Body Imaging: Genitourinary Imaging (Non-Prostate)
Oral
Body: Breast, Chest, Abdomen, Pelvis
Thursday, 21 June 2018
| S06 |
13:15 - 15:15 |
Moderators: Victoria Chernyak, Yasser Abbas |
13:15
 |
1177.
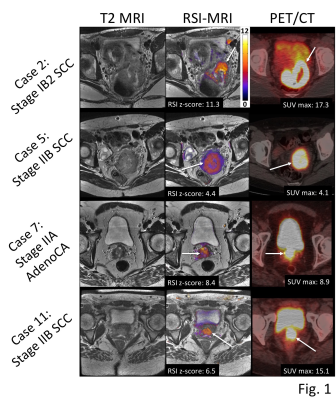 |
 Cervical cancer staging and surveillance using Restriction Spectrum Imaging (RSI)-MRI in comparison to PET-CT: Pilot Clinical Application Cervical cancer staging and surveillance using Restriction Spectrum Imaging (RSI)-MRI in comparison to PET-CT: Pilot Clinical Application
Ghiam Yamin, Kaveh Zakeri, Natalie Schenker-Ahmed, Nathan White, Hauke Bartsch, Joshua Kuperman, Loren Mell, Michael Hahn, David Karow, Anders Dale, Rebecca Rakow-Penner
This proof of concept study suggests restriction spectrum imaging (RSI)-magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) provides similar cervical cancer staging and surveillance information compared to standard of care MP-MRI and PET-CT. Advantages over the standard of care modalities may include improved cost-effectiveness, brevity, radiation-free, and contrast media-free. Pilot cases suggest that RSI-MRI cellularity index can detect residual and recurrent tumor in post-treatment cervical cancer patients with similar sensitivity to PET-CT. RSI-MRI has the advantage of minimal false positive results related to radiation-related post-treatment changes that often confound interpretation of PET-CT.
|
13:27
|
1178.
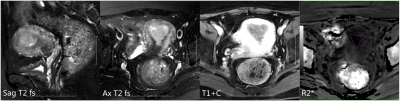 |
 MR R2* values in diagnosing the stage Ia and Ib endometrial carcinoma MR R2* values in diagnosing the stage Ia and Ib endometrial carcinoma
Meng-yao Wang, Mei-yu Sun, Xu Han, Rui Fan, Lizhi Xie
Endometrial carcinoma(EC) patients staged stage Ia or Ib have different operation methods and prognosis. To evaluate the value of enhanced T2*-weighted angiography(ESWAN) in the differential diagnosis between stage Ia and Ib of endometrial carcinoma. In this work, we found it is feasible that ESWAN sequence derived R2* value can be applied in the differential diagnosis between stage Ia and Ib of endometrial carcinoma, which can provide detailed information for clinical treatment.
|
13:39
|
1179.
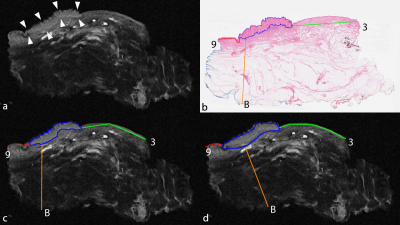 |
 Ex vivo MRI evaluation of vulvar cancer in fresh wide local excision specimens for cancer localization and prediction of the surgical tumour free margins. Ex vivo MRI evaluation of vulvar cancer in fresh wide local excision specimens for cancer localization and prediction of the surgical tumour free margins.
Jan Heidkamp, Petra Zusterzeel, Andor Veltien, Arie Maat, Ilse van Engen-van Grunsven, Maroeska Rovers, Jurgen Fütterer
Currently, perioperative information on the surgical margin status of wide local excision specimens containing vulvar cancer is only based on the surgeon’s estimation. In this study we performed both a non-blinded and a blinded annotation of vulvar cancer location and surgical tumour free margins in the ex vivo MRI obtained from fresh wide local excision specimens. Annotated whole-mount section histopathology slides obtained from totally included specimens were adhered as gold standard. There was high correlation and agreement between ex vivo MRI, and high NPV and PPV were obtained for vulvar cancer localization and identification of margins <8 mm.
|
13:51
|
1180.
 |
 Texture analysis of multiparametric MRI in cervical cancer before and after chemoradiotherapy Texture analysis of multiparametric MRI in cervical cancer before and after chemoradiotherapy
Jose Perucho, Elaine Lee, Richard Du, Varut Vardhanabhuti, Queenie Chan
Texture analysis of multiparametric MRI (mpMRI) consisting of diffusion-weighted MRI (DWI) and T2-weighted (T2W) texture features could be a promising quantitative approach in assessing tumor heterogeneity. We retrospectively studied forty patients who had paired mpMRI examinations before and at week-4 of chemoradiotherapy (CRT). Based on the changes in stable mpMRI features, we observed that initially more anatomically and functionally homogenous tumors had better response to treatment and that tumors became more functionally heterogenous after treatment.
|
14:03
 |
1181.
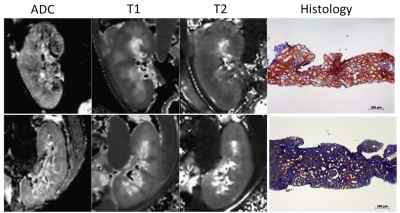 |
 Multivariate Analysis including Biological Biomarkers, Diffusion-Weighted Imaging, T1 and T2 Mapping for Renal Fibrosis Prediction Multivariate Analysis including Biological Biomarkers, Diffusion-Weighted Imaging, T1 and T2 Mapping for Renal Fibrosis Prediction
Iris Friedli, Lena Berchtold, Lindsey Crowe, Chantal Martinez, Solange Moll, Karine Hadaya, Thomas De Perrot, Pierre-Yves Martin, Jean-Paul Vallée, Sophie De Seigneux
Recently, the cortico-medullary difference in Apparent Diffusion Coefficient (ΔADC) from (RESOLVE) diffusion-weighted imaging (DWI with readout segmentation of long variable echo train) allowed the classification of kidney allograft patients according to whether they had more or less than 40% interstitial fibrosis. In this study, ΔADC was externally validated, with a very good AUC, as an index to identify patients with more than 40% fibrosis in a larger and mixed population of 130 patients. In addition, a mixed scoring including the combination of routinely obtained serologic markers including eGFR, and MRI-derived (ΔADC and ΔT1) was proposed to improve renal fibrosis prediction.
|
14:15
 |
1182.
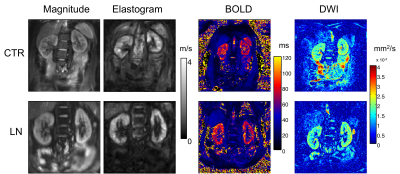 |
MR Elastography, Diffusion Imaging and BOLD-Imaging for the Detection of Early Changes of Renal Stiffness in Patients with Lupus Nephritis
Video Permission Withheld
Stephan Marticorena Garcia, Markus Grossmann, Anne Bruns, Heiko Tzschätzsch, Bernd Hamm, Jürgen Braun, Ingolf Sack, Jing Guo
Renal stiffness was investigated using MR elastography (MRE) and tomoelastography data processing in healthy controls and patients with lupus nephritis (LN). Our results showed that patients had lower renal stiffness than controls, while subregions such as medulla and inner cortex allowed to differentiate early chronic kidney disease (CKD=1) from progressed disease stages based on MRE values. The observed reduction in renal stiffness is associated with decreased ADC-values and increased T2*-values due to LN with CKD≥2. The decreased stiffness due to CKD=1 was reflected by T2*-values but not by ADC-values. MRE provided the highest diagnostic accuracy for detection of LN.
|
14:27
|
1183.
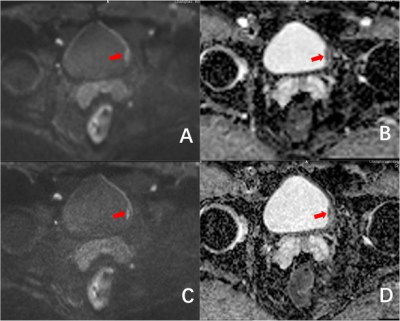 |
 Diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging in bladder cancer: comparison of readout-segmented EPI and single-shot EPI Techniques Diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging in bladder cancer: comparison of readout-segmented EPI and single-shot EPI Techniques
Haihu Chen, Luguang Chen, Fang Liu, Qingsong Yang, Jianping Lu, Li Wang
Diffusion weighted imaging showed the potential to assess bladder cancer. This study aimed to investigate whether readout-segmented EPI can offer better image quality in imaging bladder patients in comparison with single-shot EPI, and to compare quantitative image parameters, derived from RS-EPI with those of SS-EPI. Thirty-five patients were examined using both diffusion techniques. There were significant differences in susceptibility artifacts, lesion detectability, image blurring, CNR and SIR values, except for motion artifacts, SNR and ADC values of the bladder lesions. This study found that the RS-EPI technique provides significant image quality improvement compared with SS-EPI in bladder at 3 Tesla.
|
14:39
|
1184.
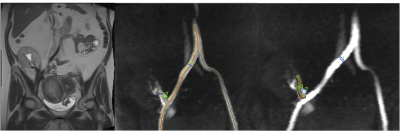 |
 4D flow MRI in renal transplant: preliminary results. 4D flow MRI in renal transplant: preliminary results.
Octavia Bane, Sara Lewis, Stefanie Hectors, Sonja Gordic, Paul Kennedy, Mathilde Wagner, Michael Markl, Rafael Khaim, Veronica Delaney, Fadi El Salem, Madhav Menon, Bachir Taouli
In this preliminary study, we sought to determine the test-retest repeatability of flow quantification in renal allograft vessels using a 4D flow phase-contrast (PC) MRI sequence, and to correlate flow parameters with renal function. We observed significantly decreased renal arterial flow in allografts with chronic dysfunction, as well as positive correlation between flow and velocities in renal transplant vessels and renal function. We conclude that 4D flow imaging is sensitive to the vascular changes that accompany renal transplant dysfunction, to be confirmed in a larger study.
|
14:51
 |
1185.
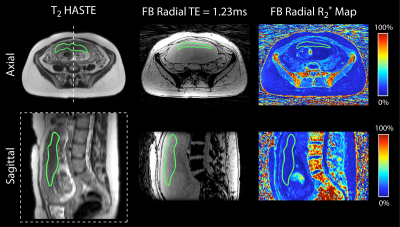 |
 Free-breathing R2* Mapping in the Entire Placenta During Early Gestation Using 3D Stack-of-Radial MRI at 3 T: Investigation of Spatial and Temporal Variation Free-breathing R2* Mapping in the Entire Placenta During Early Gestation Using 3D Stack-of-Radial MRI at 3 T: Investigation of Spatial and Temporal Variation
Tess Armstrong, Dapeng Liu, Thomas Martin, Cass Wong, Irish Del Rosario, Sherin Devaskar, Carla Janzen, Teresa Chanlaw, Rinat Masamed, Kyunghyun Sung, Holden Wu
Current methods for detecting ischemic placental disease are either invasive or have low sensitivity. MRI can be used to non-invasively characterize tissue hypoxia with R2* mapping. However, conventional Cartesian MRI methods are sensitive to motion artifacts due to maternal and fetal motion. In this study, a non-Cartesian free-breathing 3D stack-of-radial MRI technique (FB radial) for R2* mapping in the placenta during early gestation was investigated at 3T. In 20 subjects, placental R2* range, accuracy, repeatability, spatial variation, and temporal variation were analyzed. Results demonstrate that FB radial is an accurate and repeatable technique for R2* mapping in the entire placenta.
|
15:03
|
1186.
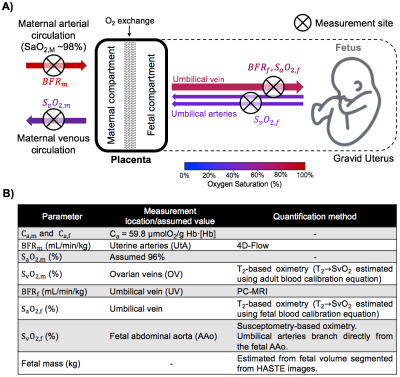 |
 Placental Metabolic Rate of Oxygen Placental Metabolic Rate of Oxygen
Ana Rodríguez-Soto, Michael Langham, Eileen Hwuang, Walter Witschey, Nadav Schwartz, Felix Wehrli
Placental dysfunction is widely accepted as a major cause of common adverse pregnancy outcomes. However, current clinically available tools are limited in their ability to assess placental function. Here, we have incorporated quantitative MRI methods to estimate placental metabolic rate of O2 (PMRO2), which may contribute to the understanding of placental dysfunction. Presented results demonstrate the feasibility of estimating PMRO2 in vivo. Further, these data suggest, in a limited number of participants, that PRMO2 may in fact contribute to the understanding of pregnancy complications.
|
|













