetal & Placenta
Electronic Poster
Body: Breast, Chest, Abdomen, Pelvis
Wednesday, 20 June 2018
| Exhibition Hall |
08:15 - 09:15 |
| |
|
Computer # |
|
4556.
 |
49 |
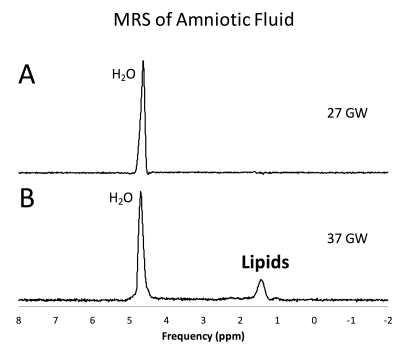
 Non-invasive estimation of fetal lung maturity using MR spectroscopy Non-invasive estimation of fetal lung maturity using MR spectroscopy
Vidya Rajagopalan, Stefan Bluml
Magnetic resonance spectroscopy (MRS) can potentially be used to non-invasively measure the lipid levels in the amniotic fluid (AF), in-utero, to determine fetal lung maturity (FLM). This would eliminate the need to perform invasive and risky amniocentesis solely to determine FLM. In this study we measured the lipid to water ratio in the amniotic fluid of women with normal pregnancies. Our results showed that this ratio remained steady until after 36 gestational weeks at which point it increased exponentially. This indicates that MRS is a potential replacement for amniocentesis for estimating FLM.
|
|
4557.
 |
50 |
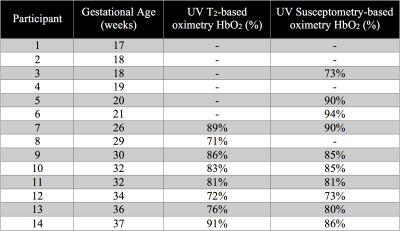
 Feasibility of Estimating Umbilical Vein Oxygen Saturation with Susceptometry-Based Oximetry Feasibility of Estimating Umbilical Vein Oxygen Saturation with Susceptometry-Based Oximetry
Ana Rodríguez-Soto, Michael Langham, Nadav Schwartz, Felix Wehrli
Quantitative MRI allows the estimation of fetal oxygen transport in vivo, for which knowledge of the oxygen saturation (HbO2) of blood in the umbilical vein (UV) is required. The method of choice to estimate HbO2 in fetal applications is T2-based oximetry, which requires a sequence-specific calibration equation to convert blood T2 to HbO2. Therefore, in the present work we examined the feasibility of using susceptometry-based oximetry (SBO) to measure HbO2 at the UV as it is calibration-free and implementable across field strengths. Results show, in a limited number of participants, no difference in HbO2 measured with both MRI-based oximetric techniques.
|
 |
4558.
 |
51 |
 Estimating global cerebral venous oxygenation in the human fetus using QSM Estimating global cerebral venous oxygenation in the human fetus using QSM
Brijesh Yadav, Sagar Buch, Uday Krishnamurthy, Pavan Jella, Edgar Hernandez-Andrade, Anabela Trifan, Lami Yeo, Sonia Hassan, E. Mark Haacke, Roberto Romero, Jaladhar Neelavalli
Unobstructed oxygen supply is important for proper health and development of the growing fetus and therefore, fetal cerebral oxygenation measurement has been attempted previously using SWI. However, vessel curvature and oblique fetal orientation posed a major challenge in the oxygenation measurement, especially in younger foetuses. To overcome these problems, we present the first application of quantitative susceptibility mapping for the fetal brain oxymetry. We also studied the effect of resolution on QSM using simulations. Results showed the mean putative fetal cerebral oxygenation was 67%±7% and minimum of 5 voxels around the vessel and 5 slices gives <3% error in oxygenation.
|
|
4559.
 |
52 |
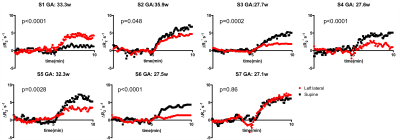
 Assessment of the effect of maternal posture on the placental oxygenation transport by means of BOLD MRI Assessment of the effect of maternal posture on the placental oxygenation transport by means of BOLD MRI
Esra Abaci Turk, Jie Luo, Natalie Copeland, Michelle Restrepo, Ata Turk, Borjan Gagoski, Lawrence Wald, Elfar Adalsteinsson, Drucilla Roberts, Polina Golland, P. Ellen Grant, William Barth Jr
Aorta-caval compression due to maternal posture can change uterine artery blood flow, which is the major determinant of maternal intervillous perfusion and may affect MRI measures of placental oxygenation. We investigated the effect of maternal posture on estimates obtained from BOLD MRI of the placenta. We observed higher oxygenation signals in the supine position for a group at younger gestational age. In the group with higher gestational age, the influence of the maternal position on oxygen transport was inconsistent. These findings underscore the need to account for the effect of maternal posture on MRI studies of utero-placental circulation.
|
|
4560.
 |
53 |
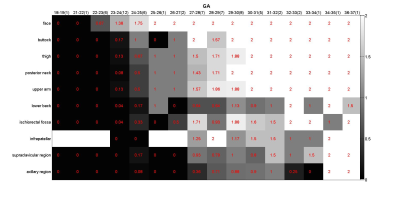
The development of fat in fetus: Observation by magnetic resonance imaging
Video Permission Withheld
TING YI CHEN, SHU HUEI SHEN, NAI CHI CHIU, HAN JUI LEE, SZ SHIAN YU, WAN YOU GUO
The fetal structures including fat change vigorously during the development progress. In this study, by using 2-point Dixon method, we demonstrated that the fetal fat development followed a predictable chronological sequence in terms of both location and composition. The fat at face appears the earliest at 22-23 weeks, followed by subcutaneous fat of other body part in the order of buttock, thigh, posterior neck, upper arm and lower back. Most subcutaneous fat could be well visualized at 27-28 weeks. The fat at deep part appeared later. The fat fraction in all body part gradually increased as the development progress.
|
|
4561.
 |
54 |
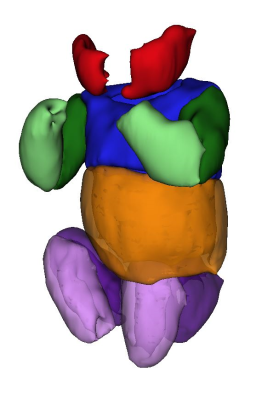
 3D Water-Fat MRI Detection of Developmental Maturity in Fetal Adipose Tissue Compartments 3D Water-Fat MRI Detection of Developmental Maturity in Fetal Adipose Tissue Compartments
Stephanie Giza, Tianna Koreman, Barbra de Vrijer, Charles McKenzie
Fetal adipose tissue begins development at different gestational ages in different regions of the body. Proton density fat fraction (PDFF) increases with gestational age as fetal adipocytes fill with lipid. The PDFF was found to be significantly different in different regions of the body in mid-late gestation fetuses.
|
|
4562.
 |
55 |
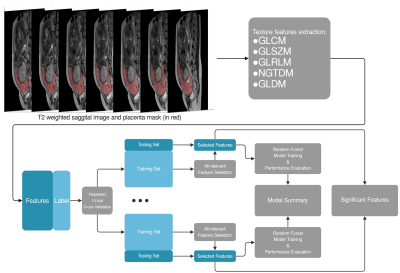
Prediction of invasive placenta with quantitative placental textures features from clinical MRI scan
Did Not Present
Huaiqiang Sun, Haoyang Xing, Haibo Qu, Yi Liao, Xiaoxia Zhou, Zhiyi Zhou, Qiyong Gong, Shu Zhou
A machine learning framework that can predict invasive placenta with MRI texture features and identify significant relevant image features
|
|
4563.
 |
56 |
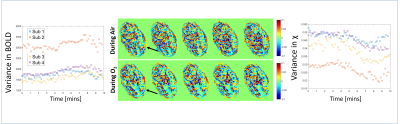
 Oxygen transfer through the placenta on hyperoxia Oxygen transfer through the placenta on hyperoxia
Simon Shah, Nia Jones, Lucy Edwards, Richard Bowtell, Penny Gowland
Rapid transport of oxygen through the placenta is important to ensure efficient exchange. The aim of this work was to measure the rate of oxygenation distribution across the placenta on hyperoxia using susceptibility mapping. It also attempts to relate the rate of uptake of oxygen in the placenta to the total flow to the placenta. It was observed that upon hyperoxia the susceptibility decreased as the BOLD signal increased in the placenta. We propose that that the rate of homogenization of susceptibility is a marker of transport through the placenta.
|
|
4564.
 |
57 |
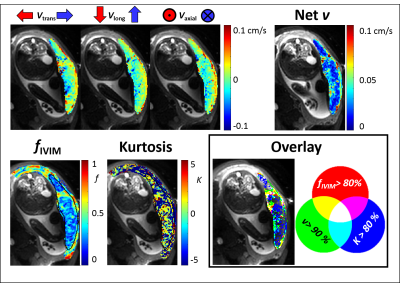
 Movement of blood within the placenta Movement of blood within the placenta
Simon Shah, Nia Jones, Lucy Edwards, Richard Bowtell, Penny Gowland
Healthy placental function requires optimum percolation of blood throughout the intervillous space to provide adequate feto-maternal exchange. This depends on blood flow from the spiral arteries and permeability of the intervillous space - both being altered in conditions leading to fetal growth restriction. This study explores the use of diffusion based MRI to visualise and depict the blood flow within the placenta and explore the underlying micro-structure, including the repeatability of the measures.
|
|
4565.
 |
58 |
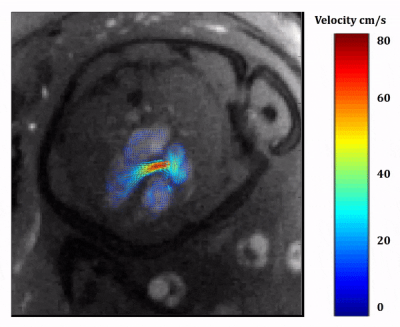
 Rapid single slice multidimensional fetal flow imaging with MRI Rapid single slice multidimensional fetal flow imaging with MRI
Datta Singh Goolaub, Christopher Roy, Dafna Sussman, Mike Seed, Christopher Macgowan
In this study, we demonstrate multidimensional fetal blood flow quantification, using a novel radial phase contrast sampling strategy combined with compressed sensing reconstruction. This acquisition and analysis pipeline provides high temporal resolution real-time reconstructions that enable image-based gating for subsequent CINE reconstruction. Experimental validation of gating and flow quantitation are presented from an adult volunteer. Preliminary results in two human fetuses show the feasibility of this novel strategy for multidimensional fetal flow in imaging in a single slice.
|
|
4566.
 |
59 |
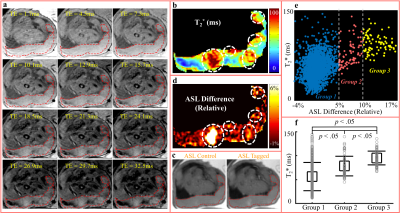
 Placental Functional Imaging with Endogenous Contrast: Preliminary Comparison of BOLD Effect and ASL FAIR in Rhesus Macaque and Human Placental Functional Imaging with Endogenous Contrast: Preliminary Comparison of BOLD Effect and ASL FAIR in Rhesus Macaque and Human
Ante Zhu, Kai Ludwig, Wei Zha, Sydney Nguyen, Thaddeus Golos, Ian Bird, Dinesh Shah, Oliver Wieben, Sean Fain, Scott Reeder, Diego Hernando, Kevin Johnson
Non-invasive MRI techniques are needed to quantify placental perfusion and oxygenation during pregnancy. In this work, we assessed the feasibility and correspondence of T2* mapping and arterial spin labeling (ASL) to evaluate placental oxygen delivery. Six pregnant rhesus macaques and seven pregnant women underwent MRI that included T2* mapping and ASL with flow-sensitive alternating inversion recovery (FAIR). Regions of locally high ASL perfusion signal correlated spatially with the regions of locally maximum T2* in animals and humans. The two imaging techniques with endogenous contrast are promising approaches for the detection of oxygen delivery via the placenta.
|
|
4567.
 |
60 |
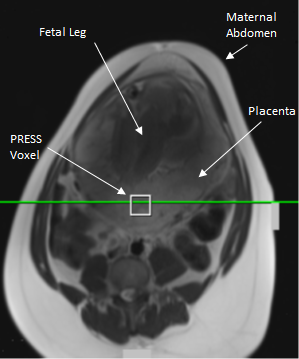
Proton Spectroscopy of the Human Placenta In-Utero to Establish Normal Ranges Throughout Gestation
Video Permission Withheld
David Morris, Gillian Macnaught, Marian Aldhous, Fiona Denison, Scott Semple
For magnetic resonance proton spectroscopy to be of potential future use in investigating placental dysfunction in-utero, a normal range of detectable metabolites is required. Seventy-seven healthy pregnant women with an uncomplicated singleton pregnancy were scanned between 20 and 40 week's gestation. Robust quality assurance removed compromised data and spectra were quantified for the commonly observed peaks and metabolites expected in the placenta. A characteristic spectrum was observed, which was independent of gestational age. Quantification of this technique in terms of the expected results and their variability will inform future studies and suggest technical improvements that may be useful.
|
|
4568.
 |
61 |
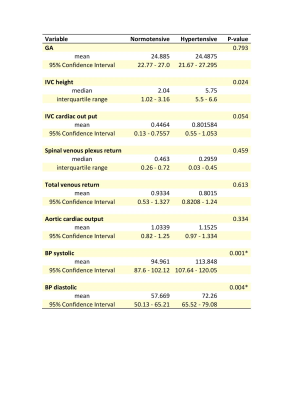
An MRI assessment of inferior vena cava vessel morphology and venous flow in chronic hypertensive and normotensive pregnant women in the supine position.
Did Not Present
Ana Dos Santos Gomes, Emer Hughes, Alison Ho, Anthony Price, Christopher Kelly, Jana Hutter, Joseph Hajnal, Lucy Chapell, Mary Rutherford
The supine position in pregnancy may develop supine hypertensive syndrome (SHS) caused by the gravid uterus compressing the inferior vena cava (IVC) and compromising venous return. The effect of positioning on vessel morphology and venous return in chronic hypertensive pregnant women has not been assessed. We used phase contrast imaging to assess matched groups of chronic hypertensive and normotensive women in the supine position. There were no significant differences in IVC morphology or venous return between the two groups, supporting the conclusion that chronic hypertensive women are not at higher risk than normotensives when supine.
|
|
4569.
 |
62 |
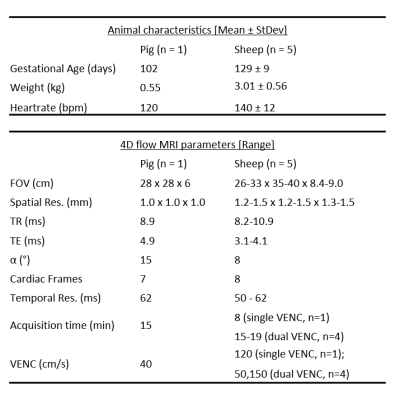
 Fetal Cardiac Hemodynamics: Initial Experience using 4D flow MRI in Large Animal Models Fetal Cardiac Hemodynamics: Initial Experience using 4D flow MRI in Large Animal Models
Eric Schrauben, Brahmdeep Saini, Jack Darby, Jia Yin Soo, Mitchell Lock, Elaine Stirrat, Aodhnait Fahy, Joshua Bradshaw, Greg Stortz, John Sled, Janna Morrison, Mike Seed, Christopher Macgowan
4D flow MRI, coupled with advanced surgical preparation of animal subjects, is performed to capture fetal cardiac hemodynamics in two animal models of late gestation pregnancy – pig and sheep. Characterization and visualization of complex flow is presented alongside quantitative measures of flow in major fetal cardiac vessels and shunts.
|
|
4570.
 |
63 |
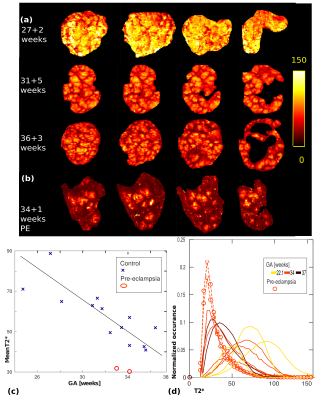
 Exploring placental function over gestation using multi-modal functional MRI Exploring placental function over gestation using multi-modal functional MRI
Jana Hutter, Paddy Slator, Laurence Jackson, Alison Ho, Ana Dos Santos Gomes, Anthony Price, Daniel Alexander, Lucy Chappell, Mary Rutherford, Joseph Hajnal
The delivery of oxygen and nutrients to the growing fetus in the human placenta is crucial for any successful pregnancy. Major pregnancy complications such as growth restriction and pre-eclampsia have been linked to placental insufficiency. This study attempts to use a comprehensive multi-modal functional MRI approach to visualize and quantify the complexity of the underlying structural and functional processes and monitor their evolution over gestation. The required placenta data can be acquired in the clinically feasible time of ~12 min and requires no contrast agent. The presented acquisition is completed by a dedicated multi-modal pipeline and a set of quantitative features.
|
|
4571.
 |
64 |
 Optimised b-values and Gradient Directions for Placental Diffusion MRI Optimised b-values and Gradient Directions for Placental Diffusion MRI
Paddy Slator, Jana Hutter, Laurence Jackson, Andrada Ianus, Ana Dos Santos Gomes, Alison Ho, Lisa Story, Laura McCabe, Eleftheria Panagiotaki, Mary Rutherford, Joseph Hajnal, Daniel Alexander
Diffusion MRI (dMRI) has the potential to assess placental microstructure and microcirculation in-vivo, and hence provide insight into conditions such as fetal growth restriction and pre-eclampsia. The utility of dMRI data depends heavily upon the choice of b-values and gradient directions, although these choices have to be weighed against scanning time restrictions. To address these issues, we developed an organ-specific, data-driven, clinically-viable protocol for placental dMRI. This optimised protocol compares favourably with a naive protocol of comparable scan time.
|
|
4572.
 |
65 |
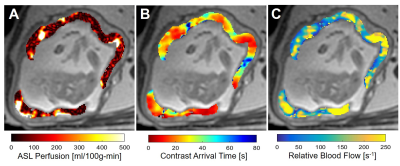
 Perfusion MRI of the Placenta by Arterial Spin Labeling (ASL) and Ferumoxytol Dynamic Contrast Enhanced (DCE) MRI in the Rhesus Macaque Perfusion MRI of the Placenta by Arterial Spin Labeling (ASL) and Ferumoxytol Dynamic Contrast Enhanced (DCE) MRI in the Rhesus Macaque
Kai Ludwig, Sean Fain, Sydney Nguyen, Thaddeus Golos, Scott Reeder, Ian Bird, Oliver Wieben, Dinesh Shah, Kevin Johnson
We evaluate two ASL based techniques for non-contrast measurement of perfusion compared with ferumoxytol-based DCE MRI in ten pregnant rhesus macaques. Localized regions of ASL perfusion were observed that coincided with regions of early contrast arrival times and high relative blood flow as seen in DCE, likely identifying locations of material spiral artery inputs into the placenta intervillous space.
|
|
4573.
 |
66 |
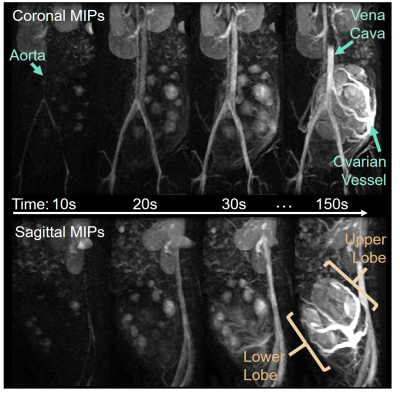
Quantitative ferumoxytol DCE MRI of the primate placenta perfusion domains
Video Permission Withheld
Kai Ludwig, Sean Fain, Erin Adamson, Sydney Nguyen, Thaddeus Golos, Scott Reeder, Ian Bird, Oliver Wieben, Dinesh Shah, Kevin Johnson
The placental vascular network is organized to effectively mediate exchange of nutrients, oxygen, and waste between mother and fetus. We report on the estimated number of placental functional domains in a healthy population of rhesus macaques using ferumoxytol DCE MRI. Noninvasive imaging of the maternal vasculature organization and localized perfusion within the placenta may be a sensitive biomarker to predict pregnancy complications.
|
|
4574.
 |
67 |
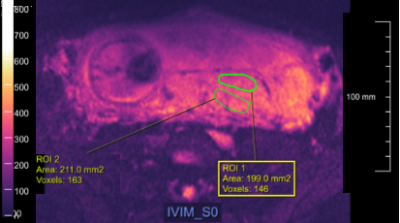
ADC and perfusion fraction f obtained by IVIM model are markers of maternal and fetal human placenta development in normal pregnancy
Video Permission Withheld
Amanda Antonelli, Silvia Capuani, Michele Guerreri, Silvia Bernardo, Carlo Catalano, Lucia Manganaro
The purpose was to investigate the potential of IVIM model to quantify diffusion and perfusion in human placenta of normal pregnancy. The relation between Apparent diffusion coefficient ADC, perfusion fraction f and pseudo-diffusion coefficient D* obtained in fetal and maternal placenta with microstructural changes occurring during placenta development was investigated. 30 pregnant women (gestational age, GA range = 19-37w) underwent DW examination with b=0,10,30,50,75,100,150,400,700,1000s/mm2. The Pearson correlations between ADC, D*, f and clinical data (GA, Body-Mass Index and basal Glycaemia) were evaluated. ADCvsGA showed significant positive and negative correlation during the II and III trimester of gestation, respectively.
|
|
4575.
 |
68 |
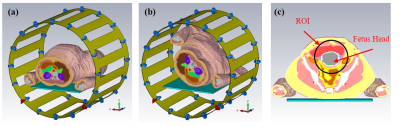
 High dielectric material application in fetal MR imaging at 3T High dielectric material application in fetal MR imaging at 3T
Chao Luo, Nan Li, Guoxi Xie, Xiaoliang Zhang, Xin Liu, Ye Li
In this paper, we evaluated the imaging performance in fetal imaging for supine and lateral positions of pregnant patients with/without high permittivity dielectric pad at 3T through numerical modeling and simulation. The results suggest that the lateral position is advantageous over the supine positions in terms of B1+ efficiency and SAR or MR safety.
|
|
4576.
 |
69 |
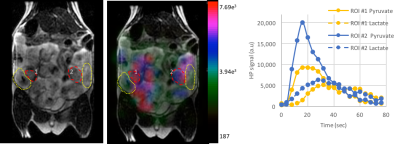
 Metabolic imaging of rodent placenta using hyperpolarized 13C pyruvate MRI Metabolic imaging of rodent placenta using hyperpolarized 13C pyruvate MRI
Renuka Sriram, Jeremy Gordon, Robert Bok, Eugene Milshteyn, Daniel Vigneron, Peder Larson, John Kurhanewicz, Priyanka Jha
We have demonstrated the initial feasibility of hyperpolarized carbon-13 MRI assessment of placental metabolism in a pregnant rat model using [1-13C]pyruvate. This opens avenues for multiple applications investigating metabolic changes of placental dysfunction detrimental to maternal and fetal health.
|
|
4577.
 |
70 |
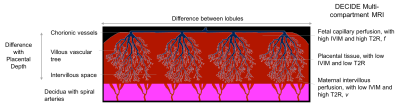
 Spatial Vascular Heterogeneity in the Normal Placenta Assessed with Multi-compartment Placental MRI Spatial Vascular Heterogeneity in the Normal Placenta Assessed with Multi-compartment Placental MRI
Rosalind Aughwane, Andrew Melbourne, David Owen, Magdalena Sokolska, Alan Bainbridge, David Atkinson, Jan Deprest, Giles Kendall, Tom Vercauteren, Sebastien Ourselin, Anna David
The placenta is perfused by the fetus and mother, allowing oxygen and nutrients to be transferred to the developing fetus. Histologically there is large variation in vascularity within normal placentae but this has not been studied in vivo. The DECIDE model was fitted to separate signals from fetal and maternal perfusion. We imaged placental perfusion using the multi-compartment MR DECIDE model over the placental volume to investigate signal heterogeneity in four uncomplicated singleton pregnancies. The spatial composition of the placenta is investigated by inspecting the parametric heterogeneity across the organ.
|
|
4578.
 |
71 |
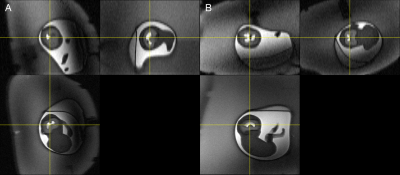
 Fast, automated slice prescription of standard anatomical planes for fetal brain MRI Fast, automated slice prescription of standard anatomical planes for fetal brain MRI
Malte Hoffmann, Borjan Gagoski, Esra Turk, Paul Wighton, M Tisdall, Martin Reuter, Elfar Adalsteinsson, P Grant, Lawrence Wald, André van der Kouwe
Motion limits MRI of the fetal brain to rapid 2D acquisitions with low resolution. Even with such sequences, it is challenging to obtain images aligned with standard anatomical planes of the brain, and views rendered retrospectively across slices typically suffer from artifacts due to between-slice motion. Here, we present an automated on-scanner slice prescription: immediately before sequence execution, the FOV/slice tilt is updated to match the orientation and position of the brain, derived from the previous acquisition. The fast update is achieved by registration to a template.
|
|
4579.
 |
72 |
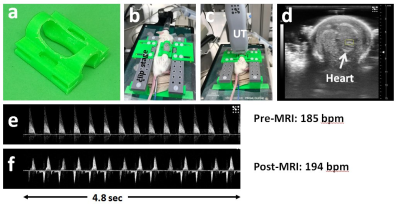
 In Utero Mouse Embryo Imaging Using Inductive Over-Coupling Clip Coil In Utero Mouse Embryo Imaging Using Inductive Over-Coupling Clip Coil
Orlando Aristizabal, Dung Hoang, Choong Lee, Zakia Gironda, Jiangyang Zhang, Daniel Turnbull, Youssef Wadghiri
In-utero fetal imaging is prone to respiratory and cardiac artifacts from the mother. These motion artifacts can be reduced via gated- or self-gated navigator acquisitions. For random fetal movements, each subject must be immobilized within the RF coil or require rapid acquisition and serial co-registration involving complex off-line image processing and high performance hardware that may not be available. We propose the use of 3D printed cylindrically shaped clip to effectively immobilize embryos incorporating a resonator mutually coupled with a surface resonator while ensuring an optimized filling factor. Our setup results in increased sensitivity demonstrated via high quality volumetric datasets.
|
|
Body Imaging: Kidney
Electronic Poster
Body: Breast, Chest, Abdomen, Pelvis
Wednesday, 20 June 2018
| Exhibition Hall |
08:15 - 09:15 |
| |
|
Computer # |
|
4580.
 |
73 |
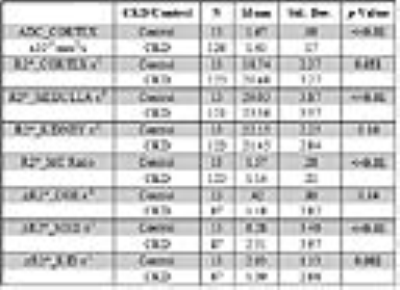
 Renal BOLD & Diffusion MRI in CKD: First Application to a Multi-center Trial Renal BOLD & Diffusion MRI in CKD: First Application to a Multi-center Trial
Wei Li, Tamara Isakova, Stuart Sprague, COMBINE Investigators, Pottumarthi Prasad
There is growing interest in applying functional MRI methods to patient studies, especially BOLD and Diffusion MRI in patients with chronic kidney disease. We have had the opportunity to analyze data from a multi-center trial involving patients with advanced CKD (stage 3B & 4) with multiple etiologies. A healthy control group was used to compare the patient cohort. Data shows small increase in cortical R2*, decrease in medullary R2* and response to furosemide in CKD. ADC was reduced in CKD and was correlated with medullary R2*.
|
|
4581.
 |
74 |
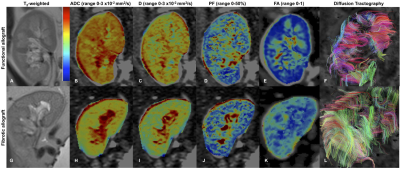
 Multiparametric MRI for assessment of renal transplant fibrosis: preliminary results. Multiparametric MRI for assessment of renal transplant fibrosis: preliminary results.
Octavia Bane, Stefanie Hectors, Sonja Gordic, Paul Kennedy, Mathilde Wagner, Rafael Khaim, Veronica Delaney, Madhav Menon, Fadi El Salem, Sara Lewis, Bachir Taouli
The goal of our study is to develop a multiparametric MRI (mpMRI) protocol for the assessment of renal transplant fibrosis. Our initial results show decrease of cortical and medullary ADC, cortical D and PF, and increase of cortical T1 in fibrotic allografts compared to functional allografts. We also observed loss of corticomedullary differentiation in ADC and T1 with fibrosis. We conclude that diffusion and T1 measurements are sensitive to renal allograft fibrosis, to be confirmed in a larger study.
|
|
4582.
 |
75 |
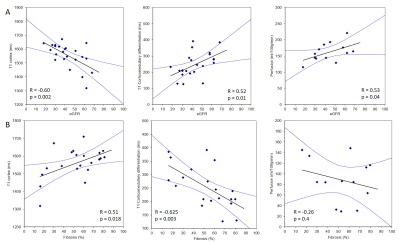
 Use of Multiparametric MRI in assessment of Chronic Kidney Disease: reproducibility, correlation with histology and progression Use of Multiparametric MRI in assessment of Chronic Kidney Disease: reproducibility, correlation with histology and progression
Charlotte Buchanan, Huda Mahmoud, Eleanor Cox, Benjamin Prestwich, Nicholas Selby, Maarten Taal, Susan Francis
We use multi-parametric renal MRI including T1, ASL perfusion and DWI to assess structural and haemodynamic changes in CKD patients compared to healthy volunteers (HV). A significant increase in renal cortex and medulla T1 (and reduced corticomedullary differentiation), and reduction in renal cortex perfusion, was found between CKD patients and HVs. MRI measures in CKD patients were highly reproducible. A significant negative correlation was found between renal cortex T1 and eGFR, and a positive correlation of corticomedullary differentiation and perfusion with eGFR. Renal cortex T1 and corticomedullary differentiation correlated most strongly with quantitative biopsy measures of renal interstitial fibrosis (IF).
|
|
4583.
 |
76 |
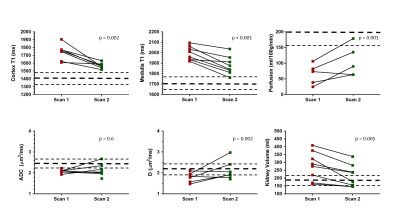
 MRI assessment of renal function in Acute Kidney Injury and associated longitudinal changes with recovery MRI assessment of renal function in Acute Kidney Injury and associated longitudinal changes with recovery
Charlotte Buchanan, Huda Mahmoud, Eleanor Cox, Benjamin Prestwich, Maarten Taal, Nicholas Selby, Susan Francis
Acute Kidney Injury (AKI), a sudden reduction in kidney function, arises from a number of causes with the degree of renal recovery varying widely between individuals. We use multi-parametric MRI to monitor renal changes at the time of AKI and during the subsequent recovery from AKI. At peak AKI, an increase in renal volume, and both renal cortex and medulla T1 was seen. Medullary T1 significantly correlated with the severity of biochemical injury as measured by serum creatinine, whilst no significant correlation was found for cortex T1. At 3 months post AKI, T1 remained elevated compared to healthy volunteers.
|
|
4584.
 |
77 |
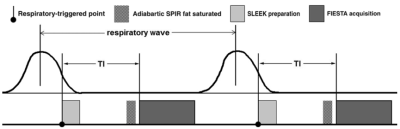
Depiction of Transplant Renal Vascular Anatomy and Complications: Unenhanced MR Angiography by Using Spatial Labeling with Multiple Inversion Pulses
Did Not Present
Hao Tang, Zhen Li, Xianlun Zou, Daoyu Hu
In this study, the preliminary data from our study demonstrate that SLEEK sequence was capable of displaying transplant renal vascular anatomy and complications. Our results show that consistantly high-quality images can be obtained by using SLEEK, which enabled visualization of even small branches within the transplant renal parenchyma and subtle accessory renal arteries. However, because the signal of the arteries depends on the cardiac output of the patient, a suboptimal blood-suppression TI may lead to poor signal-to-noise ratio and vessel depiction. We did not obtain an additional scout image, which may be helpful in evaluating the flow velocity in the aorta to optimize the blood-suppression TI; thus, a larger study for full comparative evaluation of diagnostic performance is necessary. In conclusion, unenhanced MR angiography with SLEEK preliminarily proved to be a reliable diagnostic method for depiction of anatomy and complications of renal vascular transplant. It may be used for evaluation of patients with renal transplant, and in particular for those with renal insufficiency.
|
|
4585.
 |
78 |
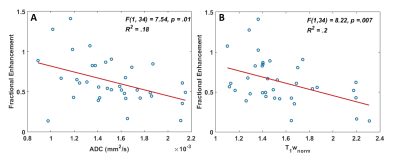
 ADC and T1-weighted MRI Identifies Necrosis in Wilms Tumours Without the Need for Contrast Agents ADC and T1-weighted MRI Identifies Necrosis in Wilms Tumours Without the Need for Contrast Agents
Harriet Rogers, Martijn Verhagen , Christopher Clark, Patrick Hales
Wilms Tumour (WT) is a paediatric renal tumour. Identifying necrosis in WT is clinically important; it can assess patients’ chemotherapy response and ultimately predict progression-free survival. It is also important for guiding biopsies. Lack of enhancement following intravenous administration of gadolinium is commonly used to identify necrosis, however, WT is a kidney tumour, and the use of gadolinium is contra-indicated in patients with renal failure. In this study we demonstrate how apparent diffusion coefficient values from DWI and pre-gad T1 imaging can predict the level of enhancement in WT, and quantify the percentage of necrotic tissue without exogenous contrast agents.
|
|
4586.
 |
79 |
IVIM DWI evaluation in assessment of of Diabetic Nephropathy: a initial clinical application
Did Not Present
long Liang, Yingjie mei, Yunfan Wu, Guomin Li, Mengchen Liu, Guihua Jiang
Previous studies using IVIM DWI in evaluating the dynamic change of renal functions both in normal and CIAKI rats’ kidney, However, to the best of our knowledge, this techniques have not been explored to evaluate Diabetic Nephropathy(DN). In oue study, we found that IVIM DWI showed potential value of clinical application in DN.
|
|
4587.
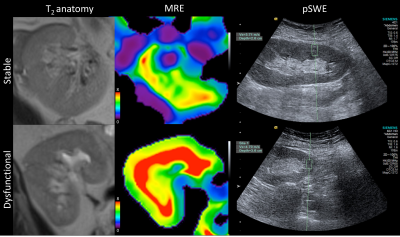 |
80 |
 MR elastography and US elastography for assessment of renal transplant dysfunction: preliminary results. MR elastography and US elastography for assessment of renal transplant dysfunction: preliminary results.
Paul Kennedy, Octavia Bane, Sonja Gordic, Stefanie Hectors, Mark Berger, Rafael Khaim, Veronica Delaney, Madhav Menon, Fadi El Salem, Sara Lewis, Bachir Taouli
The aim of this study is to determine whether MR and US elastography methods can differentiate functional and chronically dysfunctional renal allografts by measuring renal corticomedullary stiffness with MR elastography (MRE) and cortex stiffness with ultrasound point shear wave elastography (pSWE). Our preliminary results indicate that renal stiffness measured with MRE is significantly increased in dysfunctional kidneys, while no significant difference was found with pSWE. Renal stiffness measured with MRE also significantly correlated with Banff scores for interstitial fibrosis and tubular atrophy. These preliminary results suggest that MRE is sensitive to fibrotic changes in chronically dysfunctional allografts.
|
|
4588.
 |
81 |
 Usefulness of Testicular Volume, Apparent Diffusion Coefficient, and Normalized Apparent Diffusion Coefficient in the Magnetic Resonance Imaging in Evaluation of Infertile Men with Azoospermia Usefulness of Testicular Volume, Apparent Diffusion Coefficient, and Normalized Apparent Diffusion Coefficient in the Magnetic Resonance Imaging in Evaluation of Infertile Men with Azoospermia
Sung Bin Park, Byoung Hee Han, Hyun Jeong Park
It is important to distinguish the obstructive type from the non-obstructive type of azoospermia. To distinguish obstructive from non-obstructive azoospermia, it is useful and important to measure testicular volume using these techniques. To our knowledge, no reports have used DWI to evaluate the testes in case of azoospermia. Therefore, the present study aimed to evaluate the ability of testicular volume, ADC, and normalized ADC (nADC), as measured using MRI, can be used to predict the histopathological grade of azoospermia and to differentiate obstructive from non-obstructive azoospermia.
|
|
4589.
 |
82 |
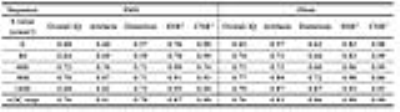
Optimizing Diffusion-Weighted MRI of the Kidneys: Comparison between Simultaneous Multi-Slice and Integrated Slice-by-Slice Shimming Echo Planar Sequences
Video Permission Withheld
Gumuyang ZHANG, Tianyi Qian, Bing Shi, Hailong Zhou, Alto Stemmer, Xiaoyan Peng, Yan Liu, Limeng Chen, Hao Sun, Huadan Xue, Zhengyu Jin
This study aimed to evaluate the image quality and scan time of the simultaneous multi-slice (SMS) technique compared to integrated slice-by-slice shimming (iShim[MB1] ) single-shot echo planar imaging (ss-epi) for diffusion-weighted imaging (DWI) of the kidneys. Six healthy subjects and 22 patients with renal disease underwent both SMS and iShim DWI scans on a 3T MR scanner. Despite the average scan time of SMS DWI being decreased by 53.5% compared to iShim DWI, the image quality of SMS DWI was slightly better, with a higher signal-to-noise ratio and similar contrast-to-noise ratio. ADC values of the kidneys were comparable in both DWI sequences. [MB1]Our product name is "SliceAdjust".
|
|
4590.
 |
83 |
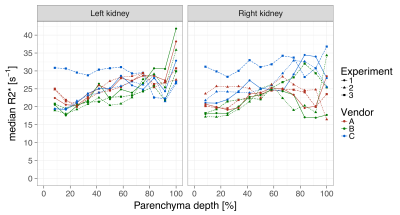
 Across vendor comparison of multi-echo GRE R2* measurements in the kidney and a tissue-mimicking phantom Across vendor comparison of multi-echo GRE R2* measurements in the kidney and a tissue-mimicking phantom
Pim Pullens, Hubert Raeymaekers
BOLD MRI may serve as an indicator of blood oxygenation in the kidney and could potentially be used as a MRI biomarker in several kidney diseases. To be effective as a quantitative imaging biomarker, BOLD MRI must be an objective measure, independent of the MRI scanner model and MRI sequence implementation details. We have compared BOLD imaging across vendors in a tissue-mimicking phantom and in the healthy kidney by assessing R2* values in 12 concentric layers.
|
|
4591.
 |
84 |
 T1? mapping for assessment of fibrosis in renal allografts. T1? mapping for assessment of fibrosis in renal allografts.
Stefanie Hectors, Octavia Bane, Paul Kennedy, Fadi El Salem, Madhav Menon, Maxwell Segall, Rafael Khaim, Veronica Delaney, Sara Lewis, Bachir Taouli
The goal of our study was to assess the utility of T1ρ measurements for the differentiation between functional and fibrotic renal allografts. We observed a significant increase in T1ρ in the cortex of fibrotic renal allografts compared to functional allografts. Our results show that T1ρ may be a suitable biomarker for the assessment of fibrosis in renal allografts, which needs to be verified in a larger cohort of patients.
|
|
4592.
 |
85 |
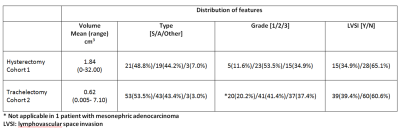
 Value of endovaginal MRI derived tumor volumes for predicting outcomes in patients selected for trachelectomy vs hysterectomy in cervical cancer Value of endovaginal MRI derived tumor volumes for predicting outcomes in patients selected for trachelectomy vs hysterectomy in cervical cancer
Katja De Paepe, Thomas Ind, Ayoma Attygalle, Veronica Morgan, Karen Thomas, Nandita deSouza
A pre-surgical endovaginal MRI was performed in 142 women with early stage cervical cancer scheduled for hysterectomy (n=43) or trachelectomy (n=99). Total tumor volume was calculated by summing MRI and LLETZ/biopsy (done prior to imaging) volumes. In the hysterectomy group, tumour volume, grade and lymphovascular space invasion (LVSI) differed significantly between those without and with an adverse outcome (need for adjuvant treatment or recurrence); only volume and LVSI were significant in the trachelectomy group where multivariate analysis demonstrated their independence. In patients eligible for trachelectomy, with tumors >1.4 cm3and with LVSI, administration of (neo)adjuvant treatment may potentially improve outcome.
|
|
4593.
 |
86 |
 Feasibility of Renal ASL in a Paediatric Cohort with Impaired Renal Function Feasibility of Renal ASL in a Paediatric Cohort with Impaired Renal Function
Fabio Nery, Enrico De Vita, Chris Clark, Isky Gordon, David Thomas
Arterial Spin Labelling (ASL) allows for non-invasive measurements of tissue perfusion. As such, it presents an attractive alternative to contrast-enhanced based methods for quantification of renal perfusion, particularly in populations with impaired renal function. In this work, we assess the feasibility of ASL in a paediatric cohort with severe kidney disease by combining a robust acquisition scheme with an optimised retrospective motion correction approach.
|
 |
4594.
 |
87 |
 Multiparametric MRI of Folic Acid Induced Renal Pathology in Mice: A Longitudinal Study Multiparametric MRI of Folic Acid Induced Renal Pathology in Mice: A Longitudinal Study
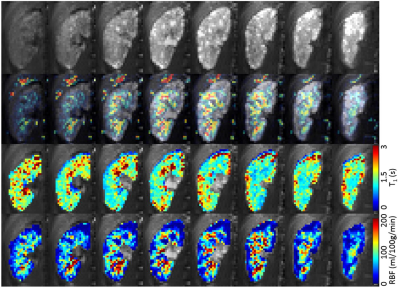
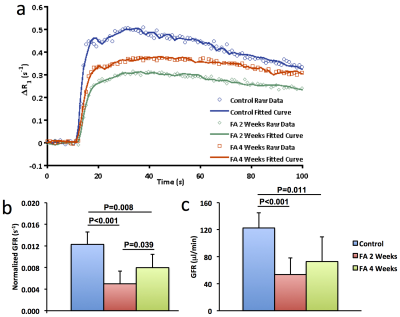
Kai Jiang, Tristan Ponzo, Hui Tang, Prasanna Mishra, Slobodan Macura, Lilach Lerman
Multiparametric MRI was used to assess folic acid-induced renal pathology in mice. Kidney volume, R2*, magnetization transfer ratio (MTR), perfusion, T1, and glomerular filtration rate (GFR) were measured at 2 and 4 weeks post-treatment. While kidney structure (volume and MTR) and hypoxia (R2*) showed progressive deterioration, renal perfusion and normalized GFR dropped dramatically at 2 weeks but recovered slightly at 4 weeks. T1 elevated at 2 weeks and slightly dropped at 4 weeks, suggesting development of transient edema. In conclusion, multiparametric MRI provides a valuable tool for investigation and monitoring of folic acid induced renal pathology.
|
|
4595.
 |
88 |
Tri- and Biexponential Diffusion Analyses of the Kidney: Effect of Respiratory Controlled Acquisition on Measurement Accuracy and Repeatability of Diffusion Parameters
Video Permission Withheld
Yuki Koshino, Naoki Ohno, Tosiaki Miyati, Naoki Hori, Yukihiro Matsuura, Toshifumi Gabata
To investigate the effect of respiratory-controlled acquisition on intravoxel incoherent motion analysis in the kidney, we compared the fitting accuracy and repeatability of diffusion parameters with tri- and biexponential models among three different methods, ie., respiratory triggering, abdominal belt, and free breathing. Respiratory triggering shows better fitting accuracy and repeatability of tri- and biexponential diffusion parameters compared with free breathing. Moreover, abdominal belt can improve the measurement repeatability even with free breathing.
|
|
4596.
 |
89 |
 Multiparametric MRI Data in Diabetic Nephropathy: Correlation with eGFR and eGFR_slope Multiparametric MRI Data in Diabetic Nephropathy: Correlation with eGFR and eGFR_slope
Lu-Ping Li, Wei Li, Bradley Hack, Orly Kohn, Stuart Sprague, Pottumarthi Prasad
BOLD, Diffusion and ASL MRI are useful in the evaluation of renal oxygenation, fibrosis and blood flow. In this study, these three functional MRI data were acquired in patients with diabetic nephropathy (DN) patients and stage-3 chronic kidney disease (CKD). For the first time, we report that the cortical blood flow and response to furosemide in renal medulla are significantly correlated with yearly rate of change in eGFR. These relationships were independent of any correlations observed with eGFR. The correlations with eGFR seem to depend on whether a control group was included.
|
|
4597.
 |
90 |
Preliminary study of evaluating Intrarenal Oxygenation in Iodinated Contrast-Induced Acute Kidney- Injured pig models by BOLD MRI
Did Not Present
Junjie Ren, Shengzhang Ji, Zhizheng Zhuo, Chenjie An
Iodinated contrast agent (CA) is important for many radiologic and interventional procedures. However, contrast-induced acute kidney injury (CIAKI) is potentially life-threatening, especially for patients with impaired renal function, and it has become one of the leading causes of hospital-acquired acute kidney injury (AKI)[1] . The pathogenesis of CIAKI is not yet fully understood, but the relevance of renal medullary hypoxia in the pathophysiology of AKI is well accepted. In recent years, many studies focused on the change of intrarenal oxygenation and showed renal hypoxia especially in medulla. Blood oxygen level dependent magnetic resonance imaging (BOLD MRI) is a noninvasive method that can assess hypoxia by utilizing the endogenous contrast generated by paramagnetic deoxyhemoglobin[2] .
|
|
4598.
 |
91 |
 Effect of orally administered aspirin on renal function in hypertensive rats Effect of orally administered aspirin on renal function in hypertensive rats
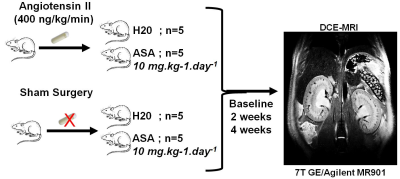
Greg Cron, Rafael Glikstein, Jean-François Thibodeau, Anthony Carter, Naomi Boisvert, Chet Holterman, Lihua Zhu, Chris Kennedy
Although aspirin and other NSAIDs are commonly perceived as harmless, they may be dangerous for hypertensive patients. We recently showed that in hypertensive mice, genetic suppression of the renal vessel EP4 receptor (which mimics downstream effects of NSAIDs) leads to a massive reduction in renal perfusion. However, direct genetic manipulation of a drug end target is not the same thing as actually administering the drug. Thus, we repeated that study, this time giving aspirin instead of using genetic manipulation. Hypertensive rats that drank aspirin water suffered severe kidney damage and 2/5 died. For hypertensive patients, NSAIDs warrant extreme caution.
|
|
4599.
 |
92 |
 Analysis of kidney function and therapy monitoring with DCE-MRI in a murine model of septic shock Analysis of kidney function and therapy monitoring with DCE-MRI in a murine model of septic shock
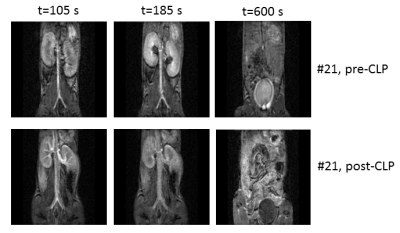
Claudia Weidensteiner, Wilfried Reichardt, Joachim Struck, Anne Kirchherr, Katja Wagner, Florian Wagner, Dominik von Elverfeldt
DCE-MRI with a 3D spoiled gradient echo sequence and injection of Gd-DTPA was used to analyze the kidney function in mice during septic shock (cecal ligation and puncture CLP model). Gd concentration time courses were analyzed without pharmacokinetic modelling. In renal cortex and medulla of septic mice a slower exponential decay compared to baseline or even non-exponential curve shapes were observed. In most septic mice there was no Gd accumulation in the urine in the bladder. Treatment with an antibody targeting adrenomedullin (a vasodilatory peptide) resulted in a faster half-life of tracer elimination in the kidneys compared to vehicle-treatment.
|
|
4600.
 |
93 |
 Assessment of Optimal Technique for Measurement of Medullary Perfusion Assessment of Optimal Technique for Measurement of Medullary Perfusion
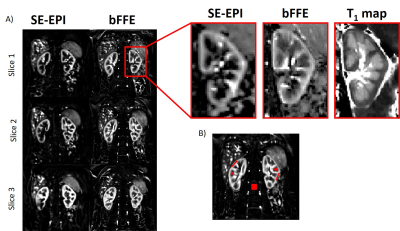
Chris Bradley, Charlotte Buchanan, Eleanor Cox, Susan Francis
The ability to assess medullary perfusion is important in kidney disease, for example in acute kidney injury (AKI) in which reduced medullary blood flow is implicated. In this study, we compare the use of a spin echo (SE) EPI and balanced FFE (bFFE) readout at multiple post label delay (PLD) times to determine the optimal readout scheme and to assess the number of ASL pairs required to compute medullary perfusion. Using a bFFE FAIR ASL scheme, it is possible to quantify tissue perfusion within the renal medulla.
|
|
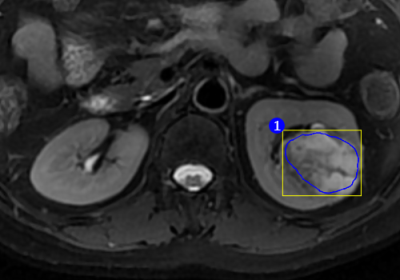
4601.
 |
94 |
 T2WI Texture Analysis in Renal Cell Carcinoma: Histologic Subtype Classification T2WI Texture Analysis in Renal Cell Carcinoma: Histologic Subtype Classification
Zhenhao Liu, Haiyi Wang, Xu Bai, Huiling Yi, Huiyi Ye
This retrospective study investigates the possibility of distinguishing between clear cell renal cell carcinoma ( ccRCC ) and non-clear cell renal cell carcinoma ( nccRCC ) using MRI-derived parameters by exploring a predictive method. We enrolled the patients with three common subtypes of renal tumor - clear cell renal cell carcinoma ( ccRCC ), papillary renal cell carcinoma ( pRCC ) and chromophobic renal cell carcinoma ( cRCC ). We combined pRCC and cRCC into one subtype - nccRCC. Our results demonstrated that MRI texture analysis can differentiate ccRCC from nccRCC with high specificity, sensitivity and accuracy and can probably facilitate the precise treatment of renal tumors in the future clinical practice.
|
|
4602.
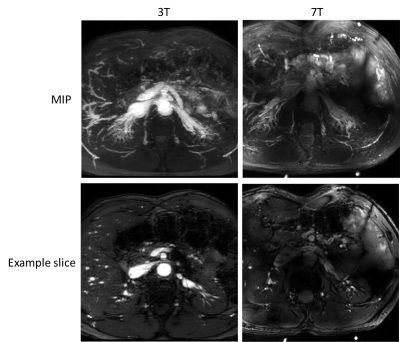 |
95 |
 A comparison of 7 and 3 Tesla time-of-flight renal MR angiography for detection of intrarenal vessels A comparison of 7 and 3 Tesla time-of-flight renal MR angiography for detection of intrarenal vessels
Emma Doran, Stephen Bawden, Christopher Mirfin, Paul Glover, Richard Bowtell, Penny Gowland, Susan Francis
Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) is thought to be due to small artery disease at the cortico-medullary border, however these vessels are too small to be imaged at conventional field strengths. Here, we assess the feasibility of 2D gradient echo Time-of-flight (TOF) renal angiography at 7 T to detect the arterial vasculature of the kidney and delineate the intrarenal vasculature network. We compare TOF MRA data collected at 3 T and 7 T in the same subjects, and illustrate the superiority of 7 T for high spatial resolution MRA.
|
|
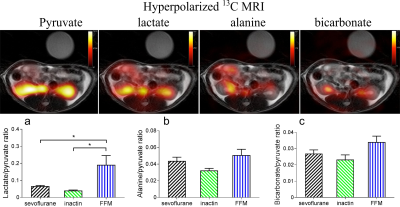
4603.
 |
96 |
 Effects of anesthesia on renal function and metabolism in rats Effects of anesthesia on renal function and metabolism in rats
Haiyun Qi, Christian Mariager, Jakob Lindhardt, Per Nielsen, Hans Stødkilde-Jørgensen, Christoffer Laustsen
Performing MRI of animals typically requires anesthesia. However, anesthesia is known to modulate a wide variety of important metabolic and functional processes, and as such represents potential limitations in study design. Here we investigated renal functional and metabolic consequences of three typical rodent anesthetics of sevoflurane, inactin and a mixture of fentanyl, fluanisone and midazolam (FFM), with hyperpolarized [1-13C] pyruvate MRI and DCE imaging. FFM increased renal lactate/pyruvate ratio and blood lactate concentration. Inactin and sevoflurane had reasonable renal metabolism and function. The results indicate inactin and sevoflurane are preferable when renal metabolism and function are the consideration of research. |
|
Body DWI & Liver Tumour
Electronic Poster
Body: Breast, Chest, Abdomen, Pelvis
Wednesday, 20 June 2018
| Exhibition Hall |
08:15 - 09:15 |
| |
|
Computer # |
|
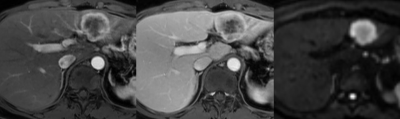
4604.
 |
97 |
 Combined hepatocellular-cholangiocarcinoma: diagnostic and prognostic values of LI-RADS v2017 categorization on gadoxetic acid-enhanced MR imaging Combined hepatocellular-cholangiocarcinoma: diagnostic and prognostic values of LI-RADS v2017 categorization on gadoxetic acid-enhanced MR imaging
Sun Kyung Jeon, Ijin Joo, Dong Ho Lee, Sang Min Lee, Hyo Jin Kang, Jeong Min Lee
Our retrospective study investigated the utility of Liver Imaging Reporting and Data System (LI-RADS) v2017 for combined hepatocellular cholangiocarcinoma (cHCC-CCs) in the differential diagnosis from HCCs and prediction of prognosis. Using LI-RADS on gadoxetic acid-enhanced MRI, among cHCC-CCs (n=70), 61.4% (43/70) were accurately categorized as LR-M (probable malignancy, not specific for HCC) while 37.1% (26/70) as LR-5/4 (definitely/probably HCC); among HCCs (n=70), 88.6% (62/70) and 10.0% (7/70) were categorized as LR-5/4 and LR-M, respectively. After surgical resection, patients with LR-M cHCC-CCs showed a higher early recurrence rate (≤6 months) than those with LR-5/4 cHCC-CCs (27.8% (10/36) vs. 4.8% (1/21), P=0.041).
|
|
4605.
 |
98 |
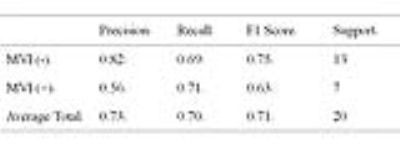
Preoperative Prediction of Microvascular Invasion in Hepatocellular Carcinoma Using Radiomic Analysis of Diffusion-weighted MRI
Did Not Present
Xiangtian Zhao, Qiang Gao, Jingliang Cheng
Microvascular invasion (MVI) in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is an independent predictor of poor outcomes subsequent to surgical resection or liver transplantation (LT); however, MVI currently cannot be reliably determined preoperatively. In this study, we investigated the association between radiomic features on preoperative ADC maps and the MVI (with or without) in resected 96 HCCs. Furthermore, we employed machine-learning methods and independently evaluated their prediction performance. Total 1029 radiomic features were extracted from cancerous VOIs on ADC maps of each patient. Finally, 7 features could differentiate HCCs with MVI versus HCCs without. The random forest classifier using the optimal feature subset achieved the best performance, with an area under the receiver operating characteristic curve 0.79, sensitivity 71.0%, specificity 85.0%, precision 73%, and recall 70%.
|
|
4606.
 |
99 |
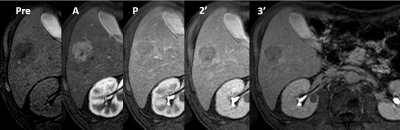
MDCT outperforms gadoxetate-enhanced MRI in differentiating stroma-rich tumors from hepatocellular carcinomas developing in patients with chronic liver diseases
Video Permission Withheld
Kengo Yoshimitsu
Consecutive 179 patients with chronic liver diseases who underwent gadoxetate enhanced-MRI and MDCT firstly developed hypervascular liver masses were retrospectively recruited, and 14 stroma-rich tumors (SRT), such as intrahepatic cholangiocellular carcinoma, and 165 hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) were found. Using rim enhancement, and target sign on DWI, which were confirmed to favor SRT over HCC by multivariate analysis on gadoxetate-enhanced MRI, 71% sensitivity and 97% specificity were obtained, however, MDCT provided almost 100% accuracy when delayed or prolonged enhancement was considered signs suggesting SRT. For diagnosing SRT, MDCT outperforms gadoxetate-enhanced MRI.
|
|
4607.
 |
100 |
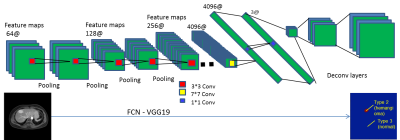
 An automated lesion detection method on hepatic hemangioma and hepatic cyst using fully convoluted network An automated lesion detection method on hepatic hemangioma and hepatic cyst using fully convoluted network
Yajing Zhang, Mo Shen, Yin Guo, Huiyu Qiao, Qian Jiang, Sussi Wang, Yi Yang
Hepatic hemangioma and hepatic cyst are two kinds of common benign liver diseases. MR has been widely used for their diagnosis due to its significance of detection on small lesions. This study proposes a deep learning based method to detect the lesion of hemangioma and cyst on MR dynamic contrast-enhanced images. The results show good alignment of automated detection boundary with the actual lesion boundary for both lesion types.
|
|
4608.
 |
101 |
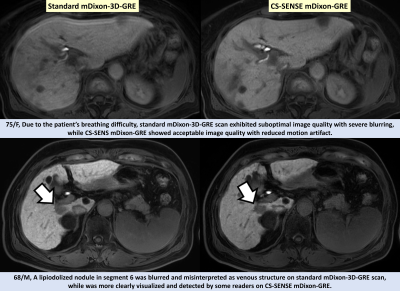
 High Acceleration Three Dimensional T1-weighted Dual Echo Dixon Imaging using Compressed Sensing-SENSE: Comparison of Image Quality and Solid Lesion Detectability with the Standard T1-Weighted Sequence High Acceleration Three Dimensional T1-weighted Dual Echo Dixon Imaging using Compressed Sensing-SENSE: Comparison of Image Quality and Solid Lesion Detectability with the Standard T1-Weighted Sequence
Ju Nam, Jeong Min Lee, Sang Min Lee, Hyo-Jin Kang, Eun Sun Lee, Bo Yun Hur, Jeong Hee Yoon, EunJu Kim, Mariya Doneva
A total of 163 consecutive patients underwent gadoxetic acid-enhanced liver MRI at 3T with two HBP protocols using the standard mDIxon-3D-GRE technique with sensitivity-encoding method (SENSE; acceleration factor (AF): 2.8, standard mDixon-GRE) and a high acceleration mDIxon-3D GRE technique using the combined compressed sensing (CS)-SENSE technique (CS-SENSE mDixon-GRE). The consensus reading revealed no significant difference in overall image quality. CS-SENSE mDixon-GRE showed higher image noise, but less motion artifact and overall artifact levels. In terms of lesion detection, reader-averaged JAFROC figures-of-merit showed non-inferior performance of CS-SENSE mDixon-GRE over standard mDixon-GRE was confirmed (JAFROC figure-of-merits difference: 0.064 [-0.012, 0.081])
|
|
4609.
 |
102 |
 Diagnostic Accuracy of Liver Imaging Reporting and Data System 2017 (LIRADS) Criteria for Hepatocellular Carcinoma Diagnostic Accuracy of Liver Imaging Reporting and Data System 2017 (LIRADS) Criteria for Hepatocellular Carcinoma
Andrea Kierans , Jasnit Makkar, Joshua Cornman-Homonoff, Preethi Guniganti, Elizabeth Hecht
The aim of our investigation is to assess the diagnostic accuracy of the LI-RADS 2017 criteria at two institutions using multiple readers with varying levels of experience with explant or imaging follow-up as the reference standard. Radiology databases from two academic institutions were searched (2013-2014) for patients with a clinical diagnosis of chronic liver disease and at least one reported hepatic observation on dynamic contrast enhanced CT or MRI. This yielded a final cohort of 103 patients with 141 hepatic observations. Two radiologists reviewed the imaging independently and assigned a LI-RADs category to each observation. Inter-reader reliability for LI-RAD assessment was moderate (ICC = 0.63). Sensitivity of LI-RADs categorization for diagnosing HCC was 62% and 59% and specificity was 96% and 84% for reader 1 and 2 respectively. LI-RADs categorization using gadoxetate disodium MR demonstrated higher specificity for HCC diagnosis for reader 2, than MR with extracellular agent.
|
|
4610.
 |
103 |
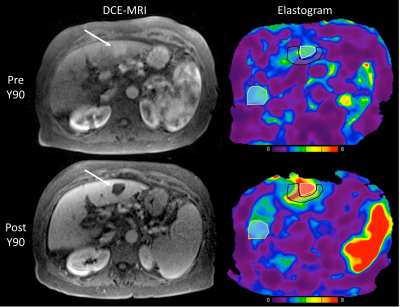
 Changes in HCC tumor stiffness post 90Yttrium radioembolization assessed with MR elastography: Early results. Changes in HCC tumor stiffness post 90Yttrium radioembolization assessed with MR elastography: Early results.
Paul Kennedy, Sara Lewis, Octavia Bane, Stefanie Hectors, Maxwell Segall, Edward Kim, Bachir Taouli
The goal of the current study was to assess the changes in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) stiffness using 2D MR elastography (MRE) at baseline and 6 weeks after 90Yttrium radioembolization (RE). Preliminary results are presented in 10 patients and show that HCC stiffness and liver stiffness adjacent to the treated lesion are both significantly increased 6w after therapy. Percentage change in tumor stiffness is significantly correlated with degree of tumor necrosis at 6w.
|
|
4611.
 |
104 |
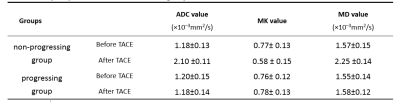
 Diffusion Kurtosis Imaging for Assessing the Therapeutic Response of Transcatheter Arterial Chemoembolization in Hepatocellular Carcinoma Diffusion Kurtosis Imaging for Assessing the Therapeutic Response of Transcatheter Arterial Chemoembolization in Hepatocellular Carcinoma
Zhenguo Yuan, Mengying Xia, Weibo Chen
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is one of the major causes of morbidity and mortality in patients with chronic liver disease. Transcatheter arterial chemoembolization (TACE) play an important role in treatment for HCC. Evaluation of the response to TACE treatment affects not only the therapeutic efficacy but also the treatment plan. Data from 43 patients with hepatic cancer between January 2017 and September 2017 were recruited for this study. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and DKI (b=0, 800, 1500, 2000 mm2/s) were performed before and 3 weeks after initiating TACE. Contrast-enhanced MRI was performed 3 months and 6 months after initiating TACE. We observed a significant decrease in MK in HCC tissues that were completely necrotic after TACE. The MK value can reflect the complexity of tissue structure. A lower MK value indicates evidence of necrosis, implying more stable lesions and hence better treatment outcomes. Therefore, the differences in MK values observed in our study reflected the differences in tissue microstructural complexity between the progressing and non-progressing groups. The change of MK values before and after TACE can thus be used to estimate the degree of tumor necrosis and to further evaluate the effect of interventional therapy.
|
|
4612.
 |
105 |
 Contrast-enhanced MR Imaging 3D texture analyses as a potential tool for preoperative prediction of microvascular invasion in hepatocellular carcinoma: Comparison with postoperative pathology Contrast-enhanced MR Imaging 3D texture analyses as a potential tool for preoperative prediction of microvascular invasion in hepatocellular carcinoma: Comparison with postoperative pathology
Yongjian Zhu, Xiaohong Ma, Xinming Zhao, Bing Feng, Lizhi Xie
Microvascular invasion (MVI) is a significant risk factor contributing to high recurrence ratio and poor prognosis of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). Therefore, it is of great clinical significance to accurately predict MVI of HCC preoperatively. Texture analyses (TA) is a novel image post-processing technique, which analyze the distribution and associations of pixel intensities in images with a series of quantitative texture parameters. However, there was limited report on applying TA on MVI of HCC . The purpose of this study was to explore the value of contrast enhanced MRI texture analyses in the preoperative prediction of MVI of HCC preoperative.
|
|
4613.
 |
106 |
 Using deep learning to investigate the value of diffusion weighted images for malignancy characterization of hepatocellular carcinoma Using deep learning to investigate the value of diffusion weighted images for malignancy characterization of hepatocellular carcinoma
Wu Zhou, Qiyao Wang, Changhong Liang, Hairong Zheng, Lijuan Zhang
The apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) derived from Diffusion-weighted imaging (DWI) has been widely used for lesion characterization. However, ADC is calculated from image intensities with different b values, which is a low-level image feature that might be insufficient to represent heterogeneous of neoplasm. Furthermore, ADC measurements are subject to the influence of motion and image artifacts. The deep feature based on the emerging deep learning technique has been considered to be superior to traditional low-level features. The purpose of this study is to effectively characterize the malignancy of HCC based on deep feature derived from DWI data using deep learning.
|
|
4614.
 |
107 |
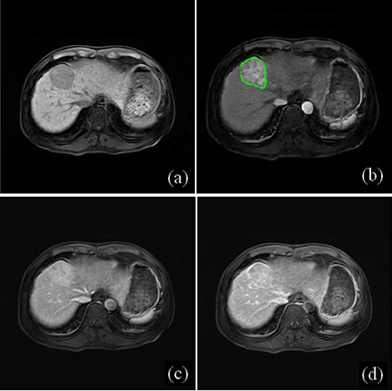
 Discriminative deep feature fusion of Contrast-enhanced MR for malignancy characterization of hepatocellular carcinoma Discriminative deep feature fusion of Contrast-enhanced MR for malignancy characterization of hepatocellular carcinoma
Wu Zhou, Tianyou Dou, Miaoyun Zhangwen, Hui Ye, Dong Cao, Honglai Zhang, Changhong Liang, Hairong Zheng, Lijuan Zhang
The malignancy of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is of great significance to prognosis. Recently, deep feature in the arterial phase of Contrast-enhanced MR has been shown to be superior to texture features for malignancy characterization of HCCs. However, only arterial phase was used for deep feature extraction, ignoring the impact of other phases in Contrast-enhanced MR for malignancy characterization. In this work, we design a discriminative multimodal deep feature fusion framework to both extract correlation and separation of deep features between Contrast-enhanced MR images for malignancy characterization of HCC, which outperforms the simply concatenation and the recently proposed deep correlation model.
|
|
4615.
 |
108 |
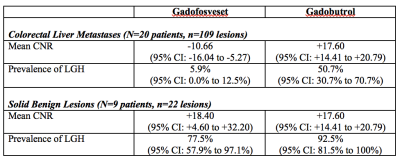
 Late gadolinium MRI hyperintensity of colorectal liver metastases with extracellular contrast agents (gadobutrol) versus intravascular contrast agents (gadofosveset) Late gadolinium MRI hyperintensity of colorectal liver metastases with extracellular contrast agents (gadobutrol) versus intravascular contrast agents (gadofosveset)
Helen Cheung, Natalie Coburn, Paul Karanicolas, Calvin Law, John Hudson, Laurent Milot
Late gadolinium hyperintensity (LGH) of colorectal liver metastases (CRCLM) using MRI with extracellular contrast agents presents a diagnostic dilemma that is commonly encountered clinically because it can be difficult to distinguish from benign hemangiomas. CRCLM may demonstrate less LGH using MRI with intravascular contrast agents due to reduced retention of contrast within these lesions. Approximately half of CRCLM demonstrate LGH on MRI with extracellular contrast agents versus only 6% on MRI with intravascular contrast agents. LGH is significantly better at excluding malignancy in patients with intravascular agents compared with extracellular contrast agents and may be a clinically useful problem-solving tool.
|
|
4616.
 |
109 |
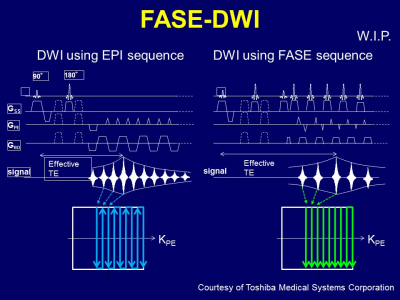
 High-b Fast Advanced Spin Echo Diffusion-Weighted Imaging in the Abdomen High-b Fast Advanced Spin Echo Diffusion-Weighted Imaging in the Abdomen
Takeshi Yoshikawa, Katsusuke Kyotani, Yoshiharu Ohno, Yoshimori Kassai, Masao Yui, Eiji Takeda, Shinichiro Seki, Yuji Kishida
High-b FASE-DWI can improve image quality and decrease image distortion without hampering abdominal lesion detection and ADC measurement.
|
|
4617.
 |
110 |
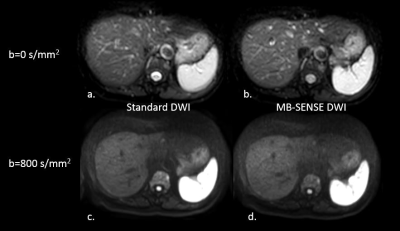
 Multiband SENSE accelerated diffusion weighted imaging of the abdomen with CAIPIRINHA: Preliminary study on clinical applicability Multiband SENSE accelerated diffusion weighted imaging of the abdomen with CAIPIRINHA: Preliminary study on clinical applicability
Yi Wang, Tyson Nunn, Noah Briller, Carolyn Wang, Sooah Kim
DWI is rapidly becoming a modality of choice to detect, characterize and monitor malignant lesions. Although diffusion imaging has benefited greatly from multiband imaging in the brain, investigation on abdomen DWI using MB has been limited. The purpose of this study was to examine the feasibility of MB-SENSE for abdominal DWI. The study demonstrated that MB-SENSE can be used to accelerate abdominal DWI with drastically reduced acquisition time (~50%) without having a significant impact on image quality. Though, refinement of the MB-SENSE free-breathing single-shot EPI sequence is necessary to ascertain the clinical value of MB-SENSE in DWI for the abdomen.
|
|
4618.
 |
111 |
 Comparison of Referenceless Methods for EPI Ghost Correction in Breast Diffusion Weighted Imaging Comparison of Referenceless Methods for EPI Ghost Correction in Breast Diffusion Weighted Imaging
Jessica McKay, Steen Moeller, Lei Zhang, Edward Auerbach, Michael Nelson, Patrick Bolan
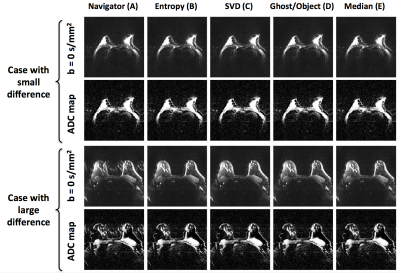
Three-line navigator correction of Nyquist ghosts in spin-echo echo-planar imaging (SE-EPI) diffusion weighted imaging (DWI) often fails in body imaging. Several alternative strategies have been proposed including referenceless methods, which do not require any type of reference information but instead minimize a cost function based on the data itself. The purpose of this work is to assess ghost correction of undersampled (R=3) breast DWI using several referenceless methods, including minimization of SVD in k-space, image entropy, a ghost/object ratio of the image, and a combination. All four referenceless strategies outperform the standard navigator correction, providing higher quality images and unbiased ADC maps.
|
|
4619.
 |
112 |
 Repeatability of Apparent Diffusion Coefficient measurements using Simultaneous Multi-slice Diffusion-Weighted imaging with elastic in-plane motion correction: a Comparison with Conventional DWI in Healthy Liver Parenchyma Repeatability of Apparent Diffusion Coefficient measurements using Simultaneous Multi-slice Diffusion-Weighted imaging with elastic in-plane motion correction: a Comparison with Conventional DWI in Healthy Liver Parenchyma
Jia Xu, Xuan Wang, Tianyi Qian, Shitian Wang, Huadan Xue, Zhengyu Jin
The simultaneous multi-slice (SMS) technique allows reducing the scan time of DWI without significant compromises in image quality. An adequate test-retest reliability of apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) is essential for clinical use. The aim of this study was to prospectively compare the ADC value and test-retest repeatability of SMS-DWI with elastic in-plane motion correction in comparison to conventional DWI in healthy liver parenchyma. SMS-DWI and motion corrected SMS-DWI images (Moco-SMS) demonstrated significantly higher ADC values than conventional DWI in almost all liver regions. Moco-SMS showed significantly higher test-retest repeatability than conventional DWI in regions close to liver edges.
|
|
4620.
 |
113 |
 CNN based Super-Resolution of Intravoxel Incoherent Motion Imaging for Liver CNN based Super-Resolution of Intravoxel Incoherent Motion Imaging for Liver
Jiqing Huang, Jin Qin, Lihui Wang, Rongpin Wang, Zi-Xiang Kuai, Chen Ye, Tianye Wang, Yuemin Zhu
We investigated the super-resolution reconstruction method for IVIM imaging based on convolution neural networks (CNN). Three-layers-CNN was constructed and trained firstly with a series of paired low- and high-resolution images, and then the super-resolution IVIM images were reconstructed with such network, the reconstruction quality was evaluated finally in terms of PSNR, SSIM, diffusivity, perfusion fraction and pseudo-diffusivity respectively. The results show that the CNN-based super resolution reconstruction for IVIM has a great performance and may enable IVIM to be analyzed with unprecedent resolution.
|
|
4621.
 |
114 |
 Comparison of Slice-specific Shim and Volume Shim for 1.5T Whole-body Diffusion Weighted Imaging Comparison of Slice-specific Shim and Volume Shim for 1.5T Whole-body Diffusion Weighted Imaging
Sarah McElroy, Jessica Winfield, Radhouene Neji, Alto Stemmer, Kiefer Berthold, Joanna Bell, John Spence, Geoff Charles-Edwards, Olwen Westerland, Vicky Goh
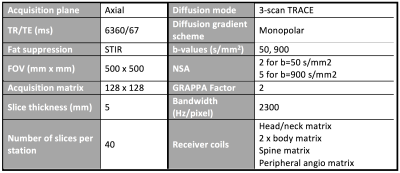
This study compared whole body diffusion weighted MR imaging (WB-DWI) acquired on a 1.5T scanner with and without integrated slice-specific shimming with retrospective distortion correction (iShim) for evaluation of monoclonal plasma cell disorders. WB-DWI with iShim showed significant reduction of the spinal displacement artefact and increased signal in the sternum.
|
|
4622.
 |
115 |
 Toward quantification of renal tubular volume fraction using diffusion-weighted split-echo RARE in conjunction with a three-compartment IVIM model Toward quantification of renal tubular volume fraction using diffusion-weighted split-echo RARE in conjunction with a three-compartment IVIM model
Joao Periquito, Katharina Paul, Till Huelnhagen, Yiyi Ji, Min-Chi Ku, Sarah Brix, Kathleen Cantow, Erdmann Seeliger, Bert Flemming, Thomas Gladytz, Dirk Grosenick, Andreas Pohlmann, Thoralf Niendorf
T2* mapping does not fully represent renal tissue oxygenation. Diffusion-weighted imaging (DWI) can provide information about confounding factors such as tubular volume fraction, which can be used to correct T2*. By using a three compartment IVIM model, tubular volume fraction can be mapped with DWI. The most widely used DWI technique is spin-echo EPI which is sensitive to magnetic field inhomogeneities and hence prone to geometric distortions. In this work we propose a diffusion-weighted Rapid Acquisition Relaxation Enhancement (RARE) variant for DWI of the rat kidney free of geometric distortions to quantify tubular volume fraction at 9.4 Tesla.
|
|
4623.
 |
116 |
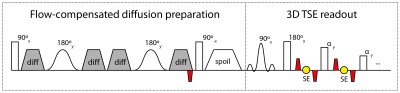
 Robustness of diffusion-prepared 3D TSE for isotropic-resolution large-FOV coronal DWI of neurogenic tumors in cervical and pelvic regions Robustness of diffusion-prepared 3D TSE for isotropic-resolution large-FOV coronal DWI of neurogenic tumors in cervical and pelvic regions
Barbara Cervantes, Alexandra Gersing, Benedikt Schwaiger, Andreas Hock, Johannes Peeters, Carolin Knebel, Klaus Wörtler, Dimitrios Karampinos
DWI of musculoskeletal tumors has been proposed as a non-invasive tool of potential valuable diagnostic utility. Large-FOV isotropic-resolution DWI can provide improved visualization of MSK tumors but deems particularly challenging for conventionally used DW-EPI in terms of geometric distortions and chemical-shift artifacts. 3D DW-TSE techniques can alleviate these challenges and have been shown to be useful in DWI of different body regions. The present work examines the robustness to distortions and artifacts of 3D DW-TSE in isotropic-resolution large-FOV coronal DWI of neurogenic tumors in two anatomical regions where DW-EPI is highly prone to distortion artifacts.
|
|
4624.
 |
117 |
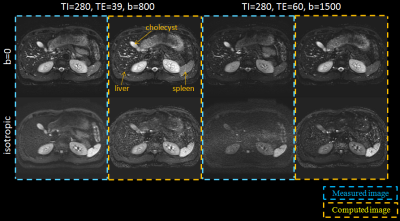
 Variable-TE STIR computed Diffusion Weighted Imaging Technique for the abdomen Variable-TE STIR computed Diffusion Weighted Imaging Technique for the abdomen
Hiroshi Kusahara, Yuki Takai, Yoshimori Kassai
In this study to the authors adapted the variable-TE cDWI (vTE-cDWI) technique to the abdominal region, using ADC map, T2 map and T1 map with IR-based images. The algorithm under evaluation allows computing diffusion images for arbitrary combinations of TE, b-value and TI based on four acquisitions (4-points method). This technique was shown to generate STIR-cDWI with higher SNR compared to the acquired STIR-DWI, as well as obtain ADC maps and T1 maps with optimal TI for any arbitrary tissue. The clinical benefits of the method and the preliminary results on volunteers are discussed.
|
|
4625.
 |
118 |
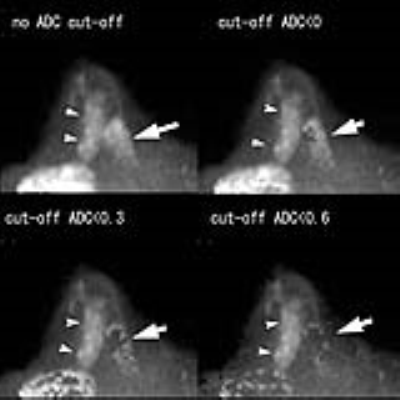
 Computed DWI for breast cancer detection: improved fat suppression and lesion-to-background contrast with a novel low ADC pixel cut-off technique Computed DWI for breast cancer detection: improved fat suppression and lesion-to-background contrast with a novel low ADC pixel cut-off technique
Toshiki Kazama, Taro Takahara, Tetsu Niwa, Jun Endo, Hiroshi Yamamuro, Tatsuya Sekiguchi, Jun Hashimoto, Thomas Kwee, Yutaka Imai
When we calculate very high b-value images using computed diffusion-weighted imaging (cDWI), a tremendous number of bright pixels (noise) appears on the images and they disturb the visualization of lesions. Bright noise on high b-value images may be suppressed by cutting off pixels with very low ADC values. Because the ADC of fat is very low, unsuppressed fat signal can be deleted using the same technique. With appropriate use of the low ADC pixel cut-off technique on cDWI, diagnostic performance of cDWI of the breast may be improved.
|
|
4626.
 |
119 |
 Prediction of treatment response based on baseline volumetric functional MR imaging criteria in patients with unresectable HCC who are candidate for Trans-Arterial Chemoembolization. Prediction of treatment response based on baseline volumetric functional MR imaging criteria in patients with unresectable HCC who are candidate for Trans-Arterial Chemoembolization.
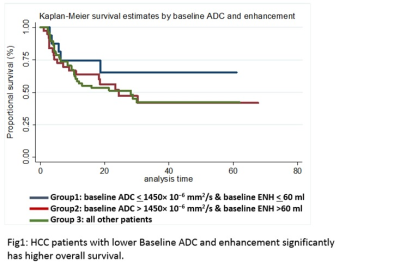
Mounes Aliyari Ghasabeh, Ankur Pandey, Sanaz Ameli, Pallavi Pandey, pegah Khoshpouri, Yan luo, Farnaz Najmi varzaneh, Manijeh Zargham pour, Ihab Kamel
Synopsis: Predicting overall survival in HCC patients before initiating treatment is essential to personalize a treatment plan for each patient. Barcelona clinic liver cancer (BCLC) is one of the current criteria for predicting pre-therapeutic overall survival (OS). Several studies suggested a valuable role of functional MRI biomarkers including diffusion-weighted imaging (DWI) with apparent diffusion coefficients (ADC), tumor venous enhancement (VE) and tumor volume (TV) in tumor response assessment. These metrics rely on changes post therapy; none of these parameters assessed baseline values of these variables in predicting OS before starting treatment.
|
|
4627.
 |
120 |
 Magnetic resonance imaging features of parenchymal mass with tumor in vein in patients with cirrhosis Magnetic resonance imaging features of parenchymal mass with tumor in vein in patients with cirrhosis
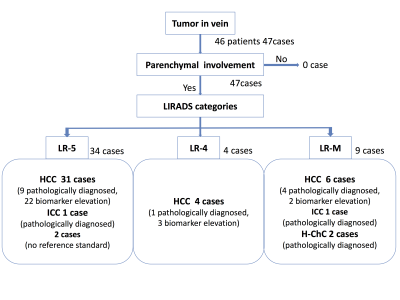
Saya Igarashi, Adrija Mamidipalli, Carolina Constantino, Atsushi Higaki, Mohanad Alhumayed, Jonathan Hooker, Chul Park, Claude Sirlin
The purpose of this study is to determine in cirrhotic patients the proportion of MRI-diagnosed TIV cases with parenchymal masses, the proportion of cases due to HCC or non-HCC malignancy, and whether assessment of the parenchymal mass allows differentiation of the malignancy type. All TIV cases had parenchymal masses. Using a composite reference standard and excluding tumors with no reference standard, the underlying malignancy was HCC in 91% (41/45), ICC in 4% (2/45), and H-ChC in 4% (2/45). LI-RADS categorization of the parenchymal mass may help identify patients in whom TIV is not due to HCC. In particular, patients with TIV and LR-M parenchymal masses may need biopsy to exclude non-HCC malignancy.
|
|
Body Imaging: GU (Non-Prostate) & Female Pelvis (Including Placenta)
Electronic Poster
Body: Breast, Chest, Abdomen, Pelvis
Wednesday, 20 June 2018
| Exhibition Hall |
09:15 - 10:15 |
| |
|
Computer # |
|
4676.
 |
49 |
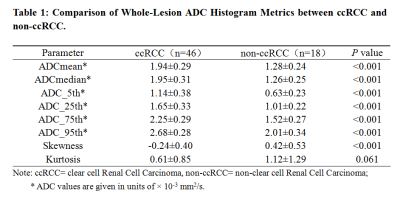
Small (< 4 cm) Renal Masses:Differentiation of clear cell Renal Cell Carcinoma from non-clear cell Renal Cell Carcinoma Using Whole Tumor ADC Histogram Analysis at r-Fov DWI
Did Not Present
Haojie Li
The combination of r-FOV DWI and the whole-lesion histogram analysis method may help in the interpretation of DWI of small renal masses and determine the optimal ADC parameter for quantitative assessment. The 75th percentile ADC value was more reliable than other histogram parameter values in distinguishing clear cell from non-clear cell RCCs with high sensitivity and specificity, potentially improving the accuracy of pretreatment diagnosis and selection of clinical therapy.
|
|
4677.
 |
50 |
Utility of 3D histogram analysis of pharmacokinetics parameters using DCE-MRI for differentiating renal clear cell carcinomas from renal harmatomas
Did Not Present
Yanping Miao, Yang Gao, Peng Cao, Lizhi Xie
The aim of this study was to assess if the histogram analysis of DCE-MRIphamocokinetics parameters (Ktrans)can differentiate renal tumors: renal clear cell carcinomas (RCCs) and renal harmatoma with minimal fat. Based on an 3D entire-tumour measurement, the following histogram parameters of Ktrans were derived from histogram analysis, skewness, Energy, Entropy, Uniformity, quartile5, quartile50, Frequency size and kurtosis respectively. We concluded that frequency size was the most significant parameter for predicting renal clear cell carcinoma by analyzing these data,the other parameters had no diagnostic performance.
|
|
4678.
 |
51 |
 The Diagnostic Accuracy of MR Imaging for Acute Pyelonephritis The Diagnostic Accuracy of MR Imaging for Acute Pyelonephritis
Amarpreet Bhowra, Iva Petkovska, Diego Martin, Bobby Kalb
MRI may offer a valuable alternative imaging method to diagnosing acute pyelonephritis without exposing patients to ionizing radiation or iodinated CT contrast. Our retrospective study evaluates the accuracy of 4 characteristic MRI findings in diagnosing acute pyelonephritis: (1) T2 hyperintense perinephric edema, (2) loss of corticomedullary differentiation on T2 images, (3) striated nephrogram on contrast-enhanced images, and (4) parenchymal restricted diffusion. Analysis of 108 MRI exams demonstrated that each of the 4 MRI findings was a significant predictor of pyelonephritis. Furthermore, assessing all 4 findings together provided a greater improvement in diagnostic accuracy when compared to any individual finding alone.
|
|
4679.
 |
52 |
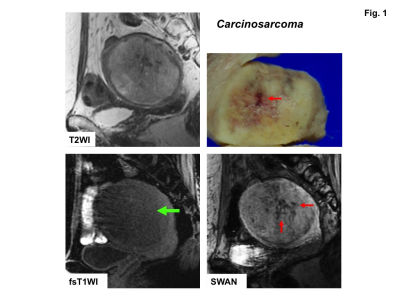
 Clinical utility of susceptibility-weighted MR sequence (SWAN) for the evaluation of uterine sarcomas Clinical utility of susceptibility-weighted MR sequence (SWAN) for the evaluation of uterine sarcomas
Mayumi Takeuchi, Kenji Matsuzaki, Masafumi Harada
Intra-tumoral hemorrhagic necrosis is one of the characteristic pathological finding of uterine sarcomas. High intensity hemorrhagic foci on T1WI may be suggestive finding, however, the prevalence is not high possibly because only methemoglobin could be detected. Signal voids on SWAN may reflect all phases of hemorrhage, especially both deoxyhemoglobin and hemosiderin and could be useful for the diagnosis. Surgically proven ten sarcomas and 22 benign leiomyomas were retrospectively evaluated. High intensity foci on T1WI were detected in four sarcomas (40%) and in none of leiomyomas, whereas signal voids on SWAN were detected in all sarcomas and in one leiomyoma (5%).
|
|
4680.
 |
53 |
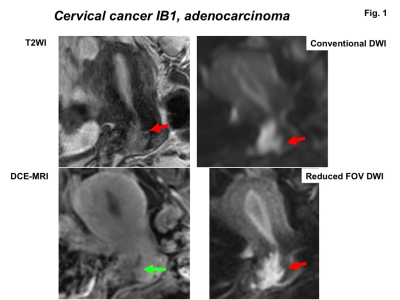
 Clinical feasibility of reduced field-of-view diffusion-weighted imaging for assessing the local extent of cervical cancer Clinical feasibility of reduced field-of-view diffusion-weighted imaging for assessing the local extent of cervical cancer
Mayumi Takeuchi, Kenji Matsuzaki, Masafumi Harada
The diagnostic performance of reduced FOV DWI (rFOV-DWI) for assessing the local extent of surgically proven 24 cervical cancers was evaluated. The delineation of tumor margin on rFOV-DWI was assessed, and invasion to the vagina and parametrium evaluated on rFOV-DWI was compared with the histologically confirmed tumor extent. rFOV-DWI delineated the tumor margins better than T2WI and 3D DCE-MRI with statistically significance. Parametrial invasion and vaginal invasion as documented by rFOV-DWI agreed with the histopathological findings in 100% and 95% of cases, respectively.
|
|
4681.
 |
54 |
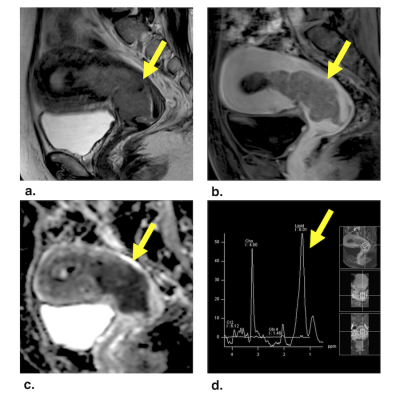
 Developing and validating a multivariable prediction model to improve the diagnostic accuracy in determination of cervical vs. endometrial origin of uterine adenocarcinomas: A prospective MR study combining diffusion-weighted imaging and spectroscopy Developing and validating a multivariable prediction model to improve the diagnostic accuracy in determination of cervical vs. endometrial origin of uterine adenocarcinomas: A prospective MR study combining diffusion-weighted imaging and spectroscopy
Gigin Lin, Yu-Chun Lin, Shang-Yueh Tsai, Yu-Ting Huang, Chyong-Huey Lai
We developed and validated an MDS score based on integrated morphological, volumetric DW MR imaging and spectroscopy which has incremental values and may be a useful clinical biomarker in distinguishing adenocarcinomas of cervical or endometrial origin.
|
|
4682.
 |
55 |
 MR neurography of the female pelvis: mapping somatic and autonomic nerves and plexi MR neurography of the female pelvis: mapping somatic and autonomic nerves and plexi
Katja De Paepe, David Higgins, Iain Ball, Veronica Morgan, Nandita DeSouza
The visualization of somatic and autonomic female pelvic nerves using a modified NerveVIEW protocol was assessed in volunteers (n=5) and cervical cancer patients (n=7) by 2 independent observers. Image quality (as assessed by visualization of the tibial and fibular components of the sciatic nerve) was high in 75% of cases. 83% of pudendal, superior and inferior hypogastric nerves were well seen by observer1 and 72% by observer2. The superior hypogastric plexus (SHP) was more difficult to identify routinely. Neurography of the female pelvis allowed for confident identification of autonomic and somatic nerve plexi and has potential for pre-surgical planning.
|
|
4683.
 |
56 |
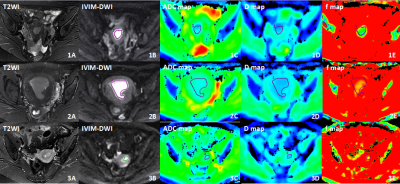
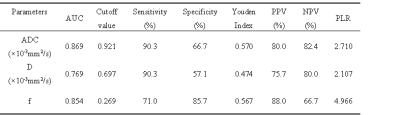
 Intravoxel incoherent motion diffusion imaging for grading endometrial cancer Intravoxel incoherent motion diffusion imaging for grading endometrial cancer
Qi Zhang, Xiaoduo Yu, Han Ouyang, Lizhi Xie
Accurate grading of endometrial cancer (EC) is invaluable owing to its relationship with the aggressiveness, prognosis, recurrence as well as its impact on treatment stratification. The differentiation of tumor correlates with the tumor density, the nuclear-to-cytoplasm ratio and microcirculation, which can be quantitatively assessed by using ADC and IVIM parameters (such as D, D* and f). The ADC, D and f values showed good or fair inverse correlation with histological grade. Therefore, IVIM DWI is a valuable supplement to predict histological grade of EC preoperatively which could contribute to treatment planning and prognosis evaluation.
|
|
4684.
 |
57 |
 Feasibility of Intravoxel Incoherent Motion (IVIM) Magnetic Resonance Imaging in Distinguishing Adenocarcinoma Originated from Uterine Corpus or Cervix Feasibility of Intravoxel Incoherent Motion (IVIM) Magnetic Resonance Imaging in Distinguishing Adenocarcinoma Originated from Uterine Corpus or Cervix
Qi Zhang, Xiaoduo Yu, Han Ouyang, Lizhi Xie
It is critical to distinguish adenocarcinoma arising from uterine corpus or cervix due to their different treatment methods and prognosis. However, it is hard to make a definite diagnosis based on MRI morphological characteristics, clinical examination., even the biopsy in some cases. The tumor biological information can be quantitatively evaluated by ADC and IVIM parameters(such as D, D* and f). Our study showed that ADC, D and f were significantly lower in the endometrial adenocarcinoma than the cervical adenocancinoma. IVIM parameters are promising biomarkers in predicting tumor origin of the uterine adenocarcinoma which contribute to treatment planning and prognosis evaluation.
|
|
4685.
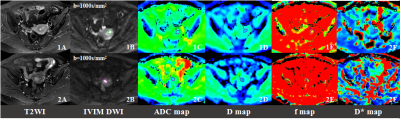 |
58 |
 Application of Intravoxel incoherent motion diffusion-weighted imaging in the assessment of local aggressiveness of endometrial cancer Application of Intravoxel incoherent motion diffusion-weighted imaging in the assessment of local aggressiveness of endometrial cancer
Qi Zhang, Xiaoduo Yu, Han Ouyang, Dandan Zheng
Local aggressiveness of endometrial cancer (EC) including the quantification of myometrial invasion, the exclusion of cervical stromal infiltration, lymphovascular space invasion (LVSI), etc, are closely related to EC risk classification, development, prognosis and surgical procedures. The ADC and IVIM-derived parameters can quantitatively assess tumor microstructure which is correlated to tumor development and aggressiveness. Our results showed that ADC and some of IVIM parameters demonstrated good diagnostic performance in the identification of deep myometrial invasion, cervical stromal infiltration and LVSI. IVIM DWI could provide valuable information about local aggressiveness of EC preoperatively which contribute to clinical decision-making and prognosis prediction.
|
|
4686.
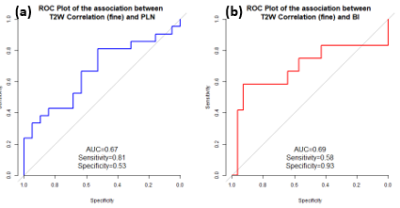 |
59 |
 Texture analysis of multiparametric MRI: interobserver variability of texture features and associations with nodal status. Texture analysis of multiparametric MRI: interobserver variability of texture features and associations with nodal status.
Jose Perucho, Elaine Lee, Richard Du, Varut Vardhanabhuti, Queenie Chan
Texture analysis of pre-treatment multiparametric MRI (mpMRI) consisting of diffusion-weighted MRI (DWI) and T2-weighted (T2W) texture features could be a promising and reproducible quantitative approach in assessing tumor heterogeneity in cervical cancer. We retrospectively studied forty treatment-naïve patients who had mpMRI examinations. We observed that around 30% of texture features had low interobserver variability, and that most of these features were from the Gray-Level Co-occurrence Matrix (GLCM) and Gray-Level Run Length Matrix (GLRLM). Furthermore, T2W features had moderate associations with pelvic lymph node (PLN) status.
|
|
4687.
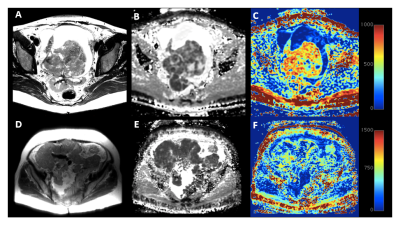 |
60 |
 Diffusion kurtosis imaging for the diagnosis and prediction of response to treatment in high grade serous ovarian cancer Diffusion kurtosis imaging for the diagnosis and prediction of response to treatment in high grade serous ovarian cancer
Surrin Deen, Andrew Priest, Mary McLean, Andrew Gill, Helena Earl, Christine Parkinson, Sarah Smith, Robin Crawford, John Latimer, Peter Baldwin, Helen Addley, Susan Freeman, Charlotte Hodgkin, Ilse Patterson, Mercedes Jimenez-Linan , James Brenton, Ferdia Gallagher
Diagnosis of high grade serous ovarian cancer (HGSOC) requires a biopsy which is both invasive and does not reflect the heterogeneity of the disease. Diffusion kurtosis imaging (DKI) was performed on 23 treatment naïve ovarian cancer patients. Both mean Dapp (apparent diffusion) and mean Kapp (apparent kurtosis) were found to be significantly different in HGSOC compared to other types of epithelial cancer. Kapp was also significantly greater in the patients who went on to respond to chemotherapy treatment compared to non-responders. DKI may therefore aid in identifying HGSOC and in the selection of the best treatment for individual patients.
|
|
4688.
 |
61 |
Combining 2d RF excitation with multishot acquisition for reduced distortion imaging of the female pelvis.
Did Not Present
Arnaud Guidon, Valentina Taviani, Holly Blahnik, Ann Shimakawa, Maggie Fung, Nan-Kuei Chen, Ersin Bayram
The combination of two-dimensional RF excitation with echo planar imaging has shown to be a useful technique for diffusion-weighted imaging of small anatomical features with high-resolution, such as in the pelvis or pancreas. However, compared to standard single shot dw-epi, the trade-off between resolution and matrix size becomes disadvantageous as the field of view increases. We propose to combine 2d RF excitation with multishot echo planar acquisition to enable high-resolution imaging with reduced distortion over larger FOV and present preliminary results obtained in the female pelvis.
|
|
4689.
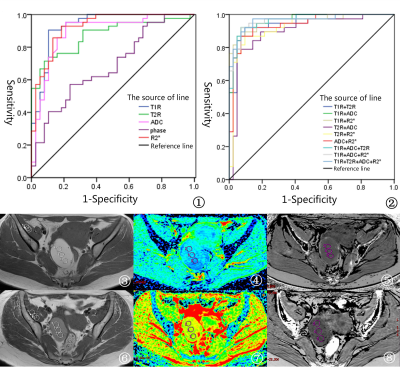 |
62 |
 To explore the diagnostic value of Multi-parameter MRI in ovarian endometriosis To explore the diagnostic value of Multi-parameter MRI in ovarian endometriosis
Ye Li, Ailian Liu, Qingwei Song, Lizhi Xie
Endometriosis is a disease characterized by the invasion of active endometrial glands and stroma into any location other than the endometrium. Clinical symptoms of ovarian endometriosis include abdominal pain, irregular menstruation, abnormal vaginal bleeding, and a tendency to malignant transformation. In this study, T1WI, T2WI, diffusion weighted imaging (DWI) and enhanced T2 star weighted angiography (ESWAN) MR measurements were performed to evaluate the feasibility of them in diagnosing ovarian endometriosis cysts, and optimize the combination of the quantitative parameters of the above MRI sequences.
|
|
4690.
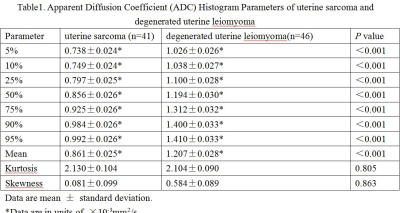 |
63 |
Utility of histogram analysis of apparent diffusion coefficient maps in differential diagnosis of uterine sarcoma and degenerated uterine leiomyoma
Did Not Present
Mengna Huang, Xuemei Gao
Histogram analysis of ADC values could provide more useful information than the mean ADC values and it has been proved to be valuable to evaluate tumor heterogeneity. We analyzed histogram features of ADC maps of uterine sarcoma and degenerated uterine leiomyoma. From our study, histogram analysis of ADC values has a high diagnostic efficiency in differential diagnosis of uterine sarcoma and degenerated uterine leiomyoma.
|
|
4691.
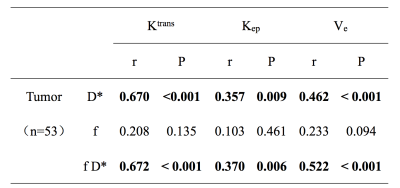 |
64 |
Investigation of correlation between IVIM and DCE-MRI on uterine cervical carcinoma
Video Permission Withheld
Xiaoduo Yu, Meng Lin, Yue Kong, Lizhi xie
Perfusion was of great importance to access tumor properties. In this study, the potential correlations of perfusion parameters derived from IVIM (D*, f, and f D*) and DCE-MRI (Ktrans, Kep and Ve) for uterine cervical carcinoma (UCC) were investigated and were compared between pathological types. D* and f D* were positively correlated with Ktrans, Kep and Ve, respectively. Adenocarcinoma had higher f, Ktrans and Kep values than those of squamous cell carcinoma. Therefore, IVIM, as a non-invasive method, has potential to replace DCE-MRI to accurately access tumor perfusion properties, especially when perfusion differs among different pathological types of UCC.
|
|
4692.
 |
65 |
 Evaluating Female Pelvic Pain with DISCO MRI: Pilot study in Pelvic Congestion and Uterine Fibroids Evaluating Female Pelvic Pain with DISCO MRI: Pilot study in Pelvic Congestion and Uterine Fibroids
Rebecca Rakow-Penner, Adrija Mamidipalli, Albert Hsiao
Pelvic congestion and uterine fibroids are two common causes of female pelvic pain that can be treated with image guided vascular embolization and often evaluated with MRI prior to treatment. Vascular as well as anatomic imaging are important in evaluation and treatment planning for these two disease processes. Differential sampling with Cartesian ordering (DISCO)-MRI is a technique that allows for both high temporal and spatial resolution. This abstract demonstrates the utility of DISCO-MRI in evaluation and treatment planning for pelvic congestion and uterine fibroids.
|
|
4693.
 |
66 |
 Characterization of uterine artery geometry in normal pregnancy with time-of-flight angiography Characterization of uterine artery geometry in normal pregnancy with time-of-flight angiography
Eileen Hwuang, M. Dylan Tisdall, Nadav Schwartz, John Detre, Walter Witschey
While measuring uterine artery (UtA) impedance is commonly used to assess for risk of preeclampsia and intrauterine growth restriction, little is understood about the remodeling process during gestation. An improved understanding of geometrical changes can lead to predictive biomarkers of adverse pregnancies. Here we present a method of measuring path length and curvature of the tortuous UtAs by segmentation and centerline extraction of time-of-flight MR angiography. We show in 8 pregnant subjects in the 2nd and 3rd trimester that this technique is feasible for investigating longitudinal trends of UtA remodeling and cases of maladaptation.
|
|
4694.
 |
67 |
 Background-suppressed pulsed arterial spin labeling of placental perfusion at 1.5T Background-suppressed pulsed arterial spin labeling of placental perfusion at 1.5T
Eileen Hwuang, Zhengjun Li, Marta Vidorreta, Sudipto Dolui, M. Dylan Tisdall, Nadav Schwartz, Walter Witschey, John Detre
We present the feasibility of measuring and quantifying placental blood flow in healthy pregnant subjects at 1.5T. We used a Flow Alternating Inverson Recovery (FAIR) scheme with background suppression. Using statistical parametric mapping, discrete regions of labeling were observed, likely corresponding to individual spiral artery distributions.
|
|
4695.
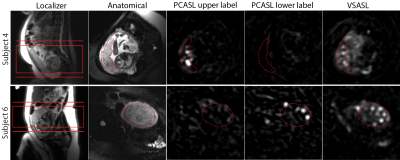 |
68 |
 Placental perfusion imaging using velocity-selective arterial spin labeling Placental perfusion imaging using velocity-selective arterial spin labeling
Zungho Zun, Catherine Limperopoulos
Recently placental perfusion imaging using velocity-selective arterial spin labeling (VSASL) was applied in pregnancies complicated by fetal heart disease. Here we demonstrate the feasibility of performing VSASL in the human placenta and provide supporting evidence that is needed for validation of placental VSASL. In our results, placental VSASL generated significantly higher ASL signal than pseudocontinuous ASL, showed high reproducibility, and demonstrated inflow-dependence. This study lays the groundwork for future investigation of placental perfusion imaging in pregnancies complicated by placental insufficiency.
|
|
4696.
 |
69 |
 Free-breathing 3D quantitative susceptibility and T2* mapping of the human placenta: Initial experience in healthy pregnancies Free-breathing 3D quantitative susceptibility and T2* mapping of the human placenta: Initial experience in healthy pregnancies
Zungho Zun, Catherine Limperopoulos
Quantitative susceptibility mapping (QSM) is an emerging imaging technique for measuring magnetic susceptibility of tissue, and may have the potential for depicting hypoxia, hemorrhage, and calcification of the placenta. In this study we demonstrate simultaneous acquisition for QSM and T2* mapping of the human placenta using a 3D multi-echo gradient echo sequence with maternal free breathing. Compared to T2-weighted images, both QSM and T2* maps demonstrate more lobulated contrast in the placenta with lower susceptibility and higher T2* values within the lobules. This is the first study to investigate QSM of the human placenta in vivo.
|
|
4697.
 |
70 |
 Textural analysis of the morbidly adherent placenta (MAP) from MR acquisitions Textural analysis of the morbidly adherent placenta (MAP) from MR acquisitions
Quyen Do, Matthew Lewis, Yin Xi, Ananth Madhuranthakam, Timothy Ng, Robert Lenkinski, Diane Twickler
The morbidly adherent placenta (MAP) is a significant obstetric condition and hysterectomy is often the outcome for severe cases. We applied region of interest (ROI)-based texture analysis on retrospective placental MR images in women with history of placenta previa and previous cesarean deliveries. Our goal was to evaluate the textural characteristics of placental tissue in proximity to previous surgical scars and compare findings to surgical outcomes. Several significant Haralick texture features were seen in placental ROI’s near previous cesarean scars in those women who underwent hysterectomy.
|
|
4698.
 |
71 |
 Evaluation of Uterine and Placenta Motion throughout Early Gestation Evaluation of Uterine and Placenta Motion throughout Early Gestation
Thomas Martin, Xinzhou Li, Irish Del Rosario, Teresa Chanlaw, Tess Armstrong, Sherin Devaskar, Carla Janzen, Rinat Masamed, Holden Wu, Kyunghyun Sung
When imaging the uterus and placenta, in pregnant patients, there are potential uterine contractions that compress the superior region of the uterus and can cause significant motion in the uterus and placenta. It is not well studied how much uterine contraction and other motion need to be accounted for during MRI scans in early gestation. In this study we observed and characterized uterine contractions and other bulk motion in pregnant women (gestational age 14-22weeks) using an image based template-matching program. This study can further help develop proper scanning protocols for MRI studies with pregnant patients to avoid potential motion artifacts.
|
|
4699.
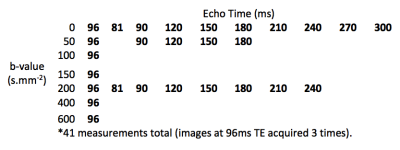 |
72 |
 Placental Insufficiency Investigated with Multi-compartment Placental MRI Placental Insufficiency Investigated with Multi-compartment Placental MRI
Andrew Melbourne, Rosalind Aughwane, David Owen, Magdalena Sokolska, Alan Bainbridge, David Atkinson, Jan Deprest, Giles Kendall, Tom Vercauteren, Anna David, Sebastien Ourselin
Efficient exchange of oxygen and nutrients across the placenta is vital for a normally grown fetus. When remodelling of maternal arteries does not occur in early pregnancy the result is placental insufficiency, and fetal growth restriction. Previous studies have shown differences in T2 relaxometry and IVIM between normal and FGR placentae. Here we use a combined T2R and IVIM signal model that separates signals from fetal and maternal blood pools over the whole placental volume. We show difference in T2R, ADC, and maternal perfusion fraction, findings in keeping with previous literature and the pathophysiology of placental insufficiency.
|
|
Pancreas/GI
Electronic Poster
Body: Breast, Chest, Abdomen, Pelvis
Wednesday, 20 June 2018
| Exhibition Hall |
09:15 - 10:15 |
| |
|
Computer # |
|
4700.
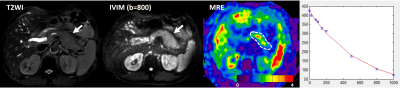 |
73 |
 Magnetic Resonance Elastography and model diffusion-weighted imaging of Autoimmune Pancreatitis: A Preliminary Study Magnetic Resonance Elastography and model diffusion-weighted imaging of Autoimmune Pancreatitis: A Preliminary Study
Yu Shi, Lizhuo Cang, Xiaoqi Wang, Yanqing Liu, Min Wang, Ruoyun Ji, Qiyong Guo
Autoimmune pancreatitis (AIP) is a benign process characterized by lymphoplasmacytic infiltration and massive fibrosis.
|
|
4701.
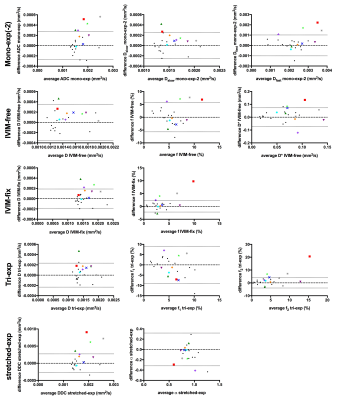 |
74 |
 Comparison of six diffusion-weighted imaging models for the detection of treatment effects in pancreatic cancer patients Comparison of six diffusion-weighted imaging models for the detection of treatment effects in pancreatic cancer patients
Oliver Gurney-Champion, Remy Klaassen, Marc Engelbrecht, Jaap Stoker, Johanna Wilmink, Marc Besselink, Arjan Bel, Geertjan van Tienhoven, Hanneke van Laarhoven, Aart Nederveen
We tested the performance of six diffusion models for detecting effects from treatment in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. All models, including the mono-exponential fit, were able to detect parameter changes after treatment in individual patients for five out of nine patients. For multi-parametric models treatment affected different parameters for different patients, allowing potentially discriminating between types of effects. The pseudo diffusion coefficient values from the intravoxel incoherent motion model were in line with instant dephasing due to bulk motion rather than capillary perfusion, limiting its clinical interpretation. Using two mono-exponential fits, one at low and one at high b-values, was preferred.
|
|
4702.
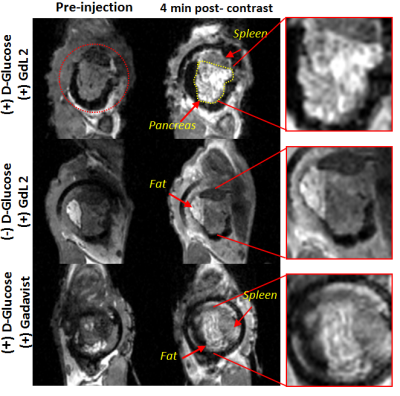 |
75 |
 Imaging beta-cell function in the mouse pancreas with an implanted imaging window by MRI Imaging beta-cell function in the mouse pancreas with an implanted imaging window by MRI
Veronica Clavijo Jordan, Xiaodong Wen, Filip Bochner, Su-Tang Lo, Andre Martins, Sara Chirayil, Michal Neeman, A. Dean Sherry
We have successfully implanted an imaging window onto the mouse abdomen to locate and hold the tail of the pancreas in place. By use of this MR-compatible window we were able to show with MRI and a Gd-based zinc sensor the non-uniform regional secretion of zinc and insulin as a response to glucose in the tail of the mouse pancreas. This surgical technique and imaging technology could be used to successfully monitor beta-cell function longitudinally through the development of the various diseases of the endocrine pancreas with MRI.
|
|
4703.
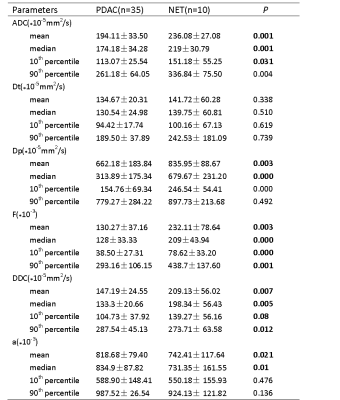 |
76 |
 Diffirentiation Between Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma and Neuroendocrine Tumors :Using Whole-tumor Histogram Analysis of Non-Gaussian Distribution DWI Models Diffirentiation Between Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma and Neuroendocrine Tumors :Using Whole-tumor Histogram Analysis of Non-Gaussian Distribution DWI Models
Jiali Li, Daoyu Hu, Zhen Li
The purpose of this paper is to explore a most helpful DWI mathematical models in differenting pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma and neuroendocrine tumors. All parameters of three models(monoexponential, biexponential, and stretched exponential) were obtained from a histogram analysis based on the entire tumor. By comparing diagnostic performance, the significant parameters that have the highest diagnostic performance were selected to the most helpful parameters. The results of this study showed that IVIM-DWI model may be the most suitable for differenting pancreatic tumors.
|
|
4704.
 |
77 |
Treatment effect of autoimmune pancreatitis: evaluation with T1 mapping
Did Not Present
Liang Zhu, Hua-dan Xue, Zhao-yong Sun, Marcel Nickel, Tianyi Qian, Zheng-yu Jin
This prospective study aims to evaluate the T1 relaxation time of autoimmune pancreatitis (AIP) in the native state and after corticosteroid treatment (CST). Thirty-four patients with AIP and twenty control subjects received pancreatic MR including T1 mapping. All AIP patients had T1 mapping data before and after CST. It turned out that the inflamed pancreatic parenchyma had significantly elongated T1 relaxation time, and after 4-12 weeks of CST, the T1 relaxation time shortened significantly towards normalization, in keeping with the serum biomarkers of disease activity. Therefore MR T1 mapping is a noninvasive, quantitative method to monitor AIP treatment effect.
|
|
4705.
|
78 |
Intravoxel Incoherent Motion Diffusion-weighted MR Imaging of Solid Pancreatic Masses: reproducibility and usefulness for characterization
Did Not Present
Riccardo De Robertis, Nicolò Cardobi, Robert Grimm, Berthold Kiefer, Alto Stemmer, Marco Zanirato, Mirko D'Onofrio
Overall intraobserver agreement for ADC- and IVIM-derived parameters was excellent. Perfusion-related IVIM-derived parameters are the most reliable for differentiation between pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma and neuroendocrine neoplasms. No significant differences were found between ADC- and IVIM-derived parameters of mass-forming pancreatitis and carcinoma.
|
|
4706.
 |
79 |
Optimal combinations of b-values in computed DWI for pancreatic cancer detection
Video Permission Withheld
Koji Tokunaga, Shigeki Arizono, Hiroyoshi Isoda, Hironori Shimizu, Koji Fujimoto, Kaori Togashi
There has been no previous report on the optimal combinations of b-values to obtain computed DWI (cDWI) with b-values above 1000 s/mm2 to evaluate pancreatic cancer. This retrospective study involved 30 pancreatic cancer patients with tumor associated pancreatitis. We aimed to evaluate the optimal combination of b-values to obtain cDWI with b-value of 1500 s/mm2 from the combinations of b-values between 0 and 500 s/mm2 (cDWI0-500), 0 and 1000 s/mm2 (cDWI0-1000), 500 and 1000 s/mm2 (cDWI500-1000), and all b-values (cDWIALL). Only cDWI0-1000 demonstrated statistically higher tumor detectability compared to measured DWI, while image quality was preserved in cDWI0-1000 and cDWIALL.
|
|
4707.
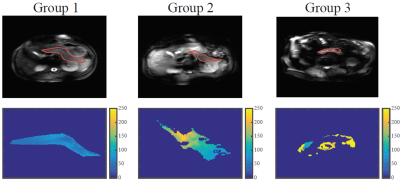 |
80 |
 Age dependency of T1 and T2 values in healthy pancreas measured at 7 Tesla Age dependency of T1 and T2 values in healthy pancreas measured at 7 Tesla
Mariska Damen, Maarten van Leeuwen, Peter Luijten, Andrew Webb, Dennis Klomp, Catalina Arteaga de Castro
Age dependency of T1 and T2 times of the healthy pancreas at 7 Tesla with a multi-transmit system was investigated for MRI protocol optimization of the pancreas. Three age groups were measured (21 -25 yo, 26 -39 yo and 40 -72 yo). Measurements resulted in average T2 times of 52 ms, 97 ms and 127 ms for the 3 different age groups respectively, revealing an age dependency of the T2 relaxation times. Average T1 times were 856 ms, 899 ms and 858 ms for each age group respectively. No age dependency was observed for the T1 relaxation times.
|
|
4708.
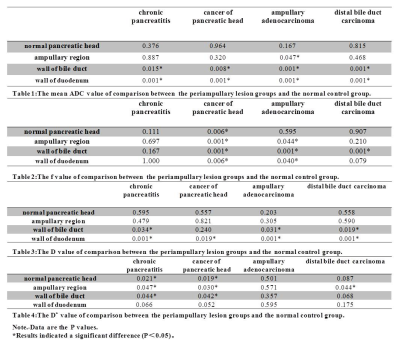 |
81 |
High-Resolution Intravoxel Incoherent Motion (IVIM) diffusion-weighted MR imaging for the characterization of periampullary lesions
Did Not Present
Haixia Yu, Chuangliang Chen, Dapeng Shi, Robert Grimm, Tianyi Qian
This study aimed to investigate the clinical diagnostic utility of ZOOMit-DWI-based IVIM imaging technology[1,2] for periampullary lesions. Forty-one patients, comprising cancer of the pancreatic head (n = 6), chronic pancreatitis (n = 9), ampullary adenocarcinoma (n = 9), and distal bile duct carcinoma (n = 17) and 28 healthy volunteers were enrolled. Our results showed that the perfusion fraction (f) of the IVIM-derived parameter has the potential to distinguish between cancer of the pancreatic head, other lesions, and normal tissue in the periampullary regions by using the zoomed DW imaging, which has the capacity to overcome some of the limitations of conventional MRI of the pancreas.
|
|
4709.
 |
82 |
 Evaluation of Extracellular Volume (ECV) Fraction of the Normal Pancreas and Correlation with Biophysical Parameters Evaluation of Extracellular Volume (ECV) Fraction of the Normal Pancreas and Correlation with Biophysical Parameters
Temel Tirkes, Kumaresan Sandrasegaran, Eugene Ceppa, Chen Lin
ECV fraction can be a very useful imaging tool for non-invasive evaluation of solid organ pathologies and is probably underutilized in abdominal imaging. There are potentially several clinical applications of ECV in the abdomen such as evaluation of chronic pancreatitis or chronic liver disease. In this study, we computed the ECV fraction of the pancreas in 60 healthy cohorts and determined that ECV fraction of the normal pancreas is 0.26 (± 0.08). ECV fraction is not influenced by pancreatic steatosis or patient’s gender, however gradually increases with age.
|
|
4710.
 |
83 |
Value of whole-tumor histogram-based texture analysis of baseline ADC map in prediction of tumor response to neoadjuvant chemoradiotherapy in locally advanced rectal cancer.
Did Not Present
lanqing Yang, bing Wu
There has been increasing interest in quantitative methods to excavate more information than traditional descriptive features, facilitated by the availability of texture analysis software platforms. By doing whole-tumor histogram-based texture analysis on pre-treatment ADC map, histogram parameters reflecting the pixel distribution of ROIs were derived. Our study found that LARC that achieved pCR after NCRT appeared less heterogeneous on ADC map and had lower high percentile pre-treatment ADC values. Whole-tumor histogram parameters of pre-treatment ADC map were feasible to predict pCR in LARC, including the absolute value of relative deviation, frequency size, quantile 75%, 90%, and 95% of ADC value histogram.
|
|
4711.
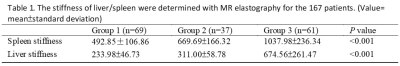 |
84 |
 Splenic MR Elastography in Prediction of Esophageal Varices Grading Splenic MR Elastography in Prediction of Esophageal Varices Grading
Chen-Te Chou, Ran-Chou Chen
To investigate the relationship between splenic MR elastography (MRE) and esophageal varices (EV). 167 patients underwent endoscopy and abdominal MR examination within 3-months interval were enrolled. MRE was performed with passive driver on right and left chest wall separately. The mean stiffness value of liver and spleen was determined. A good correlation between splenic stiffness and EV, but no correlation for liver stiffness was found. Our results demonstrated that spleen stiffness measured by MRE was significant correlated with EV grading. With 9.77 kPa spleen stiffness might be helpful in predicting presence of EV for patients with chronic liver disease.
|
 |
4712.
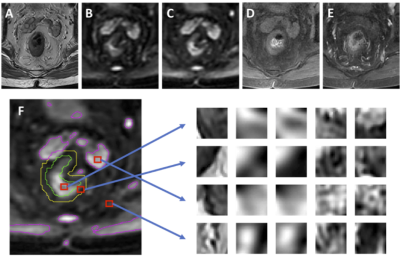 |
85 |
 Automated Localization and Segmentation of Locally-Advanced Rectal Cancer Based on T2, DWI and DCE Multi-Parametric MRI Using Deep Learning Automated Localization and Segmentation of Locally-Advanced Rectal Cancer Based on T2, DWI and DCE Multi-Parametric MRI Using Deep Learning
Yang Zhang, Liming Shi, Xiaonan Sun, Tianye Niu, Ning Yue, Peter Chang, Daniel Chow, Melissa Khy, Tiffany Kwong, Jeon-Hor Chen, Min-Ying Su, Ke Nie
A deep learning method using the convolutional neural network (CNN) was implemented to segment rectal cancer in 48 patients. Six sets of images (one T2, Two DWI, three DCE) were used as inputs. The Dice Similarity Coefficient (DSC) was used to evaluate results generated by the CNN algorithm compared to the manually outlined ground truth. When the search was done on the entire image the mean DSC was 0.64, and the errors were mainly from tissues outside the rectum. The rectum could be easily segmented, and when the search was confined within 1.5 times of rectal area, the DSC was improved to 0.75.
|
|
4713.
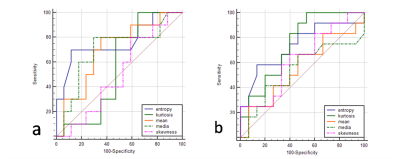 |
86 |
 Differentiation between Intestinal-type and Pancreatobiliary-type Periampullary Carcinoma and Prediction of Lymphatic Metastasis: Whole-Lesion Diffusion-Weighted Imaging Histogram Analysis Differentiation between Intestinal-type and Pancreatobiliary-type Periampullary Carcinoma and Prediction of Lymphatic Metastasis: Whole-Lesion Diffusion-Weighted Imaging Histogram Analysis
Jingyu Lu, Zhen Li, Daoyu Hu
Pancreatobiliary versus intestinal histologic type of differentiation is an independent prognostic factor in resected periampullary adenocarcinoma. To differentiate these two histologic type proactively before surgery, we tried to use whole-lesion histogram analysis of apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) derived from diffusion-weighted imaging . Entropy was significantly lower in pancreatobiliary-type periampullary carcinoma and achieved the best diagnostic performance. ADC value was relatively lower in pancreatobiliary-type. No significant difference was shown between lymph node metastasis positive and negative group. So we hypothesized that ADC histogram parameters might help to differentiate these two histologic type without the influence of lymph nodal involvement.
|
|
4714.
|
87 |
 Value of R2* for predicting the response of locally advanced rectal cancer to neoadjuvant chemoradiation therapy Value of R2* for predicting the response of locally advanced rectal cancer to neoadjuvant chemoradiation therapy
Hongliang Sun, Yanyan Xu, Queenie Chan, Wu Wang
Neoadjuvant chemoradiation therapy (CRT) followed by surgery has been established as the standard for locally advanced rectal cancer. The treatment response after CRT is normally evaluated by MRI. However, MRI morphology techniques suffer from limitations in the interpretation of fibrotic scar tissue and inflammation. Several studies have demonstrated that sensitivity to chemoradiotherapy is related to the oxygenation status of the tumor. It has been shown that the slight increase in T2* signals from paramagnetic deoxyhemoglobin can be used for reflecting the tumor oxygenation status. Therefore, R2*(=1/T2*) might have the potential to be a predictor of prognosis and treatment response for patients with locally advanced rectal cancer.
|
|
4715.
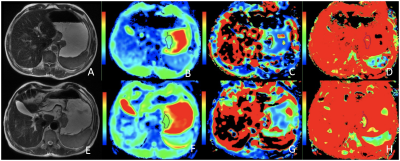 |
88 |
 Evaluating Response of Locally Advanced Gastric Adenocarcinoma to Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy using Intravoxel Incoherent Motion MRI: A Preliminary study Evaluating Response of Locally Advanced Gastric Adenocarcinoma to Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy using Intravoxel Incoherent Motion MRI: A Preliminary study
Yongjian Zhu, Liming Jiang, Ying Li, Lizhi Xie
Intravoxel incoherent motion (IVIM) diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging (DW-MRI) has been applied in research of different cancers, however its potential in gastric cancer has not been fully explored. In this study, we explored the value of IVIM parameters in evaluating the response to chemotherapy in gastric cancer. We found that the D and f values showed good diagnostic performance by differentiating responders from nonresponders, this could provide effective help for the choice of clinical treatment.
|
|
4716.
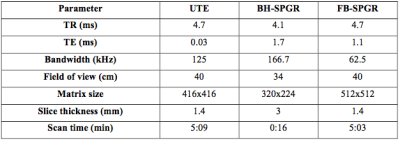 |
89 |
 Conical Ultrashort TE (UTE) MRI in the evaluation of pediatric acute appendicitis Conical Ultrashort TE (UTE) MRI in the evaluation of pediatric acute appendicitis
Zhibo Xiao, Albert Roh, Joseph Cheng, Shreyas Vasanawala, Andreas Loening
To reduce patient exposure to the ionizing radiation of CT, hospitals are increasing MRI usage in the evaluation of suspected acute appendicitis, particularly in the pediatric population. Our retrospective review of 84 pediatric patients assessed contrast-enhanced conical Ultrashort TE (UTE) of the pelvis. UTE demonstrated better qualitative Signal-to-Noise Ratio (SNR), fewer artifacts, and better overall image quality than both a 3D dual-echo SPoiled GRadient echo (SPGR) sequence and a free-breathing high-resolution 3D SPGR. Our study concluded that UTE is feasible in the evaluation of the pelvis for pediatric acute appendicitis.
|
|
4717.
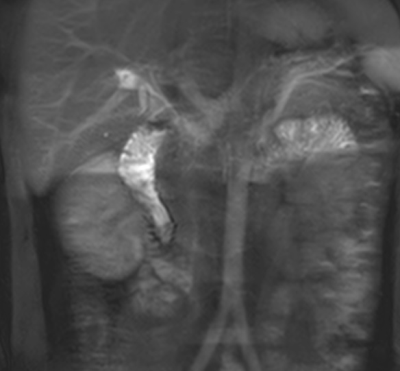 |
90 |
Direct visualization of physiological intestinal flow using unenhanced MR imaging with spin labeling
Video Permission Withheld
Jun Isogai, Mitsue Miyazaki, Kenji Yodo, Michitaka Suzuki, Takashi Yamada, Jun Kaneko
Assessment of motility and propagation of the small bowel has been reported using conventional contrast x-ray techniques with unavoidable ionizing radiation and recent MR imaging. However, MR enteroclysis and enterography require a discomforted nasoenteric intubation and an oral administration of large volumes of enteric contrast materials, respectively. Unenhanced MR imaging with a spin labeling technique provides direct visualization of physiological intestinal intraluminal flow related to bowel peristalsis.
|
|
4718.
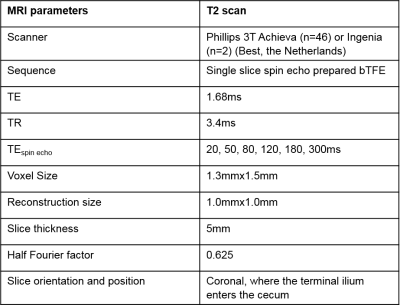 |
91 |
 Increased small bowel permeability is associated with significantly increased T2 measures of the small bowel wall. Increased small bowel permeability is associated with significantly increased T2 measures of the small bowel wall.
Hannah Williams, Robert Scott, Luca Marciani, Catherine Ortori, Guruprasad Aithal, Penny Gowland, Caroline Hoad
Available techniques to measure in-vivo bowel permeability are inadequate for stratifying patients to identify those at risk of complications. T2 weighted measurements in Crohn’s disease are sensitive markers of small bowel wall structural changes and could potentially be indicators of permeability. We have developed quantitative T2measures of the small bowel wall to characterize changes associated with increased permeability induced by indomethacin. We found a significant increase in quantitative measures of T2 of the small bowel wall associated with increased permeability provoked by indomethacin.
|
|
4719.
 |
92 |
 The Radiomic Signature as a Prognostic Biomarker for Locally Advanced Rectal Cancer The Radiomic Signature as a Prognostic Biomarker for Locally Advanced Rectal Cancer
Yuchen Zhang, Yankai Meng, Hongmei Zhang, Chunwu Zhou, Di Dong, Mengjie Fang, Yali Zang, Zhenyu Liu, Jie Tian, Di Dong, Di Dong, Di Dong
Radiomics uses a large number of medical imaging features and can demonstrate voxel-wise intratumor heterogeneity. We calculated the radiomic signature for each patient using a weighted linear combination of the radiomic features selected by machine learning methods. The study endpoint was DFS, defined as the interval between TME surgery and disease progression, which included tumor local recurrence, distant metastasis, or death, or the date of the last follow-up visit (censored). The association between the radiomic signature and DFS was explored. Then, the three models were built to estimate the DFS in patients.
|
|
4720.
|
93 |
 Rectal Cancer: Comparison of MRI Characteristics and Texture Analysis Between Different Tumor KRAS Mutation Status Rectal Cancer: Comparison of MRI Characteristics and Texture Analysis Between Different Tumor KRAS Mutation Status
Yanyan Xu, Hongliang Sun, Queenie Chan, Wu Wang
KRAS mutations are well known as predictive markers of resistance to epidermal growth factor receptor-targeted antibodies in rectal cancers. Approximately 30%-40% colorectal cancers are observed with KRAS mutation, and rectal cancer accounts for 30%-35% among CRC. The pre-operative neoadjuvant therapy including anti-EGFR chemotherapy demonstrated robust value is the current trend in the management of rectal cancer. Therefore, it is important to select suitable patients who would benefit from the aggressive multimodality approaches and tailor individual treatment to better combat disease. Currently, few data are available regarding the potential relationship between MRI characteristics and genetic biomarkers.
|
|
4721.
 |
94 |
 Rapid and noninvasive detection and dynamic quantification of gut bleeds with Magnetic Particle Imaging Rapid and noninvasive detection and dynamic quantification of gut bleeds with Magnetic Particle Imaging
Elaine Yu, Prashant Chandrasekharan, Ran Berzon, Xinyi Zhou, Zhi Wei Tay, R Ferguson, Amit Khandhar, Scott Kemp, Bo Zheng, Patrick Goodwill, Michael Wendland, Kannan Krishnan, Spencer Behr, Jonathan Carter, Steven Conolly
Magnetic Particle Imaging (MPI) is a novel, high-contrast, and quantitative imaging modality that directly detects superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticle (SPIO) tracers. These SPIOs have been previously used as a MRI contrast agent. However, with MRI SPIOs are limited by poor specificity and difficulty associated with quantifying the negative signal. Due to its direct detection, high sensitivity and positive contrast, MPI is uniquely poised as a clinically translatable platform for vascular imaging, including gastrointestinal (GI) bleed detection. Here we present in vivo GI bleed detection using long-circulating SPIOs as the vascular agent in a mouse model of Familial Adenomatous Polyposis.
|
|
4722.
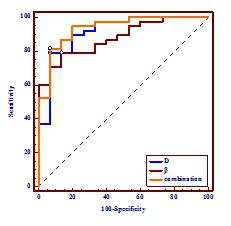 |
95 |
Diffusion-Weighted MR Imaging of rectal cancer with A Fractional Order Calculus Model
Did Not Present
Yanfen Cui, Zhizheng Zhuo, Xiaotang Yang
A novel non-Gaussian diffusion model based on fractional order calculus (FROC) were successfully applied to diffusion MRI of rectal cancer. Statistically significant differences in D and β values are observed between rectal cancer and villous adenoma (p < 0.001), indicating that individual or combined parameters from the FROC diffusion model may be useful as imaging biomarkers in predicting the biological properties of rectal cancer in clinical practice.
|
|
4723.
 |
96 |
MRI Texture Analysis in Predicting Treatment Response to Neoadjuvant Chemoradiotherapy in Rectal Cancer
Did Not Present
yankai meng, hongmei zhang, chunwu zhou
To evaluate the importance of MRI texture analysis in prediction and early assessment of treatment response before and early neoadjuvant chemoradiotherapy (nCRT) in patients with locally advanced rectal cancer (LARC). This retrospective study comprised of 59 patients. The tumoral texture parameters were compared between pre- and early nCRT. Area Under receiver operating characteristic (ROC) Curves [AUCs] were used to compare the diagnostic performance of statistically significant difference parameters and logistic regression analysis predicted probabilities for discriminating responders and nonresponders. Texture parameters as imaging biomarkers have the potential to prediction and early assessment of tumoral treatment response to neoadjuvant chemoradiotherapy in patients with LARC.
|
|
Hepatobiliary 2: Diffuse Liver Disease
Electronic Poster
Body: Breast, Chest, Abdomen, Pelvis
Wednesday, 20 June 2018
| Exhibition Hall |
09:15 - 10:15 |
| |
|
Computer # |
|
4724.
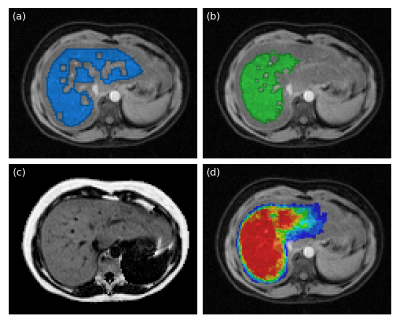 |
97 |
 Fully Automated Liver Fat Assessment using Multi-Atlas Segmentation Fully Automated Liver Fat Assessment using Multi-Atlas Segmentation
Joel Kullberg, Taro Langner, Filip Malmberg, Anders Hedström, Jonathan Andersson, Carl Sjöberg, Lars Lind, Håkan Ahlström
Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) has become the most common liver disease with an estimated global prevalence of 25%. Its link to metabolic, cardiovascular, and more severe forms of liver disease presents a major challenge for future healthcare. MRI allows accurate quantification of liver fat concentration. Since manual delineation of the liver is time-consuming, measurements are typically performed in small subjectively selected regions of interest which limits accuracy and precision. This work presents an automated method for liver fat assessment using multi-atlas segmentation. Evaluation with measurements using manual liver segmentation (n=306) demonstrates excellent agreement (R=1.000, difference -0.03%, p=0.001).
|
|
4725.
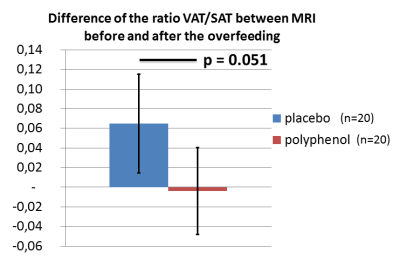 |
98 |
 Effect of polyphenols during a high-fat diet enhanced with chemical shift-encoded MRI Effect of polyphenols during a high-fat diet enhanced with chemical shift-encoded MRI
Angéline Nemeth, Hélène Ratiney, Benjamin Leporq, Kévin Seyssel, Bérénice Segrestin, Pierre-Jean Valette, Martine Laville, Olivier Beuf
In this study, 42 healthy male underwent a randomized, double blinded, parallel-group trial with either polyphenols or placebo during 31 days of high-carbohydrate and high-fat overfeeding. Changes in visceral, subcutaneous adipose tissue volumes and liver fat were measured using multi-gradient echo sequence. Visceral, subcutaneous adipose tissue volumes and liver fat increased significantly during overfeeding. The ratio VAT/SAT increased during overfeeding for the placebo group whereas this ratio slightly decreased for the polyphenol group.
|
|
4726.
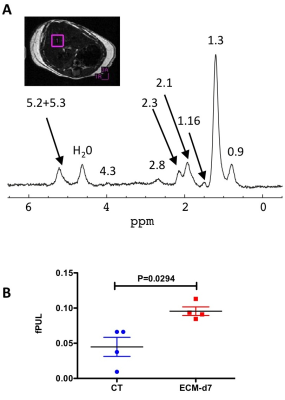 |
99 |
Assessment of liver dysfunction with 1H-MRS and relaxometry in a murine model of cerebral malaria
Video Permission Withheld
Teodora-Adriana PERLES-BARBACARU, Emilie PECCHI, Yann LE FUR, Alexandre VINTILA, Monique BERNARD, Angèle VIOLA
Cerebral malaria (CM) is the most lethal complication of Plasmodium infection and may be associated with multiple organ failure. We have investigated liver microstructure and metabolism in a widely-used murine model of CM induced with Plasmodium Berghei ANKA using in vivo anatomical MRI, relaxometry and localized proton spectroscopy at 11.75T. Our results show an increase in liver T2 value with CM progression. This increase is apparently linked to a reduction in tissue water content and to lipid remodeling. These alterations could be related to the clinical degradation occurring at the severe stage of the disease as well as to a direct effect of the parasite on the liver.
|
|
4727.
 |
100 |
Validation of gadoxetate dynamic contrast-enhanced MRI to assess liver function in rats with liver fibrosis: comparison with shear wave elastography and indocyanine green test
Video Permission Withheld
Jimi Huh, Su Jung Ham, Young Chul Cho, Seul-I Lee, Jisuk Park, Chul Woong Woo, Yoonseok Choi, Dong-Cheol Woo, Kyung Won Kim
Non-invasive imaging evaluation of the liver fibrosis and liver function has been gaining emphasis currently. In preclinical trial with animal liver fibrosis model, the gadoxetate DCE-MRI is quite feasible to evaluate histopathologic liver fibrosis and physiologic liver function in a non-invasive and repeatable manner. The best MRI index would be the iAUC-15, which is better than kPa on SWE.
|
|
4728.
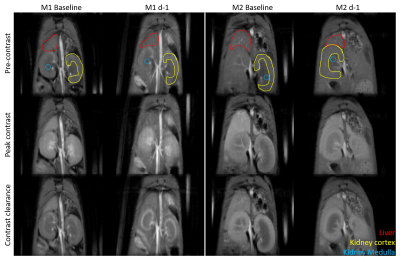 |
101 |
 Measuring hepatocyte transplant success using gadoxetate enhanced MRI Measuring hepatocyte transplant success using gadoxetate enhanced MRI
Christiane Mallett, Jeremy Hix, Kate Hammond, Alexander Wolf, Erik Shapiro
We used gadoxetate-enhanced MRI to monitor a mouse model of liver failure and hepatocyte transplantation.
|
|
4729.
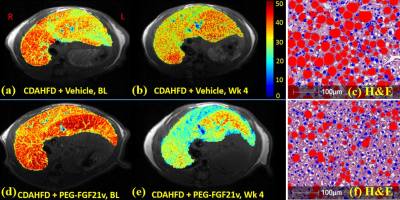 |
102 |
 PEG-FGF21 Variant Improves Hepatic Steatosis in a Mouse Model of NASH as Determined by Quantitative Water-fat MRI PEG-FGF21 Variant Improves Hepatic Steatosis in a Mouse Model of NASH as Determined by Quantitative Water-fat MRI
Haiying Tang, Matthew Fronheiser, Stephanie Boehm, Adrienne Pena, Shorts Andrea, Bradley Zinker, John Krupinski, Harold Malone, Patrick Chow, Edgar Charles, Shuyan Du, Wendy Hayes
Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) ranges from simple fatty liver to steatohepatitis (NASH) to cirrhosis. In the present study, we implemented a water-fat MRI using the gradient-reversal technique to quantify the hepatic proton density fat-fraction (PDFF), for assessment of hepatic steatosis in a diet-induced mouse model of NASH. We compared the quantitative water-fat MRI technique with conventional Dixon method and single-voxel MR spectroscopy (MRS), and correlated the MRI-PDFF with histology and biochemical triglyceride (TG) content. Lastly, the effects of a PEGylated-FGF21 variant (PEG-FGF21v) on hepatic steatosis in the mouse model was evaluated using the water-fat MRI technique.
|
|
4730.
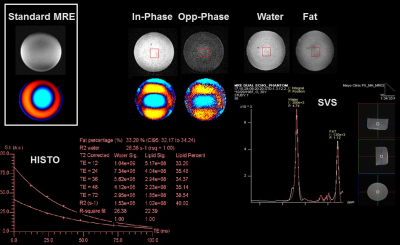 |
103 |
 Preliminary Study on the Feasibility of Simultaneously Measuring Hepatic Stiffness and Separate Water/Fat Signal Using Dual-Echo, Dixon, Spoiled-Gradient-Echo, Magnetic Resonance Elastography Preliminary Study on the Feasibility of Simultaneously Measuring Hepatic Stiffness and Separate Water/Fat Signal Using Dual-Echo, Dixon, Spoiled-Gradient-Echo, Magnetic Resonance Elastography
Yuan Le, Joshua Trzasko, Kevin Glaser, Yuxiang Zhou, William Pavlicek, Joseph Hoxworth, Bradley Bolster Jr., Joel Felmlee, Richard Ehman, Jun Chen
A novel dual-echo, Dixon MR Elastography technique was developed to simultaneously measure the liver stiffness and separate fat/water signal. Phantom tests showed that the fat signal fraction and the stiffness measured with this technique were consistent with the values measured with separate MR spectroscopy and standard MR Elastography acquisitions. Promising results were also obtained in a healthy volunteer.
|
|
4731.
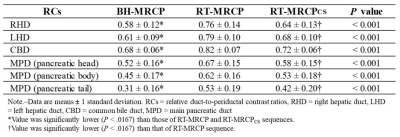 |
104 |
 Magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography using optimized integrated combination with parallel imaging and compressed sensing technique compared with conventional MRCP. Magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography using optimized integrated combination with parallel imaging and compressed sensing technique compared with conventional MRCP.
Nobuyuki Kawai, Satoshi Goshima, Kimihiro Kajita, Tomoyuki Okuaki, Masatoshi Honda, Hiroshi Kawada, Yoshifumi Noda, Yukichi Tanahashi, Shoma Nagata, Masayuki Matsuo
MR cholangiopancreatography (MRCP) plays an essential role in the noninvasive assessment of the biliary and pancreatic duct systems. The current respiratory-triggered three-dimensional turbo spin-echo MRCP sequence has an excellent duct-to-periductal tissue contrast, however, the long acquisition time and motion artifacts due to the various depth of patients’ breathing limit the benefit of this sequence. We assessed prototype sequence using optimized integrated combination with parallel imaging and compressed sensing technique (Compressed-SENSE) for MRCP. Our results demonstrated that Compressed-SENSE technique enabled significant reduction of acquisition time without image quality degradation compared with conventional method.
|
|
4732.
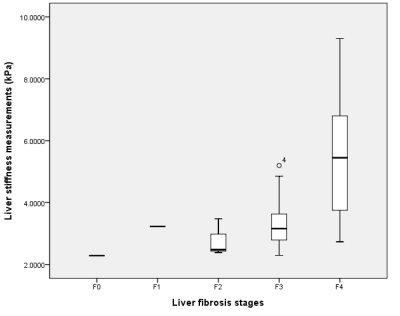 |
105 |
 MR elastography as a noninvasive marker for liver fibrosis in chronic hepatitis B patients: Comparisons with serum fibrosis markers MR elastography as a noninvasive marker for liver fibrosis in chronic hepatitis B patients: Comparisons with serum fibrosis markers
Bohyun kim, Hye Jin Kim, Jei Hee Lee, Hyo Jung Cho, Jai Keun Kim
Among various noninvasive methods for liver fibrosis quantification, we compared liver stiffness measured from MR elastography and multiple serum fibrosis markers including APRI, FIB-4, and King' score for liver fibrosis prediction. Our results showed than MR elastography performed better than serum fibrosis indices in discerning clinically significant fibrosis (≥ F3) and liver cirrhosis (≥ F4) in chronic hepatitis B patients.
|
|
4733.
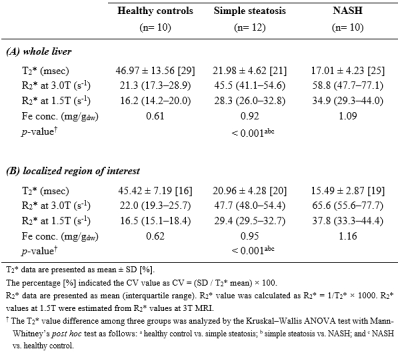 |
106 |
 Differential diagnosis of hepatic iron contents in simple steatosis and nonalcoholic steatohepatitis using multiecho Dixon magnetic resonance imaging Differential diagnosis of hepatic iron contents in simple steatosis and nonalcoholic steatohepatitis using multiecho Dixon magnetic resonance imaging
Tae-Hoon Kim, Chang-Won Jeong, Hong Young Jun, Youe Ree Kim, Ju Young Kim, SiHyeong Noh, JiEon Kim, Young Hwan Lee, Kwon-Ha Yoon
Non-invasive monitoring liver iron content (LIC) is critical for clinical management or effective therapeutic strategy of patients because the increment of iron accumulation within the liver may contribute to liver disease via the production of reactive oxygen species. Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) is the most common liver disease in the United States and is reported to between 10% and 30%, with similar rates reported from Europe and Asia. However, it is difficult to distinguish the sub-groups in NAFLD, especially simple steatosis (SS) and non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH), unless by liver biopsy. Therefore, it is important to monitor liver iron content (LIC) in NASH patients for clinical management or effective therapeutic strategy of patients.
|
|
4734.
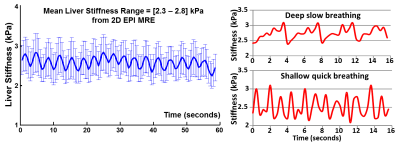 |
107 |
 Feasibility of Assessing the Nonlinear Mechanical behaviors of Liver with MR Elastography (MRE) Feasibility of Assessing the Nonlinear Mechanical behaviors of Liver with MR Elastography (MRE)
Ziying Yin, Bogdan Dzyubak, Jiahui Li, Kevin Glaser, Sudhakar Venkatesh, Armando Manduca, Richard Ehman, Meng Yin
This is a feasibility study for assessing the nonlinear mechanical behaviors of the liver while experiencing different degrees of mechanical preloads. The different loading conditions were induced by 1) diaphragm movement in a view-sharing free-breathing 2D-EPI-MRE acquisition; 2) end-expiration versus end-inspiration states in a breath-held 3D-EPI-MRE acquisition. We observed intriguing stiffness variation synchronized with the breathing pattern in the free-breathing MRE, and a difference between end-expiration and end-inspiration liver stiffness in the breath-held MRE. The promising results demonstrated that the free-breathing and/or breath-hold liver MRE at different breathing states can be useful for the assessment of nonlinear mechanical tissue behaviors.
|
|
4735.
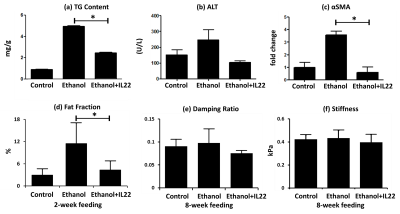 |
108 |
 Cross-validation of Multi-parametric MRI in Characterizing Steatosis, Inflammation, and Fibrosis in Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis (NASH) and Alcohol Hepatitis (AH) Mouse Models Cross-validation of Multi-parametric MRI in Characterizing Steatosis, Inflammation, and Fibrosis in Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis (NASH) and Alcohol Hepatitis (AH) Mouse Models
Ziying Yin, Rosa Mateos, Jiahui Li, Vikas Verma, Kevin Glaser, Amy Mauer, Harmeet Malhi, Vijay Shah, Richard Ehman, Meng Yin
In this preliminary study, we cross-validated the usefulness of multi-parametric MRI (fat fraction, liver stiffness, and damping ratio) in assessing the disease development and treatment response in both NASH and AH mouse models. Fat fraction has excellent agreement with the steatosis changes in both progressive and regressive AH and NASH models. In AH models, hepatic inflammation indicators have shown promising trends that well agreed each other in ALT and damping ratio. For the NASH model, both liver stiffness and damping ratio increased progressively in the fast-food-diet group, and the changes of stiffness was consistent with the end-point histology of fibrosis.
|
 |
4736.
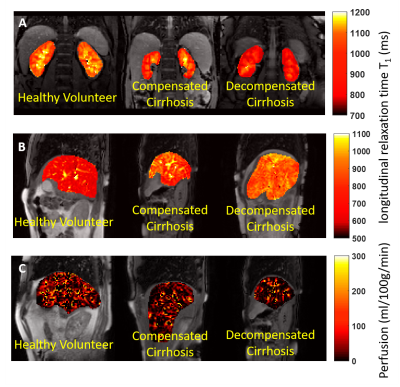 |
109 |
 MRI markers of liver related outcomes MRI markers of liver related outcomes
Chris Bradley, Eleanor Cox, Martin James, Guru Aithal, Neil Guha, Susan Francis
We used quantitative MR measures to assess changes in microstructure and haemodynamics in the liver and kidney of 60 patients with compensated cirrhosis (CC), 9 patients with decompensated cirrhosis (DC) and 40 healthy volunteers (HV). Liver T1 and perfusion was significantly reduced and renal T1 significantly increased with disease severity. In this prospective study, 1 in 6 CC patients have since had a Liver Related Outcome (LRO). These patients showed significant changes in baseline MR measures suggesting these MR measures in our multi-parametric MRI protocol can be used as a marker of LRO.
|
|
4737.
 |
110 |
 Transducer-Free Hepatic Magnetic Resonance Elastography using Cardiac Wave Induction at 0.3ms Temporal Resolution Transducer-Free Hepatic Magnetic Resonance Elastography using Cardiac Wave Induction at 0.3ms Temporal Resolution
Marian Troelstra, Alessandro Polcaro, Omar Darwish, Jose de Arcos, Torben Schneider, Khaled Abd-Elmoniem, Ahmed Gharib, Jurgen Runge, Ralph Sinkus
Hepatic MRE is a promising non-invasive tool for diagnosing liver fibrosis. To facilitate clinical translation, we developed a method to eliminate the need for mechanical actuators for wave generation. Propagation of the transient cardiac shear waves within the liver caused by cardiac-valve closure can be imaged at a very high temporal resolution (0.3ms) using a 2D motion-sensitised pencil beam, with total data acquisition time fitting into four consecutive breath holds. These images were used to estimate liver stiffness, with a high temporal resolution allowing for reliable fitting to the space-time images and thus robust speed estimates.
|
|
4738.
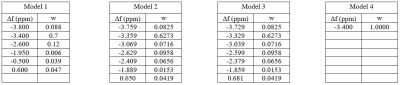 |
111 |
 Comparison of different multi-fat peak models for the assessment of hepatic iron and fat Comparison of different multi-fat peak models for the assessment of hepatic iron and fat
Christian Kremser, Michaela Plaikner, Heinz Zoller, Werner Jaschke, Benjamin Henninger
The evaluation of hepatic iron and fat by MR techniques is of increasing interest for clinical routine. The purpose of our study was to investigate the influence of different multi-peak fat models on the obtained R2*, PDFF and goodness of fit values in patients with suspicion of diffuse liver disease. It is shown that the use of multi-peak fat spectrum modeling is highly recommended for accurate quantification of R2* and PDFF . A 6-peak model resulted in the best goodness of fit. The use of a higher number of peaks seems to offer no additional advantage.
|
|
4739.
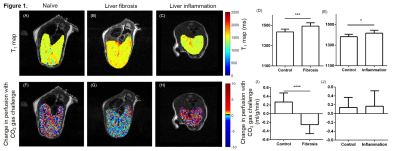 |
112 |
 Selective detection of liver fibrosis: Perfusion with hypercapnia challenge rather than T1 mapping. Selective detection of liver fibrosis: Perfusion with hypercapnia challenge rather than T1 mapping.
John Connell, Thomas Roberts, May Zaw-Thin, P Patrick, Rajiv Ramasawmy, Daniel Stuckey, Manil Chouhan, Daniel Antoine, Jack Wells, Mark Lythgoe, Tammy Kalber
Quantitative T1 mapping is starting to be used clinically as a measure of liver fibrosis, but is confounded by the presence of inflammation in the liver. Work presented here describes the development of a new quantitative MRI measure, “change in perfusion in response to CO2 gas challenge”, in mice. This vasoactive challenge takes advantage of the pathological hallmarks of perivascular collagen seen in fibrosis, which is hypothesised to attenuate increases in tissue perfusion during hypercapnia.
|
|
4740.
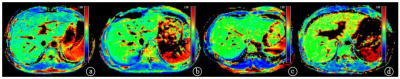 |
113 |
 The preliminary study of staging liver fibrosis in patients with chronic hepatitis B using MR T1? The preliminary study of staging liver fibrosis in patients with chronic hepatitis B using MR T1?
Qing Li, Shuangshuang Xie, Hanxiong Qi, Zhizheng Zhuo, Yue Cheng, Wen Shen
This study explored the value of MR T1ρ in patients with chronic hepatitis B. Twenty normal control subjects and forty-eight patients with chronic hepatitis B, including twenty-two patients who were confirmed by liver biopsy (F1/F2/F3=8/8/6) took the MR T1ρ scan. T1ρ value showed significant increase in patients with chronic hepatitis B compared with normal control subjects, significant correlation with liver fibrosis staging and higher sensitivity and specificity in identifying F1 to F3 of liver fibrosis. We conclude that MR T1ρ can provide reliable T1ρ values and can be used to assess liver fibrosis.
|
|
4741.
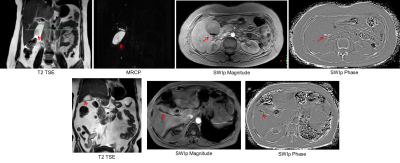 |
114 |
 Relevance of susceptibility weighted imaging with phase (SWIp) in Cholelithiasis Relevance of susceptibility weighted imaging with phase (SWIp) in Cholelithiasis
Jaladhar Neelavalli, Rakesh Kumar Gupta, Anandh Ramaniharan, Pradeep Kumar Gupta, Karthick Rajendran, Rupsa Bhattacharjee
Cholelithiasis, which is presence of stones in the biliary anatomy, is a common clinical condition with an incidence of up to 15% worldwide. Magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography (MRCP) is a standard MR technique used for diagnosing this condition. However, MRCP’s sensitivity is low when the stones are smaller than 5mm. These stones often contain trace amounts of minerals that are dia/paramagnetic. SWI is highly sensitive to susceptibility differences and hence we hypothesized that it may play a role in clinical evaluation of presence of gallstones. In this work we evaluated this hypothesis by imaging patients with Cholelithiasis using a modified SWI sequence.
|
|
4742.
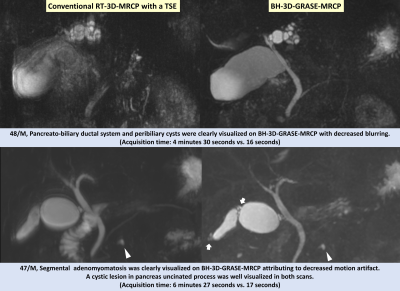 |
115 |
 GRASE Revisited: Breath-hold Three-dimensional (3D) Magnetic Resonance Cholangiopancreatography using a Gradient and Spin Echo (GRASE) Technique at 3T GRASE Revisited: Breath-hold Three-dimensional (3D) Magnetic Resonance Cholangiopancreatography using a Gradient and Spin Echo (GRASE) Technique at 3T
Ju Nam, Jeong Hee Yoon, Jeong Min Lee, Hyo-Jin Kang, Sang Min Lee, Johannes Peeters, Eunju Kim
We evaluate the clinical feasibility and image quality of breath-hold (BH) three-dimensional (3D) MRCP using a gradient and spin-echo (GRASE) technique compared to the conventional 3D respiratory-triggered (RT)-MRCP using a turbo spin-echo (TSE) sequence at 3T. Sixty-six patients underwent both 3D RT-TSE-MRCP and 3D BH-GRASE-MRCP at 3T and three radiologists independently reviewed the images. The 3D BH-GRASE-MRCP had a significantly better image quality. In detail, 3D BH-GRASE-MRCP better depicted the common bile duct, cystic duct, and bilateral 1st intrahepatic duct. The number of scans with nondiagnostic or poor image quality significantly decreased with 3D BH-GRASE-MRCP compared with 3D RT-TSE-MRCP.
|
|
4743.
 |
116 |
 Comparison of Respiratory Motion Artifacts in T1-Weighted Liver Magnetic Resonance Imaging using End-expiration and End-inspiration Breath-Holds Comparison of Respiratory Motion Artifacts in T1-Weighted Liver Magnetic Resonance Imaging using End-expiration and End-inspiration Breath-Holds
Kim Nhien Vu, Albert Tae-Hun Roh, Anshul Haldipur, Peter Lindholm, Andreas Loening
Respiratory motion artifact is a common pitfall in MRI of the liver and no standard of practice currently exists for breath-hold imaging techniques. This retrospective observational study compared image quality between end-inspiration and end-expiration breath-holding techniques. Precontrast T1-weighted 3D spoiled gradient recalled echo imaging of the liver obtained using the two techniques were compared in 50 consecutive subjects, along with postcontrast sequences in a subset of 47. Three radiologists performed blinded evaluations of respiratory motion in the sequences. Breath-holding technique at end-expiration was significantly better at reducing respiratory motion artifacts, yielding fewer images of nondiagnostic quality than end-inspiration breath-holding technique.
|
|
4744.
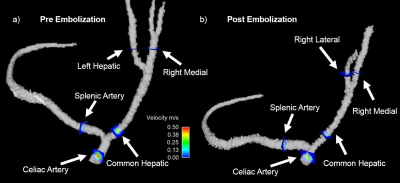 |
117 |
 4D Flow MRI: A Preliminary Analysis of Changes in Arterial Flow During Liver Embolization In Swine 4D Flow MRI: A Preliminary Analysis of Changes in Arterial Flow During Liver Embolization In Swine
Carson Hoffman, Ece Meram, Paul Laeseke, Oliver Wieben
Transarterial embolization is a common treatment for liver tumors. Currently, radiographic techniques are used clinically to provide anatomical and qualitative hemodynamic information in assessment and treatment of liver tumors. The addition of 4D Flow MRI has the potential to provide functional information about the hemodynamic changes occurring pre, during and post treatment. We completed a feasibility study in a swine, in which clear flow changes were seen in the hepatic vascular system. The additional information provided by 4D Flow MRI has potential to improve the care of cancer patients.
|
 |
4745.
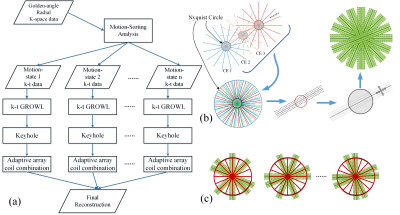 |
118 |
 Incorporating Motion-Sorting Technique into Keyhole and k-t GROWL Compound System for Rapid Golden-angle Liver DCE Imaging Incorporating Motion-Sorting Technique into Keyhole and k-t GROWL Compound System for Rapid Golden-angle Liver DCE Imaging
Zhifeng Chen, Liyi Kang, Ling Xia, Xia Kong, Allan Jin, Zhongbiao Xu, Yaohui Wang, Feng Liu
Liver DCE imaging plays an increasingly important role in the diagnosis of liver diseases, including hepatic cirrhosis, hepatocellular carcinoma, etc. Motion is an inevitable problem in liver imaging, which often leads to motion artifacts and blurring on image details. We propose to incorporate motion-sorting technique into parallel imaging GROWL and Keyhole compound system for golden-angle radial dynamic contrast-enhanced MRI. The experimental results demonstrated that the proposed scheme can generate better image quality than non-motion-sorting techniques. Compared to the tested motion-sorting techniques, similar image quality can be offered with greatly reduced computational cost.
|
|
4746.
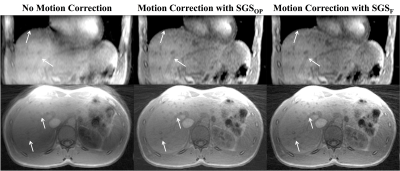 |
119 |
 Evaluation of Fat-Only Self Gated Signal for Respiratory Motion Detection and Compensation in the Liver Evaluation of Fat-Only Self Gated Signal for Respiratory Motion Detection and Compensation in the Liver
Thomas Martin, Tess Armstrong, Alibek Danyalov, Eunice Lee, Ely Felker, James Sayre, Steven Raman, Holden Wu, Kyunghyun Sung
A dual-echo 3D golden angle radial gradient echo sequence can be used for generating a fat-only self-gated signal for respiratory motion detection. We have demonstrated that respiratory motion extraction and compensation in the liver can be achieved using fat-only self-navigated signal with minimal error in the fat-water separation (< 15%). Using this technique has implications of a more robust motion correction for liver DCE-MRI due to its inherent separation between respiratory motion signal and contrast uptake.
|
|
4747.
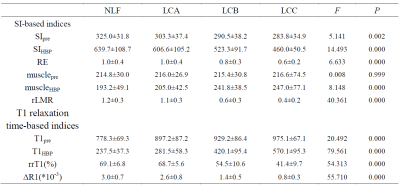 |
120 |
 Gd-EOB-DTPA-Enhanced MRI for Assessment of Liver Function: Comparison between Signal Intensity and T1 Relaxation Time-Based Indices Gd-EOB-DTPA-Enhanced MRI for Assessment of Liver Function: Comparison between Signal Intensity and T1 Relaxation Time-Based Indices
Xueqin ZHANG, Jian LU, Jifeng JIANG, Weibo CHEN
The purpose of this study was to compare the ability of Gd-EOB-DTPA-enhanced signal intensity (SI) and T1 relaxation time-based indices for evaluation of liver function. We used Gd-EOB-DTPA-enhanced MRI and Look-Locker sequences to acquire conventional MRI and T1mapping images. The SI values of the liver, paravertebral muscle, T1 relaxation times of the liver before Gd-EOB-DTPA administration and in HBP were measured, the relative enhancement of the liver, increase rates of liver-to-muscle ratio, reduction rates of T1 relaxation time and ΔR1 were calculated, our study showed that the indices derived from T1 relaxation time were superior to SI-based indices.
|
|
| Back |
| The International Society for Magnetic Resonance in Medicine is accredited by the Accreditation Council for Continuing Medical Education to provide continuing medical education for physicians. |
















































































































































