Myocardial Tissue Characterisation
Oral
Cardiovascular
Monday, 18 June 2018
| S05 |
16:15 - 18:15 |
Moderators: Pierre Croisille, Andrew Scott |
16:15
|
0282.
 |
 Magnetic susceptibility of hemorrhagic myocardial infarction: correlation with tissue iron and comparison with relaxation time MRI Magnetic susceptibility of hemorrhagic myocardial infarction: correlation with tissue iron and comparison with relaxation time MRI
Brianna Moon, Srikant Kamesh Iyer PhD, Michael Solomon, Anya Hall, Rishabh Kumar, Elizabeth Higbee-Dempsey, Andrew Tsourkas PhD, Akito Imai MD, Keitaro Okamoto MD, Yoshiaki Saito MD, Jerry Zsido II, Joseph Gorman III MD, Robert Gorman MD, Giovanni Ferrari PhD, Walter Witschey PhD
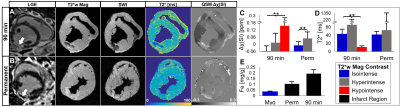
Hemorrhagic myocardial infarction (MI) is a frequent complication of primary percutaneous coronary intervention and independently associated with impaired LV remodeling, function, and arrhythmias. We demonstrate that cardiac quantitative susceptibility mapping (QSM) shows increased susceptibility in infarcts compared to remote myocardium and correlates with iron content and infarct pathophysiology. QSM is a more specific marker of hemorrhagic MI than relaxation time MRI, susceptibility-weighted imaging, and late gadolinium enhanced (LGE) MRI.
|
16:27
|
0283.
 |
 Myocardial T2 mapping using a Black-blood hEart-rate Adaptive T2-prepared bSSFP (BEATS) sequence Myocardial T2 mapping using a Black-blood hEart-rate Adaptive T2-prepared bSSFP (BEATS) sequence
Chengyan Wang, Jihye Jang, Ahmed Fahmy, Jinkyu Kang, Beth Goddu, Sophie Berg, Jue Zhang, Xiaoying Wang, Warren Manning, Reza Nezafat
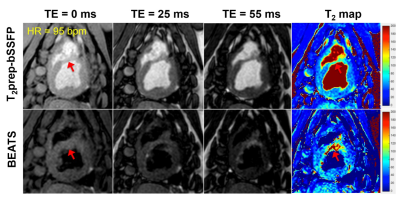
Quantification of T2 in areas bordering myocardium and blood pool is challenging due to partial volume errors. Blood signal suppression would effectively reduce partial volume effects and improve image contrast at the blood-myocardium boundaries. This study proposed a Black-blood hEart-rate Adaptive T2-prepared bSSFP (BEATS) sequence for myocardial T2 mapping to improve blood-myocardial border definition. Both phantom and in vivo studies proved the advantages of BEATS sequence compared to T2prep-bSSFP T2 mapping. The proposed BEATS sequence efficiently suppresses the blood signal, resulting in better definition of blood/myocardium border by reducing the impact of partial volume effect in T2 measurements, which improves the assessment of edema post myocardial infarction.
|
16:39
|
0284.
 |
Assessment of Myocardial Fibre Architecture in Cardiac Amyloidosis Patients using In-Vivo Cardiac Diffusion Tensor Imaging
Video Permission Withheld
Constantin von Deuster, Alexander Gotschy, Robbert van Gorkum, Mareike Gastl, Ella Vintschger, Andreas Flammer, Robert Manka, Christian Stoeck, Sebastian Kozerke
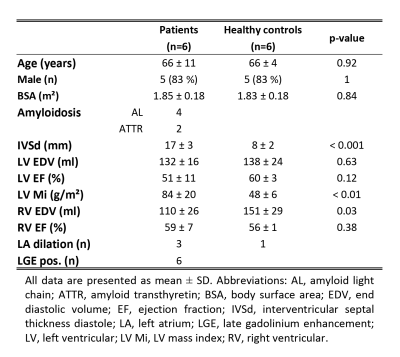
In-vivo cardiac diffusion tensor imaging (cDTI) allows imaging of alterations in the cardiac fibre architecture in diseased hearts. In this work, changes in the myocardial microstructure in patients with cardiac amyloidosis were assessed using cDTI and T1 mapping. Mean diffusivity and T1native are significantly increased in the patients and the helical fibre configuration is comparable to healthy controls. There is a trend towards higher/lower MD/FA with increased T1native, respectively. In agreement with T1 mapping, diffusion results support the presence of myocardial degeneration and emphasize the potential of cDTI as contrast agent free tool for characterizing cardiac involvement in amyloidosis patients.
|
16:51
|
0285.
 |
 Cardiac Magnetic Resonance Elastography for the Diagnosis of Patients with Heart Failure with Preserved Ejection Fraction Cardiac Magnetic Resonance Elastography for the Diagnosis of Patients with Heart Failure with Preserved Ejection Fraction
Arvin Arani, Shivaram Arunachalam, Phillip Rossman, Joshua Trzasko, Kevin Glaser, Yi Sui, Kiaran McGee, Armando Manduca, Barry Borlaug, Richard Ehman, Philip Araoz
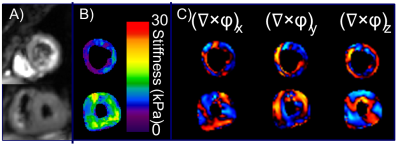
Heart failure with preserved ejection fraction (HFpEF) accounts for half of incident heart failure cases per year. Currently, the diagnostic reference standard is invasive. The objective of this study is to evaluate if cardiac MR elastography (MRE) can measure increased myocardial stiffness in patients with HFpEF. Fifty-eight volunteers and 10 patients were enrolled. The mean left-ventricle myocardial stiffness of HFpEF patients (10.5±1.7 kPa) was significantly higher (p=0.002) than control subjects (8.0±1.2 kPa).This study motivates further investigation into the use of cardiac MRE as a quantitative noninvasive imaging technique to assist in the diagnosis and therapy monitoring of patients with HFpEF.
|
17:03
 |
0286.
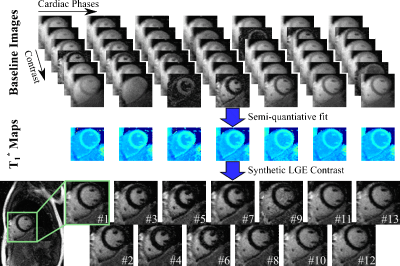 |
 Cardiac Phase-resolved Late-Gadolinium Enhancement Imaging Cardiac Phase-resolved Late-Gadolinium Enhancement Imaging
Sebastian Weingärtner, Burhaneddin Yaman, Chetan Shenoy, Marcel Prothmann, Felix Wenson, Jeanette Schulz-Menger, Mehmet Akcakaya
Late Gadolinium Enhancement (LGE) is commonly acquired during a single end-diastolic phase with inversion-recovery contrast that nulls healthy myocardial tissue. In this work, we propose a method for acquisition of cardiac phase-resolved LGE images based on an ECG triggered Look-Locker experiment with continuous FLASH imaging. Semi-quantitative evaluation of this pulsed-inversion recovery allows synthetization of LGE image contrast for all cardiac phases. Accurate functional depiction with temporal resolution up to 60 ms is obtained in healthy subjects at 3T. Images of 20 patients on a clinical 1.5T scanner show promising depiction of focal scar at a temporal resolution of 80ms.
|
17:15
 |
0287.
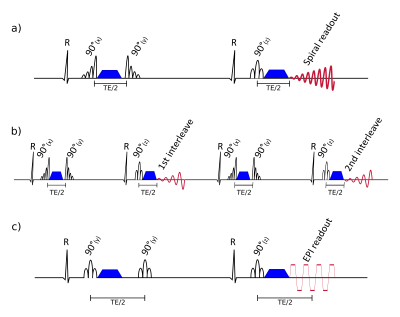 |
 High resolution in-vivo diffusion tensor cardiovascular magnetic resonance: a comparison of single-shot EPI and interleaved spiral trajectories with motion induced phase correction High resolution in-vivo diffusion tensor cardiovascular magnetic resonance: a comparison of single-shot EPI and interleaved spiral trajectories with motion induced phase correction
Margarita Gorodezky, Andrew Scott, Pedro Ferreira, Sonia Nielles-Vallespin, Peter Gatehouse, Dudley Pennell, David Firmin
The spatial resolution of DT-CMR STEAM acquisitions was increased by implementing an interleaved variable density spiral readout. Bulk motion during STEAM diffusion encoding is unavoidably encoded in the image phase which can result in signal loss for multi-shot acquisition when the multiple interleaves are combined. A phase correction was implemented using the fully sampled centres of k-space to calculate the differences in phase between interleaves. In 7 volunteers we show improved data quality at 2.0x2.0mm2 using interleaved spirals compared to single-shot EPI and we obtain similar DT-CMR parameters.
|
17:27
|
0288.
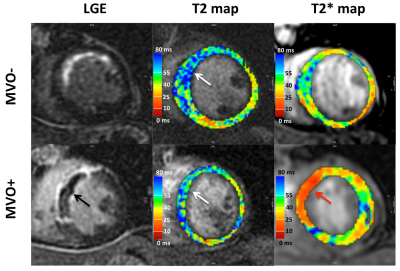 |
 Microvascular obstruction impacts recovery of T1 and T2 relaxation and strain parameters following acute myocardial infarction Microvascular obstruction impacts recovery of T1 and T2 relaxation and strain parameters following acute myocardial infarction
Dipal Patel, Venkat Ramanan, Idan Roifman, Mohammad Zia, Kim Connelly, Graham Wright, Nilesh Ghugre
Microvascular obstruction (MVO) is a frequent complication in acute myocardial infarction (AMI). A comprehensive regional and serial characterization of tissue response in the presence and absence of MVO will help assess the high-risk patients. In this study, we utilized T1 and T2 relaxation as well as tissue strain properties to evaluate tissue response in STEMI patient’s post-AMI. We observed that measures of infarct edema, hemorrhage and strain in patients with MVO fail to recover to remote levels and have significantly lower recovery rates compared to patients without MVO. Remote T2 alterations may further be an early indicator of adverse remodeling. Our study shows that MVO impacts disease progression by hindering the regional myocardial systolic function and edema recovery post-AMI.
|
17:39
|
0289.
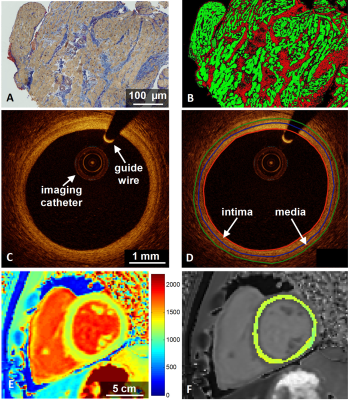 |
 The effects of cardiac allograft vasculopathy on intimal coronary artery wall thickness, myocardial fibrosis, and myocardial extracellular volume The effects of cardiac allograft vasculopathy on intimal coronary artery wall thickness, myocardial fibrosis, and myocardial extracellular volume
Ruud van Heeswijk, Jessica Bastiaansen, Juan Iglesias, Sophie Degrauwe, Samuel Rotman, Jérôme Yerly, Giulia Ginami, Matthias Stuber, Roger Hullin
Cardiac allograft vasculopathy (CAV) occurs with a high prevalence after heart transplantation (HTx) and is a major cause of mid-term to late heart transplant failure. In this study we investigated whether the presence of CAV as diagnosed by x-ray coronary angiography or intima thickness as assessed by optical coherence tomography (OCT) is linked with the myocardial T1 relaxation time, extracellular volume, or interstitial fibrosis as assessed by endomyocardial biopsies (EMB).
|
17:51
|
0290.
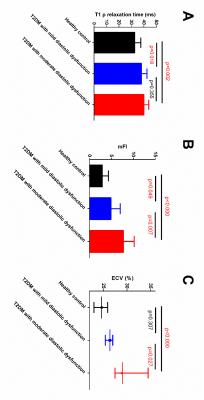 |
 The Difference between Extracellular Space Expansion and Diffuse Myocardia Fibrosis in Defferent Severity Distolic Dysfunction (DD) Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus (T2DM) Rhesus Monkeys using Excellelar Volume mapping and Non-contrast T1? mapping The Difference between Extracellular Space Expansion and Diffuse Myocardia Fibrosis in Defferent Severity Distolic Dysfunction (DD) Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus (T2DM) Rhesus Monkeys using Excellelar Volume mapping and Non-contrast T1? mapping
Yu Zhang, Li Gong, Yushu Chen, Wen Zeng, Jie Zheng, Fabao Gao
In this study, diffuse myocardial fibrosis was quantifitied in type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) rhesus monkeys with different severity diastolic dysfunction (DD) using ECV derived from T1 mapping and mFI derived from non-contrast T1ρ mapping. Different behaviors of ECV and mFI to differentiate HC from T2DM with mild DD was observed. This reflects the difference between extracellular space expansion and collagen content during the process of myocardial fibrosis. This difference is benifite for us to better understand the pathophysiology of DD.
|
18:03
|
0291.
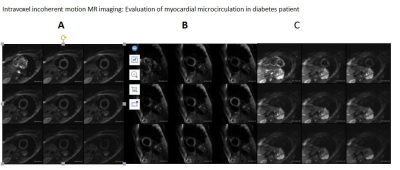 |
Intravoxel incoherent motion MR imaging: Evaluation of myocardial microcirculation in diabetes patients
Video Permission Withheld
li lan , li xin, li yong, song wei, liu lian
Because of 80% type 2 diabetic patients died of cardiovascular complications, diabetic microangiopathy in the diabetic cardiomyopathy couldn’t be ignored. At present, we lack simple and accurate methods for assessment of myocardial microcirculation. Intravoxel incoherent motion (IVIM) technology is a new noninvasive method that can be used for quantitatively assessing myocardial microcirculation status.
|
|













