Body: Breast, Chest, Abdomen, Pelvis
Digital Poster
Body: Breast, Chest, Abdomen, Pelvis
1609 -1633 Prostate MRI: Technical Developments
1634 -1657 Emerging Technologies in Body Imaging
1658 -1680 Pancreas/GI
1681 -1705 Liver Lesions: Diagnosis, Characterization & Monitoring
1706 -1730 AI & Radiomics in Body MRI
1731 -1753 Liver Fibrosis
1754 -1777 Liver Fat, Iron, Perfusion & Function
1778 -1802 What Are We, Chopped Liver?
1803 -1827 Pelvic Malignancies
1828 -1852 Prostate MRI: Clinical Practice
1853 -1876 Breast: Clinical Practice
1877 -1900 Second Wind: Xenonphobic
1901 -1925 Kidney: Clinical & Preclinical
1926 -1950 Metabolism/Multisystem
Digital Poster
| Exhibition Hall | 13:45 - 14:45 |
| Computer # | |||
1609. 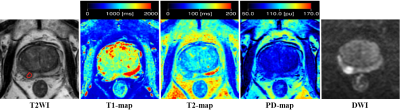 |
1 | The Use of Relaxation Maps from Synthetic MRI in Differential Diagnosis of Prostate Cancer
Yadong Cui, Yue Lin, Chunmei Li, Jianxun Qu, Bing Wu, Min Chen
Synthetic MRI enables absolute quantification of T1, T2 and (proton density) PD value. The aim of the study was to primarily evaluate the feasibility of synthetic MRI in differential diagnosis of (prostate cancer) PCa. We analyzed 18 PCa lesions in 14 PCa patients, 26 SH (stromal hyperplasia), 25 GH (glandular hyperplasia) nodules and 21 prostatitis areas in 22 non-PCa patients who underwent multi-parameter MRI before needle biopsy. T1WI, T2WI, DWI and MAGiC (magnetic resonance image compilation) sequences were acquired respectively. Our results showed the T1 and T2 value of PCa lesion was significantly lower than GH nodule and prostatitis area. The PD value of PCa lesion was significantly lower than GH nodule. We concluded that synthetic MRI was helpful for differential diagnosis of PCa.
|
|
1610. 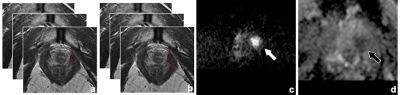 |
2 | Two exploratory radiomics segmentation algorithms in T2-weighted imaging analysis for predicting apical positive surgical margins of prostate cancer: A pilot study
Xiang Liu, Shuai Ma, Xiaodong Zhang, Xiaoying Wang
SynopsisThis retrospective study aims to compare the two different segmentation algorithms of radiomics analysis for predicting the apical surgical margin (SM) status before radical prostatectomy (RP). Preoperative prostate MR scans were performed for 76 enrolled patients and T2-weighted images was assessed by a radiomics model, using two different delineating methods: including the surrounding tissues of the targeted lesions or not. Finally 152 bilateral surgical margins’ status (training dataset: n = 110, testing dataset: n = 38) were evaluated. The result demonstrated the segmentation algorithms were comparable, of which the new method might reduce the delineation work for future radiomics research.
|
|
1611. 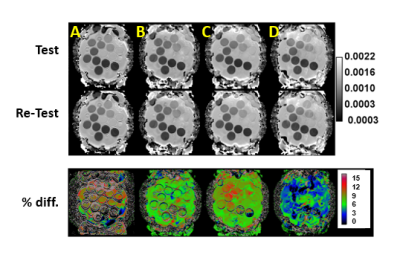 |
3 | Test-retest repeatability of ADC measurements using MUSE: Evaluation in phantoms and prostate
Fuad Nurili, Maggie Fung, Yulia Lakhman, Ricardo Otazo, David Yusupov, Elena Kaye, Oguz Akin, Yousef Mazaheri
In this study, we evaluated the repeatability of multiplexed sensitivity-encoding (MUSE) DW-EPI apparent diffusion coefficient measurements (ADC) in phantom and prostate images. High quality test-retest prostate and phantom ADC maps obtained from phantom and volunteer studies measured values using MUSE (2-4 interleaves) were within 1.4-4.7% (phantom) and 3.2-14.7% (prostate) of one another. In comparison, test-retest repeatability results for standard single-shot EPI (acceleration factor=2) were 4.5-9.4% (phantom) and 15.2-19.2% (prostate). MUSE images exhibit reduced geometric distortion.
|
|
1612. 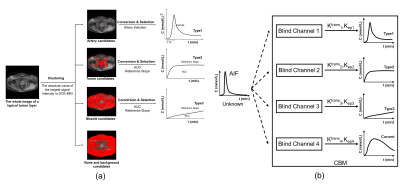 |
4 | A Fully Automatic Blind Estimation of Tumor Microvascular Permeability using Embedded Unsupervised Regularizations based on Prostate DCE-MRI
Junjie Wu, Ya Cao, Xiaodong Zhang, Xiaoying Wang, Jue Zhang
Vascular permeability can reflect tumorigenesis and metastasis. Previous dynamic contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance
|
|
1613 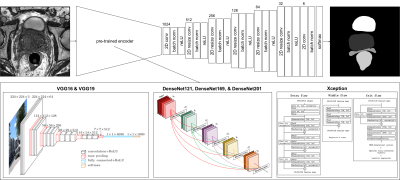 |
5 | Comparison of 12 different constructs of pre-trained convolutional encoders for semantic segmentation in prostate brachytherapy MRI Video Permission Withheld
Jeremiah Sanders, Steven Frank, Gary Lewis, Jingfei Ma
Anatomy contouring is essential in quantifying the dose delivered to the prostate and surrounding anatomy after low-dose-rate prostate brachytherapy. Currently, five anatomical structures including the prostate, rectum, seminal vesicles, external urinary sphincter, and bladder, are contoured manually by a radiation oncologist. In this work, we investigated six convolutional encoder-decoder networks for automatic segmentation of the five organs. Six pretrained convolutional encoders and two loss functions were investigated. This yielded twelve different models for comparison. Results indicated that classification accuracy of convolutional encoders pretrained on the ImageNet dataset positively correlated with semantic segmentation accuracy in prostate MRI.
|
|
1614. 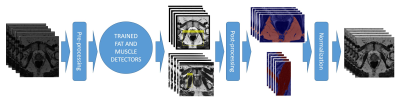 |
6 | Object Recognition for Fully Automated Reference Tissue Normalization of T2-weighted MR Images of the Prostate
Mattijs Elschot, Gabriel Nketiah, Mohammed Sunoqrot, Tone Bathen
T2-weighted MRI, an integrated part of multi-parametric MRI for prostate cancer diagnostics, is indispensable for qualitative evaluation of prostate anomalies. For quantitative assessment, however, normalization is necessary for comparison within and between patients. In this study, we developed and validated a fully automated object recognition method for multi-reference tissue normalization. The performance of the method was superior to existing fully automated normalization strategies, and the resulting pseudo T2 values were close to true T2 values from literature. The developed multi-reference tissue normalization method may thus improve the reproducibility and diagnostic performance of T2-weighted image features in future quantitative applications.
|
|
1615. 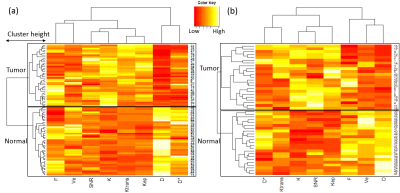 |
7 | Application of hierarchical clustering to multi-parametric MR in prostate: Differentiation of tumor and normal tissue with high accuracy
Yuta Akamine, Yu Ueda, Yoshiko Ueno, Takamichi Murakami, Masami Yoneyama, Makoto Obara, Marc Van Cauteren
Recently, machine learning (ML) or deep learning (DL) techniques has gain more attention for prostate cancer (PCa) detection. However, DL is often described as “black boxes” and difficult to explain results. In this study, hierarchical clustering (HC),an unsupervised ML technique, was applied to multi-parametric MR to differentiate PCa. DWI (IVIM and DKI) and permeability parameters were used for HC. Comparison of HC methods was conducted. We demonstrated that HC can accurately differentiate PCa and normal tissue (PZ: 97.5%, TZ: 95.7%), with an comparable to state-of-the-art D and K. Contrary to DL, HC produces results that can be interpreted (heatmaps).
|
|
1616. 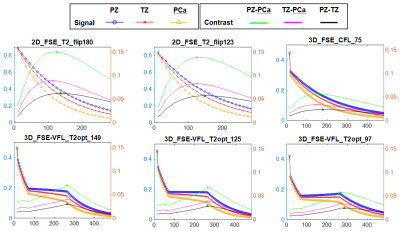 |
8 | Optimized 3D Variable Flip Angle Fast Spin Echo: Simulating Different Prostate Tissue Types to Improve Contrast for Prostate Cancer Detection
Steven Shea
MRI of the prostate has become a crucial component of prostate cancer diagnosis. Most clinical sites use 2D FSE for T2 imaging. However, drawbacks exist and some institutions have moved to 3D using FSE-VFL. While groups have presented clinical results using FSE-VFL, none have published detailed investigations of different flip angle trajectories and parameter choices for maximizing lesion contrast in prostate cancer imaging. Flip angle trajectories were simulated for 3D FSE-VFL using T1 and T2 appropriate for prostate and then tested in a phantom. Overall, signal simulations proved useful for analyzing different parameters and flip angle trajectories for T2-weighted sequences.
|
|
1617. 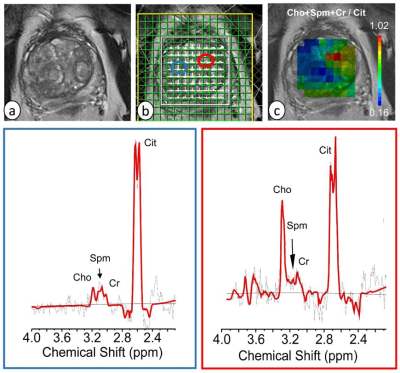 |
9 | Computer aided diagnosis of prostate cancer in central gland using GOIA-sLASER 1H MRS
Neda Gholizadeh, Peter Greer, John Simpson, Peter Lau, Arend Heerschap, Saadallah Ramadan
The aim of the work described in this paper is twofold. First, evaluate the efficacy of the GOIA-
|
|
1618. 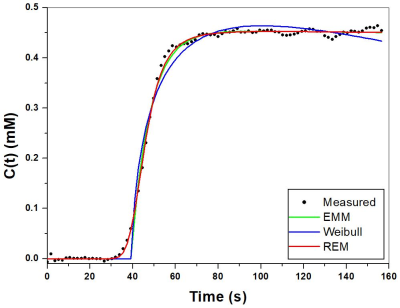 |
10 | New three-parameter mathematical model for accurately fitting early enhancement of ultrafast dynamic contrast enhanced MRI to improve diagnosis of prostate cancer
Xiaobing Fan, Aritrick Chatterjee, Shiyang Wang, Federico Pineda, Ty Easley, Aytekin Oto, Gregory Karczmar
Ultrafast DCE-MRI shows promise for detection of cancers. However, existing simple mathematical models do not have a smooth transition from baseline to early uptake phase and thus do not accurately model the early kinetics. Here we developed a new three-parameter model by combining a 4th-order rational and exponential function, namely REM (rational-exponential-model). Ultrafast prostate DCE-MRI was used to verify the accuracy of REM and compare the REM with two other models. The curvatures during initial enhancement and transition to washout were calculated. The REM characterized contrast agent kinetics for ultrafast DCE-MRI more accurately than previously developed models and thus improved diagnostic accuracy.
|
|
1619. 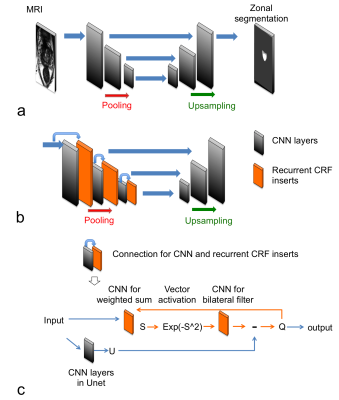 |
11 | Developments of Unet, Unet plus Conditional Random Field Insert, and Bayesian Vnet CNNs for Zonal Prostate Segmentation
Peng Cao, Susan Noworolski, Sage Kramer, Valentina Pedoia, Antonio Westphalen, Peder Larson
We studied 2d and 3d fully convolutional neural network for zonal prostate segmentation from T2 weighted MRI data. We also introduce a new methodology that combines Unet and conditional random field insert (CRFI) to improve the accuracy and robustness of the segmentation.
|
|
1620. 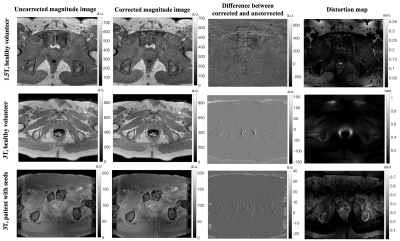 |
12 | Joint estimation of the field inhomogeneity and geometrical distortion for quantitative susceptibility mapping of the prostate
Reyhaneh Nosrati, Wilfred Lam, Ana Pejovic-Milic, Greg Stanisz
The geometrical distortions of MR images are potential source of error in MR-based radiation therapy planning (RTP) which requires accurate anatomical delineation. Beside the system-specific residual distortions, presence of any susceptibility-mismatch within the region of interest may lead to image distortion. We have recently proposed an algorithm based on quantitative susceptibility mapping (QSM) for post-implant dosimetry of prostate brachytherapy seeds. In this study, the undistorted field map in patients with and without implanted seeds was estimated and images were corrected accordingly, then QSM was performed. In patients with implanted seeds, distortion correction improved the accuracy of the QSM reconstruction.
|
|
1621. 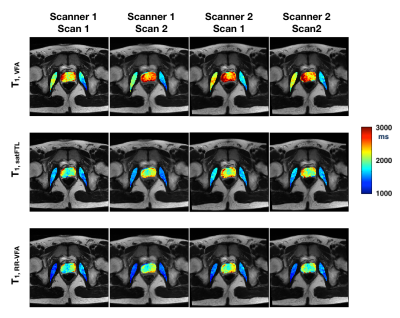 |
13 | Variable Flip Angle T1 Consistency with and without Compensating for B1+ inhomogeneity in 3T Prostate MRI
Xinran Zhong, Sepideh Shakeri, Dapeng Liu, James Sayre, Steven Raman, Holden Wu, Kyunghyun Sung
Reliable pre-contrast T1 estimation is crucial for quantitative DCE MRI. Variable flip angle is widely used for pre-contrast T1 measurements and is sensitive to B1+inhomogeneity. Although various B1+ techniques have been proposed, the application of B1+ compensation is not widely accepted yet. In this study, by evaluating T1 intra-scanner and inter-scanner consistency with and without B1+ compensation, we confirmed the necessity to perform B1+ compensation and a B1+ estimation method named reference region variable flip angle (RR-VFA) is recommended due to its consistent T1 estimation and wide availability.
|
|
1622. 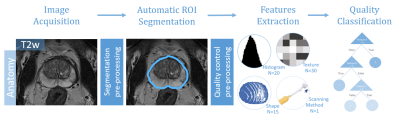 |
14 | A quality control system for automated prostate segmentation on T2-weighted MRI
Mohammed Sunoqrot, Kirsten Selnæs, Olmo Zavala-Romero, Radka Stoyanova, Tone Bathen, Mattijs Elschot
Computer-aided detection and diagnosis (CAD) systems have the potential to improve robustness and efficiency compared to traditional radiological reading of MRI in prostate cancer. Fully automated segmentation of the prostate is a crucial step of CAD. With the advent of the deep learning-based (DL) methods in medical imaging, series of networks have been developed to segment the prostate. Automated detection of poorly segmented cases would therefore be a useful supplement. Therefore, we proposed a quality control (QC) system to detect the cases that will result in poor prostate segmentation. The performance results shows that the proposed QC system is promising.
|
|
1623.  |
15 | Prostate cancer detection using an integrated slice-by-slice shimming acquisition scheme and three MR diffusion models: correlation with in-bore transperineal MR-guided biopsy
JIE BAO, Xi-ming Wang, Robert Grimm, Alto Stemmer, Zhong-shuai Zhang, Chun-hong Hu
Multiparametric magnetic resonance imaging (mpMRI) of the prostate gland is increasingly being used in the setting of newly diagnosed disease to identify occult, higher-grade, or stage elements missed by conventional biopsy. In this study, a prototype diffusion weighted single shot EPI sequence with integrated slice-by-slice shimming (iShim) technique was applied to reduce the susceptibility artifacts of DW images[1]. Conventional mono-exponential DWI, intravoxel incoherent motion (IVIM), and diffusional kurtosis imaging (DKI) models were applied to preoperatively predict prostate cancer (PCa)[2, 3]. Our research showed that the diffusion coefficient in the peripheral zone, mean kurtosis, and the PSA level in the transition zone are potential predictive biomarkers for PCa.
|
|
1624  |
16 | Automatic detection of prostate cancer lesion using various deep neural network in multi-parametric MRI combined including quantified parameters. Video Permission Withheld
Jinseong Jang, Jeong Kon Kim, Subeom Park, Won Tae Kim, Shin Uk Kang, Myung Jae Lee, Dongmin Kim
we used qualitative and quantitative parametric MRI in various deep convolutional neural networks for fully-automatic detection of prostate cancer. region. various deep neural networks were compared with pathology map-based ground truth. The 3D convolutional neural networks achieved the highest performance in our experiments.
|
|
1625. 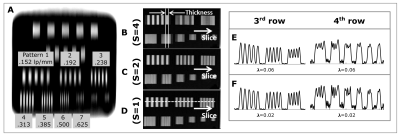 |
17 | Use of kz-Space for Sub-mm Through-Plane Resolution in Multi-slice MRI: Application to Prostate
Soudabeh Kargar, Eric Borisch, Adam Froemming, Roger Grimm, Akira Kawashima, Bernard King, Eric Stinson, Stephen Riederer
The goal of this work is to demonstrate sub-mm through-plane resolution in multislice T2SE MRI using kZ-space processing of overlapping slices and to show applicability in prostate MRI. Multiple overlapped slices are acquired and Fourier transformed in the slice-select direction. The slice profile is taken into account in the reconstruction using Tikhonov regularization. Sub-mm resolution is possible from 3.2mm thick slices. The method is applied to 16 consecutive subjects for whom prostate MRI was indicated. The in vivo results from prostate MRI show improved sharpness in the axial reconstructions when compared to the standard axial multislice method.
|
|
1626. 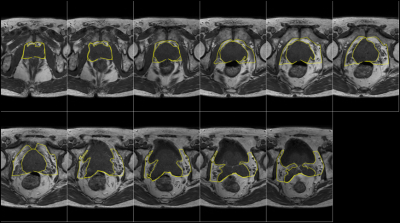 |
18 | Association of peri-prostatic adipose tissue (PPAT) and prostate cancer (PCa)
Qiong Ye, Qi Zhang, Zhao Zhang
The association between peri-prostatic adipose tissue (PPAT) and prostate volume (PV) was controversial in literatures. In our study, we adapted more reasonable definition of PPAT according to the observation during the surgery of radical prostatectomy (RP), and used histological finding from RP as reference, to explore the association between PPAT and PCa.
|
|
1627.  |
19 | Heterogeneous alternation of fat content of varied adipose deposits in prostate cancer patients
Qiong Ye, Zhao Zhang
Prostate cancer (PCa) is characterized with dysregulated lipid metabolism. The function and fat content of adipose deposits varied with anatomical location. In our study, we explored the characteristic alternation of fat content of adipose tissues and muscle of pelvic region in prostate cancer (PCa) patients using mDixon.
|
|
1628. 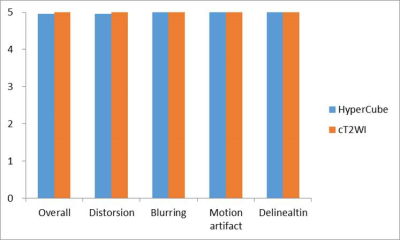 |
20 | Assessment of the prostate cancer with HyperCube T2-weighted imaging
Motoyuki Katayama, Takayuki Masui, Kazuma Terauchi, Mitsuteru Tsuchiya, Masako Sasaki, Kenshi Katayama, Takahiro Yamada, Mitsuharu Miyoshi
We compare delineation of prostate cancers in HyperCube T2WI with those in conventional T2WI using PIRADS. HyperCube 3D T2WI can provide useful information about prostate cancer, and contribute to the PI-RADS.
|
|
1629 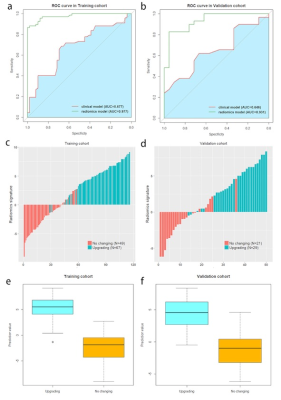 |
21 | Radiomics based on Multiparametric MRI for Predicting Upgrading of Prostate Cancer from Biopsy to Radical Prostatectomy Video Permission Withheld
Gumuyang Zhang, Yuqi Han, Jingwei Wei, Yafei Qi, Dongsheng Gu, Jing Lei, Yu Xiao, Weigang Yan, Huadan Xue, Feng Feng, Hao Sun, Zhengyu Jin, Jie Tian
The disparity of biopsy Gleason score of prostate cancer (PCa) with that of the corresponding radical prostatectomy (RP) remains an unsolved problem. We developed and validated radiomics model based on T2-weighted, fat-suppressed T2W, apparent diffusion coefficient and dynamic contrast enhancement images to predict upgrading from biopsy to RP. The radiomics model achieved the area under the curve values of 0.977 and 0.931 for the training and validation cohorts, and outperformed the clinical model combining clinical stage and time from biopsy to RP. The radiomics model could serve as a non-invasive tool for individualized prediction of upgrading of PCa.
|
|
1630. 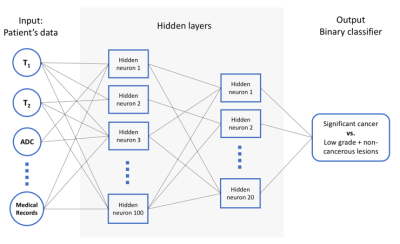 |
22 | MR Fingerprinting and Diffusion Mapping based Neural Network Classifier for significant prostate cancer characterization in Peripheral Zone and Transition Zone Presentation Not Submitted
Kun Yang, Ananya Panda, Verena Obmann, Jesse Hamilton, Katie Wright, Vikas Gulani
This study demonstrates the utility of a neural network classifier in separating significant cancer from low-grade cancer and non-cancerous lesions, based on the quantitative MRF and diffusion mapping. Using targeted biopsy data for training, the neural network classifier outperforms the linear regression model in both peripheral zone (PZ) and transition zone (TZ). The differentiation results showed an AUC of 0.90 in PZ and AUC of 0.89 in the TZ, comparing to AUC of 0.86 and 0.81 using Logistic Regression respectively. After applying the adaptive data oversampling algorithm, the AUC in characterizing TZ lesions can reach 0.96. Further classification utilizing patient clinical information showed statistically better accuracy in PZ while worse in TZ.
|
|
1631. 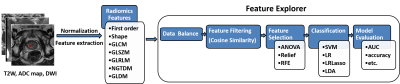 |
23 | Classification of prostate cancer by radiomics
Jing Zhang, Yu-dong Zhang, Yang Song, Xu Yan, Guang Yang
Timely diagnosis and treatment could effectively reduce patient risk for clinical significant prostate cancer (PCa). In this abstract, we extracted 327 quantitative features from prostate mp-MRI images, then we used a homemade open-source tool named Feature Explorer to study combinations of radiomics algorithms and hyper-parameters in order to find the best model for classification of PCa into non-clinical–significant and clinical significant. We obtained a candidate model with AUC of 0.823, accuracy of 0.827. Four features selected for classification are easily understandable in the sense of image characteristics. Feature Explorer was demonstrated to be an efficient tool for radiomics studies.
|
|
1632.  |
24 | Quantitative comparison of luminal water imaging with DWI for characterization of prostate cancer aggressiveness: early experience
Stefanie Hectors, Daniela Said, Jeffrey Gnerre, Ashutosh Tewari, Bachir Taouli
Luminal water imaging (LWI) is an emerging technique for noninvasive characterization of prostate cancer (PCa) aggressiveness. The goal of our ongoing study is to compare the diagnostic performance of LWI to DWI for assessment of PCa aggressiveness. We observed that the luminal water fraction (LWF) from LWI showed high diagnostic performance for differentiation between Grade Group (GG) 2 (i.e. Gleason 3+4) and GG 3 and higher (i.e. Gleason 4+3 and higher) cancers (AUC=0.86), while ADC showed an AUC of 0.62. These initial results suggest additional value of LWI for PCa characterization, which will be verified in a larger cohort.
|
|
1633. 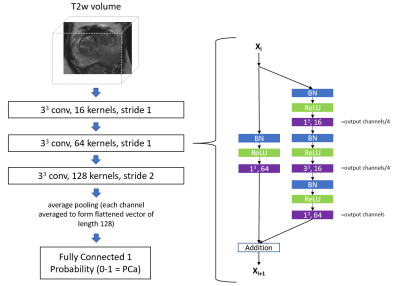 |
25 | A 3D convolutional neural network for diagnosing prostate cancer using volumetric T2-weighted MRI.
Pritesh Mehta, Michela Antonelli, Shonit Punwani, Sebastien Ourselin
In this work, we designed and evaluated a convolutional neural network for prostate cancer diagnosis using volumetric T2-weighted MRI. Our key contribution is a 3D implementation of a residual network (ResNet), optimised to perform a classification between patients with prostate cancer and patients with benign conditions. On this task, cross-validation on a dataset consisting of 240 patients, produced a mean area under the receiver operating characteristic curve of 0.78, which was on par with an experienced radiologist.
|
Digital Poster
| Exhibition Hall | 13:45 - 14:45 |
| Computer # | |||
1634. 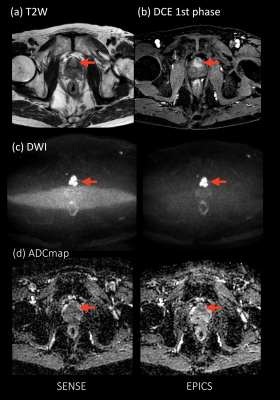 |
26 | Noise Reduction in Prostate Single-Shot DW-EPI utilizing Compressed SENSE Framework
Masami Yoneyama, Kosuke Morita, Johannes Peeters, Takeshi Nakaura, Marc Van Cauteren
DWI is a key component of the prostate MRI examination, but current prostate DWI images have limited resolution. Small-FOV DWI with SENSE often suffers from increased noise artifacts. We attempt to utilize a combination of parallel imaging and compressed sensing technique (C-SENSE) framework for reducing the noise artifacts in single-shot DW-EPI images (EPI with C-SENSE: EPICS). EPICS clearly reduces noise-like artifacts and significantly improves the accuracy and robustness of ADC values in small FOV high b-value prostate DWI compared with conventional SENSE DW-EPI, without any penalty for scan parameters.
|
|
1635. 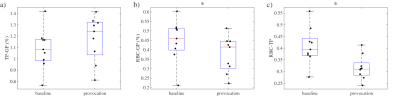 |
27 | Hyperpolarized 129Xe dissolved-phase MR detects physiological changes in human lungs after low-dose inhaled lipopolysaccharide challenge
Agilo Kern, Filip Klimes, Andreas Voskrebenzev, Marcel Gutberlet, Heike Biller, Julius Renne, Olaf Holz, Frank Wacker, Jens Hohlfeld, Jens Vogel-Claussen
Low-dose inhalation of lipopolysaccharide (LPS) provides a disease model in humans for development of anti-inflammatory drugs but sensitive methods for assessment of the inflammatory response to LPS are lacking. The feasibility of hyperpolarized 129Xe dissolved-phase imaging and chemical shift saturation recovery (CSSR) was investigated in this setting. The ratio of 129Xe in red blood cells and in tissue/plasma was found to decrease and the capillary transit time derived from CSSR was found to increase after LPS inhalation. These effects are attributed to pulmonary edema and vasodilation. In conclusion, hyperpolarized 129Xe MR is sensitive even for low-dose LPS challenges in humans.
|
|
1636. 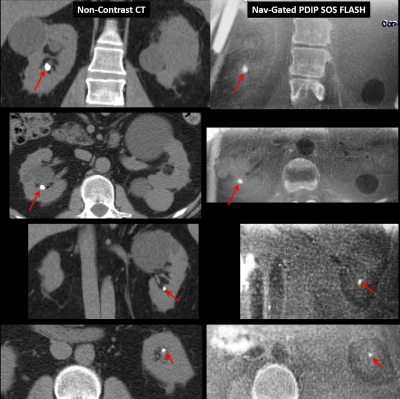 |
28 | Motion-Corrected Proton Density-Weighted In-Phase Stack-of-Stars (PDIP SOS) FLASH MR Imaging of Kidney Stone Disease
Robert Edelman, Emily Aherne, Sangtae Park, Jianing Pang, Ioannis Koktzoglou
Kidney stones affect 1 in 11 people in the United States and renal colic resulting from obstructing stones is a frequent cause of emergency department visits. Non-contrast CT of the abdomen and pelvis is the primary imaging test but has the drawback of exposing the patient to potentially significant amounts of ionizing radiation. A motion-corrected proton density-weighted in-phase stack-of-stars (PDIP SOS) FLASH pulse sequence was developed to provide a potential imaging alternative. Using this approach, we have demonstrated for the first time the feasibility of using MRI to detect kidney stones with image quality that is competitive to CT.
|
|
1637. 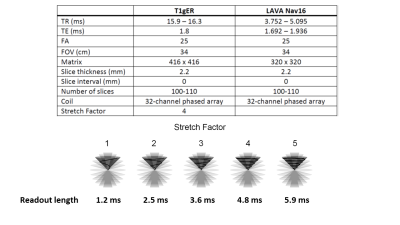 |
29 | Motion robust two-minute free-breathing hepatobiliary phase imaging of the liver using a golden-angle ordered conical acquisition with extended readout.
Ryan Brunsing, Joseph Cheng, David Zeng, Vipul Sheth, Signy Holmes, Shreyas Vasanawala
Imaging of the liver can be compromised by motion artifacts which are especially problematic in patients with breathing difficulties. Non-Cartesian k-space sampling trajectories are motion robust and have shown promise in hepatobiliary-phase (HBP) imaging of the liver. Here we demonstrate that free-breathing HBP imaging can be obtained using a 3D cones k-space trajectory with golden angle ordering and extended readout (T1gER). The protocol shows similar performance to a conventional respiratory navigated sequence and can be acquired in less than half the time.
|
|
1638. 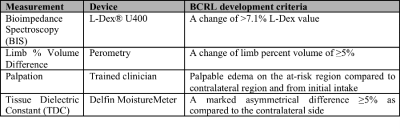 |
30 | Axillary MRI relaxometry as a tool for assessing risk of lymphedema development
Paula Donahue, Rachelle Crescenzi, Manus Donahue
We applied a novel application of T2 mapping in a longitudinal study to evaluate whether MRI relaxometry may hold more potential than current measures for portending breast-cancer-treatment-related-lymphedema (BCRL) progression. Baseline biophysical and T2 measurements were performed in patients following lymph node removal. Patients were then monitored for BCRL progression (duration=two years). Baseline descriptive (age, BMI, number of nodes removed) and biophysical (bioimpedance, tissue dielectric, and arm volume) measures did not discriminate between patients who did vs. did not progress, yet baseline T2 was regionally elevated in those who progressed. MRI relaxometry may serve as a tool to identify BCRL risk.
|
|
1639.  |
31 | Texture Analysis Comparison between MR and PET for Prostate Cancer MRI Guided Biopsy
Raisa Rasul, Joshua Cornman-Homonoff, Sadek Nehmeh, Daniel Margolis
PET scans can detect prostate lesions, locations in the prostate where biopsy could reveal about treatment strategy. PET has low resolution compared to MRI and doesn't show surrounding anatomy necessary for accessing the prostate. Texture feature maps in MRI might include information about lesion location. MRI prostate texture features maps were compared with superimposed PET scans. Preliminary data suggest correlation between PET intensity and PI-RADS score, and weak correlation between less texture and lesion location. Though low texture values might correlate with higher tumor recurrence risk and lead to improved MRI-guided biopsy, finding exact lesion location in MRI remains challenging.
|
|
1640.  |
32 | Cylinder 3D radial acquisition for reduced imaging artifacts and better resolution at 1.5 T
Yajing Zhang, Jiazheng Wang, Chenguang Zhao
We have developed a novel 3D radial sequence for motion insensitive MRI, which replaces the frequency encodings in the radial plane in prior-art stack-of-star sequences with stepwise phase encodings to reduce the streaking artifacts that can arise from chemical shifts and system imperfections. The sequence achieved better image homogeneity with less imaging artifacts when compared to the prior-art sequence at 1 mm isotropic resolution with golden angle acquisition, both in phantom and in human brain and abdomen imaging.
|
|
1641.  |
33 | How long a 4D-MRI do we need for abdominal radiotherapy treatment planning? A time dependence analysis of abdominal motion probability distribution function using ultra-fast volumetric dynamic MRI
Yihang Zhou, Jing Yuan, Oi Lei Wong, Kin Yin Cheung, Siu Ki Yu
Radiotherapy (RT) treatment planning (TP) based on probability distribution function (PDF) is an evolving approach for tumor motion management. In PDF-TP, the dose distribution is weighted by the probability of the tumor being in that location during the treatment, thus the determination of reliable tumor motion PDF from time resolved dynamic imaging, named 4D-imaging, is essential. Ideally, a 4D-MRI should be as long as or even longer than the real abdominal RT treatment to represent the real motion pattern and account for any motion irregularity in the treatment, but it is actually impractical. Thus, another unanswered question is how long a 4D-MRI scan is really needed in order to obtain a tumor motion PDF as reliable as possible but keep acquisition as short as possible. In this study, we aim to determine the optimal 4D-MRI duration for PDF-TP by analyzing the time dependency of different abdominal organs’ PDF using an ultrafast volumetric 4D-MRI.
|
|
1642. 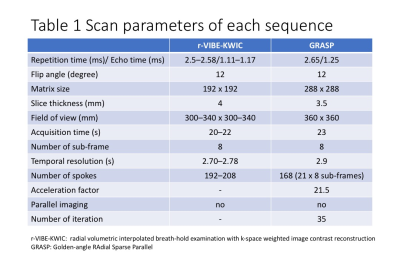 |
34 | Dynamic contrast-enhanced MRI of the liver: comparison between radial VIBE with k-space weighted image contrast reconstruction (r-VIBE-KWIC) and Golden-angle RAdial Sparse Parallel (GRASP)
Yasunari Fujinaga, Akira Yamada, Ayumi Ohya, Hirokazu Tokoro, Takeshi Suzuki, Hayato Hayashihara, Aya Shiobara, Yasuo Adachi, Yoshihiro Kitou, Marcel Nickel, Terumasa Takemaru, Hirokazu Kawaguchi, Katsuya Maruyama
We aimed to evaluate the differences of the DCE-MR images between radial VIBE with k-space weighted image contrast reconstruction (r-VIBE-KWIC) and Golden-angle RAdial Sparse Parallel (GRASP). DCE-MRI using r-VIBE-KWIC and GRASP was performed in 36 and 35 patients, respectively. The most optimal arterial phase image was selected from eight sub-frame images at arterial phase, and factors of image quality in the both two groups were assessed using five-point scales. In GRASP, the median scores for all factors except for one were significantly higher than those in r-VIBE-KWIC. In conclusion, GRASP provided the better DCE-MR images than r-VIBE-KWIC.
|
|
1643.  |
35 | Cerebral Venous Oxygenation in the Human Fetuses With Enlarged Ventricles Using QSM
Brijesh Yadav, Taotao Sun, Feifei Qu, E Haacke, Ling Jiang, Zhaoxia Qian
Fetal growth and development is a delicate process which relies on the optimal oxygen supply to the fetus. Obstruction to this supply might cause delayed myelination or white matter damage which in turn, may lead to enlargement of cerebral ventricles. therefore, cerebral venous oxygenation (SvO2) was estimated in second and third trimester fetuses with enlarge ventricles using quantitative susceptibility mapping. Average SvO2 was found to be 68.2%±5.1% and a decreasing trend in SvO2 across gestation was observed in the fetal cohort with enlarge ventricles.
|
|
1644 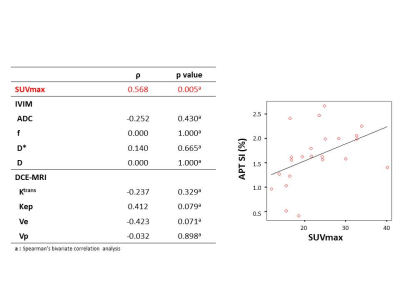 |
36 | Amide proton transfer imaging for rectal cancer: correlation with IVIM, DCE MRI and 18F-FDG-PET/CT Video Permission Withheld
Yuichi Kumagae, Yoshihiko Fukukura, Hiroto Hakamada, Hiroaki Nagano, Jochen Keupp, Yuta Akamine, Takashi Yoshiura
This study focused on the correlation between amide proton transfer (APT) imaging and IVIM, DCE MRI or 18F-FDG PET/CT in rectal cancer. Our results showed a significant positive correlation between APT signal intensity (APT SI) and SUVmax (p = 0.005, ρ = 0.547). No significant correlation was shown between APT SI and IVIM (ADC, f, D* or D) or DCE MRI parameters (Ktrans, Kep, Ve or Vp). These results suggested that APT imaging reflects some metabolism of the rectal cancer and may be useful for response prediction after chemotherapy.
|
|
1645 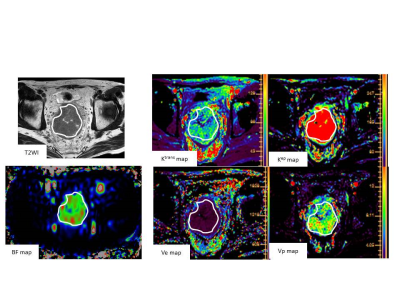 |
37 | Pseudo continuous arterial spin labeling perfusion MRI of advanced rectal cancer: utility in predicting response to neoadjuvant chemotherapy Video Permission Withheld
Yuichi Kumagae, Yoshihiko Fukukura, Hiroto Hakamada, Hiroaki Nagano, Masanori Nakajo, Tomoyuki Okuaki, Takashi Yoshiura
This study focused on the feasibility of pseudo continuous arterial spin labeling (pCASL) perfusion MRI as a tool for predicting the response of advanced rectal cancer treated with neoadjuvant chemotherapy. Correlation between reduction rate of rectal cancer after chemotherapy and blood flow (BF) derived from pCASL or DCE MRI parameters within tumors was evaluated. Our results showed significant positive correlations between tumor reduction rate and BF (p = 0.001, ρ = 0.644) or Ktrans (p = 0.003, ρ= 0.579). These results suggested pCASL may have the potential to predict the treatment response of neoadjuvant chemothoerpy for advanced rectal cancer.
|
|
1646. 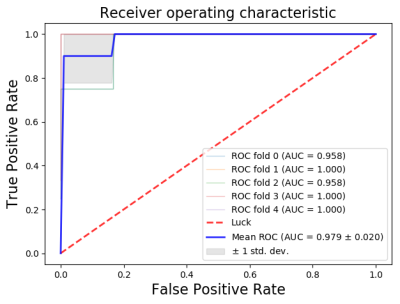 |
38 | Radiomics Based on MR Imaging of Rectal Cancer: Assess Treatment Response to Neoadjuvant Chemoradiotherapy
Fu Shen, Jie Li, Jianping Lu
The goal of this study was to investigate the value of high resolution T2-weighted–based radiomics in prediction of treatment response to neoadjuvant chemoradiotherapy (nCRT) in patients with locally advanced rectal cancer (LARC). The result demonstrated that the MRI based radiomics machine learning model could assess tumoral treatment response to nCRT in patients with LARC.
|
|
1647. 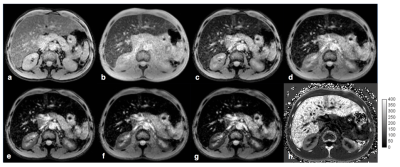 |
39 | MRI-based R2* Mapping in Patients with Suspected or Known Iron Overload
An Lesage, Philippe Paquin, Jack Luo, Milena Cerny, Anne Shu-Lei Chin, Damien Olivié, Guillaume Gilbert, Denis Soulières, An Tang
The purpose of this study is to analyze the cross-sectional relationships of MRI-based R2* relaxometry values in organs across patients with various types of iron overload. Further analyses were conducted to analyze R2* values in organs according to the treatment regimen of patients (transfusion, phlebotomy, and chelation therapy). This retrospective, cross-sectional study includes 82 adult patients with known or suspected iron overload due to primary and secondary hemochromatosis. Results revealed differences between degree of iron overload in organs according to the underlying pathology and treatment regimens.
|
|
1648. 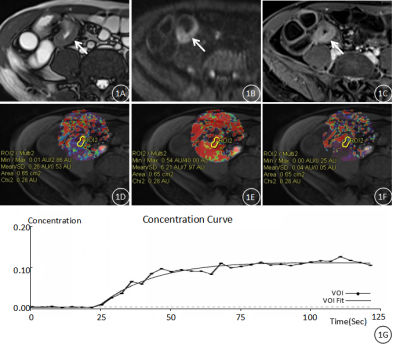 |
40 | MRI Quantitative Parameters of Small-Bowel Perfusion for Early Diagnosing and Assessing Activity of Crohn’s Disease: A Preliminary Study Presentation Not Submitted
Xianying Zheng
The purpose of this present study is to explore the potential of MR small-bowel perfusion, and to achieve more insights in MRE of CD patients. To this end, the changes of microcirculation of CD are investigated by comparing the quantitative parameters of MR perfusion of inflammatory segments with normal ones and the correlation of the former with CDAI and intestinal wall thickness.
|
|
1649. 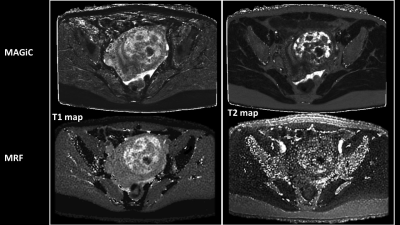 |
41 | Comparison of MAGiC and MR Fingerprinting for Quantitative Relaxation of T1 and T2 Maps in Female Pelvis
Gigin Lin, Guido Buonincontri, Jianxun Qu, Ching-Yi Hsieh, Chien-Yuan Lin
T1 and T2 mapping of tissues provides valuable information for characterization of tissue pathologies but is limited by long scan time and consequently hampered the clinical practice. Magnetic resonance image compilation (MAGiC) and Magnetic resonance fingerprinting (MRF) are novel imaging techniques to simultaneously provide quantitative maps of tissue relaxation times in a single acquisition. This study aimed to compare the quantitative values of T1 and T2 in the female pelvic region using the MAGiC and MRF.
|
|
1650. 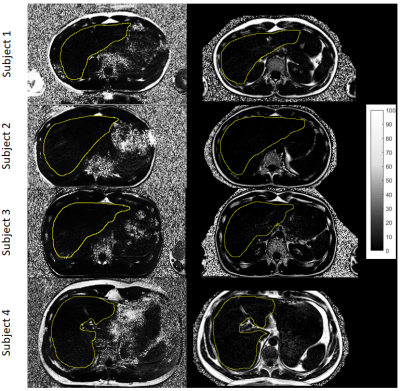 |
42 | Feasibility of abdominal quantitative imaging at 7T: pilot study.
Radim Korínek, Korbinian Eckstein, Zenon Starcuk jr., Siegfried Trattnig, Martin Krššák
This work demonstrates abdominal proton density fat fraction (PDFF)-MRI quantification at 7T magnetic field. Four healthy volunteers with low liver fat infiltration assumption were measured with a 3D-MGE-T1w sequence using 32-channel Rx/Tx array coil at 7T whole body MR scanner. 7T data were reconstructed by complex-based multiecho water-fat separation methods. The same volunteers were measured at a 3T MR system with multiecho Dixon MRI and multiecho single voxel MRS as reference measurements. The results show the feasibility of quantitative liver imaging at 7T.
|
|
1651. 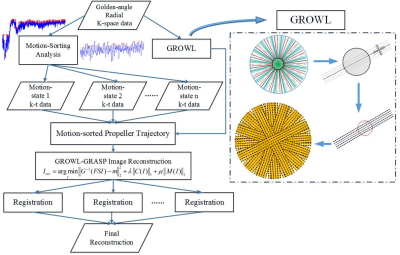 |
43 | RM-GROWL-GRASP: Image Registration Involved Two-step Motion Compensation System for Real-time Non-Cartesian Liver DCE-MRI
Zhifeng Chen, Peiwei Yi, Zhongbiao Xu, Jucheng Zhang, Yingjie Mei, Xia Kong, Zhenguo Yuan, Yaohui Wang, Ling Xia, Yanqiu Feng, Feng Liu
Motion is an inescapable problem in abdominal MRI. Involuntary organ movements caused mainly by respiratory often results in motion artifacts and image details blurring in liver MRI. For dynamic imaging, motion also harms temporal information. Recently, high spatiotemporal resolution free-breathing liver DCE-MRI have attracted much attentions of radiologists and scholars. We propose to combine mutual-information-based image registration with motion-sorted GROWL-GRASP approach for golden-angle radial liver DCE-MRI, which enable free-breathing imaging. The results demonstrate that better image quality including SNR benefit, lower motion artifacts and more diagnostic information can be generated compared to current motion compensation methods.
|
|
1652.  |
44 | Multi-frequency spin echo- magnetic resonance elastography (SE-MRE) to non-invasively assess kidney allograft injury - preliminary findings
Eyesha Hashim, Prateek Kalra, Arunark Kolipaka, Darren Yuen, Anish Kirpalani
Chronic allograft injury (CAI) is typically indicated too late with blood work and its cause is determined invasively (e.g. via biopsy). It is thus important to develop non-invasively tools to identify CAI early. We used multi-frequency spin-echo magnetic resonance elastography (SE-MRE) to assess shear modulus as an estimate of CAI in a group of kidney allograft patients with stable but sub-normal graft function. We observed a negative trend approaching significance, between the graft function as determined by estimated glomerular filtration rate and the shear modulus at 90Hz suggesting that SE-MRE can potentially be used for non-invasive assessment of renal injury.
|
|
1653.  |
45 | Towards systematic evaluation of velocity-selective ASL in the measurement of placental perfusion
Anita Harteveld, Jana Hutter, Suzanne Franklin, Laurence Jackson, Mary Rutherford, Joseph Hajnal, Matthias van Osch, Clemens Bos, Enrico De Vita
The placenta’s role as a nutrient and oxygen source for the fetus highly depends on blood supply and thus perfusion may be a sensitive marker of placenta function. Velocity-selective arterial spin labeling (VSASL) placental perfusion measurements have previously been demonstrated using standard parameter settings from the brain. In this study, the influence of different VSASL parameter settings was assessed to optimize measurement of placental perfusion. The results of this study will improve our understanding and interpretation of the measured perfusion signals in the placenta.
|
|
1654. 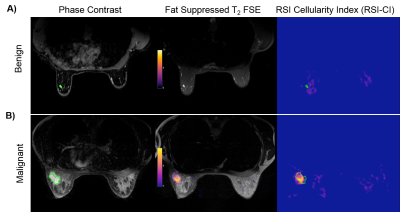 |
46 | Delineating Benign from Malignant Breast Lesions Using Restriction Spectrum Imaging
Alexandra Besser, Ana Rodriguez-Soto, Hauke Bartsch, Helen Park, Andrew Park, Haydee Ojeda-Fournier, Anders Dale, Rebecca Rakow-Penner
Non-contrast diffusion MRI holds great potential to screen women for breast cancer. Restriction spectrum imaging (RSI) is an advanced diffusion-weighted imaging (DWI) technique that reflects the high nuclear to cytoplasm ratio observed in cancer cells. This abstract explores RSI as a technique to non-invasively identify malignant from benign masses on non-contrast MRI by measuring RSI cellularity index (RSI-CI). Biopsy-proven malignant masses demonstrate high cellularity index compared to benign lesions. In this pilot study, RSI differentiates malignant from benign masses without contrast imaging, and could prove useful as a screening tool.
|
|
1655. 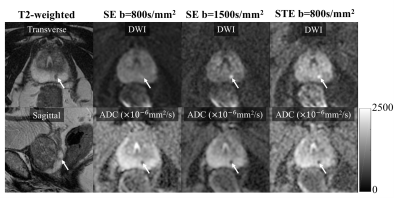 |
47 | Reducing T2-shinethrough effects in prostate diffusion-weighted imaging with Stimulated Echo imaging
Yuxin Zhang, Shane Wells, Benjamin Triche, Frederick Kelcz, Diego Hernando
The bright appearance of long-T2 tissues in DWI, termed “T2-shinethrough”, reduces the contrast between healthy tissue and cancer and is prominent in spin-echo based DWI acquisitions. In prostate DWI, the need to avoid T2-shinethrough has led to the acquisition of very high b-values in clinical practice, which may result in low SNR and other image artifacts. In this work, we have assessed the ability of stimulated-echo DWI to provide high contrast between PCa and healthy peripheral zone, without the need for high b-values. Preliminary results in 19 patients show reduced T2-shinethrough effects in stimulated-echo DWI compared with spin-echo DWI.
|
|
1656. 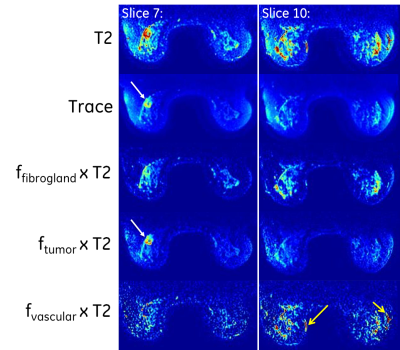 |
48 | Denoising and Multi-Compartment Visualization of Multi-b-Valued Breast Diffusion MRI
Ek Tan, Lisa Wilmes, Nola Hylton, Thomas Chenevert, David Newitt
Multi-b-valued diffusion-weighted imaging (DWI) of the breast is highly susceptible to image and fitting noise. A multi-compartment approach was developed to denoise multi-b-value breast DWI without spatial smoothing. In human subject exams (N=12), the denoising approach resulted in a significant reduction in variability of all perfusion and diffusion maps in breast tumor and normal fibroglandular tissue with minimal bias to the mean values, and increased statistical separation of diffusivity metrics between tumor and normal tissue. The denoising algorithm provides compartment fractions for tumor, tissue, and vascularity, which may improve visualization of tissue compartments in DWI.
|
|
1657. 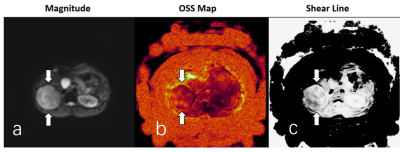 |
49 | Slip-interface imaging preoperatively predicts hepatocellular carcinoma microvascular invasion
Bing Hu, Ziying Yin, Kevin J. Glaser, Ying Deng, Sichi Kuang, Li Quan, Jun Chen, Arvin Arani, Meng Yin, Sudhakar K. Venkatesh, Richard L. Ehman, Jin Wang
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is the most common type of primary liver cancer in adults. One of the most strongly correlated factors predicting outcome is the presence or absence of vascular invasion. Since microvascular invasion cannot be found with conventional CT or MRI examination, we investigated whether slip-interface imaging (SII) could identify HCC microvascular invasion. The results showed that in 32 of 33 patients with HCC, SII-assessed microvascular invasion agreed with pathology, indicating that this technique may become useful for detecting HCC microvascular invasion and guiding treatment planning.
|
Digital Poster
| Exhibition Hall | 13:45 - 14:45 |
| Computer # | |||
1658 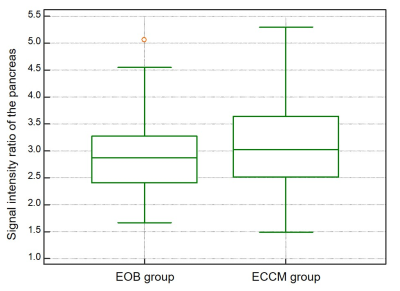 |
51 | Detection of Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma and Liver Metastases: Comparison of Contrast-enhanced MR Imaging with Ga-EOB-DTPA and Extracellular Contrast Materials Video Permission Withheld
Yoshifumi Noda, Satoshi Goshima, Yukiko Takai, Nobuyuki Kawai, Hiroshi Kawada, Yukichi Tanahashi, Kimihiro Kajta, Masayuki Matsuo
Ga-EOB-DTPA-enhanced MR imaging is well established imaging modality for the detection of liver metastases. On the other hand, it is expected that the arterial enhancement of solid organs is weaker comparing with extracellular contrast materials (ECCMs) because of its lower dosage. Our results demonstrated that the signal intensity ratio of the pancreas, tumor-to-pancreas contrast-to-noise ratio, and diagnostic performance for detecting pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC) were comparable, but the sensitivity for detecting liver metastases was better in Ga-EOB-DTPA compared with ECCMs, which suggests the usefulness of Ga-EOB-DTPA for evaluating patients with PDAC.
|
|
1659. 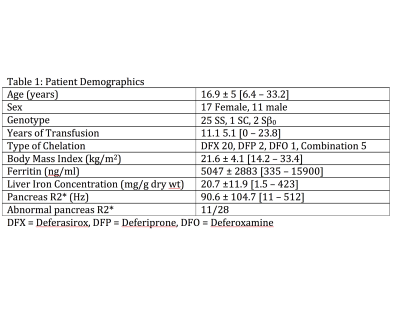 |
52 | Pancreatic and hepatic iron predict prediabetes in chronically transfused patients with sickle cell disease.
Andrew Cheng, Thomas Coates, John Wood
Pancreatic iron is common in transfused sickle cell disease(SCD) patients but the functional significance is unknown. We compared pancreatic function with hepatic and pancreatic iron burden by MRI in 28 SCD patients. Six patients had impaired fasting glucose(IFG) values and one had impaired glucose tolerance. Insulin resistance was positively associated with body mass index and negatively associated with liver iron concentration (r2 = 0.50, p<0.004). Liver iron and serum ferritin predicted IFG with an AUROC of 0.82 and 0.86 respectively. Beta cell function was inversely proportional to pancreatic R2* (r2 = 0.17, p=0.01). Thus, prediabetic changes were common and related to liver and pancreatic iron.
|
|
1660. 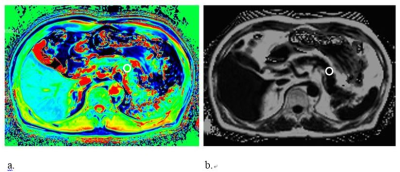 |
53 | MR measurement of T1 relaxation time and fat signal fraction of the pancreas: Association with HbA1c values
Mayumi Higashi, Masahiro Tanabe, Katsuyoshi Ito
The purpose of this study was to evaluate the association of the T1 relaxation time and FSF of the pancreatic parenchyma measured by MRI with HbA1c value. The T1 relaxation time on the T1 map images with fat suppression and FSF on fat fraction images of the pancreatic parenchyma were measured. We assessed the correlation between the MRI measurements and HbA1c values. The FSF (%) of the pancreatic parenchyma was significantly correlated with HbA1c values while the T1 relaxation times were not. The FSF (%) of the pancreas may be a potential imaging biomarker for impaired glucose tolerance.
|
|
1661. 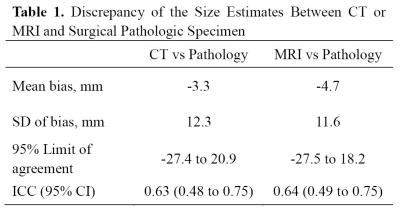 |
54 | Pancreatic adenocarcinoma: Variability in measurements of tumor size among CT, MRI and pathologic specimen
Chao Ma, Panpan Yang, Yun Bian, Jing Li, Li Wang, Jianping Lu
The aim of the study is to investigate the measurements obtained from the preoperative contrast-enhanced both computed tomography (CT) and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) with pathologic specimen in measuring the size of pancreatic cancer. It was found in this study, both contrast-enhanced CT and MRI underestimate mean tumor size by 3.3 mm and 4.7 mm respectively, when compared with the size of pathologic specimen.
|
|
1662. 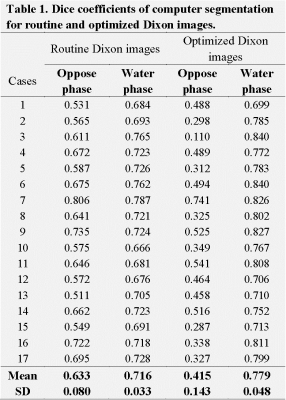 |
55 | Computer-aided pancreas segmentation based on 3D GRE Dixon MRI
Chao Ma, Xiaoliang Gong, Panpan Yang, Yufei Chen, Chaolin Du, Caixia Fu, Xu Yan, Jianping Lu
Pancreas segmentation is of great significance for pancreatic cancer radiotherapy positioning, pancreatic structure and function evaluation, etc. In the study, we purposed a simple computer-aided pancreas segmentation method based on 3D GRE Dixon images by using a free open source software system.
|
|
1663. 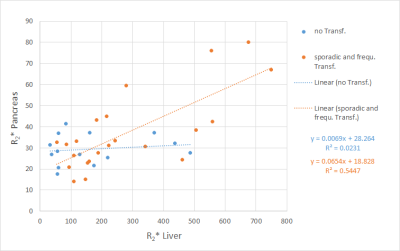 |
56 | MRI Relaxometry: Comparing R2* Values in Liver and Pancreas with respect to Disease Characteristics
Arthur Wunderlich, Stephan Kannengießer, Lena Kneller, Berthold Kiefer, Holger Cario, Meinrad Beer, Stefan Schmidt
To study pancreatic iron accumulation in liver overloaded patients with respect to disease characteristics, 116 patients were investigated at 1.5 T MRI with a prototype breathhold 3D GRE protocol with in-line R2*calculation. Mean R2* values were determined in liver and pancreas by manually drawn ROIs. Pancreatic R2* values were correlated with liver R2* in patient subgroups according to transfusion frequency. Pancreatic R2* correlated significantly to liver R2* for sporadic or frequently transfused patients, was normal in patients requiring no transfusion, and elevated in most regular transfused patients. After bone marrow transplant, most patients showed only slightly raised pancreatic R2*.
|
|
1664.  |
57 | Quantitative dynamic contrast-enhanced MR imaging for prediction of the response to gemcitabine in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma: a preliminary study Presentation Not Submitted
TANG WEI, Cai-xia Fu, Wei LIU, Wei-jun PENG
This study aimed to explore the feasibility of dynamic contrasted enhancement MRI (DCE-MRI) for predicting the response to gemcitabine in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma, as well as the influence of different region of interests (ROIs) on quantitative parameters. We compared the differences of DCE-MRI parameters between responders and non-responders. Kep based on periphery ROI was the best predictive marker, showed the highest areas under ROC curve (AUC) of 0.806. Quantitative DCE-MRI may be a feasible method, and the parameters are useful for the prediction of response to gemcitabine in patients with PAC. The positions of ROI influenced the DCE-MRI parameters.
|
|
1665.  |
58 | Quantification of Pancreatic Fat Content in Patients with Essential Hypertension using IDEAL-IQ sequence
Zhang Qinhe, Liu Ailian, Xie Lizhi
The study aims to assess the pancreatic fatty quantitation in patients with hypertension using IDEAL-IQ. IDEAL-IQ is a new way to evaluate the pancreatic fat quantification in patients with hypertension. The fat fraction of the pancreas in patients with hypertension is significantly higher than that in normal subjects,and the longer the length of the duration of the disease is, the higher the fat fraction of the pancreas is.
|
|
1666.  |
59 | Differentiation of Pancreatic Head Ductal Adenocarcinoma from Inflammatory Pancreatic Pseudomass by MR Cholangio-pancreatography: Utility of the Duct-interrupted, Corona and Attraction Signs
Alejandro Garces-Descovich, Kevin Beker, Leo Tsai, Karen Lee, Tarek Hegazi, Alexander Brook, Adrian Jaramillo-Cardoso, Koenraad Mortele
To properly treat and determine a truthful prognosis, accurate pancreatic head mass differentiation is fundamental. Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC) of the head and inflammatory pancreatic pseudomass (IPP) simulate significantly to each other in clinical imaging. We proposed the use of three radiological signs ("duct-interrupted”, “
|
|
1667. 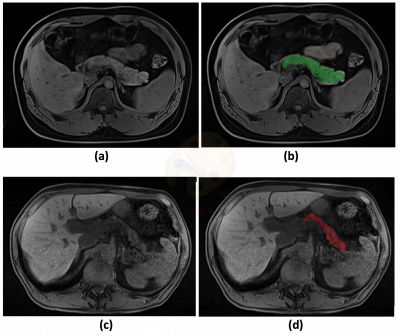 |
60 | Radiomics of Magnetic Resonance Imaging of Pancreas-Towards Improved Diagnosis and Management of Pancreatic Cancer
Touseef Ahmad Qureshi, Lixia Wang, Srinivas Gaddam, Nan Wang, Zixin Deng, Simon Lo, Andrew Hendifar, Zhaoyang Fan, Stephen Pandol, Debiao Li
The MRI-based Radiomics of pancreas can identify several imaging-characteristics (e.g. texture, shape, signal intensity, etc.) that are distinct in healthy and cancerous pancreas. We performed MRI-based radiomics of pancreas to demonstrate that radiomics play an important rule to differentiate healthy and cancerous pancreas and can assist diagnosis and management of PC. Multiple statistical tests demonstrated that 18% of the total 250 radiomic features were significantly different between healthy and cancerous pancreas. These features have high diagnostic accuracy to detect PC. We conclude that MRI-based radiomics of pancreas can potentially have a future role in early detection, prognosis, and prediction of treatment outcome of PC.
|
|
1668. 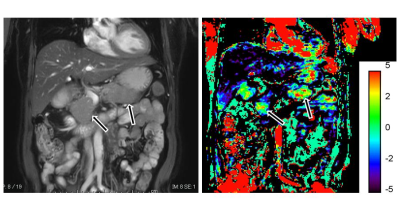 |
61 | Usefulness of amide proton transfer imaging in the evaluation of autoimmune pancreatitis activity
Yoshihiko Fukukura, Yuichi Kumagae, Hiroto Hakamada, Hiroaki Nagano, Takashi Iwanaga, Jochen Keupp, Yuta Akamine, Takashi Yoshiura
This study focused on the potential of amide proton transfer (APT) MR imaging at 3.0T as an objective imaging biomarker in patients with autoimmune pancreatitis (AIP). Correlation of serum immunoglobulin G4 (IgG4) levels with APT SI, the apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) values or the maximum standardized uptake value (SUVmax) on 18F-fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography (18F-FDG PET) was evaluated in eleven patients with AIP. Our results showed a significant positive correlation between serum IgG4 levels and APT signal intensity (SI). Therefore, APT imaging might be useful for monitoring AIP activity.
|
|
1669. 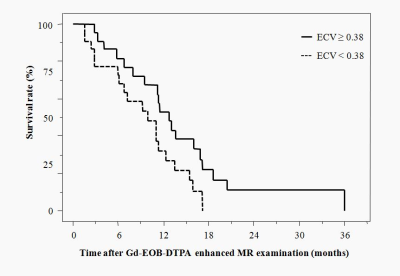 |
62 | Extracellular volume fraction on Gd-EOB-DTPA-enhanced MRI for predicting overall survival in patients with metastatic pancreatic adenocarcinoma
Yoshihiko Fukukura, Yuichi Kumagae, Hiroto Hakamada, Hiroaki Nagano, Kiyohisa Kamimura, Tomohide Yoneyama, Masanoari Nakajo, Takashi Yoshiura
This study focused on the potential of extracellular volume (ECV) fraction measured by Gd-EOB-DTPA-enhanced MRI as a prognostic factor in patients with metastatic pancreatic adenocarcinomas. The effect on survival of variables including age, sex, tumor location, tumor size, TNM factors, serum carbohydrate antigen (CA) 19-9 and carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA) levels and tumor ECV fraction was assessed in patients with metastatic adenocarcinoma. Our results showed that pancreatic adenocarcinoma with higher ECV fraction had
|
|
1670. 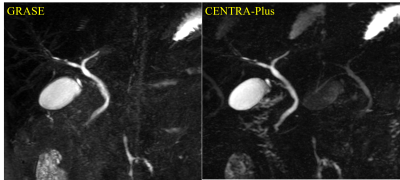 |
63 | Robust Breath-hold Three-Dimensional (3D) MRCP using Contrast-Enhanced Timing Robust Acquisition Order with a Preparation of the Longitudinal Signal Component(CENTRA-Plus) Technique at 3T
Yoshihiro Ikeda, Yasuhiro Goto, Masami Yoneyama, Isao Shiina, Yutaka Hamatani, Kazuo Kodaira, Yu Nishina, Satoru Morita, Shuji Sakai
The present study investigates the clinical utility of motion-insensitive breath-hold 3D MRCP using contrast-enhanced timing robust acquisition order with a preparation of the longitudinal signal component(CENTRA-Plus). 3D MRCP image derived from breath0holding with CENTRA-Plus showed good correlations to those from conventional respiratory triggering technique. Breath hold 3D MRCP with CENTRA-Plus can reduce scan time (around 80% of the scan time) without any penalty for the image quality; therefore, it might contribute to great advantages in routine clinical work.
|
|
1671.  |
64 | Quantitative dynamic contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging as a potential tool for preoperative predicting the response to neoadjuvant chemotherapy in locally advanced gastric adenocarcinoma
Yongjian Zhu, Ying Li, Jun Jiang, Wen Zhang, Liming Jiang, Lizhi Xie
Dynamic contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging (DCE-MRI) has been applied in diagnosis of different cancers, however its potential in gastric cancer has not been fully explored. In this study, we research into the value of DCE-MRI parameters in evaluating the response to chemotherapy in gastric cancer. It was found that the Ktrans and Ve values showed good predictive performance through distinguishing responders from non-responders, which could provide effective technical assistance for the choice of clinical treatment.
|
|
 |
1672. 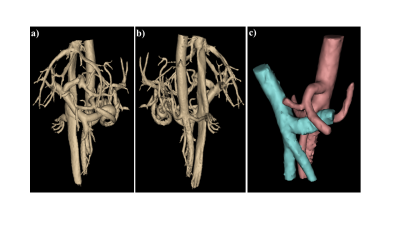 |
65 | Pulsatility and Resistivity Indices in Mesenteric Vasculature in Patients Suspected of Chronic Mesenteric Ischemia using 4D Flow MRI
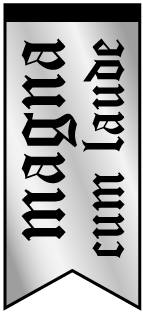
Grant Roberts, Christopher Francois, Alejandro Roldan-Alzate, Oliver Wieben
Chronic mesenteric ischemia (CMI) causes blood flow reduction in the intestines, often due to atherosclerosis. This study uses 4D flow MRI to quantify and compare pulsatility (PI) and resistivity indices (RI) in
|
 |
1673. 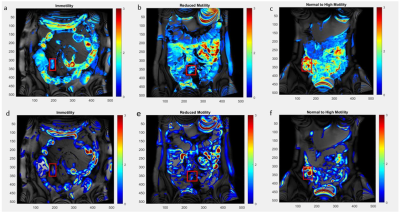 |
66 | Assessment and Classification of Motility of Terminal Ileum in Crohn’s Disease on Cine Magnetic Resonance Enterography
Basak Bayrambas, Esin Ozturk-Isik, Oktay Algin
Crohn’s disease is an inflammatory bowel disease mostly affecting motility in terminal ileum of small bowel. In this study, cine magnetic resonance enterography scans were used to assess the terminal ileum motility. Motility was quantified using optical flow based and gradient based analysis. ROC statistical analysis showed that immotility and motility were separable with 87% accuracy when analyzed with optical flow based algorithm and 89% accuracy with gradient based algorithm. The best classification accuracy of 90.5% was obtained when both optical flow and gradient based analysis results were used as features to train a kNN algorithm with 15-fold cross validation.
|
1674. 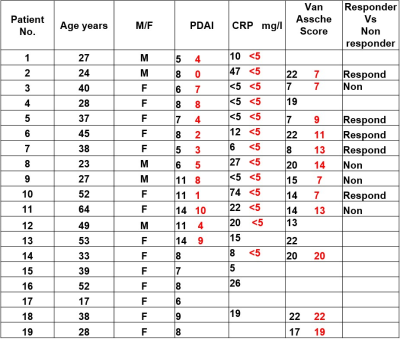 |
67 | A new MR-based Perianal Crohn’s disease activity score: Multicentre study
Ali Alyami, Caroline Hoad, Konstantinos Argyriou, White Jonathan, Uday Bannur, Khalid Latief, Christopher Clarke, Phillip Lung, Penny Gowland, Gordon Moran
Perianal Crohn’s disease (pCD) is a potential complication in CD. Absence of reliable disease measures makes disease monitoring unreliable. MRI is an effective imaging method for the evaluation of patients with pCD. Quantitative MRI sequences, such as diffusion-weighted image (DWI), and magnetization transfer (MT) offer opportunities to improve diagnostic capability. The aim of this study was to measure disease activity within a pCD patient cohort using quantitative MRI sequences (DWI and MT), at different field strengths, before and after biological therapy. The study is ongoing with patients presenting with a range of clinical and inflammatory markers of disease activity.
|
|
 |
1675.  |
68 | Quantification of MT in the bowel wall from the z-spectrum
Andrew Carradus, Olivier Mougin, Hannah Williams, Caroline Hoad, Penny Gowland
We have developed a protocol able to measure and quantify MT in the bowel wall through acquisition of the z-spectrum at 3T, and have developed a protocol capable of eliminating respiratory artefacts which have the potential to invalidate MT abdominal imaging.
|
1676. 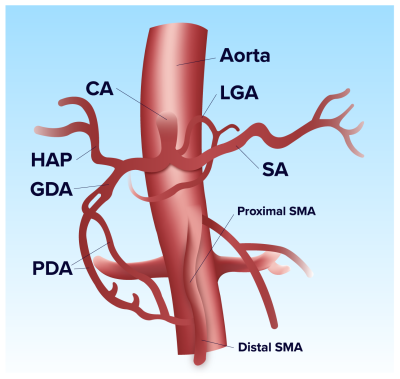 |
69 | Pre and Postprandial Hemodynamics of the Gastroduodenal Artery in Patients Suspected of Chronic Mesenteric Ischemia using 4D Flow MRI
Grant Roberts, Christopher Francois, Alejandro Roldan-Alzate, Oliver Wieben
Chronic mesenteric ischemia (CMI) causes reduced intestinal blood flow, often from mesenteric occlusions. However, collaterals exist and help compensate for reduced blood flow. This study utilizes 4D flow MRI to quantify hemodynamics in the gastroduodenal artery (GDA), a collateral between the celiac and superior mesenteric arteries, in controls (N=14) and patients suspected of CMI (N=14) before and after a meal. There was no significant difference in preprandial, postprandial, or percent flow change values between groups. However, pathology-dependent flow patterns were evident within the ischemia group. Follow-up studies with larger cohorts are warranted to further examine this finding.
|
|
1677.  |
70 | Radiomics features of gastrointestinal stromal tumors (GISTs) based on whole-tumor analysis: the robust imaging biomarkers to stratification and monitoring purpose
ziling zhou, zhen li, jingyu lu, hao yu, daoyu hu, yaqi shen
The diagnosis and treatment plans of GISTs are relied on pathological confirmation, yet the biopsy for unresectable GISTs cannot always provide comprehensive information, which will have an impact on the treatment plan and duration. Radiomics features based on whole tumor analysis have been confirmed as a robust imaging biomarkers with good repeatability in some solid tumors. The present study using the method described above to analyze a group of patients with pathological confirmed GISTs, to determine which radiomics features are useful for stratification and monitoring purpose.
|
|
1678. 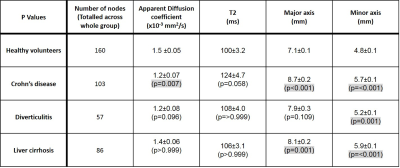 |
71 | Comparison of abdominal lymph nodes between healthy volunteers and patients with inflammatory gastrointestinal diseases.
Hannah Williams, Caroline Hoad, Robert Scott, Gordon Moran, Guruprasad Aithal, Luca Marciani, Penny Gowland
Inflammatory diseases of the gastrointestinal tract are likely to cause enlargement of the abdominal lymph nodes which could potentially act as a biomarker of local inflammation. Lymphatics have been identified using a range of MRI sequences but previous work has largely focused on changes in cancer rather than chronic inflammatory diseases. We present here the first comparison of quantitative non-invasive MRI measures of T2, Apparent Diffusion Coefficient (ADC) and size of lymph nodes in healthy volunteers and patients with a range of inflammatory gastrointestinal diseases.
|
|
1679.  |
72 | Comparison between 3T MRI and CT for preoperative T staging of resectable esophageal cancer, with histopathological correlation
Jinrong Qu, Xu Yan
Seventy fourth patients with endoscopically proven EC and indeterminate T1/T2/T3/T4a stage by CT and EUS were enrolled prospectively. The diagnostic performances of MRI and CT were evaluated based on the sensibility, specificity and accuracy rate, the difference of accuracy rates between MRI and CT was analyzed by c2 test. This study showed MRI can obtain clear images of esophageal wall for preoperative T staging of EC with significantly higher accuracy rate than that of CT, and provide another high-accuracy non-invasive examination method for preoperative T staging of EC.
|
|
1680. 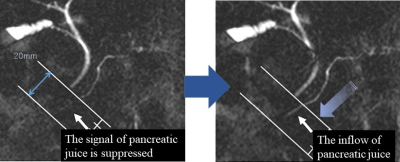 |
73 | Relationship Between Exocrine Pancreatic Function and Abdominal Symptoms: Evaluation Using Cine-Dynamic MRCP
Akira Yamamoto, Katsuyoshi Ito, Teruki Sone, Kazuya Yasokawa, Akihiko Kanki, Tsutomu Tamada
The purpose of this study was to elucidate the relationship between exocrine pancreatic function and abdominal symptoms. Cine-dynamic MRCP was performed and an 18-item questionnaire on abdominal symptoms was administered to 42 patients. The relationship between exocrine pancreatic function, which was quantified as an exocrine pancreatic score, and the abdominal symptoms was assessed. Symptoms for 3 of the 18 abdominal symptom items were significantly associated with decreased exocrine pancreatic function, as measured by cine-dynamic MRCP If a patient complains of such symptoms, the possibility of decreased exocrine pancreatic function should be considered, and should be evaluated by cine-dynamic MRCP.
|
Digital Poster
| Exhibition Hall | 13:45 - 14:45 |
| Computer # | |||
1681. 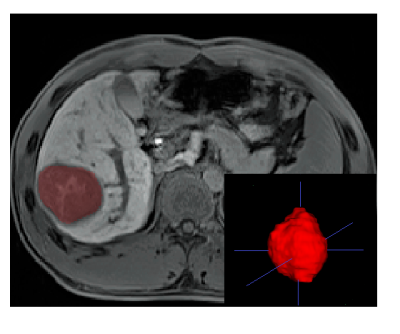 |
76 | Hepatocellular carcinoma: whole-lesion radiomics nomogram on gadoxetic acid-enhanced MR imaging for postoperative early recurrence prediction
Zhen Zhang, Jie Chen, Likun Cao, Song Bin, Zhen Zhang
The high recurrence rates after curative resection has become a major obstacle for the treatment of HCC. Radiomics has been proposed as a robust and effective imaging analysis method to quantify tumor phenotypic characteristics. In this prospective study, a radiomics model based on preoperative gadoxetic acid-enhanced magnetic resonance (MR) images for preoperative prediction of early recurrence in HCCs was generated, with good discrimination and calibration, and may act as an accurate tool to preoperatively identify high-risk patients and guide clinical decision-making of this population.
|
|
1682. 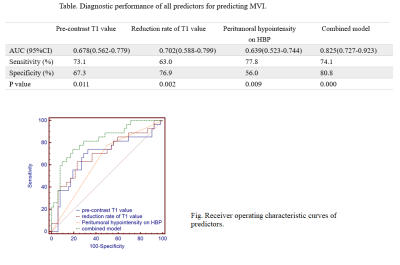 |
77 | T1 mapping on gadoxetic acid-enhanced MR imaging for preoperative prediction of microvascular invasion in hepatocellular carcinoma
Zhen Zhang, Song Bin, Zhen Zhang
Microvascular invasion (MVI) is regarded as one of the independent risk factors for recurrence and poor prognosis of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). However, reliable diagnosis of MVI can only be obtained postoperatively. In this study, preoperative T1 mapping on gadoxetic acid-enhanced MR imaging were performed on 79 patients to demonstrate potential imaging biomarkers in prediction of MVI and early recurrence. As a result, pre-contrast T1 relaxation time, reduction rate of T1 relaxation time combined with the presence of peritumoral hypointensity on HBP were found to be potential predictive biomarkers in the preoperative prediction of MVI in HCCs.
|
|
1683. 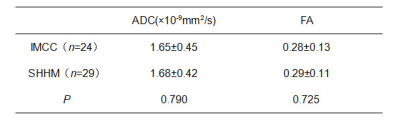 |
78 | Differential Diagnosis of Intrahepatic Mass-forming Cholangiocarcinoma and Solitary Hypovascular Hepatic Metastasis Using Whole-Tumor Texture Features Based on Apparent Diffusion Coefficient and Fractional Anisotropy Signal Intensity Maps
Ying Zhao, Ailian Liu
This work aimed for ADC and FA texture features based strategy to identify intrahepatic mass-forming cholangiocarcinoma (IMCC) and solitary hypovascular hepatic metastasis (SHHM) which may represent a diagnostic challenge due to many overlapping MRI features. The results showed that ADC and FA texture features can differentiate IMCC and SHHM. The Grey Level Non-uniformity (GLN) achieved the best result (AUC: 0.820; sensitivity: 79.2%; specificity: 86.2%) on ADC signal intensity map, forming a valuable strategy for clinical practice.
|
|
1684.  |
79 | MR-based Radiomics Signature to Discriminate Different Pathologic Grade of Hepatocellular Carcinoma
Ying Zhao, Ailian Liu, Jingjun Wu, Jingjing Cui
Recently, the term radiomics (the extraction of multiple quantitative features from images) has drawn attention. Several cancer-related radiomics studies suggested that some quantitative imaging descriptors (such as texture features derived from MRI) could provide more information for cancer diagnosis. In the current study, MR-based radiomics signature was demonstrated to be capable to assess different pathologic grade of hepatocellular carcinoma, which will provide more prognostic information and facilitate clinical management.
|
|
1685 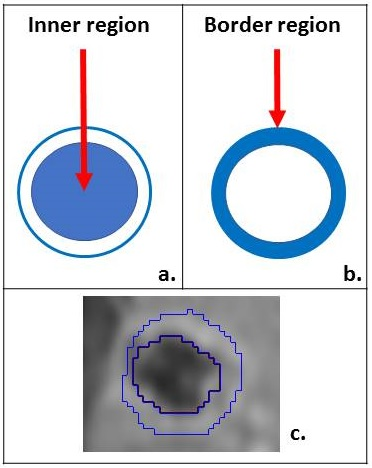 |
80 | Quantitative MR image analysis for predicting histopathological growth patterns of liver metastases from colorectal cancer: standard mono-compartmental vs bi-compartmental model Video Permission Withheld
Pietro Bonaffini, Peter Savadjiev, Sahir Bhatnagar, Ayat Salman, Zu-Hua Gao, Anthoula Lazaris, Peter Metrakos, Benoit Gallix, Caroline Reinhold
Morphologic and quantitative imagine biomarkers able to reliably and noninvasively determine the different histopathological growth patterns (HGP) of colorectal cancer liver metastases (CRCLM) are currently missing. We aimed to evaluate if a bi-compartmental model (tumour border region, in addition to an inner core region) can outperform the traditional mono-compartmental model for HGP subtype prediction. Our results show an improvement in HGP subtype classification when using the bi-compartmental tumour model, likely because the information arising from the borders are separate from those pertaining to the inner core. As reported, the main differences for HGP tend to occur at the tumour-liver parenchyma interface. This would allow accurate and potentially more effective patient treatment stratification, since the different HGP subtypes have reported variable response rates to anti VEGF-A therapy.
|
|
1686. 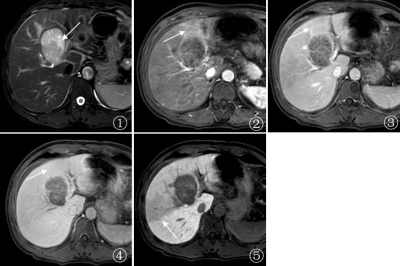 |
81 | The prediction value of gadolinium-ethoxybenzyl-diethylenetriamine pentaacetic acid enhanced MRI in Microvascular Invasion of Hepatocellular Carcinoma Presentation Not Submitted
Peipei Chen, Jian Lu, Tao Zhang, Xueqin Zhang, Xiaofen Miao
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is a common malignant tumor in the liver. Microvascular invasion (MVI) is one of the important risk factors affecting the recurrence and prognosis of HCC. Some scholars have predicted MVI through various imaging methods such as CT, MRI and PET, but has not yet reached a unified forecasting standard. Gadoxetate disodium(Gd-EOB-DTPA)is a novel hepatobiliary contrast agent. Peritumoral hypointension in hepatobiliary phase is of great value in predicting MVI, but the related studies are few. In this study, we used multiple parameters to analyze the value of Gd-EOB-DTPA enhanced MRI in predicting MVI qualitatively and quantitatively.
|
|
1687. 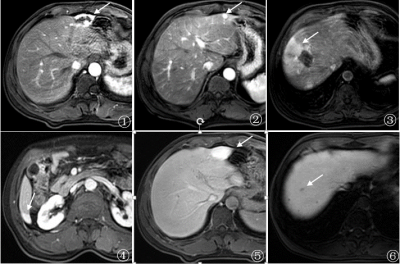 |
82 | Imaging features of hepatic hemangiomas with Pseudo washout sign on Gd-EOB-DTPA enhanced MRI
Peipei Chen, Jian Lu, Tao Zhang
Gadoxetate disodium(Gd-EOB-DTPA)is a novel hepatobiliary contrast agent with characteristics of conventional contrast agents and can also be taken up by liver cells specifically, which is beneficial in characterization of focal liver lesions. In clinical practice, some small hemangiomas usually show low signal in transitional phase of Gd-EOB-DTPA enhanced MRI, defined as Pseudo washout sign(PWS), which can be easily misdiagnosed as hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) if diagnostic physician do not have sufficient experience. Our study intended to improve the understanding of hepatic hemangiomas with atypical imaging features by summarizing the imaging features of hepatic hemangioma with PWS in Gd-EOB-DTPA-enhanced MRI.
|
|
1688.  |
83 | Prediction for early recurrence of intrahepatic mass-forming cholangiocarcinoma: quantitative MRI combined with prognostic immunohistochemical marker Presentation Not Submitted
Li Zhao, Xinming Zhao, Lizhi Xie, Sicong Wang
The aim of this study was to develop a nomogram based on pathological characteristics, immunohistochemical molecules, conventional radiological features and texture parameters for predicting the early recurrence (ER) of intrahepatic mass-forming cholangiocarcinoma (IMCC). It was concluded that combining the texture parameters, enhancement pattern and VEGFR could significantly improve the predictive performance of ER.
|
|
1689. 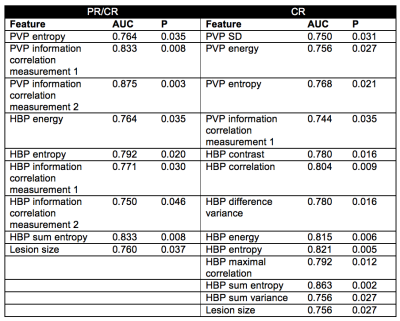 |
84 | Radiomics analysis of gadoxetic acid-enhanced MRI for the evaluation of HCC treatment response to Yttrium-90 radioembolization
Stefanie Hectors, Amy Law, Edward Kiim, Sara Lewis, Bachir Taouli
The goal of our study was to assess the predictive value of radiomics features assessed on pre-treatment multi-phasic gadoxetic acid-enhanced (EOB-)MRI for prediction of response of hepatocellular carcinoma to 90Yttrium radioembolization (RE). We found that radiomics features measured at baseline were predictive of response assessed at 6 weeks and 6-12 months after treatment. These results indicate value of radiomics for prediction of RE response, which needs to be validated in a larger study.
|
|
1690. 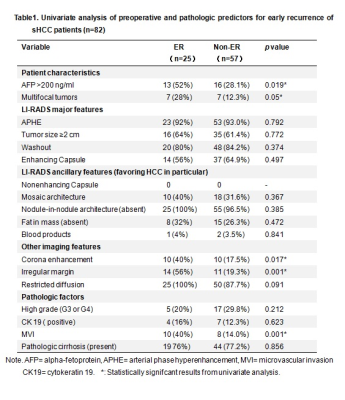 |
85 | Features of Preoperative Dynamical Contrast Enhanced 3-T MR Imaging Predicting Early Recurrence for Small (< 3 cm) Hepatocellular Carcinomas after Curative Resection
Linqi Zhang, Jingbiao Chen, Sichi Kuang, Yao Zhang, Bingjun He, Hao Yang, Ying Deng, Yuanqiang Xiao, Kritisha Rajlawot, Kathryn Fowler, Jin Wang, Claude B. Sirlin
Small hepatocellular carcinoma (sHCC, < 3 cm) is generally thought to have a good prognosis after surgical resection. However, the prognosis of patients with sHCC is still unsatisfactory because of frequent early recurrence (ER, <1 year) after resection. In our series, 30 % of patients with resected sHCC had ER. Preoperative MR imaging features (corona enhancement and irregular tumor margin) were independent predictors for ER after resection of sHCC.
|
|
1691.  |
86 | LI-RADS treatment response criteria for hepatocellular carcinoma after locoregional treatment on contrast-enhanced CT and gadoxetic acid-enhanced MRI: a retrospective validation study using pathologic diagnosis as the reference standard
Sungeun Park, Ijin Joo, Dong Ho Lee, Jae Seok Bae, Jeongin Yoo, Joon Koo Han
The liver imaging reporting and data system (LI-RADS) recently introduced a new treatment response algorithm, namely LI-RADS treatment response (LR-TR), for HCCs treated with locoregional therapy. Using pathologic tumor viability as the reference standard, our study showed that LR-TR viable category resulted in sensitivities of 67.3%/74.5% on CT and 75.5%/80.9% on Gd-EOB-MRI; and specificities of 88.6%/88.6% on CT and 80.0%/82.9% on Gd-EOB-MRI, in reviewers 1/2, respectively, which were not significantly different between CT and Gd-EOB-MRI. In addition, our modified TR criteria applying MRI ancillary features demonstrated significantly higher sensitivity (83.6%/88.2%) and comparable specificity (80.0%/77.1%) than LR-TR on CT or MRI.
|
|
1692. 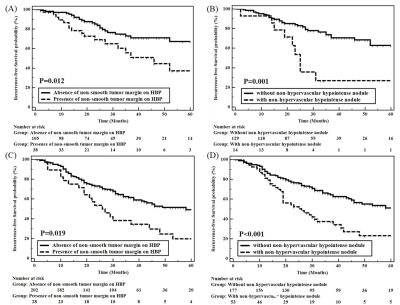 |
87 | Gadoxetic acid-enhanced Liver MR can predict tumor recurrence after curative treatment for small single hepatocellular carcinoma
Dong Ho Lee, Jeong Min Lee
Non-smooth tumor margins and the presence of non-hypervascular HBP hypointense nodules were demonstrated to be independent significant predictive factors of tumor recurrence after either hepatic resection or RFA.
|
|
1693. 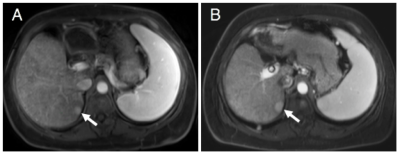 |
88 | Can hepatocellular carcinoma surveillance be performed annually instead of every 6 months in at-risk patients with a negative initial MRI examination?
Islam Zaki, Benjamin Wildman-Tobriner, Rajan Gupta, Rendon Nelson, Mustafa Bashir
This retrospective study investigated the frequency and timing of development of significant hepatic lesions in patients at risk for HCC undergoing surveillance with an initially negative MRI. Out of 70 patients with an initially negative MRI who had mean follow-up of 36 months (range 12-60 months) by contrast-enhanced CT or MRI, no patients developed positive follow up at 1 year. One patient developed a low-risk LI-RADS 3 lesion at 24 months. It may be reasonable to extend the surveillance interval from six months to 12 months in such patients when the first screening examination is negative.
|
|
1694 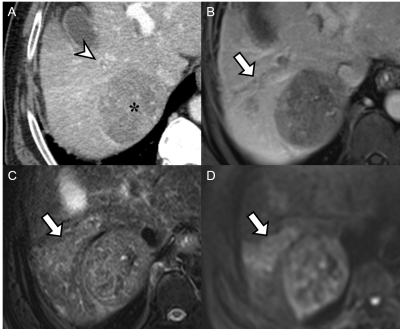 |
89 | Detection of Portal Vein Thrombosis in Patients with Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Can Gadoxetic Acid–enhanced MR Imaging Replace CT? Video Permission Withheld
Jae Seok Bae, Jeong Min Lee, Jeong-Hee Yoon, Siwon Jang, Jin Wook Chung, Joon Koo Han
Gadoxetic acid-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging (GA-MRI) provides higher sensitivity for the detection of HCCs than CT or MRI using extracellular contrast media, but may have a disadvantage in detection of portal vein thrombosis (PVT) related with decreased contrast between the portal vein and liver parenchyma during dynamic phase. For detection of PVT in patients with HCC, we demonstrated that GA-MRI was noninferior to CT for sensitivity (78.8% versus 77.7%, respectively) and was superior to CT for specificity (95.4% versus 92.4%, respectively). For characterization of the PVT as benign or malignant, the GA-MRI showed noninferior accuracy to CT (93.7% versus 92.4%).
|
|
1695 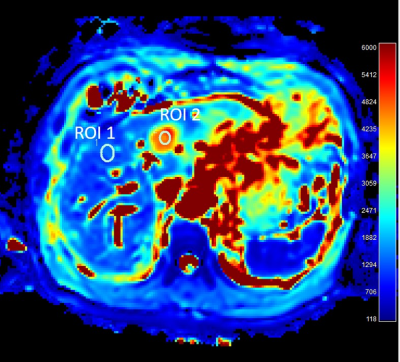 |
90 | Comparison of Diagnostic Values of Mono-exponential, Bi-exponential, and Stretched Exponential Diffusion-weighted Magnetic Resonance Imaging in Differentiating Benign and Malignant Hepatic Lesions Video Permission Withheld
Yoshifumi Noda, Satoshi Goshima, Kimihiro Kajta, Yuta Akamine, Masatoshi Honda, Tomoyuki Okuaki, Hiroshi Kadohara, Nobuyuki Kawai, Hiroshi Kawada, Yukichi Tanahashi, Masayuki Matsuo
Intravoxel incoherent motion, a bi-exponential model of diffusion-weighted imaging with multiple b values, can represent pure molecular diffusion and perfusion, and be used in characterizing focal hepatic lesions. Recently, stretched exponential model has been used in glioblastoma and prostate cancer. In this study, we evaluated the feasibility of stretched exponential model for differentiating benign and malignant hepatic lesions. Our results showed that DDC value from a stretched exponential model was the highest diagnostic potential, so it could be a quantitative imaging biomarker for differentiating benign and malignant hepatic lesions.
|
|
1696. 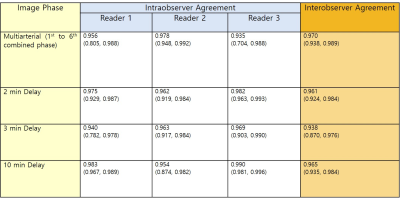 |
91 | Agreement of MRI Liver Observations Size Measurements and Impact on LIRADS v2017 categories (Determinant of size variability and Impact on LI-RADS v2017 category code)
Heejin Kwon, Yong Eun Chung, Min-Jeong Kim, Sang Won Kim, Guilherme M Cunha, Tanya Wolfson, Claude B Sirlin
While intra- and inter-observer agreement rates for size measurement is“excellent” for radiologists, variability across imaging phases could potentially impact LI-RADS categorization. Measurement variations were mostly seen across different postcontrast dynamic phases, as well as, related to specific imaging features (eg, presence of APHE and/or a capsule). In our opinion, the standardization of the most adequate imagingphase to perform size measurements of focal liver observations may increase thereproducibility of LI-RADS categories.
|
|
1697. 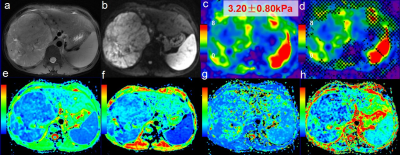 |
92 | A comparative study of MR elastography and intravoxel incoherent motion based on volumetric analysis in the evaluation of histological grade of Hepatitis B virus-related hepatocellular carcinoma
Qungang Shan, Yao Zhang, Tianhui Zhang, Bingjun He, Sudhakar K Venkatesh, Bing Wu, Kevin J Glaser, Richard L Ehman, Jin Wang
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is the most common primary malignancy of the liver. Poorly differentiated HCC is associated with higher recurrence and worse survival compared with well and moderately differentiated HCC and preoperative prediction of histological grade is useful for deciding treatment strategy. We compared the value of MR elastography (MRE) and intravoxel incoherent motion (IVIM) in predicting the histological grade of hepatitis B virus (HBV)-related HCCs using volumetric analysis. Our results demonstrated that only mean tumor stiffness, and not ADC or IVIM metrics, could predict the histological grade of HCCs.
|
|
1698. 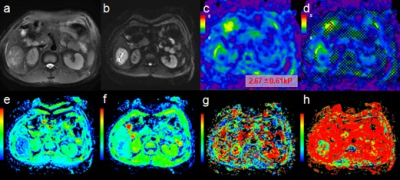 |
93 | Comparison of MR elastography and intravoxel incoherent motion for the prediction of hepatocellular carcinoma tumor capsule formation in hepatitis B virus-related patients using whole-tumor analysis
Yao Zhang, Qungang Shan, Sichi Kuang, Bingjun He, Jingbiao Chen, Bing Wu, Tianhui Zhang, Ying Deng, Kevin J Glaser, Sudhakar K Venkatesh, Richard L Ehman, Jin Wang
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is the most common primary malignant hepatic tumor worldwide and the prognosis remains poor. Tumor capsule formation is a favorable factor for predicting invasiveness and prognosis. We explored the potential value of MR elastography(MRE)and intravoxel incoherent motion(IVIM)for the prediction of tumor capsule formation in patients with hepatitis B virus-related (HBV) HCCs using whole-tumor analysis. Results showed that mean tumor stiffness may be useful for the prediction of capsule formation of HCCs. The utility of the mean value of IVIM metrics may need to be further explored.
|
|
1699. 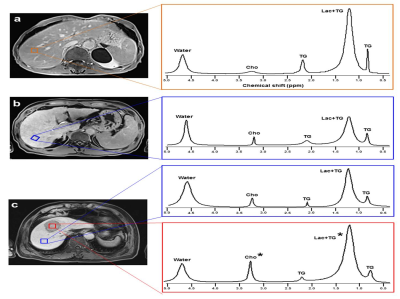 |
94 | Metabolic biomarkers associated with occurrence of hepatocellular carcinoma in patients with liver cirrhosis: in vivo 1H magnetic resonance spectroscopy Presentation Not Submitted
Chung Man Moon, Sang Soo Shin, Yong Yeon Jeong, Suk Hee Heo
Liver cirrhosis (LC) secondary to chronic hepatitis can lead to serious complications. More severely, liver cirrhotic patients may eventually develop hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), thus monitoring disease progression is clinically important. The purpose of this study was to investigate the utility of 1H magnetic resonance spectroscopy (1H-MRS) with long echo time to quantify the differences in hepatic metabolites of normal, cirrhotic liver with and without HCC, and HCC. These findings would be helpful for understanding of liver metabolic changes related with developing HCC in the cirrhotic liver.
|
|
1700 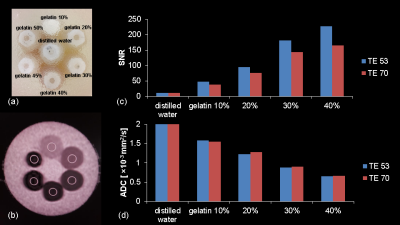 |
95 | Impacts of different b and TE values on quality of 3T diffusion-weighted imaging of the liver using a high gradient magnetic field: feasibility of ultrahigh b value of 3000 Video Permission Withheld
Keita Fukushima, Katsuhiro Sano, Haruhiko Machida, Toshiya Kariyasu, Isao Miyazaki, Tatsuya Yoshioka, Sanae Takahashi, Saori Yuda, Yuta Shimizu, Takayuki Yonaha, Akihito Nakanishi, Hiroshi Kusahara, Youhei Matsuoka, Miho Kitamura, Takao Yamamoto, Kenichi Yokoyama
Diffusion-weighted imaging (DWI) with an ultrahigh b value is expected to improve assessment of tumor cellularity and fluid viscosity in the liver but can decrease signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) of the hepatic parenchyma. A state-of-the-art 3T MR scanner with the maximal gradient magnetic field of 100 mT/m can achieve sufficient SNR on liver DWI even at ultrahigh b value of 3000 with use of short TE. The present study using our original phantom and healthy volunteers shows that use of shorter TE significantly increased the SNR with preserved ADC value on DWI even at ultrahigh b value of 3000.
|
|
1701. 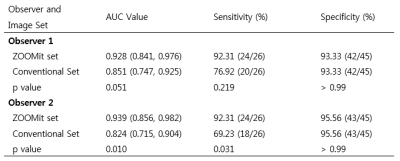 |
96 | The efficacy of coronal ZOOMit diffusion-weighted MR imaging at 3T MRI for differentiation of malignant distal bile duct stricture
Ki Choon Sim, Beom Jin Park, Min Ju Kim, Deuk Jae Sung, Na Yeon Han
For the evaluation of distal bile duct, diffusion weighted imaging should be routinely included in MR protocol for detection and differentiation of malignant distal bile duct stricture. If possible, it would be better to be able to acquire images in a coronal plane.
|
|
1702. 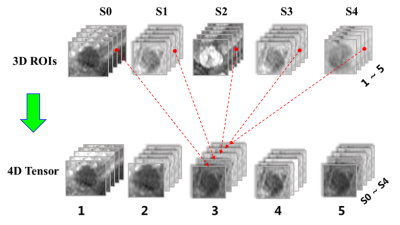 |
97 | Noninvasive evaluation of the pathologic grade of hepatocellular carcinoma using MCF-3DCNN: A pilot study Presentation Not Submitted
Da-wei Yang, Xiao-pei Wang, Zheng-han Yang, Zhen-chang Wang, Xi-bin Jia
This pilot study indicated that the MCF-3DCNN model may be valuable for the noninvasive evaluation of the pathologic grade of HCCs; however, further improvement would be necessary to achieve a better diagnostic performance for moderately and poorly differentiated HCCs.
|
|
1703. 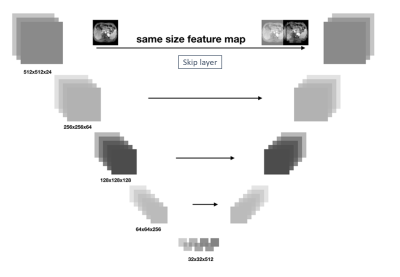 |
98 | Volume-wise lesion detection on hepatic hemangioma and cyst considering inter-slice information through a 3D convolutional neural network
Yajing Zhang, Qitong Hu
MR has been widely used for the diagnosis of hepatic hemangioma and cyst due to its significance of detection on small lesions. This study proposes a deep learning based method to detect the lesion volume in a three-dimensional manner on the dynamic contrast-enhanced MR images with hemangioma and/or cyst lesions. The results show good alignment of automated detection contour with the manually labelled lesion contour by professional radiologists, as well as accurate classification of lesion types.
|
|
1704. 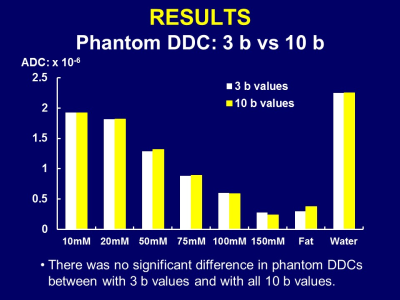 |
99 | Abdominal Diffusion-Weighted Imaging with Stretched-Exponential Model: Phantom and Clinical Studies
Takeshi Yoshikawa, Yoshiharu Ohno, Seiya Kai, Masao Yui, Yoshimori Kassai, Ryuji Shimada, Katsusuke Kyotani, Shinichiro Seki
Abdominal DWI with stretched-exponential model was assessed in phantom and clinical studies. Our results suggest it is a useful tool for evaluating abdominal organs and diseases.
|
|
1705. 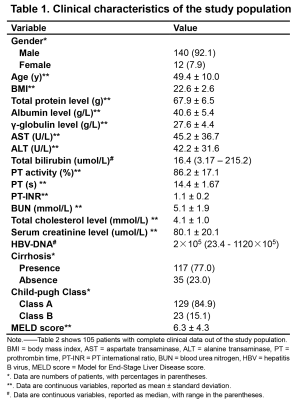 |
100 | The Diagnostic Performance of LI-RADS version 2018 and the Value of Ancillary Features Favoring Hepatocellular Carcinoma (HCC) in the Diagnosis of 10-19 mm HCC on Extracellular Contrast-enhanced MRI.
Jingbiao Chen, Sichi Kuang, Bingjun He, Yao Zhang, Hao Yang, Ying Deng, Kathryn Fowler, Jin Wang, Claude B. Sirlin
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is the second most cause of cancer death worldwide. Early detection of small HCC can prolong patient survival. Recent updates have changed diagnostic criteria for LI-RADS v2018 for 10-19 mm HCC, and the impact on accuracy has not yet been studied. We found that LI-RADS v2018 provides 68.2% sensitivity, 91.7% specificity, and 71.8% accuracy for 10-19 mm HCC diagnosis in a Chinese population with chronic liver disease. Several modifications of LI-RADS were explored (e.g., pooling LR-4 and LR-5; allowing ancillary features favoring HCC to upgrade LR-4 to LR-5 and/or convert LR-M to LR-5), some sensitivities were mild improved without specificities increase.
|
Digital Poster
| Exhibition Hall | 13:45 - 14:45 |
| Computer # | |||
1706.  |
101 | Improved, rapid fetal-brain localization and orientation detection for auto-slice prescription
Malte Hoffmann, Esra Abaci Turk, Borjan Gagoski, Paul Wighton, M Tisdall, Martin Reuter, Elfar Adalsteinsson, P Grant, Lawrence Wald, André van der Kouwe
MRI has become an invaluable tool for assessing the development of the fetal brain and can remove diagnostic doubt after routine ultrasound exams. Motion between slice prescription and acquisition, however, poses a challenge to obtaining images aligned with the standard anatomical planes, essential for evaluating morphometry. To address this, we recently presented automated slice prescription for fetal-brain MRI based on registration to a template. Here, we propose improved and fully automated fetal-brain orientation detection to advance both reliability and speed. The fast estimation is achieved by localizing the brain and eyes in an EPI scout using blob detection techniques.
|
|
1707. 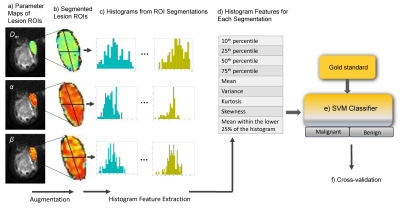 |
102 | Discrimination of Malignant and Benign Breast Lesions Using Machine Learning on Non-Gaussian Diffusion MRI Parameters
Muge Karaman, Yangyang Bu, Zheng Zhong, Shiwei Wang, Changyu Zhou, Weihong Hu, Mark Balich, Maosheng Xu, Xiaohong Zhou
Breast cancer is the second leading cause of cancer death among women in the US. Recognizing the complexity of cancerous tissue, several non-Gaussian diffusion MRI models, such as the continuous-time random-walk (CTRW) model, were suggested to probe the underlying tissue environment. In this study, we employed a support-vector-machine-based analysis on the histogram features of CTRW model parameters to differentiate malignant and benign breast lesions. This multi-parameter multi-feature approach provided the best diagnostic performance compared to the conventional single-parameter or single-feature analysis techniques. The combination of machine-learning with non-Gaussian diffusion MRI can facilitate comparable diagnostic performance to that of dynamic-contrast-enhanced MRI.
|
|
1708. 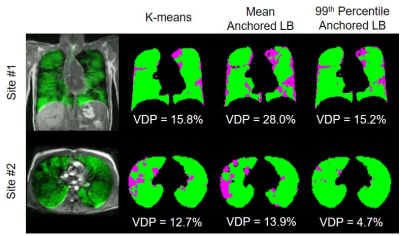 |
103 | A Two-Center Analysis of Hyperpolarized 129Xe Lung MRI in Stable Pediatric Cystic Fibrosis: Comparison of Image Analysis Approaches
Marcus Couch, Robert Thomen, Felix Ratjen, Jason Woods, Giles Santyr
The ventilation defect percent (VDP), measured from hyperpolarized 129Xe MRI, is sensitive to functional changes in early cystic fibrosis (CF) lung disease; however, there is no consensus on which VDP calculation method is most appropriate for future multi-center clinical trials in CF. This study compared VDP analysis methods in hyperpolarized 129Xe datasets acquired in stable pediatric CF subjects at two institutions. In a combined dataset, a comparison of k-means, mean-anchored linear binning, and 99th percentile-anchored linear binning demonstrated that all three methods provide a good characterization of the disease, but mean-anchored linear binning provided the strongest correlation to pulmonary function tests.
|
|
1709.  |
104 | Partial velocity-compensated optimized diffusion encoding for combined motion compensation and residual vessel signal suppression in liver ADC mapping
Sean McTavish, Anh Van, Johannes Peeters, Tetsuo Ogino, Andreas Hock, Ernst Rummeny, Rickmer Braren, Dimitrios Karampinos
Despite its strong clinical significance in lesion detection and tumor staging, liver DWI remains challenged by its strong sensitivity to motion effects. Motion-compensated diffusion encoding schemes have recently been proposed to improve DW liver signal homogeneity especially in the left liver lobe, a region typically affected by cardiac motion. However, motion-compensated diffusion encoding is associated with hyperintense vessel signal even at high b-values, which can obscure lesion detection. The present work proposes a partial velocity-compensated diffusion encoding using asymmetric diffusion gradients for combined motion compensation and residual vessel signal suppression in liver DWI, optimized for short echo times.
|
|
1710. 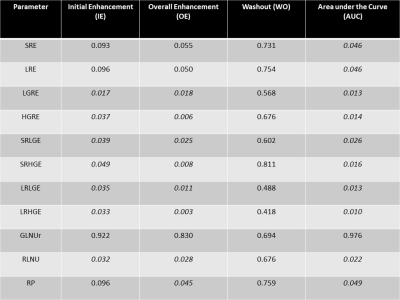 |
105 | Characterization of sub 1 cm Breast Lesions using Radiomics Analysis
Peter Gibbs, Natsuko Onishi, Meredith Sadinski, Elizabeth Morris, Elizabeth Sutton
DCE MRI of breast lesions has high sensitivity (>90%) and reasonable specificity (>70%). However, the specificity for smaller lesions is known to be poorer due to the inability to confidently distinguish morphological and kinetic features. This work utilizes radiomics of model free parameter maps to improve the diagnostic accuracy of sub 1cm lesions with a PPV of 100% and a NPV of 91% obtained in a test dataset. The high level of correlation between texture features calculated from initial enhancement, overall enhancement, and area under the enhancement curve maps indicate that data acquisition beyond peak enhancement may be unnecessary.
|
|
1711. 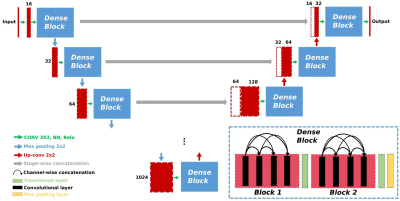 |
106 | Automatic prostate and prostate zones segmentation of magnetic resonance images using convolutional neural networks
Nader Aldoj, Federico Biavati, Miriam Rutz, Sebastian Stober, Marc Dewey
The purpose was to develop a fully automatic and accurate tool for prostate and prostate zone segmentation using T2-weighted MRI. Thus, we developed a new neural network named Dense U-Net which was trained on 143 patient datasets and tested on 45 patient datasets. This Dense U-Net compared with the state-of-the-art U-Net achieved an average dice score for the whole prostate of 89.4±0.8% vs. 88.4±0.8%, for the central zone of 83±0.2% vs. 83±0.2%, and for the peripheral zone of 76.9±0.2% vs. 74.6±0.2%, respectively. In conclusion, the developed Dense U-Net was more accurate than the state-of-the-art U-Net for prostate and prostate zone segmentation.
|
|
1712. 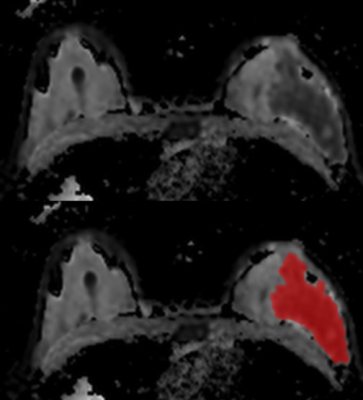 |
107 | Radiomic Characteristics Derived from Diffusion-Weighted Imaging for the Assessment of Breast Cancer Receptor Status and Molecular Subtypes
Doris Leithner, Joao Horvat, Maria Adele Marino, Daly Avendano, Sunitha Thakur, Blanca Bernard-Davila, Maxine Jochelson, Danny Martinez, Elizabeth Morris, Katja Pinker
To evaluate the diagnostic performance of DWI radiomic signatures for the assessment of breast cancer receptor status and molecular subtypes. Ninety-one patients with breast cancer were included. Lesions were manually segmented on high b-value DWI and propagated to ADC maps. To compare different segmentation approaches a subgroup was directly segmented on the ADC map. Results demonstrate that DWI radiomic signatures enable the assessment of breast cancer receptor status and molecular subtypes with high accuracy. Higher accuracies are achieved when segmentations are performed directly on ADC maps that cancel out T2 shine-through indicating as the preferred approach for radiomic analysis.
|
|
1713. 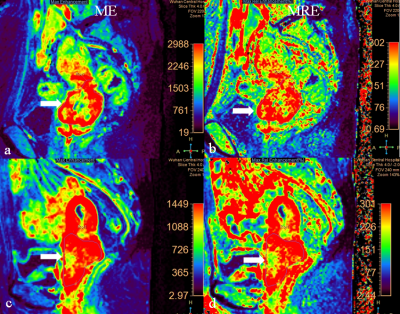 |
108 | Prediction of stage, differentiation and Ki-67 status of locally advanced cervical cancer by DCE-MRI texture analysis Presentation Not Submitted
Xie Yuanliang, Jiang Yanping, Wang Xiang, Du Dan, Xie Wei, Sun Jianqing
This retrospective study explored the value of texture analysis in predicting the stage, differentiation and Ki-67 status of pretreatment advanced cervical cancer. Multi-class radiomics feature extraction was performed on the maximum enhancement (ME) and maximum relative enhancement (MRE) maps from DCE-MRI. A prediction model using a machine learning-XGB classifier showed the mean sensitivities of predicting FIGO?b-?a, poor differentiation and high Ki-67 status were 0.767, 0.963 and 0.967; specificities were 0.958, 0.361 and 0.694 , and AUCs were 0.910, 0.920 and 0.840 respectively. DCE-MRI textural parameters have potential as non-invasive imaging biomarkers in predicting histopathology in advanced cervical cancer.
|
|
1714. 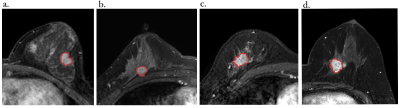 |
109 | Prediction molecular subtypes of Breast Cancer by MRI Radiomics Presentation Not Submitted
Shuangyan Sun, Dingli Ye, Changliang Yang, Jianqing Sun, Jihong Zhao
Breast cancer molecular subtypes are indicators of disease free and overall survival. This study aimed to investigate whether quantitative radiomic features extracted from MRI images are associated with molecular subtypes of breast cancer. 135 women diagnosed with invasive breast cancer were enrolled and divided into 3 groups as follow: triple-negative vs non–triple-negative, HER2-enriched vs non–HER2-enriched, and luminal (A + B) vs nonluminal. A machine learning scheme was employed for the classification. The mean AUC of the three models are 0.76, 0.85 and 0.73, respectively. There is a moderate association between tumour molecular biomarkers and radiomic features extracted from MRI images.
|
|
1715. 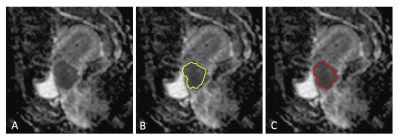 |
110 | Fully Automated Segmentation of Cervical Cancer in Diffusion MR Imaging Using U-Net Convolutional Neural Networks
Yu-Chun Lin, Chia-Hung Lin, Hsin-Ying Lu, Ho-Kai Wang, Su-Han Ng, Jiunjie Wang, Gigin Lin
The aim of the study is to evaluate the performance of U-Net in tumor segmentation on diffusion MR imaging for patients with cervical cancer. Diffusion weighted imaging of b0, b1000 and ADC maps were used for training. The ADC histogram parameters of predicted region of tumor were assessed for accuracy and reproducibility. The results show the triple-channel training algorithm exhibited the best performance in both training and testing datasets. The predicted voxels of tumor can be used to generate the volumetric ADC data for Radiomics study.
|
|
1716  |
111 | Texture Analysis based on functional magnetic resonance imaging for evaluation of renal function Video Permission Withheld
Gumuyang Zhang, Hao Sun, Jianfeng Sun, Hailong Zhou, Yanhan Liu, Ning Guo, Jing An, Huadan Xue, Zhengyu Jin
Texture analysis (TA) based on apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC), T1 and T2 mapping to evaluate glomerular filtration rate (GFR) has not been explored before. A total of 116 participants underwent DWI, T1 and T2 mapping of both kidneys on a 3T MR scanner and texture features were measured for the cortex and medulla of each kidney. Models incorporating texture features mainly quantified from ADC and T1 maps produced a satisfactory performance for detecting abnormal renal function and characterizing the different severity of GFR decline. It’s promising that TA based on ADC and T1 maps could serve as imaging markers to evaluate renal function.
|
|
1717. 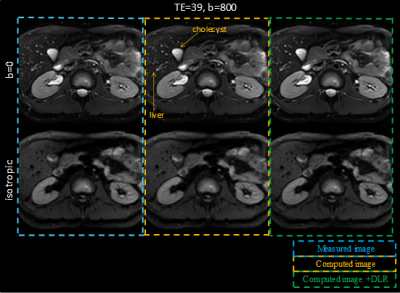 |
112 | Evaluation of Variable-TE computed Diffusion Weighted Imaging Technique using Deep Learning based Noise Reduction
Hiroshi Kusahara, Yuki Takai, Kensuke Shinoda, Yoshimori Kassai
In this study to the authors adapted the variable-TE cDWI(vTE-cDWI) technique applying denoise approach with deep learning reconstruction(dDLR) to the abdominal region, using ADC-map, T2-map and T1-map with IR-based images. The algorithm under evaluation allows computing diffusion images for arbitrary combinations of TE, b-value and TI based on four acquisitions(4-points method). This technique was shown to generate vTE-cDWI with higher SNR compared to the acquired DWI, and dDLR increased the SNR more, as well as obtain ADC-maps and T1-maps with optimal TI for any arbitrary tissue. The clinical benefits of the method and results on volunteers are discussed.
|
|
1718. 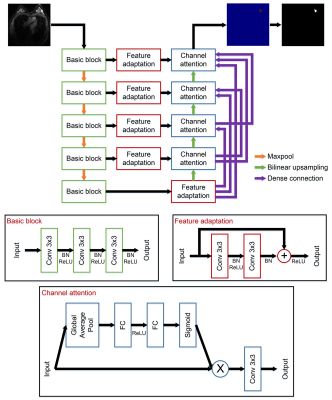 |
113 | Automatic breast lesion segmentation in MR images employing a dense attention fully convolutional network
Cheng Li, Hui Sun, Qiegen Liu, Zaiyi Liu, Meiyun Wang, Hairong Zheng, Shanshan Wang
Despite its high sensitivity, MR imaging has low specificity and high false positive issues. Therefore, automatic breast lesion detection algorithms are necessary. To this end, we propose a new network, dense attention network (DANet), for breast lesion segmentation in MR images. In DANet, we designed a feature fusion and selection mechanism. Features from the corresponding encoder layer and from all previous decoder layers are fused by concatenation. To highlight the rich-informative channels, a channel attention module is introduced. DANet showed better segmentation results compared to commonly applied segmentation networks on our 2D contrast-enhanced T1-weighted breast MR dataset.
|
|
1719. 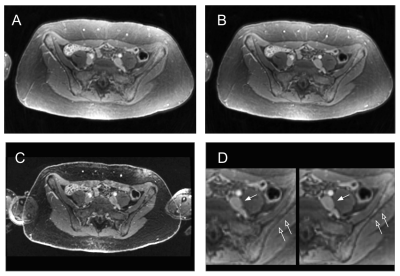 |
114 | Deep Learning off-resonance correction for faster free-breathing contrast-enhanced conical ultrashort echo time (UTE) MRI of the pelvis
Signy Holmes, David Zeng, Joseph Cheng, Marcus Alley, Michael Carl, Dwight Nishimura, Preeti Sukerkar, Vipul Sheth, Ryan Brunsing, Shreyas Vasanawala
MRI sequences with 3D cones k-space trajectories allow decreased motion artifacts while achieving ultrashort echo times (UTE). Extending readout durations allows decreased scan times but lead to worsening off-resonance artifacts. We assessed the performance of extended-readout, free-breathing UTE 3D cones MRI with and without a deep learning off-resonance correction in the evaluation of the adult pelvis. UTE imaging performed significantly better than 3D Cartesian spoiled gradient echo (SPGR) in noise, and after off-resonance correction also performed significantly better in artifact reduction.
|
|
1720. 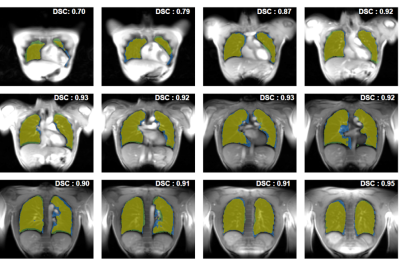 |
115 | Deep Learning Assisted Fully Automatic Post-Processing for Quantitative Lung MRI
Andreas Weng, Christian Kestler, Andreas Kunz, Simon Veldhoen, Thorsten Bley, Herbert Köstler, Tobias Wech
Functional lung MRI still suffers from a time consuming post-processing with manual image segmentation being its most time consuming part. We introduce and evaluate a deep learning based semantic image segmentation technique to enable fully automated post-processing in SENCEFUL-MRI. Obtained segmentations were compared to manual segmentations using the DICE similarity coefficient (DSC). Furthermore, quantitative ventilation values were obtained after manual and automatic segmentation. Mean DSC of the binary segmentation masks was 0.83 ± 0.09 and no significant difference in quantitative ventilation values was observed. Obtained results show that the time consuming manual post-processing in functional lung MRI can be automated by the proposed neural network.
|
|
1721. 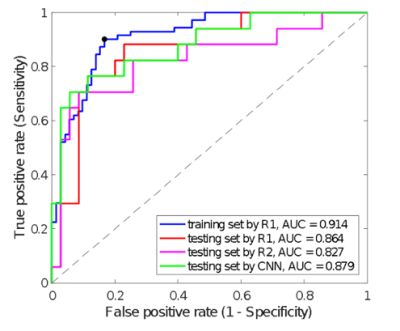 |
116 | A task-based endpoint assessment for CNN segmentations in radiomics processing
Karl Spuhler, Jie Ding, Mario Serrano-Sosa, Chuan Huang
In this study, we present evidence that CNN-based segmentations are sufficient for automated ROI delineation in radiomics processing.
|
|
1722. 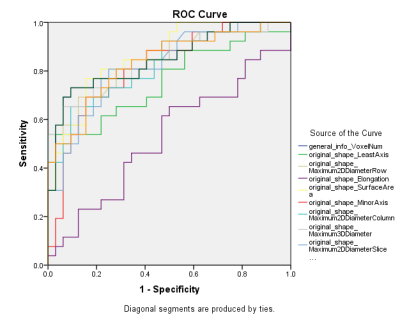 |
117 | Validation of Radiomics Signature for Chemoradiotherapy Prediction of Advanced Cervical Cancer Based on a High Resolution T2WI Images
Defeng Liu, Qinglei Shi, Xu Yan, Lanxiang Liu, Yujie Cui, Xiaohang Zhang, Juan Du
This study performed a radiomics signature analysis based on a high resolution T2WI images, and evaluate the value of these quantitative features in prediction the treatment effect of neoadjuvant chemotherapy-radiation therapy for advanced cervical cancer (>IIb) . And found that Shape and first-order features seems can provide valuable information and showed potential in prediction treatment effect of this disease.
|
|
1723. 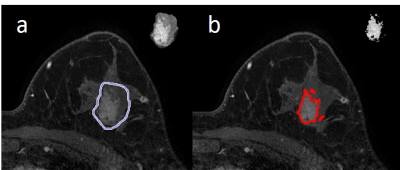 |
118 | Predicting Pathological Response to Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy Using 3D Texture Feature Radiomics on Baseline Dynamic Contrast-Enhanced (DCE) MRI
Yifan Wu, Daniel Hippe, Ginger Lash, Lanell Peterson, Jennifer Specht, Savannah Partridge
There is emerging data supporting the value of texture and other radiomics features extracted from dynamic contrast-enhanced (DCE) MRI to characterize breast cancer subtypes and recurrence risk. DCE texture features may also provide unique value in predicting response to neoadjuvant chemotherapy (NAC). Our study investigated the predictive value of pretreatment DCE tumor texture features in 30 women with triple negative and luminal-B cancers undergoing NAC. We found higher-order texture features significantly predicted pathologic response, while other standard quantitative metrics did not. Our findings suggest texture features on DCE MRI may provide valuable information prior to treatment to help tailor therapies.
|
|
1724. 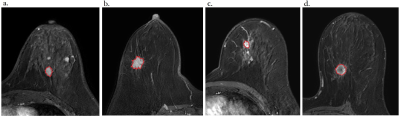 |
119 | Application research on 3D texture analysis technology based on MRI in the identification of molecular subtypes of breast cancer Presentation Not Submitted
Dingli Ye, Shuangyan Sun, Jianqing Sun, Jihong Zhao
The purpose of this work was to use radiomics features to build a classification model that can classify breast cancer into different molecular subtypes. Our result shows that some radiomics features have great potential to be an useful index in predicting the subtype of breast cancer, therefore providing helps for the development of clinical treatment decisions for breast cancer.
|
|
1725. 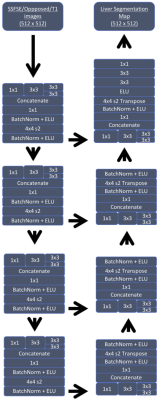 |
120 | Deep Learning Model for Liver MRI Segmentation
Amber Mittendorf, Lawrence Ngo, Erol Bozdogan, Mohammad Chaudhry, Steven Chen, Gemini Janas, Jacob Johnson, Zhe Zhu, Maciej Mazurowski, Mustafa Bashir
Hepatic segmentation is an important but tedious clinical task used in a variety of applications. Existing techniques are relatively narrow in scope, requiring a particular type of MRI sequence or CT for accurate segmentation. We developed a Convolutional Neural Network (CNN) capable of automated liver segmentation on single-shot fast spin echo, T1-weighted, or opposed phase proton-density (OP-PD) weighted sequences using separate training/validation and testing data sets. Compared to human segmenters, the CNN performed well, with volumetric DICE coefficients of 0.92-0.95. The CNN performed least consistently on OP-PD sequences, which had the smallest number of cases in the training/validation data set.
|
|
1726. 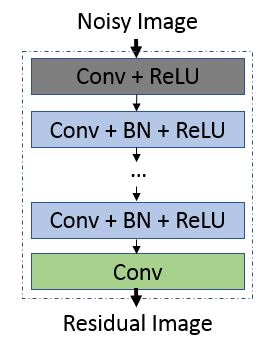 |
121 | Deep-Learning-Based Denoising of Diffusion-Weighted Prostate Images
Elena Kaye, Yousef Mazaheri, Maggie Fung, Ross Schmidtlein, Ricardo Otazo, Oguz Akin, Herbert Alberto Vargas
Despite its unique capabilities, diffusion-weighted imaging (DWI) in prostate is inherently limited by low signal-to-noise ratio (SNR). Currently, gains in SNR of high b-value images are achieved through increase in the number of excitations (NEX), at the cost of increase in total acquisition time. We demonstrate feasibility of improving prostate DWI image quality by leveraging denoising convolutional network. Using pairs of "noisy" NEX4 and "clean" NEX16 DWI images, reconstructed from raw data, CNN was trained to denoise prostate DWI images. Denoising of images significantly improved SNR and increased overall image quality, reviewed by two experienced genitourinary radiologists.
|
|
1727. 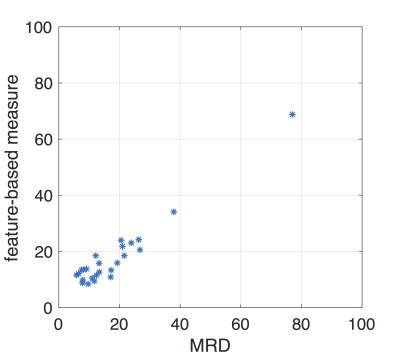 |
122 | The associations between breast density and the radiomic features derived from T1-weighted MRI
Jie Ding, Karl Spuhler, Mario Serrano Sosa, Alison Stopeck, Patricia Thompson, Chuan Huang
Breast density (BD) has been recognized as a biomarker of breast cancer risk. We previously developed a highly reproducible MRI-based BD measurement (MRD), that is directly comparable to mammographic density, using fat-water decomposition MRI to assess the breast cancer risk in clinical trials. However, this method requires a specific sequence which cannot be applied to previously acquired data. In this work, we investigate possibility of using the radiomic features extracted from routine T1-weighted MRI to represent MRD. This finding enables a possibility of evaluating the breast cancer risk using the routine MRI data in clinical practice.
|
|
1728. 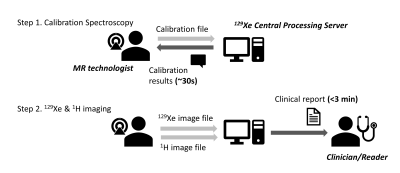 |
123 | A Real-Time Centralized Pipeline for Reconstructing and Quantifying Hyperpolarized 129Xe Gas Exchange MRI
Ziyi Wang, Mu He, Alexander Culbert, John Nouls, Elianna Bier, Bastiaan Driehuys
Hyperpolarized 129Xe MRI is emerging as a powerful means to provide 3D quantitative mapping of ventilation, interstitial barrier uptake, and red blood cell transfer. However, this capability requires non-standard radial reconstruction and accurate lung segmentation to enable quantitative analysis. Such reconstruction and image processing would ideally be standardized and centralized to facilitate using 129Xe gas exchange MRI in multi-center clinical trials. To this end, we developed a neural-network based lung segmentation approach that automatically generates accurate masks. With this capability, we demonstrate a fully centralized processing pipeline for real-time reconstruction and quantitative reporting of 129Xe gas exchange MRI.
|
|
1729. 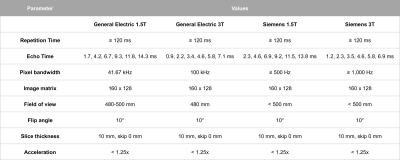 |
124 | Proton density fat fraction results derived from deep learning auto-segmentation correlate strongly with results obtained by manual analysis
Ashley Louie, Kang Wang, Timoteo Delgado, Michael Middleton, Gavin Hamilton, Tanya Wolfson, Robert Myers, C. Stephen Djedjos, Rohit Loomba, Claude Sirlin
A widely-accepted method to estimate hepatic proton-density fat fraction (PDFF) is by averaging values derived from manually drawn regions-of-interest (ROIs) in the nine Couinaud segments. An automated deep-learning-based segmentation tool has been developed to potentially replace this labor-intensive and technically-challenging method. The purpose of this study was to compare whole-liver PDFF values obtained using this auto-segmentation tool to results obtained using manual analysis for a longitudinal multi-center clinical trial of 72 patients with nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. We found that PDFF values estimated using the auto-segmentation tool were in near agreement with values derived by manually drawing ROIs.
|
|
1730. 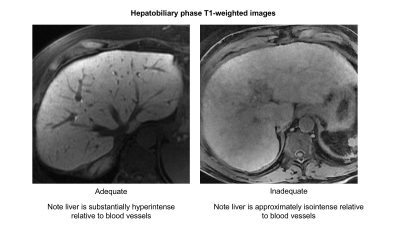 |
125 | Automated Assessment of Liver Parenchymal Enhancement on Hepatobiliary Phase MR Images Using a Convolutional Neural Network
Guilherme Cunha, Kyle Hasenstab, Kang Wang, Timo Delgado, Atsushi Higaki, Ryan Brunsing, Alex Schlein, Armin Schwartzman, Albert Hsiao, Claude Sirlin
Adequate hepatocellular enhancement (HCE) in Gd-EOB-DTPA-enhanced MRI studies can often deviate from the standard delay of 20 minutes. In this study, we proposed a fully-automated CNN-based approach for real-time assessment of HCE adequacy and retrospectively evaluated performance using 1201 T1w HBP 3D image sets from 406 unique patients. Our proposed model classified images with inadequate uptake with an AUC of 97%. With further validation, this approach could be used to identify the earliest time point HCE adequacy is achieved, potentially shortening scanning time by tailoring the exam length to the individual liver’s ability to uptake contrast.
|
Digital Poster
| Exhibition Hall | 13:45 - 14:45 |
| Computer # | |||
1731. 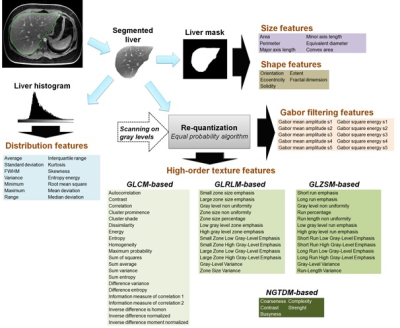 |
126 | A virtual liver biopsy based on mixed MRI radiomics and biological data: a proof of concept
Benjamin Leporq, Sophie Gaillard, Liadeh Cuminal, Valerie Hervieu, Olivier Guillaud, Jerome Dumortier, Pierre-Jean Valette, Olivier Beuf
Whereas NASH is associated with poor long-term outcome, widespread screening is not currently feasible given that a definitive diagnosis of NASH can only be made through liver biopsy. In this study, a virtual liver biopsy was developed with machine learning from mixed multiparametric MRI radiomics and biological data.
|
|
1732. 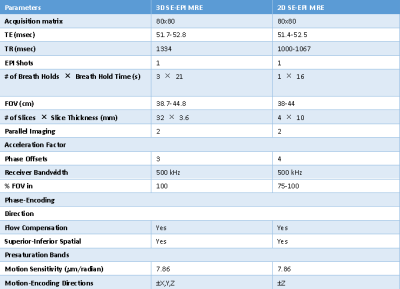 |
127 | Three-dimensional MR Elastography (MRE) can replace 2D MRE in staging liver fibrosis: Noninferiority test of the area under the ROC curve and comparison of image quality.
Hao Yang, Hezhi Lu, Yong Liu, Sichi Kuang, Bingjun He, Kevin J Glaser, Meng Yin, Sudhakar K Venkatesh, Bing Wu, Richard L Ehman, Jin Wang
2D MR elastography (MRE) has been shown to be the most accurate noninvasive technique for the detection and staging of liver fibrosis. Tissue stiffness quantification based on 3D MRE is theoretically more accurate while having comparable diagnostic accuracy for staging fibrosis. Our results showed that the diagnostic performance of 3D MRE is not inferior to 2D MRE in assessing liver fibrosis by using a noninferiority test of the area under the ROC curve based on the restricted maximum likelihood (REML) method. Moreover, 3D MRE had better image quality and has the potential to replace 2D MRE in clinical applications.
|
|
1733. 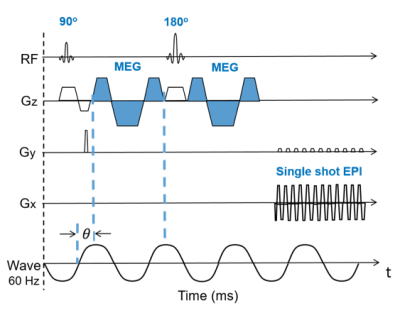 |
128 | Comparison of Spin-echo Echo-planar imaging (SE-EPI) MR elastography (MRE) and Gradient-recalled echo (GRE) MRE at 3.0T in pediatric nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD)
Skorn Ponrartana, Michael Chiang, Quin Lu, Hui Wang, Tania Mitsinikos, Rohit Kohli
Currently, most MRE performed clinically at 3.0T uses a GRE sequence. However, recent literature describes susceptibility effects from fat that may confound MRE performance, especially at 3.0T. SE-EPI is a faster technique that is less sensitive to susceptibility artifacts and signal loss and has recently been developed at 3.0T. In this work, we compare measures of liver stiffness between SE-EPI and GRE MRE techniques in pediatric patients with NAFLD at 3.0T.
|
|
1734. 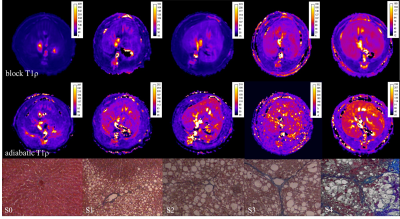 |
129 | Liver fibrosis detection and staging in rats: a comparative study of T1 relaxation time in the rotating frame block sequence and adiabatic sequence.
Da Shi, Xianyue Quan, Yingjie Mei, Shisi Li, Genwen Hu
Objective: To compare diagnostic performances on staging liver fibrosis of T1 relaxation time in the rotating frame block sequence and adiabatic sequence. Materials and Methods: 65 healthy Sprague Dawley (SD) rats were randomly divided into model and black groups. Block T1ρ and adiabatic T1ρ were performed on the rats with a 3.0-T clinical scanner. Results: T1ρ values were significantly different among stages (P <0.05), except for stages S1 and S2 with block T1ρ. AUC for block T1ρ values were 0.989, 0.924, 0.932 and 0.923, respectively. AUC for Adiabatic T1ρ values were 0.992,0.948,0.967 and 0.963, respectively. Conclusions: Adiabatic T1ρvalues had higher diagnositic performances on staging liver fibrosis in rats.
|
|
1735. 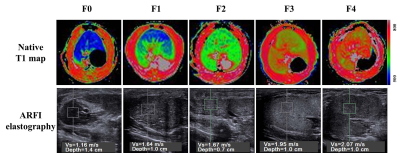 |
130 | Comparison of native T1 mapping and acoustic radiation force impulse elastography for noninvasively assessing liver fibrosis: repeatability, reproducibility, and staging and monitoring the fibrosis process Presentation Not Submitted
Jinning Li, Huanhuan Liu, Caiyuan Zhang, Shuyan Yang, Yanshu Wang, Weibo Chen, Xin Li, Dengbin Wang
To investigate the performances of native T1 mapping for noninvasively assessing liver fibrosis, including repeatability, reproducibility, and staging and monitoring the process of fibrosis, and to compare them with those of acoustic radiation force impulse (ARFI) elastography. The results of our experimental study suggest that native T1 mapping may be a reliable, accurate, and noninvasive tool for assessing liver fibrosis. Compared with ARFI elastography, native T1 mapping is a more robust quantitative technique with similar performances for staging fibrosis. Furthermore, it has a higher accuracy for monitoring liver fibrosis, especially for detecting fibrosis regression.
|
|
1736. 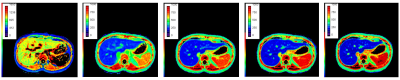 |
131 | The quantitative evaluation of Gd-EOB-DTPA enhanced magnetic resonance imaging T1mapping imaging on liver fibrosis
Tian Qiu, Yuxin Shi, Weibo Chen
Liver biopsy is an invasive inspection method of staging liver fibrosis,but we study was to evaluate a new procedure by injecting a Gd-EOB-DTPA that hepatobiliary specific contrast to stage the liver fibrosis non-invasively.
|
|
1737. 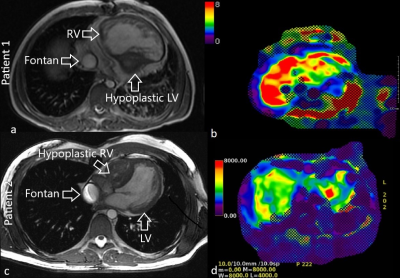 |
132 | Evaluation of Fontan Associated Liver Disease (FALD) with MRI: Does cardiac function play a role?
Kathan Amin, Liisa Bergmann, Alejandro Roldan, Scott Reeder, Christopher Francois
The Fontan procedure prolongs survival in patients with congenital heart disease with mono-ventricle physiology but is associated with multiple long-term complications, including Fontan associated liver disease (FALD). The pathophysiology of FALD is poorly understood. In this study, the relationship between ventricular ejection fraction (EF) and FALD was investigated through a retrospective review of 24 Fontan patients who underwent cardiac and liver MRI. No correlation was identified between systemic ventricular EF and liver stiffness. This demonstrates the need for further investigation into the pathophysiology of FALD. Potential exploration may include flow related differences, or variations in systemic venous pressures.
|
|
1738. 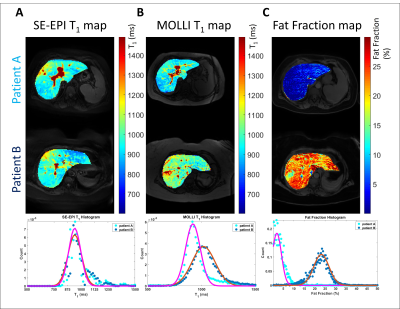 |
133 | Quantitative MRI to assess portal hypertension in cirrhosis patients at 3T
Chris Bradley, Rob Scott, Eleanor Cox, Naaventhan Palaniyappan, Indra Guha, Guruprasad Aithal, Susan Francis
We have previously validated MRI as a surrogate measure of Hepatic Venous Pressure Gradient (HVPG) at 1.5T using T1 relaxation time and splanchnic haemodynamics. Here, we explore the use of quantitative 3T MRI to assess portal hypertension. A strong correlation between HVPG and fat suppressed IR SE-EPI T1 (p<0.0001) and a correlation with superior mesenteric artery (SMA) velocity (p=0.02) was observed. MOLLI T1 showed a weak correlation with HVPG (p=0.11) compared with SE-EPI (p<0.001) in a matched patient subset. A fat suppressed IR SE-EPI T1 scheme and SMA velocity can be used as a surrogate for HVPG at 3T.
|
|
1739. 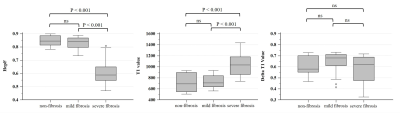 |
134 | The value of hepatocyte fraction based on pharmacokinetic model using gadoxetate disodium in assessment of liver fibrosis stage
En-Ming Cui, Wan-Sheng Long, Fan Lin, Qing Li, Jun-Hua Wu, Zhuo-Yong Li, Yong Lan, Ying-Jie Mei
Liver fibrosis is prevalent in patients with chronic liver disease, and the early diagnosis of liver fibrosis is still challenging in clinical practice. In this study, the hepatocyte fraction (HepF) was calculated using the T1 value before and 20min after Gd-EOB-DTPA injection (hepatobiliary phase). Patients with severe liver fibrosis showed significantly higher T1 value and lower HepF value. In addition, HepF achieved the best performance in differentiation of liver fibrosis from non-fibrosis (AUC = 0.74), and mild liver fibrosis from severe liver fibrosis (AUC = 0.95), proving HepF can be a better noninvasive quantitative method for liver fibrosis evaluation.
|
|
1740. 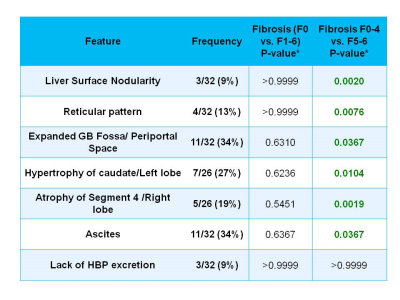 |
135 | Texture analysis Using Hepatobiliary Phase Gadoxetic-acid MRI for the Detection of Liver Allograft Fibrosis
Miriam Hulkower, Sara Lewis, Nicholas Vountsinas, Xing Chin, Priyanka Kadaba, Andrew Lee, Ayushi Singh, Joseph Song, Stefanie Hectors, Octavia Bane, Paul Kennedy, Juan Putra, Swan Thung, Thomas Schiano, Maria Isabel Fiel, Bachir Taouli
The goal of our study was to assess the value of qualitative and quantitative texture features on gadoxetic-acid enhanced MRI compared to blood tests for the detection of liver allograft fibrosis. We found that quantitative texture analysis and laboratory FIB-4 score exhibited complementary information for prediction of fibrosis stage, while qualitative MRI features were only valuable for identifying advanced fibrosis/cirrhosis.
|
|
1741. 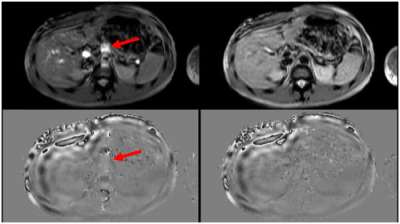 |
136 | A Rapid MR Elastography Sequence with Spatial Saturation Pulses to Suppress Vascular Flow
Hui Wang, Andrew Trout, Jean Tkach, Tom Cull, Jonathan Dillman, Charles Dumoulin
We describe a rapid fast field echo (FFE) Magnetic Resonance Elastography (MRE) pulse sequence for measurement of liver stiffness in reduced breath hold times (from 13.3s to 9.2s/slice). The key features of the sequence include: 1) modified motion encoding gradients to allow a shorter TR while maintaining appropriate synchronization with the period of the applied mechanical motion; 2) flow saturation pre-pulses to suppress ascending and descending vascular flow; and 3) SENSE reconstruction. Through validation in a gel phantom and subsequent measurement of liver stiffness in vivo, we demonstrate the effectiveness of the new pulse sequence.
|
|
1742. 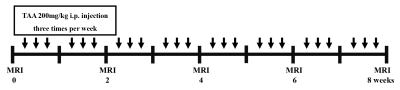 |
137 | Building an animal liver fibrosis bioimaging database for the MR imaging severity index establishment: progress report
Yeon Ji Chae, Chul-Woong Woo, Sang-Tae Kim, Young-Jin Kim, Ji-Yeon Suh, Ji-heon Kang, Kyung-Won Kim, Yoonseok Choi, Dong-Cheol Woo
The purpose of this study is to establish the imaging severity index of thioacetamide (TAA)-induced animal liver fibrosis model by magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) techniques.
|
|
1743 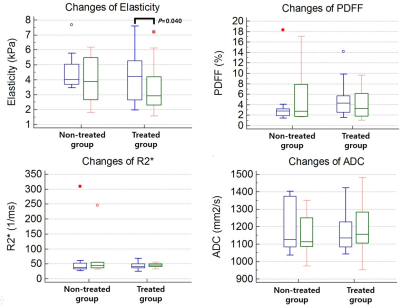 |
138 | Monitoring of antiviral treatment with MR elastography in chronic hepatitis patient: Feasibility study Video Permission Withheld
Yong Eun Chung, Mi-Suk Park, Seung Up Kim, Beom Kyung Kim, Myeong-Jin Kim
Multi-parametric MR including MR elastography (MRE), IDEAL IQ and diffusion weighted image were performed in patients with chronic liver disease. Among them, 15 patients were treated with antiviral agents which could improve liver fibrosis. In patients who underwent antiviral treatment, liver stiffness measured by MRE after treatment was significantly decreased. Liver stiffness in non-treated group and other MR parameters in both groups were not significantly changed. In conclusion, MRE could be used for the response evaluation of antiviral therapy in patients with chronic hepatitis
|
|
1744. 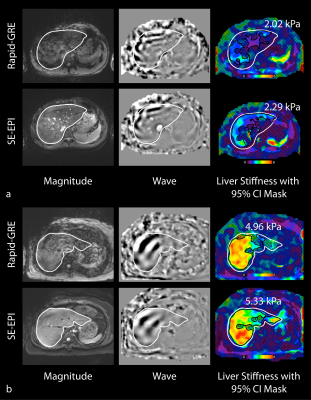 |
139 | Assessment of Spin-Echo and Gradient-Echo Liver MRE in Healthy Children and Children with Suspected Fibrosis at 3 T
Tess Armstrong, Sarai Santos, Karrie Ly, Ely Felker, Shahnaz Ghahremani, Xinran Zhong, Robert Venick, Joanna Yeh, Grace Hyun Kim, Kyunghyun Sung, Kara Calkins, Holden Wu
Magnetic resonance elastography (MRE) accurately measures liver stiffness and correlates with liver histopathology. However, conventional gradient-echo (GRE) MRE sequences require multiple breath-holds. Spin-echo echo-planar-imaging (SE-EPI) MRE only requires a single breath-hold. In this study we compared 2D SE-EPI and 2D rapid-GRE MRE sequences at 3T in healthy children and children with suspected fibrosis. Both SE-EPI and rapid-GRE had good repeatability, reproducibility, inter-reader agreement, and quantitative agreement in liver stiffness. SE-EPI provided larger measurable liver ROI sizes than rapid-GRE. SE-EPI may be desirable for measuring fibrosis in children with limited or inconsistent breath-hold ability and reduce scan times.
|
|
1745. 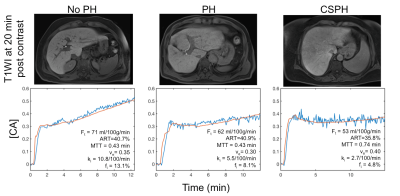 |
140 | Gadoxetic acid-enhanced perfusion quantification in the liver and spleen in portal hypertension
Stefanie Hectors, Octavia Bane, Paul Kennedy, Scott Friedman, Thomas Schiano, Maria Isabel Fiel, Swan Thung, Aaron Fischman, Bachir Taouli
The goal of our study was to assess the potential value of perfusion quantification using DCE-MRI with gadoxetic acid in the liver and spleen for noninvasive assessment of portal hypertension (PH). We found that the liver uptake fraction was significantly negatively correlated with hepatic venous pressure gradient measurements. We conclude that liver perfusion quantification is promising for noninvasive assessment of PH. After validation of these findings in a larger cohort of patients, DCE-MRI may potentially decrease the need of invasive portal pressure measurements.
|
|
1746 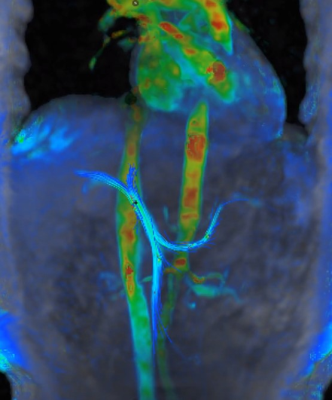 |
141 | Alteration of blood flow in hepatic fibrosis: preliminary results Video Permission Withheld
JeongHee Yoon, Jeong Min Lee, Moon Jung Hwang, Hiroyuki Kabasawa, Joon Koo Han
Portal flow is believed to relate to liver regeneration and may reflect the hemodynamic change of liver cirrhosis. So far, it has been relied on Doppler examination, which only sampled in local two-dimensional (2D) acquisition planes. Recently, four-dimensional (4D) flow acquisition of MRI may provide more accurate vascular flow information. However, there have been only a few studies of the liver in the literature.
|
|
1747. 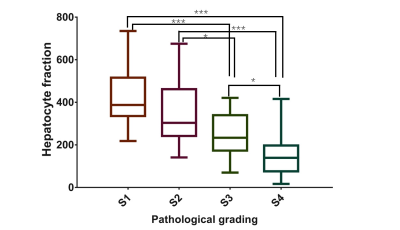 |
142 | A Promising Procedure for the Staging of Liver Fibrosis Using Hepatocyte Fraction
Weibo Chen, Tian Qiu, Eunju Kim, YuXin Shi*
Liver biopsy is an invasive and painful procedure for staging liver fibrosis. This study aimed to evaluate a new procedure by injecting a hepatobiliary-specific contrast agent Gadolinium
|
|
1748. 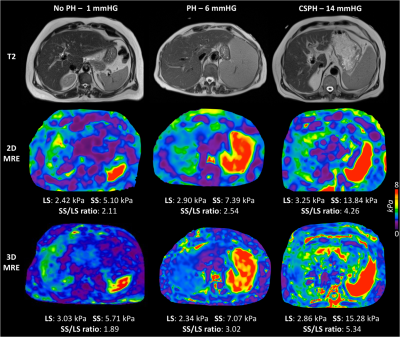 |
143 | Non-invasive assessment of portal hypertension using magnetic resonance elastography and ultrasound shear wave elastography of the liver and spleen.
Paul Kennedy, Octavia Bane, Stefanie Hectors, Scott Friedman, Thomas Schiano, Maria Isabel Fiel, Swan Thung, Aaron Fischman, Bachir Taouli
The aim of this ongoing prospective study is to investigate the utility of both 2D and 3D MR elastography (MRE) and ultrasound shear wave elastography (SWE) for the assessment of portal hypertension in patients with chronic liver disease. Initial results indicate that 3D MRE measured spleen stiffness and the spleen to liver stiffness ratio measured with 3D MRE and SWE significantly correlate with hepatic venous pressure gradient measurement. This suggests that 3D MRE is sensitive to physiological changes associated with portal hypertension. Confirmation in a larger patient cohort may validate 3D MRE as a non-invasive surrogate for portal pressure measurement.
|
|
1749. 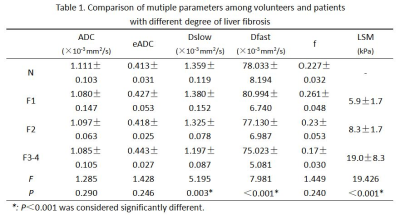 |
144 | Assessment of chronic hepatitis B liver fibrosis staging using Intravoxel incoherent motion MRI compared with ultrasonic transient elastography
Qing Li, Shuangshuang Xie, Zhizheng Zhuo, Wen Shen
we compare the value of IVIM and ultrasonic transient elastography in evaluating the fibrosis staging of patients with chronic hepatitis B, and we found that IVIM is potential to assese chronic hepatitis B liver fibrosis and inferior to ultrasonic transient elastography, however Dslow and f have comparable diagnostic value with ultrasonic transient elastography in evaluating in liver fibrosis stage≥F3.
|
|
1750. 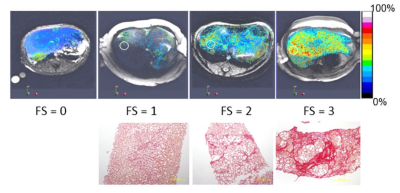 |
145 | New MRI Method for the Detection of Liver Fibrosis: Validation and Staging
Jie Zheng, Lichuan Yang, Joseph Gabriel, Guangzhong Wang, Shaozhu Liu, Tony Wang, Bob Zhang
The purpose of this study was to develop a MR imaging markers for quantitative assessment of liver fibrosis and validate the method. Both normal monkeys and monkeys with non-alcoholic steatohepatitis were used for the validation study compared to histopathology of liver biopsy specimens. Liver extracellular volume was quantified and correlated strongly with biopsy fibrosis scores.
|
|
1751. 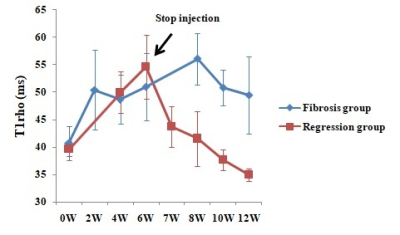 |
146 | Liver injury monitoring, fibrosis staging and inflammatory grading with T1rho MR imaging: an experimental study in rats with carbon tetrachloride intoxication
shuangshuang xie, Qing Li, hanxiong qi, Kun Zhang, zhizheng zhuo, Yue Cheng, Wen Shen
In this article, we investigate the value of T1rho MRI in monitoring CCl4-induced liver injury, staging liver fibrosis and grading inflammation activity in a rat model. Forty-one model rats underwent black blood T1rho MRI in multiple time points, and eleven normal rats selected as control group. Liver T1rho values were measured in different time points and compared between different fibrosis stages and inflammation grades. Our result showed that T1rho MRI can be used to monitor CCl4-induced liver injury. Changes of liver T1rho values were the result of a combination of liver fibrosis and inflammation activity, and inflammation activity had a greater impact on liver T1rho values than fibrosis.
|
|
1752. 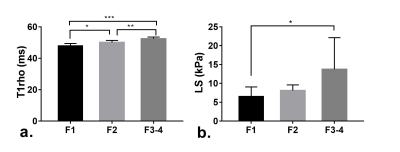 |
147 | Staging liver fibrosis with T1rho MR imaging and ultrasonic elastography alone and in combination in patients with chronic hepatitis B
shuangshuang xie, Qing Li, hanxiong qi, Kun Zhang, zhizheng zhuo, Yue Cheng, Wen Shen
In this article, we compare the diagnostic efficiency of T1rho, ultrasonic elastography (UE) and the combination of them in staging liver fibrosis. Thirty-two patients with chronic hepatitis B underwent T1rho MRI and UE were analyzed. T1rho is better than UE in staging liver fibrosis, and the combination of T1ho and UE can improve the diagnostic efficiency in differentiating F1 from F2-4.
|
|
1753. 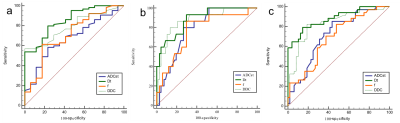 |
148 | Non-invasive assessment of hepatic fibrosis and inflammatory activity in patients with chronic hepatitis B:Comparison of multiple diffusion-weighted MR imaging models
Fang fang Fu, Xiaodong Li, Yan Bai, Qiuyu Liu, Da peng Shi, Yusong Lin, Meiyun Wang
In this study, we assessed the value of various diffusion parameters obtained from monoexponential, biexponential, and stretched-exponential DWI models in predicting the hepatic fibrosis (HF) stage and inflammatory activity grade in patients with chronic hepatitis B (CHB). We found that true diffusion coefficient (Dt) and distributed diffusion coefficient (DDC) are promising indicators and outperform the standard apparent diffusion coefficient (ADCst) for HF staging and inflammatory activity grading. We believe that biexponential and stretched-exponential model could be more helpful compared with monoexponential model in monitoring the progression of HF and inflammatory activity, guiding therapy, and assessing the effect of the treatment.
|
Digital Poster
| Exhibition Hall | 13:45 - 14:45 |
| Computer # | |||
1754. 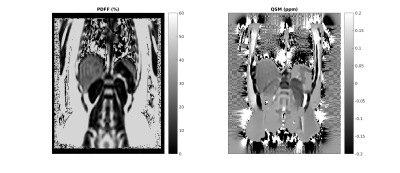 |
151 | Correlation between susceptibility, R2* and PDFF in liver
Ramin Jafari, Adrija Mamidipalli, Walter Henderson, Gavin Hamilton, Pascal Spencemille, Mark Bydder
A susceptibility difference between the water and fat components in liver should give rise to a linear increase in R2* with proton density fat fraction (PDFF). This is observed empirically although the value of the susceptibility difference is subject to variability (from ~0 ppm to 0.75ppm). The present abstract aims to measure the susceptibility difference directly by measuring liver susceptibility as a function of the PDFF in patients with fatty liver.
|
|
1755. 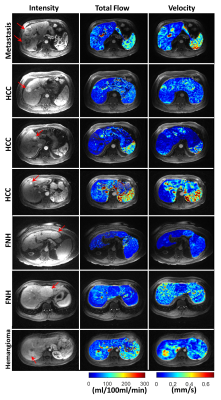 |
152 | Quantitative DCE-MRI Analysis without an Arterial Input Function: A Comparison Study with Compartment Modeling in Liver Lesions
Ramin Jafari, Pascal Spincemaille, Martin Prince, Liangdong Zhou, Yi Wang
Dynamic contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging (DCE-MRI) is a noninvasive
|
|
1756. 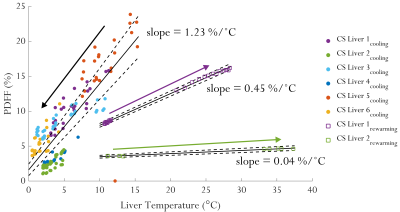 |
153 | Temperature sensitivities of T1, fat fraction and water resonance frequency characterised in ex vivo human livers
Liam Young, Carlo Ceresa, Ferenc Mozes, Jane Ellis, Ladislav Valkovic, Constantin Coussios, Peter Friend, Christopher Rodgers
MR techniques enable viability assessment of ex vivo organs for transplantation and non-invasive post-mortem examinations. However, temperature variations in ex vivotissue and cadavers can drastically alter MR measurements of T1 and fat fraction, which risks masking underlying pathology if not considered carefully. Therefore, we investigated the changes observed in fat fraction and T1 in ex vivo human livers during a period of cooling and re-warming. Obtaining multiple measurements at different temperatures enabled determination of temperature sensitivity independent of underlying pathology, which could be used to perform a “temperature correction” of ex vivodata allowing greater sensitivity to pathological changes.
|
|
1757. 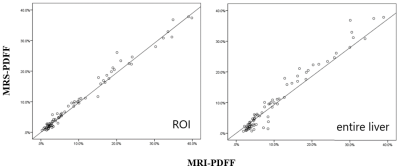 |
154 | Accuracy of multi-echo Dixon sequence in the quantification of hepatic steatosis in Chinese children and adolescents, with reference to HISTO
Yuzhen Zhao, Jianli Zhou, Jiaqi Liu, Shaoming Zhou, Yungen Gan, Weiguo Cao, Mengzhu Wang
This study investigated the accuracy of MRI in quantifying liver fat of 86 Chinese children and adolescents, with magnetic resonance spectroscopy (MRS) as reference. MRI and MRS were performed with multi-echo Dixon (ME Dixon) and HISTO sequence respectively to calculate hepatic proton density fat fraction (PDFF). Hepatic steatosis was diagnosed using MRS-PDFF > 5% as threshold. Spearman analysis indicated excellent correlation between ME Dixon and MRS (r>0.9,P<0.01). Bland-Altman analysis demonstrated good agreement between these two methods, indicating that ME Dixon can be an accurate way to detect hepatic steatosis in children and adolescents.
|
|
1758. 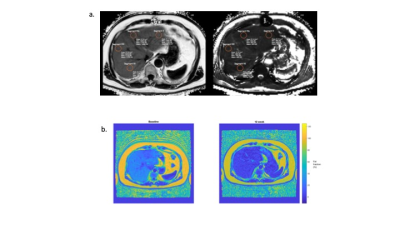 |
155 | Liver proton density fat fraction as a trial endpoint in an international multi-site phase-II trial in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus following treatment with duodenal mucosal resurfacing
Naomi Sakai, Alan Bainbridge, David Maggs, Margaret Hall-Craggs, Rachel Batterham, Stuart Taylor, Manil Chouhan
Vendor-certified proton density fat fraction (PDFF) sequences are commercially available across multiple scanner systems and represent a robust method for quantification of liver fat and liver T2* mapping. Type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) is associated with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and dysregulation of iron homeostasis. Duodenal mucosal resurfacing (DMR) is a novel treatment for patients with T2DM who have poor glycaemic control. We describe our technique for quality assurance across multiple sites using custom fat-water phantoms and report preliminary liver PDFF and liver iron concentration results from a cross-site, multi-vendor study in patients at baseline and 12 weeks after DMR.
|
|
1759. 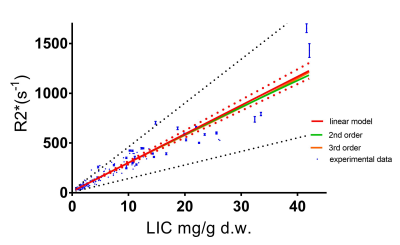 |
156 | A new calibration between R2* and Liver Iron Concentration derived from 167 clinical cases
Gregory Brown, Gary Cowin, Graham Galloway
The commonly used equation to determine Liver iron concentration (LIC) from R2* was developed from a very small cohort (n=23) and an acquisition approach significantly different to that currently used in clinic. Three subsequent calibrations used progressively larger moderate (n=43-88) to derive divergent results. This study measured liver R2* from 835 gradient echo relaxometry acquisitions in 167 clinical examinations. Correlation between R2* and reference LIC measurement was evaluated for first to third order polynomials. A linear equation provided the best fit, delivering a new calibration equation that differs significantly from earlier work.
|
|
1760. 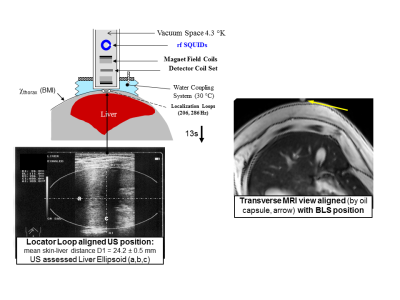 |
157 | IRON MEASUREMENTS BY QUANTITATIVE MRI-R2* AT 3.0 AND 1.5 T IN COMPARISON TO SQUID BIOMAGNETIC LIVER SUSCEPTOMETRY (BLS)
Jin Yamamura, Björn Schönnagel, Sarah Keller, Christoph Berliner, Enver Tahir, Regine Grosse, Zhiyue Wang, Gerhard Adam, Roland Fischer
In this study the suitability of a 3.0 T imager for iron measurements over the whole range of possible iron concentrations in the liver and other organs or glands is investigated. For this purpose the results on liver iron is compared for the feasibility of 3.0T to both 1.5T MRI and SQUID BLS.
|
|
1761. 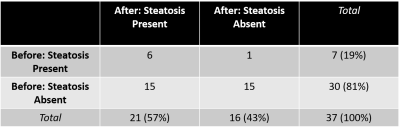 |
158 | Correlation Between Somatostatin Treatment and Elevated Hepatic Fat Fraction on MRI in Patients with Neuroendocrine Tumors
Preeti Sukerkar, Kathleen Hornbacker, Jarrett Rosenberg, Pamela Kunz, Pejman Ghanouni
Up to 90% of neuroendocrine tumor patients have metastatic disease in the liver at diagnosis. These patients are treated with somatostatin analog therapy and monitored with CT or MRI. We demonstrate in a retrospective study that somatostatin therapy is associated with the development of elevated liver fat fraction on MRI. Furthermore, preliminary results suggest that hepatic steatosis decreases lesion detectability on CT compared to MRI. Studies are ongoing to determine the severity of steatosis and relationship to cumulative somatostatin dose, variation in fat fraction over time and the response to change in medication, and effect on liver function.
|
|
1762. 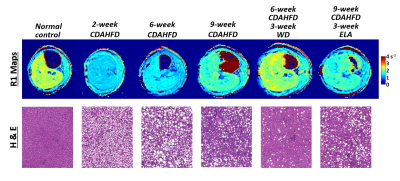 |
159 | MRI Relaxometry in a Rat Model of Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis (NASH)
Iris Zhou, Nicholas Rotile, Veronica Clavijo Jordan, Gunisha Arora, Smitha Krishnan, Hannah Slattery, Noah Warner, Christian Farrar, Bryan Fuchs, Peter Caravan
Nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH), characterized by the presence of steatosis, inflammation
|
|
1763. 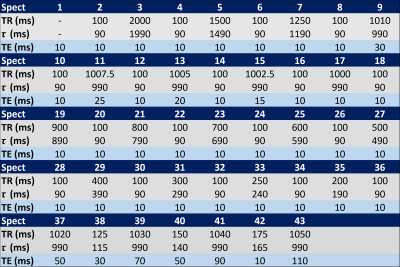 |
160 | Relation between T1 and T2 of liver water and fat and Proton Density Fat Fraction estimated by a flip angle corrected multi-TR, multi-TE single breath-hold 1H MRS STEAM sequence
Gavin Hamilton, Alexandra Schlein, Michael Middleton, Rohit Loomba, Claude Sirlin
We examine the relationship between liver water and fat T1 and T2, and PDFF in adult subjects undergoing non-contrast exams using a version of the multi-TR, multi-TE 1H MRS sequence that estimates and corrects for flip angle based on a non-steady-state approach.
|
|
1764. 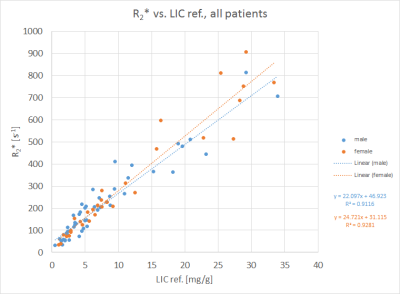 |
161 | MRI Relaxometry based Liver Iron Content Determination: Comparing Gradient-Echo R2* and Spin-Echo with respect to Age and Gender
Arthur Wunderlich, Valeria Mauro, Meinrad Beer, Stefan Schmidt, Holger Cario
To address probable differences in signal characteristics between spin-echo (SE) and gradient-echo (GRE), 83 patients suspected for liver iron overload were investigated with 1.5 T MRI with the approved Ferriscan® method based on SE, and a prototype breathhold 3D GRE protocol employing parallel imaging with in-line R2* calculation. R2* values were correlated with reference LIC for all patients together and in subgroups according to age and gender. Highly significant differences (P=0.009) were found between males and females in the age range from 12 to 45 years, possibly reflecting different underlying iron storage mechanisms.
|
|
| 1765 |
162 | Susceptibility-weighted imaging (SWI) compared to T2* mapping in the presence of hepatic steatosis and fibrosis Video Permission Withheld
Verena Obmann, Nando Mertineit, Annalisa Berzigotti, Christina Marx, Lukas Ebner, Michael Ith, Johannes Heverhagen, Andreas Christe, Adrian Huber
We hypothesized, that susceptibility weighted imaging (SWI) and T2*-mapping are dependent on liver steatosis, which should be taken into account when using these parameters to grade liver fibrosis and cirrhosis. In this study 184 patients underwent multiparametric MRI at 3T including SWI, T1/T2* mapping as well as proton density fat fraction quantification and MR elastography as reference standard. SWI and T2* were both highly dependent on the degree of liver steatosis (p<0.001). However, SWI allowed a better differentiation between liver fibrosis grades (p <0.001) than T2*. Nevertheless, both parameters are useful predictors for liver fibrosis when using a multiparametric approach.
|
|
1766. 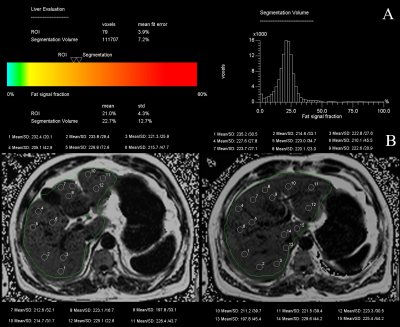 |
163 | Quantitative evaluation of hepatic steatosis using rapid multi-echo Dixon technique in patients with obesity Presentation Not Submitted
Wei Wei, Yan Bai, Yusong Lin, Meiyun Wang
This study aimed to demonstrate the feasibility and accuracy of magnetic resonance imaging multi-echo Dixon rapid liver fat quantitative analysis for liver fat content in the obese patients. In the first of our study, we performed liver scan on 17 obese patients using multi-echo Dixon rapid liver fat quantification technique and then we re-measured the entire liver fat content by previous method manually drawing ROIs on each liver segment. The Bland-Altman plots and Pearson correlation analysis were performed on the quantitative results of the above two methods. There statistical analysis showed there were good consistence and highly correlated with the two methods. We found the multi-echo Dixon rapid liver fat quantitative can simply, feasibility and accurately assess the liver fat content in the patients with obese .
|
|
1767. 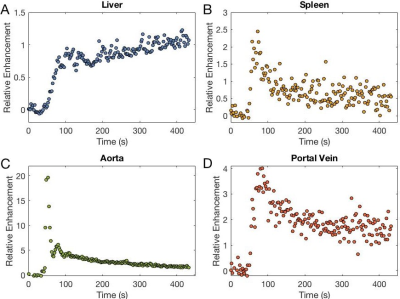 |
164 | Determining Liver Function: Comparison of Gadoxetate Pharmacokinetic Models Using Perfusion Imaging
Markus Karlsson, Susmita Basak, David Longbotham, Steven Sourbron, Gunnar Cedersund, Peter Lundberg
Hepatic uptake rate of Gadoxetate is a liver function biomarker. Different approaches for pharmacokinetic modelling exists, both with regards to model architecture and choice of input data, with both blood and spleen being used to estimate input-function. We fitted three models to perfusion data, using both aorta and portal venous inputs, as well as splenic input. We showed that the hepatic uptake rate of Gadoxetate is robust, in that the uptake rate is not very dependent on how the liver perfusion is modelled. However, the choice of vascular or splenic input can affect the uptake rate.
|
|
1768. 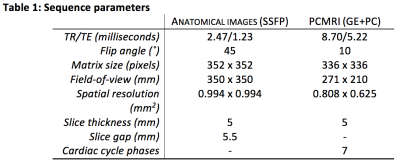 |
165 | Phase-contrast MRI-based estimation of labeling efficiency for liver pseudo-Continuous Arterial Spin Labeling
Magdalena Sokolska, Lucy Caselton, Stuart Taylor, Manil Chouhan
Chronic liver disease is associated with profound changes in the dual portal venous (PV) and hepaticarterial (HA) blood supply to the liver. Pseudo-continuous arterial spin labeling (pCASL) canmeasure hepatic blood non-invasively and separate PV and HA contributions, however quantification is directly proportional to the labeling efficiency (alpha), and can therefore significantly affect overall quantification. This study estimates alpha for the PV, descending aorta (DA) and HA using a Bloch equation simulator and velocities measured directly using phase-contrast MRI at the level of the labeling plane, taking into account the effects of labeling plane angulation. We demonstrate that it is reasonable to assume a labeling efficiency of 0.85 for hepatic pCASL in normal volunteers.
|
|
1769. 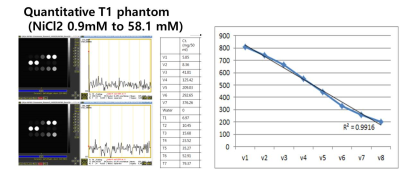 |
166 | Validation of T1 map on Gd-EOB-DTPA-enhanced liver MRI as a quantitative biomarker of liver function: Calibration, reproducibility, and diagnostic value
Jimi Huh, Gyeongmin Park, Tae Young Lee, Jisuk Park, Bohyun Kim, Hye Jin Kim, Jei Hee Lee, Jai Keun Kim, Kyung Won Kim
T1 map using MOLLI sequence on EOB-MRI showed promise for evaluating liver function in patients with liver cirrhosis. Especially, T1-map was accurate to evaluate T1 values based on quantitative phantom study and accurate to diagnose decompensated liver cirrhosis. However, test-retest reproducibility was moderate, requiring further technical improvement.
|
|
1770. 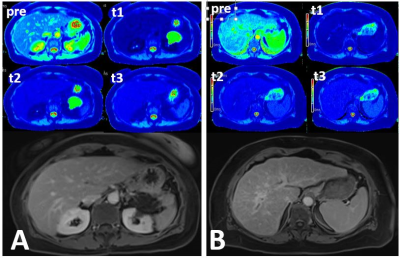 |
167 | Quantitative Measurement of Serial Contrast Agent Distribution between Liver and Blood in Patients with Chronic Liver Disease using T1 mapping
Puneet Sharma
This study investigates the post-contrast time sensitivity of liver-to-blood partition coefficient. In vivo change in liver-to-blood contrast distribution was calculated at 3 time-points following contrast administration using a fast inversion-recovery Look-Locker T1 mapping approach. While measurement and exam time variation did not reveal a consistent equilibrium time threshold, results show that contrast distribution becomes increasingly different between chronic and non-chronic liver disease groups at least 5 minutes post-contrast, allowing possible measurement of liver extracellular volume fraction.
|
|
1771. 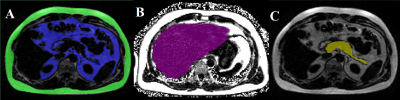 |
168 | Noninvasive Assessment of Abdominal Adipose Tissues and Fat Quantification of the Liver and Pancreas in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
Manoj Sarma, Andres Saucedo, Daniel Kohanghadosh, Edward Xu, Ely Felker, Christine Darwin, M. Albert Thomas
Type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) is a chronic metabolic disorder effecting millions of people worldwide. T2DM is associated with insulin resistance and adipose tissue dysfunction which promote ectopic fat deposition and lipotoxicity in muscle, liver, and pancreatic beta cells. However, the impact of dysfunctional adipose tissue has not been fully elucidated. Here we examined the adipose tissue (SAT), visceral adipose tissue (VAT), hepatic fat fraction (HFF) and pancreatic fat fraction (PFF) difference between T2DM and age-matched healthy controls using the 6-point Dixon MRI technique and assess relationship with biochemical markers of insulin resistance. We observed trend of increasing VAT, SAT and TAT volume in T2DM patients along with significantly higher HFF% and PFF%. HbA1c in T2DM patients were positively correlated with VAT, total adipose tissue and HFF%. Our preliminary results of increased SAT and VAT reaffirmed that central obesity is connected with the evolution of T2DM. Increased HFF% and correlation of increased HbA1c with increased HFF% in T2DM suggested that T2DM patients suffer from nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. In summary, increased liver, pancreatic fat, and adipose tissue characterize T2DM patients and the insulin resistance. Better understanding of these results will help us in formulate early intervention strategies and to evaluate the efficacy of therapies.
|
|
1772 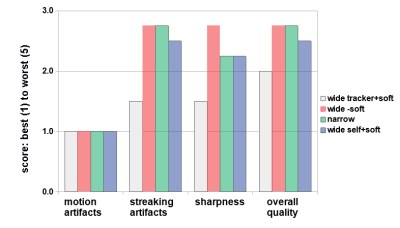 |
169 | 3D Stack-of-Stars Radial Imaging for Motion-Robust Free-Breathing Hepatobiliary Phase Imaging Video Permission Withheld
Matthias Muehler, Ty Cashen, Kang Wang, Ali Ersoz, Ersin Bayram, Scott Reeder
Free-breathing hepatobiliary phase imaging with gadoxetate disodium is challenging due to respiratory motion. This study examines an intrinsically motion-robust fat-suppressed T1-weighted 3D stack-of-stars gradient echo technique (LAVA Star) with soft gating. An estimate of respiratory motion is derived either from a navigator tracker with a wide acceptance window, which produces the best image quality, or self-navigation, which offers the most convenient workflow, particularly in challenging clinical situations. In either case, the retrospective soft gating reduces scan time variability compared to a conventional prospective navigator.
|
|
1773.  |
170 | Inter-site repeatability and quantitative assessment of hepatic transporter function with DCE-MRI in rats
Claudia Green, Sirisha Tadimalla, Denise Steinmann, Steven Sourbron, Sascha Koehler, Hans-Paul Juretschke, Iina Laitinen, John C. Waterton, Paul D. Hockings, Catherine D. G. Hines, Gunnar Schuetz
Drug-induced liver injury can halt liver-metabolized drug development or cause withdrawal from the market. Toxicologists lack appropriate and reproducible assays. We present repeatability and reproducibility results from a multi-center study with dynamic gadoxetate-enhanced MR imaging biomarkers of hepatic transporter-mediated injury in rats. Our study supports the development of a validated liver function-specific quantitative MR imaging biomarker, and we demonstrate that the biomarkers are repeatable and that the previously reported MR assay findings are reproducible across three centers.
|
|
1774.  |
171 | Preoperative Remnant Liver Function Evaluated by a Clinical-Available Gd-EOB-DTPA-Enhanced MR Imaging Protocol: Independently Significant Indicator in Predicting Posthepatectomy Liver Failure in HCC Patients
Yajie Wang, Lin Zhang, Jia Ning, Xinjing Zhang, Xuedong Wang, Shizhong Yang, Jiahong Dong, Huijun Chen
Preoperative remnant liver function evaluation is important for surgery planning and reducing posthepatectomy liver failure (PHLF) rate in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) patients. This study demonstrated that the remnant liver functions preoperatively evaluated by a clinical available Gd-EOB-DTPA-enhanced imaging protocol were the independently significant indicator in predicting PHLF after adjusting for other PHLF risk factors including sex, age, hepatitis, cirrhosis, preoperative blood serum indices, operation time, intraoperative blood loss and intraoperative blood transfusion in the multivariate logistic regression.
|
|
1775.  |
172 | Clinical, technical, and biochemical predictors of adequate hepatobiliary phase enhancement on Gadobenate-Dimeglumine-enhanced MRI of the liver in patients with chronic liver disease and HCC
Jingbiao Chen, Sichi Kuang, Yao Zhang, Hao Yang, Ying Deng, Bingjun He, Kathryn Fowler, Claude B. Sirlin, Jin Wang
Liver dysfunction impairs the uptake of gadobenate dimeglumine by liver parenchyma, which reduces hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) conspicuity on hepatobiliary phase (HBP) images. Although the effect of Child-Pugh class and some biologic factors have been investigated, there is a paucity of data on other plausible predictors of HBP adequacy. Here we show that elevated albumin level, prolonged HBP delay time, and absence of liver cirrhosis predict HBP adequacy on gadobenate-MRI in patients with chronic liver disease and HCC. In the subset of patients with cirrhosis and HCC, adequate HBP was associated with elevated serum creatinine level and prolonged HBP delay time.
|
|
1776. 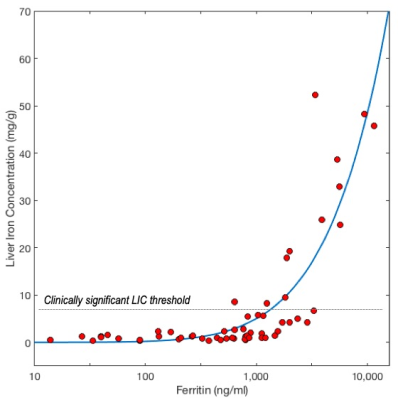 |
173 | Bayesian selection of dedicated liver iron quantification MRI for patients with clinically-significant iron overload
Takeshi Yokoo, Ivan Pedrosa, Diego Hernando, Scott Reeder
R2- and R2*-MRI has become an important clinical tool to noninvasively quantify liver iron concentration (LIC) in patients with significant iron overload who may require iron-reducing therapy. However, these highly specialized exams can only be performed on dedicated 1.5T scanners meeting certain technical specifications. Therefore, a priori selection of patients according to their pre-test probabilities of significant iron overload may help correctly match the patients’ clinical needs to the appropriate MRI scanner and exam protocol. This study derives a Bayesian patient selection criterion based on serum ferritin to identify patients who may and may not benefit from dedicated liver iron quantification MRI.
|
|
1777. 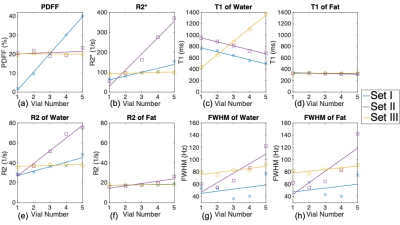 |
174 | A Quantitative MRI Phantom to Mimic the Simultaneous Presence of Fat, Iron, and Fibrosis
Ruiyang Zhao, Gavin Hamilton, Jean Brittain, Scott Reeder, Diego Hernando
Fat, iron and fibrosis are important features of liver disease that commonly coexist. Emerging quantitative MRI biomarkers including proton density fat fraction (PDFF), R2*/R2 and T1 enable quantification of fat, iron, and fibrosis, respectively, and require quantitative MR phantoms for validation and quality assurance. Although current phantoms enable separate adjustment of PDFF, R2*/R2 or T1, there is an unmet need for phantoms that accurately mimic MRI signals in the presence of simultaneous fat, iron and fibrosis by jointly controlling PDFF, R2*/R2 and T1. In this work, we develop and validate a novel phantom that jointly controls PDFF, R2*/R2 and T1.
|
Digital Poster
| Exhibition Hall | 14:45 - 15:45 |
| Computer # | |||
1778. 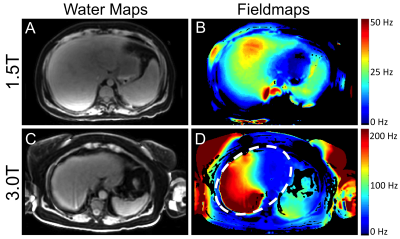 |
1 | B0 and B1 Inhomogeneities in the Liver at 1.5T and 3.0T
Nathan Roberts, Diego Hernando, Timothy Colgan, Louis Hinshaw, Dylan Kernan, Scott Reeder
Inhomogeneities in the static (B0) and transmitted (B1) magnetic fields can lead to artifacts and image degradation for a large variety of imaging applications. Quantitative MRI applications that fail to account for B0 and B1 inhomogeneities may suffer from substantial errors. Understanding the range of expected B0 and B1 inhomogeneities experienced in vivo is essential to engineer solutions aimed at avoiding or correcting for these effects. In this work, we measure the B0 and B1 inhomogeneities in the liver of 60 and 312 patients, respectively, at both 1.5T and 3.0T.
|
|
1779. 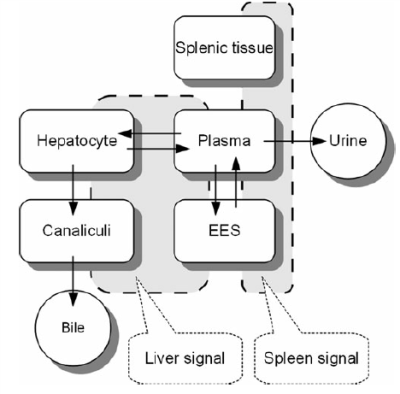 |
2 | Quantitative Assessment of Liver Function using Hepatocyte Fraction on Gd-EOB-DTPA-Enhanced MRI
Xueqin ZHANG, Jian LU, Jifeng JIANG, Ding DING, Weibo CHEN
The purpose of this study was to investigate the ability of hepatocyte fraction on Gd-EOB-DTPA-enhanced MRI for the assessment of liver function of HBV-induced cirrhosis. We used Look-Locker sequences to acquire T1 mapping images pre and post-contrast at 20 minutes after Gd-EOB-DTPA administration, hepatocyte fraction (HeF) and KHepvalues were measured. Our study showed that hepatocyte fraction is useful for the evaluation of liver function of HBV-induced cirrhosis.
|
|
1780. 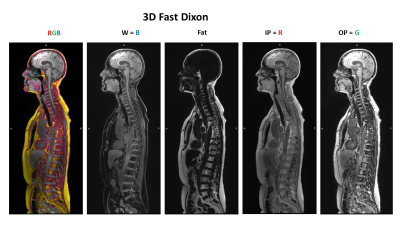 |
3 | Color-Encoded Multiparametric 3D Fast Dixon
Kenneth Weiss, Judd Storrs, Manohar Roda
We developed a novel color-encoding technique for Dixon imaging that combines in-phase, out-of-phase and water images into a single intuitive color image. We demonstrate its potential to facilitate interpretation of these complex information-rich datasets, reduce the number of requisite images to be stored and reviewed, and thereby extend Dixon’s clinical utility across the body.
|
|
1781. 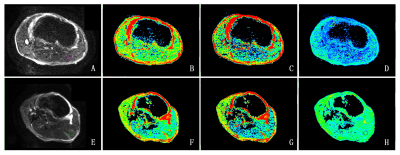 |
4 | Stretched exponential diffusion-weighted imaging model in quantitative diagnosis of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease : a rabbit model study Presentation Not Submitted
Chang li, Xianfu luo, Weiqiang Dou, Yun Peng, Jingtao wu, Jing Ye
We aimed to investigate if a stretched exponential diffusion weighted imaging model (SEM) can be applied to assess nonalcoholic liver disease (NAFLD) disease by providing distributed-diffusion-coefficient (DDC) and α separately evaluating mean intravoxel diffusion rate and diffusion heterogeneity. The SEM model was then applied to analyze NAFLD in a rabbit model and compared with a mono-exponential (ME) model. While DDC from the SEM model showed comparable values with apparent-diffusion-coefficient (ADC) estimated in the ME model, alpha indicated more robust performance in the diagnosis of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH). Therefore, SEM model showed a great potential in early diagnosis of NASH.
|
|
1782. 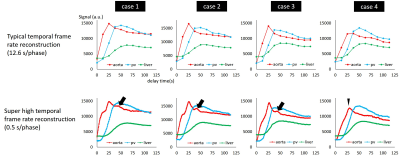 |
5 | Super high temporal frame rate reconstruction in abdominal dynamic contrast-enhanced MRI using stack-of-stars acquisition (LAVA-Star) under free breathing toward comprehensive hemodynamic analysis of the abdominal vessels and organs: a feasibility study
Tetsuya Wakayama, Daiki Tamada, Kang Wang, Ty Cashen, Ali Ersoz, Shintaro Ichikawa, Hiroshi Onishi, Utaroh Motosugi
We demonstrated the feasibility of breath hold-free dynamic MRI of the liver using stack-of-stars acquisition with super high temporal frame rate (0.5s/phase) reconstruction. Stack-of-stars acquisition with soft gating technique enabled to acquire sufficient quality of dynamic MRI without breath-holdings. The super high frame rate reconstruction provided the better time-intensity curves, which enabled to capture accurate time-to-peak enhancement of each vessel, a second bolus pass in the aorta, and the peak delay from splenic vein to main portal vein. This technique is feasible for the comprehensive understandings of hemodynamics in arterial and portal venous circulation and abdominal organs.
|
|
1783. 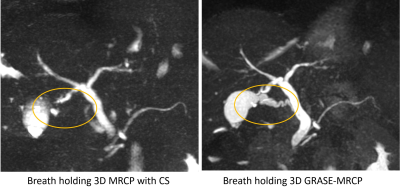 |
6 | Better Depiction of Cystic Duct with Breath-hold 3D MRCP accelerated with GRASE as compared with FSE-based MRCP with Compressed Sensing at 1.5T
Mamoru Takahashi, Yasuo Takehara, Norihiro Tooyama, Katsutoshi Ichijo, Yasutomo Katsumata, Akira Suwa, Harumi Sakahara
We compared the depiction of the cystic duct between two types of 3D breath-holding MRCP accelerated with GRASE (GRASE-MRCP) and FSE with compressed sensing (CS-MRCP) at 1.5T. Although imaging time and overall image quality
|
|
1784. 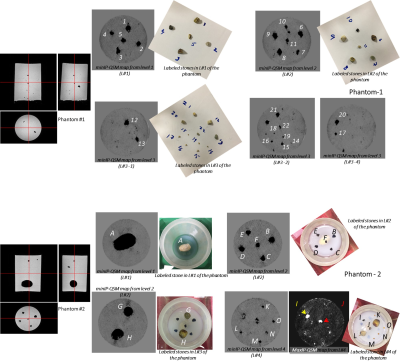 |
7 | Magnetic susceptibility of gallbladder stones
Rakesh Gupta, Jaladhar Neelavalli, Manoj Kumar, Indrajit Saha, Pradeep Gupta, Jitender Saini, Sunita Ahlawat
Quantification of volume magnetic susceptibility of extracted gallbladder stones, with 28 different types of textures, was performed using quantitative susceptibility mapping. Both dia- and para-magnetic stones are seen and the susceptibility values were found to be comparable in magnitude to those found in venous vessels and blood products – and hence could be detected in-vivo using SWI. This is in agreement with a recent work reporting visualization of gall-stones using SWI.
|
|
1785. 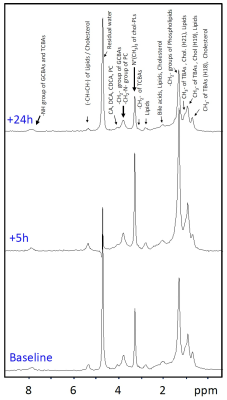 |
8 | High-fat stimulation in healthy subjects: Longitudinal monitoring of bile acid and diffusivity changes in the gallbladder by MRS and MRI
Peter Vermathen, Dino Kroell, Philipp Nett, Guido Stirnimann, Reiner Wiest
Bile exerts multiple functions in the liver and gut and is a key player in disease processes. In this pilot study we implemented a standardized stimulation test with high-fat diet in lean physically fit individuals and performed MRS and MRI measurements longitudinally to monitor bile acid composition and diffusivity changes in the gallbladder, with the long term aim to determine a specific bile-acid-microbiota “signature”. Strongly increased bile acid and lipid resonances and reduced diffusivity after lipid ingestion were determined as well as reversal to base values within 24h, demonstrating the feasibility and potential of the method.
|
|
1786. 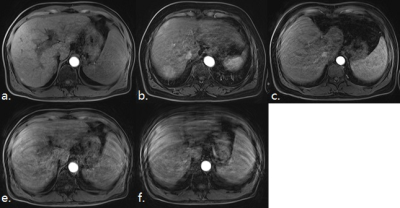 |
9 | Artifacts in the arterial phase during gadoxetic-acid-enhanced MRI: multiple arterial phases versus single arterial phase from two different vendors
shuangshuang xie, hanxiong qi, Qing Li, Kun Zhang, Jinxia Zhu, Wen Shen
In this article, we compare the usefulness of multiple arterial phases (APs) and a relatively short breath-hold single AP to reduce the motion artifact in gadoxetic-acid-enhanced MRI. The transient motion artifact (TMA) score and phase timing of the AP in 540 consecutive patients were retrospectively analyzed. Our results showed that the best mean TMA score for multiple APs was significantly lower than that for the conventional single AP, but a relatively short breath-hold single AP did not reduce the incidence of TMA. In addition, multiple APs can capture more satisfactory ones, which meets clinical diagnostic requirements.
|
|
1787. 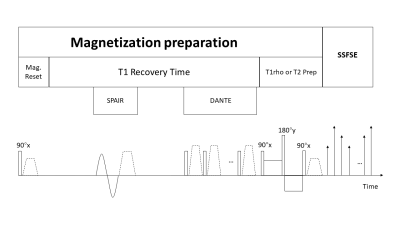 |
10 | Breathhold Black Blood Quantitative Parametric Imaging of the Liver Using Magnetization Prepared Single Shot Fast Spin Echo with DANTE Preparation
Jian Hou, Baiyan Jiang, Weibo Chen, Queenie Chan, Weitian Chen
|
|
1788. 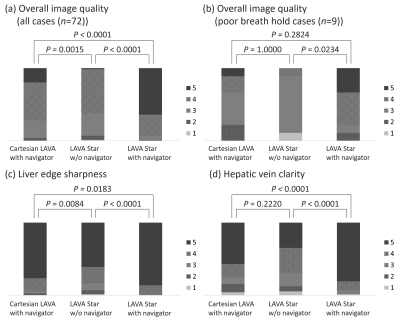 |
11 | Breath hold free hepatobiliary phase imaging: usefulness of stack-of-stars acquisition
Shintaro Ichikawa, Utaroh Motosugi, Marie-Luise Kromrey, Daiki Tamada, Tetsuya Wakayama, Kang Wang, Ty Cashen, Ali Ersoz, Hiroshi Onishi
We compared the quality of hepatobiliary phase (HBP) imaging using the prototype pulse sequences stack-of-stars liver acquisition with volume acceleration (LAVA) (LAVA Star) with or without navigator echoes (LAVA Starnavi+ and LAVA Starnavi-) and Cartesian LAVA with navigator echoes (Cartesian LAVAnavi+). LAVA Starnavi+ showed better image quality, liver edge sharpness, and hepatic vein clarify than others. The images of LAVA Starnavi+ had less streak artifacts than those of LAVA Starnavi- The use of both stack-of-stars acquisition and navigator echo is the best solution to obtain HBP images without breath hold in terms of quality of images.
|
|
1789. 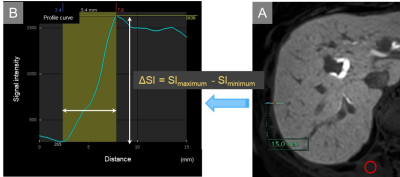 |
12 | Interface Analysis of the Liver and Focal Hepatic Lesions in Hepatobiliary Phase Imaging: A Comparison between Free-breathing Radial and Conventional Breath-hold Acquisition Technique.
Nobuyuki Kawai, Satoshi Goshima, Yoshifumi Noda, Kimihiro Kajita, Hiroshi Kawada, Yukichi Tanahashi, Shoma Nagata, Masayuki Matsuo
The free-breathing radial k-space sampling technique is especially useful for patients with limited breath-holding capacity in liver MR imaging, however, its degradation of spatial resolution in the plane compared with the Cartesian sampling is the greatest disadvantage. We assessed the fat-suppressed three-dimensional T1-weighted fast field echo imaging with pseudo-golden-angle radial stack-of-stars sampling technique with gate and track (3D-VANE) compared with the conventional breath-hold Cartesian sampling (BH-eTHRIVE) in hepatobiliary phase imaging. Our results demonstrated that 3D-VANE with thinner effective slice thickness (thin-slice 3D-VANE) achieved comparable interface resolution, less artifact and better image quality compared with BH-eTHRIVE.
|
|
| 1790. |
13 | Deep Learning Infrastructure for Fast Magnetic Resonance Imaging Annotation of Hepatocellular Carcinoma
Brett Marinelli, Trevor Ellison, Kaustubh Kulkarni, Dudley Charles, Bachir Taouli, Anthony Costa, Edward Kim
Deep learning is an important tool that can help drive important new innovations in medicine, including in MRI tumor segmentation for HCC. Large annotated data sets will be needed for effective deep learning, however, current techniques are tedious and inefficient for annotating images on a large scale. We propose a streamlined infrastructure to optimize and standardize the process of anonymizing patient information, structuring the data, and annotating images efficiently. We show that our streamlined infrastructure increases the speed at which ground truth annotations can be generated.
|
|
1791. 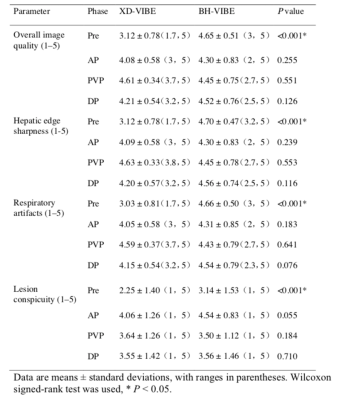 |
14 | Dynamic contrast-enhanced MR imaging of hypervascular liver lesions: comparison of conventional breath-hold and a free-breathing acquisition technique with compressed sensing and motion-state-resolved reconstruction
Xiangtian Zhao, Mengyue Huang, Yingyu Che, Jinxia Zhu, Dominik Nickel, Jingliang Cheng
We investigated a prototype free-breathing Cartesian volumetric interpolated breath-hold examination (VIBE) protocol with compressed sensing (CS) and motion-state-resolved reconstruction as extra-dimension (XD-VIBE) for Gd-DTPA-enhanced dynamic liver imaging by comparing it with conventional breath-hold VIBE. We found that it provided good image quality and diagnostic performance for hypervascular liver lesion detection except for the pre-contrast phase. This is a promising option for patients with poor breath-holding capacity.
|
|
1792. 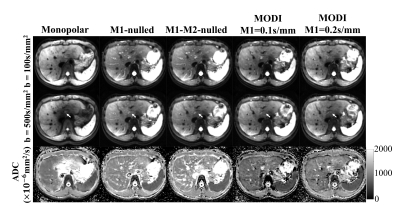 |
15 | Motion-Robust and Blood-Suppressed M1-Optimized Diffusion MR Imaging of the Liver
Yuxin Zhang, Óscar Peña-Nogales, James Holmes, Diego Hernando
Liver DWI is complicated by multiple challenges, including the relatively short T2 of liver tissue and the motion sensitivity of diffusion encoding sequences. In this study, a novel approach for the design of diffusion weighting waveforms, termed M1-Optimized Diffusion Imaging (MODI), is proposed for motion-robust, blood-suppressed liver DWI. MODI includes an echo-time optimized motion-robust diffusion weighting gradient waveform design, with a moderate non-zero first-moment (M1≠0) value to enable blood signal suppression. This work describes the proposed MODI method, and evaluates its effectiveness in healthy volunteers as well as in patients.
|
|
1793. 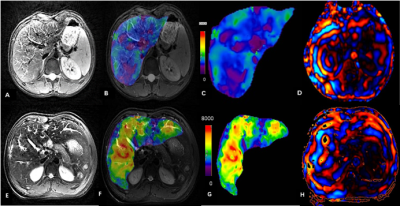 |
16 | The magnetic resonance elastography of liver for patients with Gaucher disease after enzyme replacement therapy
Di Li, Yang Fan, juan tao, Yun Peng
Gaucher disease (GD) is one of the most prevalent lysosomal storage disorders, which may lead to long term liver complications including fibrosis and cirrhosis. At present, enzyme replacement therapy (ERT) is widely used for GD in clinic.Magnetic resonance elastography (MRE) is the most accurate noninvasive technique for detection and staging of liver fibrosis.No significant difference was detected for GD patients after ERT in this study. It may indicate that enzyme replacement therapy is effective for most patients.
|
|
1794. 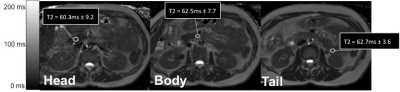 |
17 | Patient free-breathing Quantitative T2 Mapping in the Pancreas
Naik Vietti Violi, Tom Hilbert, Jessica Bastiaansen, Jean-Francois Knebel, Jean-Baptiste Ledoux, Alto Stemmer, Reto Meuli, Tobias Kober, Sabine Schmidt
In this study, we test the feasibility of free-breathing quantitative T2 measurement in the pancreas and we correlate T2-values with demographical and clinical parameters in 88 patients whom were subject to a liver MRI. We found that using a 10-fold accelerated multi-echo-spin-echo MRI prototype sequence at 3T, we were able to measure pancreatic T2-values in a short acquisition time, with low variability and a good inter-reader agreement. We found significant differences in T2-values depending on age, measurement location, main pancreatic duct dilatation and diffuse pancreatic disease.
|
|
1795. 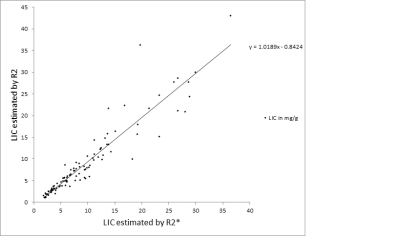 |
18 | Real World Experience Measurement of R2 vs R2 star in Hemoglobinopathies
Riad Abou Zahr, Barbara Burkhardt, Lubaina Ehsan, Zora Rogers, Tarique Hussain
This study is a real world experience comparing liver iron concentration (LIC) estimation by R2* vs R2 method in 107 patients with hemoglobinopathies on chronic transfusion therapy. It demonstrates a strong correlation of R2* with R2 and furthermore highlights the advantageous short scan time of R2* in the pediatric age group.
|
|
1796.  |
19 | Relationship between Brown Adipose Tissue and Intrahepatic Triglyceride in Children with Non-alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease
Steve Hui, Dorothy Chan, David Yeung, Winnie Chu
This study reported preliminary results for relationship between brown adipose tissue (BAT) and intrahepatic triglycerides (IHTG) in young subjects and tested whether non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) affected the association among liver fat accumulation and the activity and volume of BAT. Results showed that T2* in BAT was significantly lower in non-NAFLD group possibly due to higher blood flow and iron concentration which further implied the possibility of higher activation state of BAT in non-NAFLD. Correlation analysis also indicated NAFLD possibly changed the association between body weight and accumulation of IHTG as well as the volume and activity of BAT.
|
|
1797. 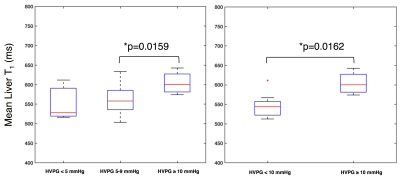 |
20 | Pre-contrast T1 measurement in the liver and spleen for the non-invasive assessment of portal hypertension
Octavia Bane, Stefanie Hectors, Paul Kennedy, Scott Friedman, Thomas Schiano, Maria Isabel Fiel, Swan Thung, Aaron Fischman, Bachir Taouli
The purpose of our prospective study was to assess the diagnostic value of liver and spleen T1 for diagnosis of portal hypertension based on hepatic venous pressure gradient (HVPG) in patients with chronic liver disease. We found that mean and median liver T1 were significantly elevated in patients with clinically significant portal hypertension versus those without clinically significant portal hypertension. We conclude that liver T1 is potentially sensitive to parenchymal changes associated with portal hypertension, to be confirmed in a larger number of patients.
|
|
1798. 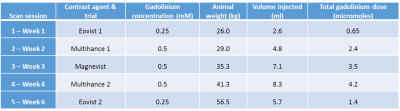 |
21 | Dynamic contrast enhanced MRI with clinical hepatospecific MRI contrast agents in pigs: initial experience
Jeremy Hix, Christiane Mallett, Matt Latourette, Kirk Munoz, Erik Shapiro
Pigs are a valuable translational biomedical tool for liver disease, and imaging can play an important role in early detection and disease characterization, but hepatic functional MRI has never been reported in pigs. Here we characterized baseline hepatic functional MRI in pigs, by performing DCE-MRI studies using two FDA-approved hepatospecific MRI contrast agents, and determined optimal animal protocols for acquiring robust data. Porcine liver has rapid accumulation of Gd-EOB-DTPA and Gd-BOPTA, following IV injection of equivalent human doses. Given the disparity in contrast agent uptake with humans for Gd-BOPTA, Gd-EOB-DTPA should be used in porcine models for biomedical imaging.
|
|
1799 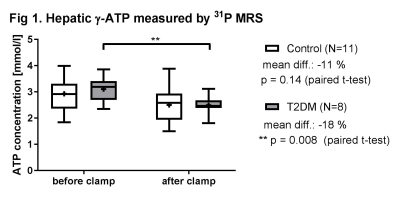 |
22 | Quantitative 31P magnetic resonance spectroscopy detects insulin-mediated reduction of hepatic ATP content in type 2 diabetic patients Video Permission Withheld
Jong-Hee Hwang, Frithjof Wickrath, Alessandra Bierwagen, Sofiya Gancheva , Maria Apostolopoulou, Yuliya Kupriyanova , Dominik Pesta, Michael Roden
Decreased insulin sensitivity precedes the onset of type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM). Hepatic energy metabolism is assumed to be impaired in T2DM with reduced insulin sensitivity. However, little is known about changes of ATP content in response to acutely elevated insulin. Therefore utilizing 31P MRS, we quantified ATP content before and after acute hyperinsulinemia. After a hyperinsulinemic clamp test, hepatic γ-ATP concentrations (ATP) were significantly reduced by 18% (p=0.008) in T2DM but not in controls. This study demonstrated that quantitative 31P MRS allows to monitor acute changes in hepatic ATP concentrations in vivo in various metabolic conditions.
|
|
1800. 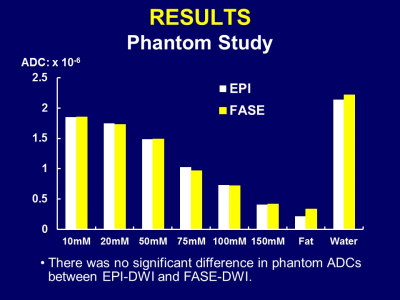 |
23 | High-b Abdominal FASE-DWI: Phantom and Clinical Studies
Takeshi Yoshikawa, Yoshiharu Ohno, Masao Yui, Yoshimori Kassai, Ryuji Shimada, Katsusuke Kyotani, Shinichiro Seki
Abdominal FASE-DWI at high-b value was evaluated in phantom and clinical studies. Our results showed FASE-DWI can improve image quality and accuracy of ADC, and decrease image distortion.
|
|
1801  |
24 | Liver mDixon at 7T Video Permission Withheld
Hannah Williams, Emma Doran, Stephen Bawden, Christopher Mirfin, Penny Gowland
mDixon imaging can provide robust anatomical images at 7T. These images have also been used to provide preliminary initial measurements of fat fraction in the liver at 7T.
|
|
1802. 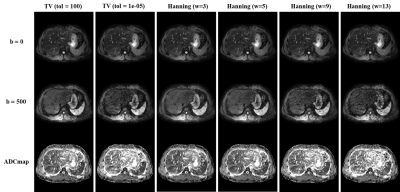 |
25 | Comparison of Liver Apparent Diffusion Coefficient (ADC) Measurement Using Single-shot and Multi-shot Diffusion-weighted EPI
Liyuan Liang, Hing Chiu Chang, Edward S. Hui
Diffusion-weighted imaging has been shown useful in measuring liver apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) that can provide valuable information for clinical diagnosis. Single-shot diffusion-weighted echo-planar imaging (ssDW-EPI) is the preferred acquisition technique for ADC measurement on clinical MRI scanner. Recently, a multiplexed sensitivity encoding (MUSE) framework has been developed to reconstruct high-quality multi-shot DW-EPI (msDW-EPI) image in brain. In this study, we aim to evaluate the msDW-EPI technique on liver ADC measurement by quantitatively comparing measured ADC values obtained from either msDW-EPI or ssDW-EPI.
|
Digital Poster
| Exhibition Hall | 14:45 - 15:45 |
| Computer # | |||
1803 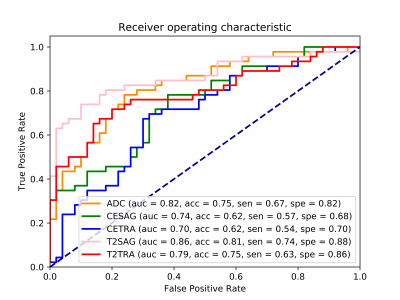 |
26 | Using Radiomics Analysis derived from Multiple MR Series to Differentiate Adenocarcinoma and Squamous cell carcinoma of Cervix Video Permission Withheld
wei wang, Yining Jiao, LiChi Zhang, Jianhui Ding, Weijun Peng, Qian Wang
In this study, we investigated the feasibility of differentiating AC from SCC using radiomics features extracted from multiple MR series (T2TRA, T2SAG, ADC, CETRA and CESAG). The results indicated that radiomics features identified by careful feature selection and machine learning can have good performance for distinguishing AC from SCC. In particular, T2SAG sequences had the best ability, followed by ADC and T2TRA sequences, as demonstrated by both unsupervised clustering and supervised classification. In general, we conclude that ACs have greater textural heterogeneity than SCCs, which was revealed through radiomics.
|
|
1804. 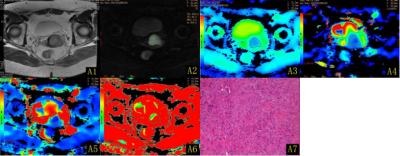 |
27 | Correlation study between parameters of intravoxel incoherent motion diffusion-weighted imaging and different pathological differentiation of cervical squamous cell carcinoma Presentation Not Submitted
peipei wang, lixiang zhang, jiangning dong
Correlation study between parameters of intravoxel incoherent motion diffusion-weighted imaging and different pathological differentiation of cervical squamous cell carcinoma
|
|
1805. 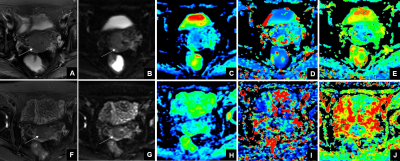 |
28 | Predictive value of intravoxel incoherent motion imaging (IVIM) and diffusion kurtosis imaging (DKI) in patients with locally advanced cervical cancers treated with neoadjuvant chemoradiotherapy Presentation Not Submitted
Hangqi Yu, Jie Bian, Jiawen Luo, Xiyou Zhang, Lizhi Xie
The purpose of this study was to investigate the use of IVIM and DKI to predict the efficacy of neoadjuvant chemoradiotherapy (NACT) in locally advanced cervical cancer. We found that the ADC, D and f values of IVIM and the MK value of DKI were significantly changed before and after NACT. Therefore, these parameters are predictive in cervical cancer treated with NACT.
|
|
| 1806. |
29 | Diffusion kurtosis imaging in the assessment of complete regression to chemoradiation therapy in locally advanced rectal cancer
Hongliang Sun, Yanyan Xu, Queenie Chan
Neoadjuvant chemoradiation therapy (CRT) followed by surgery has been established as the standard for locally advanced rectal cancer1. The treatment response after CRT is normally evaluated by MRI. However, MRI morphology techniques suffer from limitations in the interpretation of fibrotic scar tissue and inflammation. Diffusion kurtosis imaging (DKI) is an emerging technique, which could reflect restricted water diffusion within the complex microstructure of most tissues based on non-Gaussian diffusion model2. There is limited research reported about the clinical application of DKI in rectal cancer, and the value of DKI in monitoring rectal cancer treatment was still mysterious.
|
|
| 1807. |
30 | Dynamic contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging parameters for characterizing rectal cancer with different KRAS status
Hongliang Sun, Yanyan Xu
DCE-MRI can noninvasively reveal the presence and the permeability of micro-capillaries by the kinetic analysis of the contrast concentration1. It has been used in the studies for diagnosis, characterization of predictive prognostic factors, monitoring of treatment response, and evaluation of the efficacy of novel treatment developments2-3. KRAS mutation has been well known as predictive markers of resistance to epidermal growth factor receptor-targeted antibodies, may be useful as molecular markers for the clinical prognosis of CRCs4. However, There a are few data about whether the DCE-MRI parameters would behave different characteristics in rectal cancers with different KRAS status.
|
|
1808. 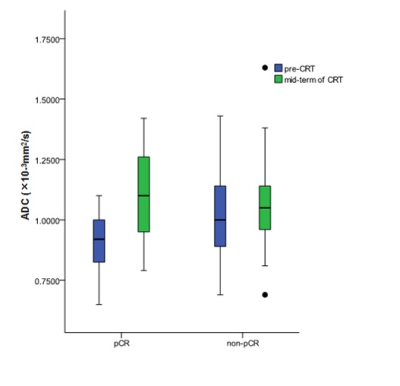 |
31 | Locally advanced rectal cancer: IVIM derived parameters for assessment of complete regression during mid-term of neoadjuvant chemoradiotherapy
Yanyan Xu, Hongliang Sun, Qiaoyu Xu
Neoadjuvant chemotherapy has been widely applied in treating locally advanced rectal cancer (LARC) for effectively decreasing the local recurrence after total mesorectal excision(TME). The imaging technique of intravoxel incoherent motion(IVIM) model could estimate tissue perfusion and diffusion components individually using multi-b-values1-3. Here, we try to investigate the value of intravoxel incoherent motion (IVIM) derived parameters in predicting pathological complete regression (
|
|
1809. 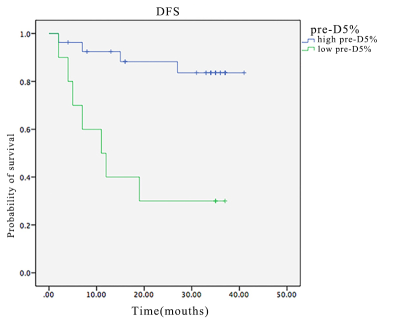 |
32 | Assessment of the Prognostic Factors for Rectal Cancer Treated with Neoadjuvant Chemoradiation: Utilizing Whole-Tumor Histogram Analysis of Diffusion Kurtosis Imaging Presentation Not Submitted
Sun Yiqun, Tong Tong, Fu Caixia, Yan Xu, Peng Weijun, Gu Yajia
We assess the prognostic factors for rectal cancer treated with neoadjuvant chemoradiation utilizing whole-tumor histogram analysis of diffusion kurtosis imaging. Our study demonstrated that whole-tumor histogram analysis of diffusion kurtosis imaginghas potential to be a predictor for DFS and provide evidence for individualized follow-up and treatment of locally advanced rectal cancer patients.
|
|
1810. 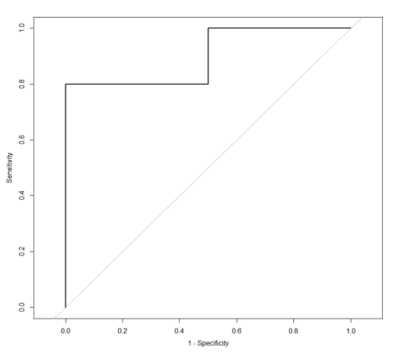 |
33 | Whole-Tumor Histogram Analysis of Diffusion Kurtosis Imaging as A Predictive Biomarker of Tumor Response in Locally Advanced Rectal Cancer Treated with Neoadjuvant Chemoradiation Presentation Not Submitted
Sun Yiqun, Tong Tong, Fu Caixia, Yan Xu, Peng Weijun, Gu Yajia
We investigate the potential of thewhole-tumor histogram of conventional DWI and DKI derived parameters to predict the tumor response to neoadjuvant chemoradiation therapy in locally advanced rectal cancer. Our study demonstrated that whole-tumor histogram analysis of DKI derived parameter maps has potential value to predict tumor response.
|
|
1811. 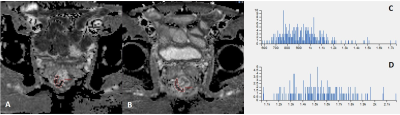 |
34 | The role of high-resolution apparent diffusion coefficient histogram analysis in evaluating tumor response of locally advanced rectal cancer after neoadjuvant chemeradiotherapy Presentation Not Submitted
lanqing Yang, bing Wu
This study analyzed both pre- and post-chemoradiotherapy ADC map of rectal cancer to evaluate tumor regression by using histogram metrics. The ADC map was generated from high-resolution DWI using read-out segmented echo-plannar imaging sequence, with less distortion and susceptibility artifact. Our study did not find any added value of histogram metrics of ADC map in assessing tumor response, and post-treatment mean ADC value alone may be enough in clinical.
|
|
1812. 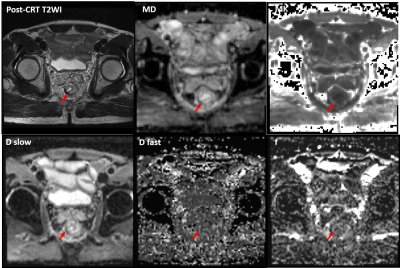 |
35 | Locally Advanced Rectal Cancer: The Value of Intravoxel Incoherent Motion Imaging and Diffusion Kurtosis Imaging in Assessing Tumor Response to Neoadjuvant Chemoradiotherapy Presentation Not Submitted
lanqing Yang, bing Wu
This study combined IVIM and DKI sequences in assessing tumor response to neoadjuvant chemoradiotherapy in locally advanced rectal cancer. Although both IVIM and DKI model derived parameters in our study could help to identify complete responders, ADC value was found to outperform both IVIM and DKI paramters in selecting complete responders.
|
|
1813 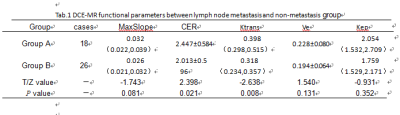 |
36 | Value of DCE-MRI and texture analysis in preoperative prediction of lymph node metastasis in rectal cancer Video Permission Withheld
Yue Lv, Ailian Liu, Jingjun Wu, Anliang Chen, Xinying Li, Yan Guo
Rectal cancer is the third most common cancer in the world.DCE-MRI is better at diagnosis and evaluation of rectal cancer.Texture analysis is a non-invasive analysis method based on image pixel level. It can reflect the heterogeneity of tumors by quantifying the distribution of pixels and the relationship between pixels.
|
|
1814. 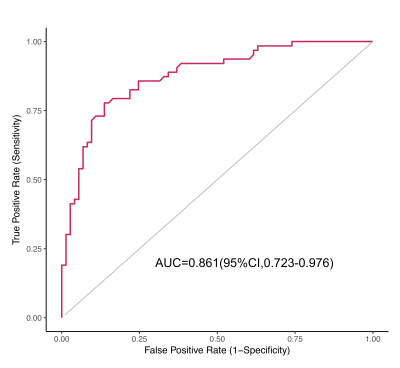 |
37 | A radiomics approach to assess tumor-stromal ratio and predict treatment response to neoadjuvant chemoradiotherapy in rectal cancer: a preliminary study Presentation Not Submitted
Tingdan Hu, Tong Tong, Dan Huang, Jun Yang
This study concentrated on the correlation between radiomics parameters and the tumor-stromal ratio. We identified several radiomics parameters that may reflect the content of tumor-stroma. After constructed a radiomics signature based on the tumor-stromal ratio and furtherly applied the signature into the LARC patients with neoadjuvant chemoradiotherapy, we found that the TSR-conducted radiomics signature was significantly correlated with pCR and non-pCR. The radiomics signature may serve as a non-invasive imaging biomarker for pretreatment prediction of treatment response.
|
|
1815. 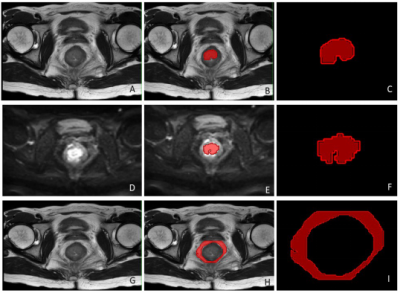 |
38 | Rectal cancer: preoperative prediction of perineural invasion by machine learning modeling of multiregional radiomics features from multiparametric MRI Presentation Not Submitted
Yu Fu, Xiangchun Liu, Kan He, Jianqing Sun, Chunyu Zhang, Xiaochen Huai, Huimao Zhang
Defined by tumor invasion of nervous structures and nerve sheaths, the presence of perineural invasion (PNI) is thought to indicate an increased risk for progressive disease in rectal cancers. Here, we developed and validated a radiomics model for individualized prediction of PNI in rectal cancer based on pre-procedure MRI. The Ridge Classifier is found to have the best prediction accuracy score (80.8%), its specificity, sensitivity and F1 score are 90.5%, 60.4%, and 67.0%, respectively. So, the radiomics features from MRI of rectal cancer is a useful tool for predicting PNI preoperatively and has marked discrimination accuracy.
|
|
1816. 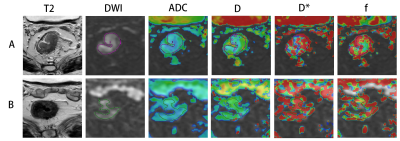 |
39 | Quantitative intravoxel incoherent motion (IVIM) parameters derived from whole-tumor volume for predicting and assessing pathological complete response to neoadjuvant chemotherapy in locally advanced rectal cancer
Qiaoyu Xu, Yanyan Xu, Queenie Chan, Hongliang Sun
Neoadjuvant chemotherapy has been widely applied in treating locally advanced rectal cancer (LARC) for effectively decreasing the local recurrence after total mesorectal excision(TME)1. Some of
|
|
1817. 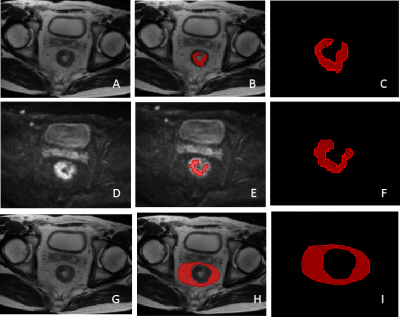 |
40 | Multiregional radiomics features from multiparametric MRI for prediction of lymphovascular invasion in rectal cancer Presentation Not Submitted
Kan He, Xiangchun Liu, Yu Fu, Jianqing Sun, Xiaochen Huai, Mingfei Wang, Yu Guo, Huimao Zhang
The presence of lymphovascular invasion (LVI) is thought to indicates an increased risk for progressive disease in rectal cancers according to the National Comprehensive Cancer Network (NCCN) Guidelines. Here, we developed and validated a radiomics model for prediction of LVI in rectal cancer based on pre-treatment MRI. The Ridge Classifier have the best prediction accuracy score( 73.3%), its specificity, sensitivity and F1 score are 83.9%, 59.4 % and 65.1 %, respectively. So, the radiomics features from MRI of rectal cancer is a useful tool for predicting LVI preoperatively and has marked discrimination accuracy.
|
|
1818.  |
41 | MRI-detected extramural vascular invasion is a strong risk factor in predicting synchronous distant metastasis in rectal cancer Presentation Not Submitted
Pratik Tripathi, Shengxiang Rao, Weifeng Guo, Bimal Rai, Mengsu Zeng, Daoyu Hu
MRI detected extramural vascular invasion (mrEMVI) is potential imaging predictive biomarker for selecting optimum treatment method and is closely correlated with poor prognosis. Several studies have been done to understand the correlation between EMVI and metastasis, but not synchronous metastasis to be specific. We aimed to analyze the correlation between clinical factors including mrEMVI with synchronous metastasis. Moreover, we analyzed the correlation between grades of mrEMVI and synchronous metastasis.
|
|
1819. 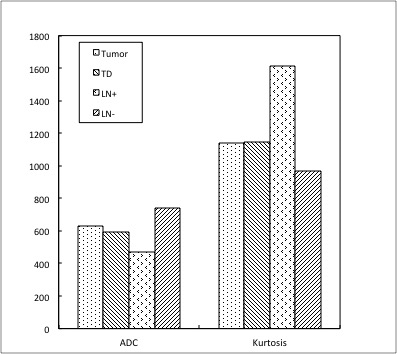 |
42 | DKI and DCE-MRI in Identifying the Malignancy of Lymph Node during the Primary Staging of Rectal Cancer: MRI with Node-for-Node Matched Histopathology validation Presentation Not Submitted
Jie Yuan, Mengxiao Liu, Zhigang Gong, Kun Liu, Hua Yang, Yu Cao, Songhua Zhan
We investigated the potential of Diffusion kurtosis imaging (DKI) and Dynamic Contrast Enhancement (DCE) to accurately detect lymph node (LN) metastases in rectal cancer. Our study showed that DKI and DCE-MRI may be useful to differentiate the TD and metastatic LN from benign LN.
|
|
| 1820. |
43 | Correlation of MR based textural analysis parameters with MR tumor regression score and its potential role in predicting response to long course chemoradiotherapy in patients with locally advanced rectal cancers [LARC].
Karthik Ganesan, Ankit Jain, Shivsamb Jalkote, Alam Shah, Slesha Bhalja, Balaji Ganeshan, Swarup Nellore
Treatment of locally advanced rectal cancers (cT3/4, cN1/2) with neoadjuvant chemoradiotherapy leads to a reduction in tumor size and enhances the likelihood of tumor resectability and sphincter preservation with low local recurrence rates. In this study we attempted to correlate first order MR textural parameters with the MR tumor regression [TRG] score determined on the post-treatment MRI and to also predict response to long course chemoradiotherapy in locally advanced rectal cancers. We retrospectively included 20 patients with pathologically proven rectal carcinoma who underwent long course chemoradiotherapy [LCCRT] following a pre-treatment MRI. All 20 patients had a post-treatment MRI after a 6-week interval at which MR tumor regression [TRG] scores were determined based on the T2-w and DW-ADC maps. TRG was represented as MR_TRG [TRG 1,2 - Complete Response [CR] = 7; TRG 3 - Partial Response [PR] = 11; TRG 4,5 - Minimal / No response [NR] = 2). Texture analysis was carried out on axial T2-w and ADC images by delineating a 2-D region of interest around the tumour. The results showed that First order MRTA features derived from the post-treatment MR T2-w and ADC images can help differentiate between responders [TRG 1 and 2] and non-responders [TRG 3, 4 and 5] in patients with locally advanced rectal cancers who underwent long course chemoradiotherapy.
|
|
| 1821. |
44 | MR based textural analysis parameters as potential imaging biomarkers to differentiate between the mucinous and non-mucinous variants of rectal cancers.
Karthik Ganesan, Shivsamb Jalkote, Ankit Jain, Alam Shah, Slesha Bhalja, Balaji Ganeshan, Swarup Nellore
Mucinous adenocarcinoma [MAC] is a histological subtype of colorectal cancer with a poor response to long course chemoradiotherapy [LCCRT] and an overall poor oncologic outcome. In this study, we explored the utility of pre-treatment MR texture analysis as a potential imaging biomarker to differentiate mucinous and non-mucinous variants of rectal cancer. We retrospectively evaluated 39 patients with pathologically proven rectal carcinoma on T2-w images and ADC maps. First order MRTA features including the mean and mpp derived from T2-w images at moderate and coarse texture showed statistically significant difference between mucinous and non-mucinous variants of rectal cancers. The results demonstrate that first order MRTA may help differentiate between mucinous and non-mucinous rectal cancer subtypes and select patients for individualized therapy and also potentially aid in accurate prediction of response to LCCRT.
|
|
1822. 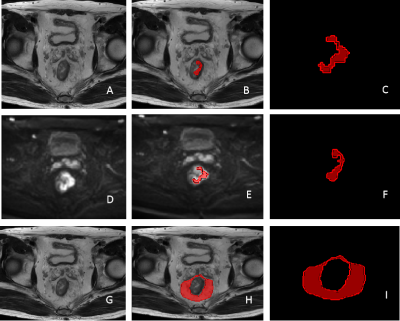 |
45 | Preoperative prediction of lymph node metastasis in rectal cancer by multiregional radiomics features from multiparametric MRI Presentation Not Submitted
Xiangchun Liu, Yu Fu, Kan He, Jianqing Sun, Chunyu Zhang, Xiaochen Huai, Huimao Zhang
Preoperative accurate assessment of lymph node (LN) status in rectal cancer is essential for precise individualized decision-making. Nevertheless, preoperative LN staging in rectal cancer remains a challenge for the radiologist. Therefore, we develop and validate a radiomics prediction model based on MRI for the preoperative individualized prediction of LN metastasis. The Ridge Classifier is found to give the best prediction accuracy score(73.9%).The mean specificity, sensitivity and F1 score are 84.6%, 60% and 66.4 % , respectively. So, radiomics features from MRI of rectal cancer is a useful tool for predicting LN metastasis preoperatively and has marked discrimination accuracy.
|
|
1823. 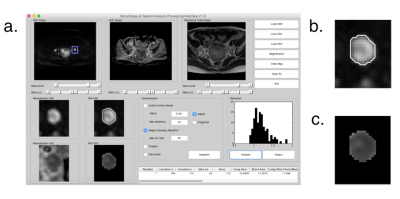 |
46 | Diffusion-Weighted Imaging for Predicting Lymph Node Metastasis in Endometrial Cancer: Added Values of Computer-Aided Segmentation and Radiomic Machine Learning Presentation Not Submitted
Tiing Yee Siow, Yu-Chun Lin, Lan-Yan Yang, Yu-Ting Huang, Yen-Ling Huang, Gigin Lin
We aim to investigate added values of computer-aided segmentation and radiomic machine learning based on diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance (MR) imaging for predicting nodal metastasis in endometrial cancer. Decision-tree machine learning comprised the apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC), whole tumor volumetric and lymph nodes (LNs) segmentations, MR morphological measurement, and relevant clinical parameters. We concluded that a combination of clinical and MR radiomics generates a prediction model for LNmetastasis in endometrial cancer, with diagnostic performance surpassing the conventional ADC and size criteria.
|
|
1824. 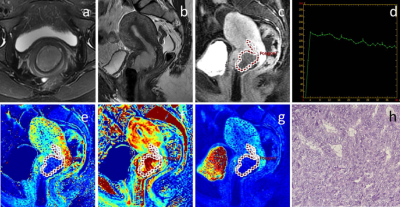 |
47 | Using kinetic parameters from DCE-MRI to differentiate endometrial adenocarcinoma from adenocarcinoma of cervix
Xiaoduo Yu, Meng Lin, Qi Zhang, Lizhi Xie, Yuqing Shang, Han Ou-Yang
This study attempted to use parameters derived from DCE-MRI to quatitatively investigate the perfusion difference between adenocarcinoma of endometrium and cervix. It was concluded that values of kinetic parameters were lower in uterine endometrioid adenocarcinoma (EAC) and adenocarcinoma of cervix (AdC). When encountered uterine adenocarcinoma with uncertain biopsy pathology and a confusing morphology of MRI, DCE-MRI would be a reliable supplementary method to improve diagnostic confidence.
|
|
1825. 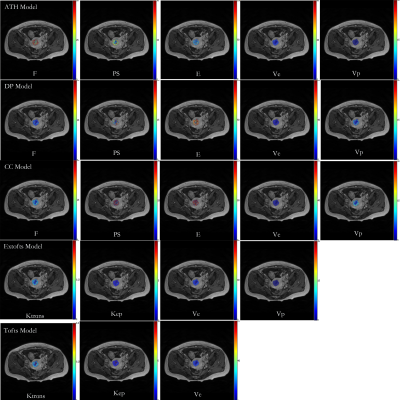 |
48 | Comparative Study of DCE-MRI Pharmaceutical Kinetic Models and MVD for Characterizing Endometrial Carcinoma Microcirculation Presentation Not Submitted
Zhijun Ye, Gang Ning
Using five models of DCE MRI and histomorphological marker in assessing 69 cases tumour microcirculation in endometrial carcinoma and predict imaging markers of depth of myometrial invasion and assessment surgical methods.The permeability and blood flow in tumor was significantly lower,which may be related to the hypoxic environment. And the plasma and extravascular extracellular space volume in tumor are both lower, which is considered to be due to the increased tumor parenchymal cells.ATH model derived Veattained highest value,which is closest to the MVD, may provide an imaging marker for predicting depth of myometrial invasion and assessment surgical methods.
|
|
1826. 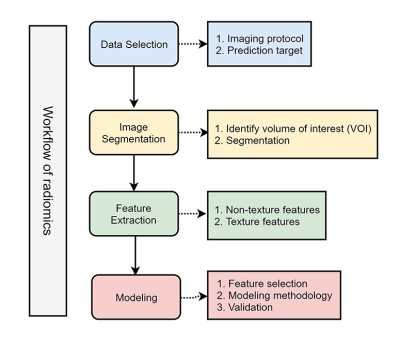 |
49 | Preoperative Differentiation of Uterine Sarcoma from Leiomyoma: Comparison of Three Models Based on Different Segmentation Volumes Using Radiomics
Huihui Xie, Xiaodong Zhang, Xiaoying Wang
This study aimed to explore that if the segmentation of different volume of interests (VOIs) may influence the diagnostic performance of radiomic model. We included 78 patients with pathologically confirmed uterine sarcomas or atypical leiomyomas. 3 different VOIs were manually drawn on images of ADC maps. Radiomic models were built based on three feature set. Features extracted from VOI covered the whole uterus had the best diagnostic performance than VOI covered the lesion or lesion and some surrounded tissue. It suggested VOI covered the whole uterus added relevant information for distinguishing uterine sarcoma from atypical leiomyoma.
|
|
1827.  |
50 | Comparative Analysis of the Value of Diffusion Kurtosis Imaging and Diffusion-weighted Imaging in Evaluating the Histological Features of Endometrial Cancer
Nan Meng, Jing Wang, Wenling Liu, Xuejia Wang, Hongxia Wang, Minghuan Yan, Dandan Zheng, Mengyan Hou, Dongming Han*
Diffusion kurtosis imaging (DKI) can quantify the diffusion state of non-Gaussian water molecules in tissues, thus correcting the offset of the diffusion-weighted imaging(DWI) model and improving the detection of lesions compared with DWI.At present, there is only a few comparative studies of DWI and DKI in endometrial cancer(EC).Our results show that compared with DWI, the DKI model is a more complete mathematical model with more sensitive parameters, which can more effectively evaluate the pathological and physiological characteristics of EC.
|
Digital Poster
| Exhibition Hall | 14:45 - 15:45 |
| Computer # | |||
1828 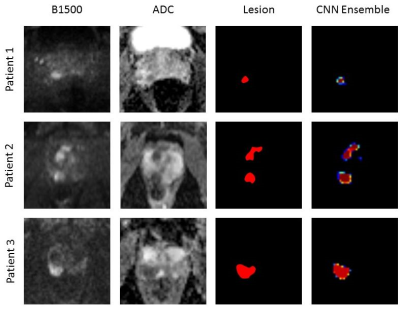 |
51 | A U-Net applied to diffusion-weighted images compared to full multiparametric clinical PI-RADS assessment for detection and segmentation of significant prostate cancer Video Permission Withheld
Patrick Schelb, Simon Kohl, Jan-Philipp Radtke, Markus Hohenfellner, Heinz-Peter Schlemmer, Klaus Maier-Hein, David Bonekamp
A U-Net applied to diffusion-weighted imaging (DWI) only was trained with 3T MRI data from a single system in 316 consecutive patients. All clinical MR lesions were targeted with fusion biopsy in addition to extended 24-core systematic biopsy. The performance of the final CNN ensemble on the test set achieved comparable sensitivity in comparison to multiparametric clinical assessment and demonstrated the method’s ability to generate stable results in an unseen subset. These findings highlight the ability of computer vision to closely model the clinical task with fewer data and encourage development of the method in larger cohorts.
|
|
1829  |
52 | Visualization of gold fiducial markers in the prostate using phase-cycled bSSFP MRI for MR-only radiotherapy Video Permission Withheld
Yulia Shcherbakova, Stefano Mandija, Lambertus Bartels, Chrit Moonen, Cornelis van den Berg
Existing MR techniques for the visualization of fiducial markers (FMs) in the prostate are usually based on spoiled-gradient-echo imaging. FMs appear as signal voids in magnitude images. It is therefore difficult to distinguish them from hemorrhages and calcifications. FMs detection is crucial for MR-only radiotherapy, where CT images are not available. Automatic FMs detection methods are available, but require special software which is not available at the MR console. With this work, we propose a new method for distinctive FMs visualization in the prostate for MR-only radiotherapy which facilitates FMs detection directly at the MR console without using any additional post-processing or software.
|
|
1830. 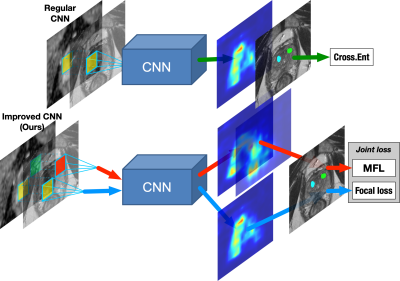 |
53 | Improving prostate cancer detection in mp-MRI via CNN using the joint loss
Ruiming Cao, Xinran Zhong, Amirhossein Mohammadian Bajgiran, Sohrab Afshari Mirak, Sepideh Shakeri, Fabien Scalzo, Steven Raman, Kyunghyun Sung
We proposed an improved CNN using joint loss to fully utilize multi-parametric imaging for the automated prostate cancer detection in mp-MRI. 397 pre-operative mp-MRI exams were collected in our medical center, and lesion ROIs were retrospectively annotated with whole-mount histopathology confirmations. The improved CNN achieved 75.1% detection sensitivity at 1 false positive per patient and had an AUC 0.901 in the ROC analysis.
|
|
1831. 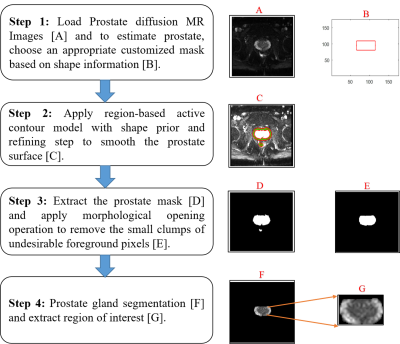 |
54 | Gland and Zonal Segmentation of Prostate using Diffusion-Weighted MR Imaging
Dharmesh Singh, Virendra Kumar, Chandan Das, Anup Singh, Amit Mehndiratta
Accurate segmentation of the prostate gland and its zones is a challenging task due to the high variability of prostatic anatomic structures. Gland and zonal segmentation of prostate is a useful tool for computer-aided diagnosis of prostate cancer because characteristics of cancer in prostate zones differ significantly. In this study, we used an active contour model for prostate gland segmentation and atlas-based approach for prostate zonal segmentation in diffusion-weighted MR imaging. We have assessed the performance of segmentation methods using different similarity parameters. The proposed methods are highly robust and show relatively good performance compared to previously reported work.
|
|
1832. 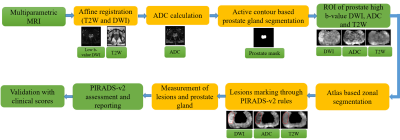 |
55 | Automated Detection and PIRADS v2 Scoring of Prostate Cancer using Multiparametric MRI
Dharmesh Singh, Virendra Kumar, Chandan Das, Anup Singh, Amit Mehndiratta
Accurate diagnosis of prostate cancer (PCa) remains challenging due to high sensitivity of biopsy and low specificity of the screening test. Multiparametric MRI (mpMRI) is an effective imaging tool for the diagnosis of PCa by providing morphological and functional information about the prostate. In this study, we propose an image-processing framework for the assessment of PCa based on mpMRI data comprised of images from T2-weighted and diffusion-weighted. It shows the relatively better performance of PCa assessment when we compare our results against radiologist assessment and histopathological score.
|
|
1833. 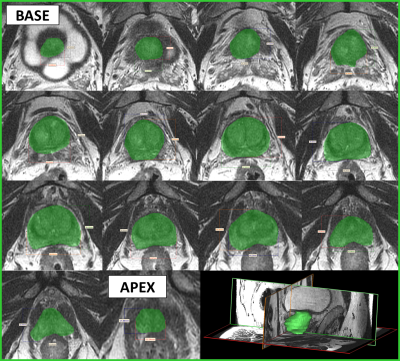 |
56 | MRI-Derived Patient Specific Molds for Cancer Lesion Analysis in the Prostate
David Rutkowski, Shane Wells, Brian Johnson, Wei Huang, David Jarrard, Joshua Lang, Steve Cho, Alejandro Roldán-Alzate
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI), and emerging Prostate Specific Membrane Antigen (PSMA) Positron Emission Tomography (PET)/MRI, can be used to detect and locate prostate cancer. The accuracy of this method can be validated by comparing post-prostatectomy histopathology information to MRI and PET image data with the help of a custom prostate-sectioning device. This study is aimed at addressing sectioning device limitations proposed by previous studies and at developing a three-dimensional (3D) comparison method for MRI data and post-prostatectomy prostate geometries.
|
|
1834. 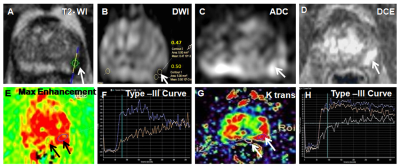 |
57 | Comparison of detection rate of prostate cancer between mpMRI guided in-bore biopsy and routine TRUS biopsy
Sujeet Mewar, Sanjay Sharma, Ekta Dhamijia , Sanjay Thulkar, Sridhar Panaiyadiyan, Pradeep Kumar, S. Senthil Kumaran, Virendra Kumar, S. Datta Gupta, Rajeev Kumar, Naranamangalam Jagannathan
The present study demonstrated the role of mpMRI guided in-bore biopsy for detection of prostate cancer (PCa). Patients were recruited based on PSA > 4 ng/ml and abnormal DRE. The PCa detection rate between the two groups of patients, namely 25 patients (Group I) who underwent in-bore biopsy and 73 patients (Group II) who underwent TRUS biopsy were compared. The PCa detection rate of in-bore targeted biopsy was 52% compared to 34.3% for TRUS biopsy. Our data also indicated that in-bore MR targeted biopsy significantly increased the detection rate of PCa when compared with the standard 12 core TRUS biopsy.
|
|
1835. 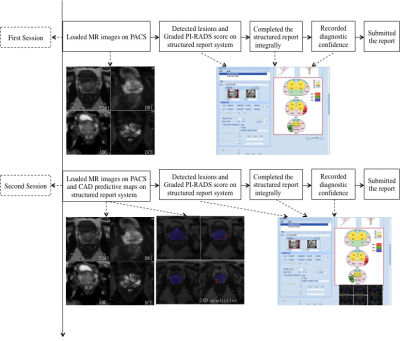 |
58 | Integrating Computer-aided Diagnosis as Concurrent Reader into Prostate Multiparametric MRI Diagnostic Process - Reader Performance Study
Lina Zhu, Ge Gao, Yi Liu, Jing Liu, Chao Han, Xiaoying Wang
Many computer-aided diagnosis (CAD) systems based on prostate multiparametric MRI (mpMRI) have been developed with good stand-alone diagnostic efficacy. Before its widely use in daily clinical work, further study still should be done for CAD reading paradigm and the interaction between CAD and radiologists. In this article, we integrated CAD as concurrent reader into prostate mpMRI diagnostic process in real clinical practice to determine effect on radiologist performance. The results showed that concurrent CAD reading could improve radiologist sensitivity and reduce the reading time.
|
|
| 1836. |
59 | Interobserver Agreement and Accuracy of Six Scoring Systems(Likert, PI-RADS V1, PI-RADS V2, MLS, SQS, UCSF)for Prostate Lesions by Using Mp-MR imaging Presentation Not Submitted
Li Zhang, Longchao Li, Jin Zhang, Jianfeng Li
Some institutions have used other prostate scoring systems except for PI-RADS. The purpose of this study was to determine for expert and novice radiologists the agreement and accuracy of six scoring systems for categorization of prostate lesions seen at mp-MRI. 129 lesions were scored for four readers. Experts and novices had fair to moderate agreement for most scores (k: 0.2176~ 0.4533). Novices were less consistent and less likely to diagnose prostate cancer than were experts. The Likert and PI-RADS V1 scores allowed significantly more accurate categorization of prostate lesions than others.
|
|
1837 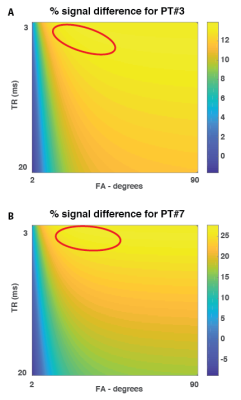 |
60 | T1 Imaging of Transition Zone Prostate Cancer: Why Quantitative Maps But Not T1 Weighted Images Are Helpful Video Permission Withheld
Verena Obmann, Rasim Boyacioglu, Ananya Panda, Irina Jaeger, Lee Ponsky, Mark Griswold, Vikas Gulani
It has been shown that quantitative T1 relaxation times measured on T1 maps may help differentiate transition zone (TZ) cancer from normal transition zone (NTZ). However, T1 weighted images are not utilized for non-contrast detection of prostate cancer. In this study, we explored scientific reasons why T1w images have not been found to be of utility for this purpose. Fat suppressed T1w 3D gradient echo (VIBE) sequence acquisition settings were adjusted based on simulated acquisition parameters and our measured differences between cancer and NTZ, to try to maximize differences in calculated signal between tumor lesions and NTZ. The resulting contrast remains too subtle to utilize for detection; though quantitative differences are readily measureable.
|
|
1838. 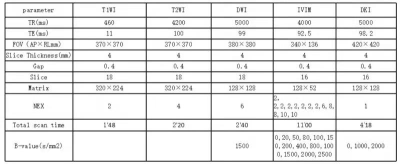 |
61 | Advanced diffusion-weighted imaging with multiple parameters in differential diagnosis of prostate transitional zone carcinoma and benign prostatic hyperplasia
Huipeng Ren, Zhuanqin Ren, Xiaochen Wei
Conventional MRI sequences and DWI sequences are difficult to identify prostate transitional cell carcinoma and benign prostatic hyperplasia. In this study, traditional DWI sequences, intravoxel incoherent motion diffusion weighted imaging (IVIM-DWI), stretch index DWI sequences and DKI sequences were used to compare the accuracy of these sequence parameters in the differential diagnosis of prostate cancer and benign prostatic hyperplasia. The results showed that ADC-slow, DDC, Md, Da, Dr, MK, Ka and Kr were helpful in differentiating prostate cancer from benign prostatic hyperplasia, and MK value had the highest accuracy in differentiating prostate cancer from benign prostatic hyperplasia.
|
|
1839. 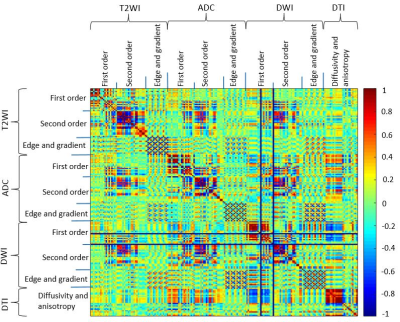 |
62 | Detection of prostate cancer in the peripheral zone using machine learning and multiparametic MRI
Neda Gholizadeh, John Simpson, Saadallah Ramadan, Peter Lau, Peter Greer
The aim of this study is to provide a non-invasive voxel based malignant lesion detection tool and probability map for the peripheral zone (PZ) using multi parametric magnetic resonance imaging incorporating DTI as well as standard sequences. A combination of radiomics features extracted from MRI and DTI and supervised machine learning was to develop a tool for cancer detection. Our results demonstrated DTI, when used within the framework of supervised classification, can play a role in the prostate cancer detection. In addition, the posterior probability provide useful information about tumor heterogeneity and may offer better detection of PZ prostate cancer.
|
|
1840.  |
63 | The Diagnostic Evaluation of PI-RADS V2 based on Simplified Biparametric MRI for Clinically Significant Prostate Cancer
JIE BAO, Xi-ming Wang, Chun-hong Hu, Zhong-shuai Zhang
This study compare the performance of the PI-RADS scores obtained by using biparameter MRI (T2W and diffusion) and multi-parameter MRI (T1W, T2W, diffusion and DCE) for clinically significant PCa, respectively. The results show that the PI-RADS score acquired from biparameter MRI is comparable with that from the traditional multi-parameter MRI.
|
|
1841.  |
64 | The Diagnostic Value of PI-RADS V2 Scoring System Combining with MRI-TRUS Fusion Targeted Biopsy for Detecting the Clinical Significant Prostate Cancer
Jie Bao, Xi-ming Wang, Chun-hong Hu, Zhong-shuai Zhang
Transrectal ultrasound-guided systematic (TRUS) biopsy is commonly used in clinical practice to detect clinically significant prostate cancer (PCa)[1-3]. In this study, a more advanced biopsy, MRI-TRUS fusion targeted biopsy, is used together with MRI-derived PI-RADS V2 scoring system for the diagnosis of clinical significant PCa. The values of the two biopsy methods are compared.
|
|
 |
1842. 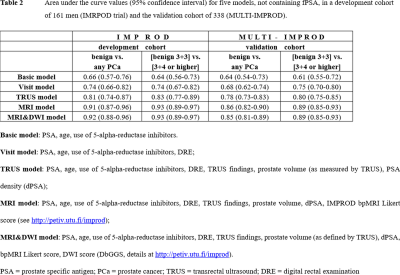 |
65 | Development and external validation of IMPROD biparametric MRI-based nomogram for the prediction of prostate biopsy outcome in men with a clinical suspicion of prostate cancer (IMPROD and MULTI-IMPROD trials, #opensourcetrial)
Ivan Jambor, Ileana Montoya Perez, Janne Verho, Otto Ettala, Juha Knaapila, Pekka Taimen, Kari Syvänen, Aida Kiviniemi, Esa Kähkönen, Marjo Seppänen, Antti Rannikko, Outi Oksanen, Jarno Riikonen, Sanna-Mari Vimpeli, Tommi Kauko, Harri Merisaari, Tapio Pahikkala, Markku Kallajoki, Tuomas Mirtti, Jani Saunavaara, Peter Boström, Hannu Aronen
Nomograms for prediction of prostate biopsy outcomes incorporating qualitative and quantitative findings of IMPROD biparametric MRI (IMPROD bpMRI consists of T2 weighted imaging and three separate DWI acquisitions) were developed using data of 161 men enrolled as a part of the single-institutional IMPROD (NCT01864135) trial and externally validated in 338 men enrolled as a part of the multi-institutional MULTI-IMPROD(NCT02241122) trial. A nomogram using IMPROD bpMRI findings had area under the curve values (95% confidence interval) of 0.92 (0.88-0.96), and 0.88 (0.84-0.92) in the development and validation cohorts, respectively, for the detection of prostate cancer with Gleason score 3+4 or higher.
|
1843. 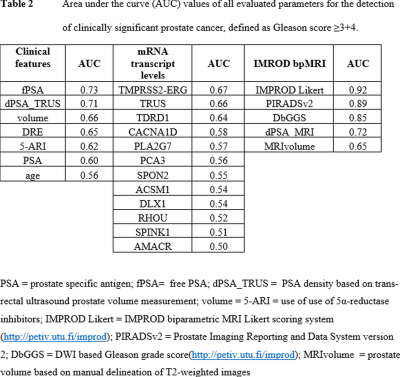 |
66 | Prostate cancer detection in men with a clinical suspicion of prostate cancer using IMPROD biparametric MRI and expression of 11 genes (IMPROD trial, #opensourcetrial): evaluation using machine learning methods
Ileana Montoya Perez, Tapio Pahikkala, Antti Airola, Harri Merisaari, Pekka Taimen, Saeid Alinezhad, Janne Verho, Otto Ettala, Jani Saunavaara, Aida Kiviniemi, Kim Pettersson, Peter Boström, Hannu Aronen, Ivan Jambor
Eighty men with a clinical suspicion of prostate cancer (PCa) were enrolled as a part of IMRPOD trial (NCT01864135). The performance of 9 clinical parameters, 11 mRNA transcript levels and 4 IMPROD biparametric MRI (bpMRI) parameters for detection of PCa with Gleason score ≥3+4 was evaluated using GreedyRLS feature selection and nested cross-validation with area under the curve obtained from tournament leave-pair-out cross validation. IMPROD bpMRI reported using qualitative IMPROD Likert scoring system demonstrated high accuracy for PCa detection and none of the remaining parameters led to further improvement. All data are freely are available at the following address: http://petiv.utu.fi/improd
|
|
1844. 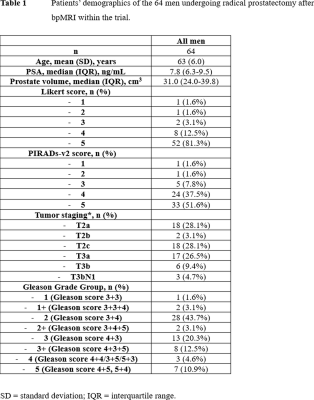 |
67 | Accuracy of IMPROD biparametric pre-biopsy MRI for prostate cancer detection in correlation with whole mount prostatectomy sections: implications for focal therapy (IMPROD trial, #opensourcetrial)
Harri Merisaari, Pekka Taimen, Otto Ettala, Peter Boström, Ileana Montoya Perez, Janne Verho, Aida Kiviniemi, Kari Syvänen, Esa Kähkönen, Tapio Pahikkala, Jani Saunavaara, Hannu Aronen, Ivan Jambor
In this prospective single institutional trial(NCT01864135), we evaluated the accuracy of a unique prostate MRI acquisition and reporting protocol, IMPROD biparametric MRI, in men with a clinical suspicion of prostate cancer who were subsequently diagnosed with prostate cancer and underwent prostatectomy. IMPROD biparametric MRI correctly detected 75% (75/99) of prostate cancer lesions with diameter ≥5 mm or any Gleason grade 4, and only two of the missed prostate cancer lesions had Gleason score >3+4. However, only a limited accuracy on isotropic voxel level was achieved potentially limiting focal therapy planning. All data are freely are available at the following address: http://petiv.utu.fi/improd
|
|
1845. 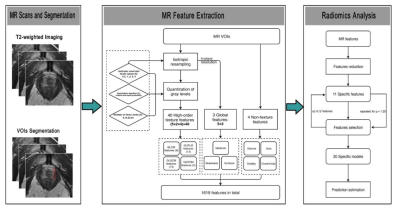 |
68 | The apical surgical margin status prediction of prostate cancer based on radiomics analysis derived from T2-weighted imaging: Clinical implementation
Shuai Ma, Huihui Xie, Huihui Wang, Ge Gao, Zhiyong Lin, Xiaodong Zhang, Xiaoying Wang
This retrospective study aims to validate a computer-aided diagnosis (CAD) system based on radiomics analysis in predicting the apical surgical margin (SM) status before radical prostatectomy (RP). 81 patients who received preoperative prostate T2-weighted MR imaging were evaluated by the CAD system and experienced radiologists, according to the sign of extracapsular extension (ESE), using pathological findings as a reference standard. The resulting algorithm was then validated from another external dataset of 38 patients in the same way. The results demonstrated this CAD system performed well and might help radiologist and surgeons make appropriate decisions concerning RP surgical approaches.
|
|
1846. 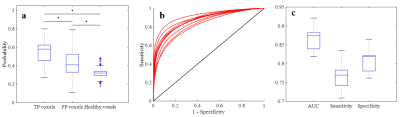 |
69 | mpMRI-based Tumor Probability Maps for Guidance of Targeted Prostate Biopsies
Gabriel Nketiah, Nienke Bakx, Kirsten Selnæs , Adrian Breto, Radka Stoyanova , Mattijs Elschot , Tone Bathen
Despite the improvement offered by the integration of multiparametric magnetic resonance imaging (mpMRI) in biopsy acquisition for prostate cancer diagnosis, the number of negative biopsies remains high with increasing risk of post-biopsy infection and complications. We evaluated the utility of machine learning-based tumor probability maps computed from pre-biopsy mpMR images for predicting and visualizing potential biopsy targets representing clinically significant cancer foci. The median [range] AUC, sensitivity and specificity of the classifier were 0.87 [0.82–0.92], 0.77 [0.71-0.83] and 0.82 [0.76-0.86], respectively. This approach has a potential to reduce the number of biopsy cores, and thus the risk of post-biopsy infection/complications.
|
|
1847.  |
70 | Pelvic MRI with Segmentation and 3D Anatomical Renderings Provide a Novel Method for Quantifying Clinically Relevant Parameters of the Lower Urinary Tract
Lucille Anzia, Shane Wells, Diego Hernando, Alejandro Roldán-Alzate
Prior imaging studies with ultrasound and CT have shown that bladder wall thickness (BWT), detrusor muscle volume (DMV) and prostate volume (PV) increase with age. We found a significant increase in DMV, BWT and PV when comparing males aged 30-39 to 60-69. There was no significant increase in BWT in females from the third to the sixth decade. While DMV increased significantly for women, the percent increase in muscle volume was substantially higher for men, likely the result of prostate hypertrophy. This is the first study, to our knowledge, to correlate physiologic changes of the urinary system in men and women using MRI.
|
|
1848. 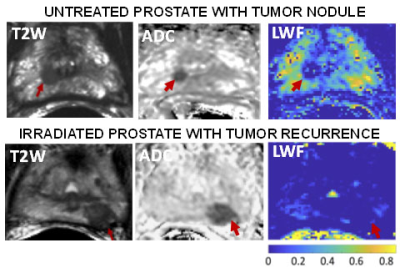 |
71 | Probing Structure of Normal and Malignant Prostate Tissue before and after Radiation Therapy with Luminal Water Fraction and Diffusion-Weighted MRI
Dominic Carlin, Matthew Orton, David Collins, Nandita deSouza
Luminal Water Fraction (LWF) is higher in peripheral than transitional zone of the untreated prostate; in comparison, it is significantly reduced in tumors. LWF is correlated with ADC in untreated non-malignant prostate. LWF is not correlated with ADC in tumors or in post irradiated prostate indicating that the morphological factors affecting LWF and ADC in these tissues are independent.
|
|
1849.  |
72 | Towards a clinic-radiologic-biopsy based predictive model for the detection of pelvic lymph node invasion in patients with prostate cancer before surgery Presentation Not Submitted
ying hou
Pelvic lymph node invasion in patients with prostate cancer is associated with different treatment selection and planning while there is no clear consensus on nomograms that can be clinically available for prediction of lymph node invasion. Our predictive model, based on preoperative clinical characteristics, MR image features and biopsy findings of 248 consecutive patients, was trained with a support vector machine and compared to a logistic regression analysis, allowing for improved differentiation in assessing the risk of lymph node invasion. Use of this machine-learning-based predictive tool potentially connect to better selection of optimal type of treatment and long-term excellent prognosis.
|
|
1850. 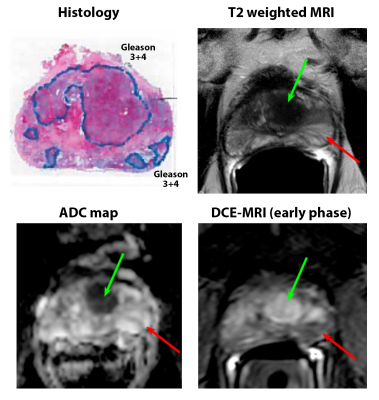 |
73 | Prostate cancers invisible on multi-parametric MRI: Pathologic feature in correlation with whole mount prostatectomy
Aritrick Chatterjee, Alexander Gallan, Tatjana Antic, Gregory Karczmar, Aytekin Oto
This study investigates why some prostate cancers are not identified on mpMRI using ground truth reference from whole mount prostatectomy specimens. Unidentified cancers tend to exhibit lower Gleason grade and pathologic stage, smaller size, lower density of glands compared to surrounding tissue (sparse cancer lesions) and have different tissue composition, specifically higher lumen (associated with high ADC and T2) and lower epithelium (associated with low ADC and T2) compared to cancer lesions identified on MRI.
|
|
1851. 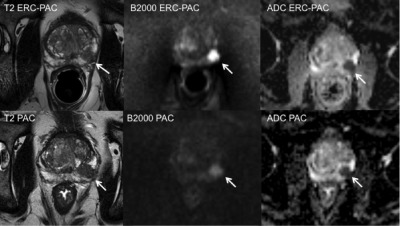 |
74 | MRI of the prostate using a two-channel phased-array endorectal receive coil compared to phased array coil acquisition
Sara Lewis, Aasrith Ganti, Pamela Argiriadi, Ally Rosen, Stefanie Hectors, Sahar Semaan, Christopher Song, Steven Peti, Maxwell Segall, Kezia George, Vaneela Jaikaran, Sebastian Villa, Nicholas Vountsinas, David Kestenbaum, Ashutosh Tewari, Ardeshir Rastinehad, Bachir Taouli
In this study, 3T MRI of the prostate using a two-channel solid phased-array endorectal receive coil (ERC) (Sentinelle, InVivo Corporation, Philips Healthcare) combined with phased array coil (PAC) was compared to PAC only for image quality and lesion conspicuity on T2WI and DWI. Improved image quality was found for T2WI and high b-value DWI and improved lesion contrast using ERC-PAC, while there was no difference in lesion conspicuity. These preliminary results show that the use of ERC-PAC improves prostate MRI image quality, without necessarily impacting lesion detection.
|
|
1852.  |
75 | Initial evaluation of an automated acquisition workflow for multiparametric MR (spectroscopic) imaging of the prostate
Carlijn Tenbergen, Elisabeth Weiland, Kirsten Selnaes, Tone Bathen, Arend Heerschap, Tom Scheenen
Standardization of imaging and automated adjustment of MR parameters could homogenize and expedite multiparametric MRI of the prostate. If automated and robust, spectroscopic imaging (MRSI) could be a part of this protocol. In this dual-centre study, an automated workflow was validated by patient measurements at 3T MR systems and the robustness of the spectroscopic imaging approach was evaluated. Automation of the acquisition protocol of multiparametric MR imaging of the prostate needed only minor manual adjustments. On average, 84% of the MRSI voxels within the prostate passed our quality control, illustrating the current robustness of the automated semi-LASER MRSI technique.
|
Digital Poster
| Exhibition Hall | 14:45 - 15:45 |
| Computer # | |||
1853. 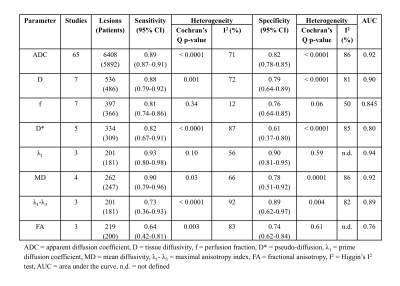 |
76 | A meta-analysis comparing the diagnostic performance of Diffusion-Weighted Imaging (DWI), Diffusion Tensor Imaging (DTI), and Intra-voxel Incoherent Motion (IVIM) in breast cancer
Gabrielle Baxter, Martin Graves, Fiona Gilbert, Andrew Patterson
The performance of parameters from diffusion-weighted imaging (DWI), diffusion tensor imaging (DTI) and intra-voxel incoherent motion (IVIM) in the differential diagnosis of malignant and benign breast lesions were compared through a meta-analysis. 73 eligible studies were included and pooled estimates of sensitivity, specificity and area under the curve were obtained for each of the model parameters. The highest performing parameters for DTI and IVIM were the prime diffusion coefficient (λ1) and the tissue diffusivity (D), respectively. DWI, DTI and IVIM are diagnostically comparable, though there is a lack of standardisation in methodology for each technique.
|
|
1854. 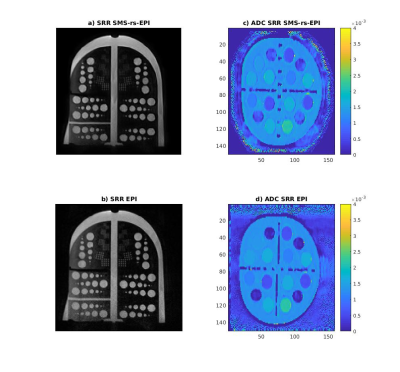 |
77 | One millimeter isotropic breast DWI combining readout-segmented EPI, super-resolution and simultaneous multi-slice acceleration: validation in a diffusion/resolution phantom and volunteers.
Maya Delbany, Roman Fenioux, Isabelle Thomassin-Naggara, Jacques Felblinger, Pierre-André Vuissoz, Freddy odille
The low resolution of diffusion-weighted imaging (DWI) is the main limiting factor in screening breast MRI. Recently a method was proposed for one millimeter isotropic DWI covering the entire breasts. Based on a readout-segmented DW-EPI sequence, 3 stacks of thick slices (3 mm) are acquired with 1mm-shifts in the slice direction; then a 1x1x1 mm3 dataset is obtained using a super-resolution reconstruction (SRR). In this study we further validate the method using a commercial diffusion breast phantom, in terms of SNR, resolution and ADC values. Additionally, SMS acceleration is investigated to reduce the total scan time below 10 min.
|
|
1855. 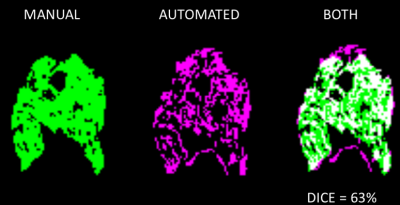 |
78 | A comparison of visual, automated and semi-manual approaches in assessing background parenchymal enhancement as a biomarker for response to neoadjuvant therapy
Fredrik Strand, Vignesh Arasu, Wen Li, Alex Nguyen, Roy Harnish, Ella Jones, David Newitt, Nola Hylton
We have examined different approaches to segmenting the fibroglandular tissue in breast MRI when calculating quantitative background parenchymal enhancement (BPE) as a potential predictor of response to neoadjuvant treatment (pCR). Our results suggest that quantitative approaches to measure BPE might be preferable to visual BI-RADS as a biomarker of response. Change in quantitative BPE with treatment was associated with pCR; but pre-treatment BPE was not. Further research may be directed towards handling wrongful inclusion of non-parenchymal voxels.
|
|
1856.  |
79 | Change in breast cancer functional tumor volume and contralateral background parenchymal enhancement is associated with pathological complete response to neoadjuvant therapy
Fredrik Strand, Vignesh Arasu, Wen Li, Roy Harnish, Ella Jones, David Newitt, Bonnie Joe, Laura Esserman, Nola Hylton
For women with locally advanced breast cancer, we have examined the change in quantitative measures of MRI tumor volume and background parenchymal enhancement between pre-treatment and after 12 weeks of treatment. In a multivariate model, we found that a larger decrease in MRI tumor volume or in quantitative BPE was associated with higher probability of pathological complete response.
|
|
1857 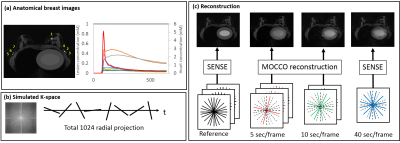 |
80 | Breast DCE-MRI using Radial Acquisition with Data-Driven Model Consistency Condition Reconstruction Video Permission Withheld
Ping Wang, Julia Velikina, Roberta Strigel, Leah Bancroft, Kang Wang, Ty Cashen, Kevin Johnson, Alexey Samsonov, Ali Ersoz, Edward Jackson, James Holmes
Advanced data acquisition and reconstruction methods have been proposed to improve temporal and spatial resolution DCE imaging for breast. However, few studies have validated these techniques. In this work we propose a radial acquisition with MOCCO reconstruction and assess performance of these methods using a simulated digital reference object breast phantom including pharmacokinetic simulation. An improvement to the MOCCO formulation is proposed using independent component analysis to learn the temporal components. Finally, the extended Tofts model was used to extract pharmacokinetic parameters from time series with different temporal resolution. Dynamic data were then use for pharmacokinetic (PK) fitting to assess the ability to recover PK parameters.
|
|
1858. 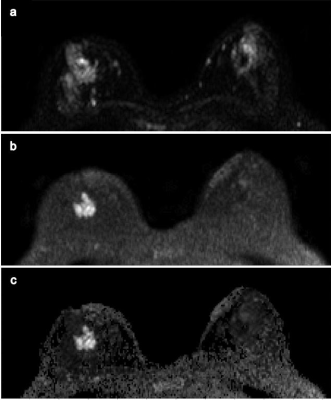 |
81 | Diffusion-Weighted MRI for Non-Contrast Breast Screening: Lesion Conspicuity on Computed vs. Acquired High b-Value Images
Michaela DelPriore, Debosmita Biswas, Madeline Dang, Adrienne Kim, Habib Rahbar, Savannah Partridge
On breast DWI, the relative signal intensity of a lesion can be increased by exploiting the differences in signal decay between tumor and normal tissue at higher b values. Computing high b-value images rather than acquiring them directly can increase lesion conspicuity and decrease scan times, improving the potential utility of breast DWI for non-contrast screening. In women with invasive breast cancer, we investigated the differences in lesion conspicuity across b-values and between acquired and computed diffusion weighted images. Our findings showed maximal lesion conspicuity at higher b-values (1200-1500s/mm2), with acquired images generally providing higher conspicuity than computed images.
|
|
1859. 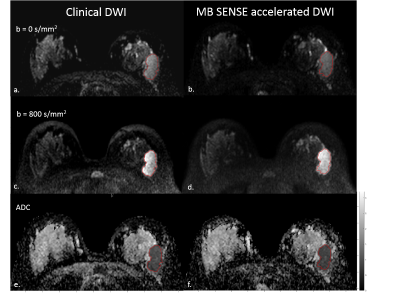 |
82 | Multiband SENSE accelerated diffusion weighted imaging with CAIPIRINHA: Preliminary study of clinical utility in the breast
Debosmita Biswas, Yi Wang, Michaela DelPriore, Madeline Dang, Adrienne Kim, Habib Rahbar, Savannah Partridge
Advanced DWI techniques necessitate acquisition of a large number of image slices such as to obtain a greater number of b values for IVIM or more gradient directions for DTI. These increase the acquisition time, making it difficult to incorporate advanced techniques within the clinical workflow. The purpose of this study was to examine the utility of MB-SENSE acceleration for reducing scan times of breast DWI. Our qualitative and quantitative assessments showed MB-SENSE could dramatically reduce scan time without reducing image quality and accuracy of lesion ADC measures in breast DWI.
|
|
1860. 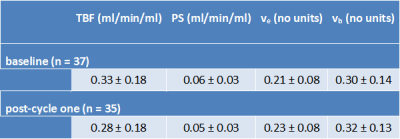 |
83 | Changes in breast tumor blood flow measured by dynamic contrast-enhanced MRI after one cycle of neoadjuvant chemotherapy
William Stevens, Leonidas Georgiou, Andrew Hanby, Daniel Wilson, Nisha Sharma, Timothy Perren, David Dodwell, Barbara Dall, David Buckley
Early assessment of response to neoadjuvant chemotherapy (NACT) in breast cancer is important and it has been suggested that functional changes, such as tumor blood flow (TBF), may precede size changes. We measured TBF using dynamic contrast-enhanced MRI in 40 patients before and after one cycle of NACT and compared these measures to pathological response. There was no correlation between change in TBF and pathological response in the full sample. However, several tumors shrank after one cycle of NACT; if these were removed then change in TBF in tumors that didn’t shrink correlated well with pathological response
|
|
1861. 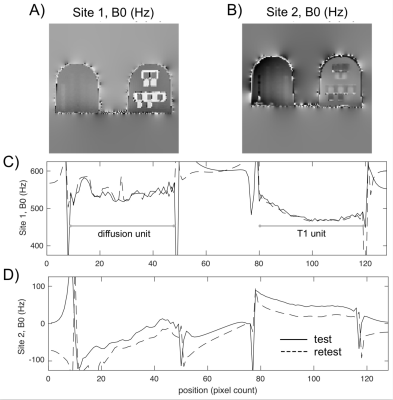 |
84 | Effect of DWI sequence on geometric measurement errors in a breast phantom
Lisa Wilmes, Adele Peskin, Xinran Zhong, David Newitt, Kyung Sung, Nola Hylton, Kathryn Keenan
Previously, when using the UCSF/NIST breast phantom, we discovered an x-direction distortion in DW-EPI and the resulting ADC maps that was dependent on spatial location within the scanner and was also present in patient images. The distortion was unaffected by switching the phase encode direction and did not change with increasing b-value, and thus was most likely not due to gradient nonlinearity nor eddy currents. Here, we demonstrate that the distortions decrease when using multi-shot EPI, which is less sensitive to off-resonance distortion, and change direction when reversing the gradient polarity.
|
|
1862. 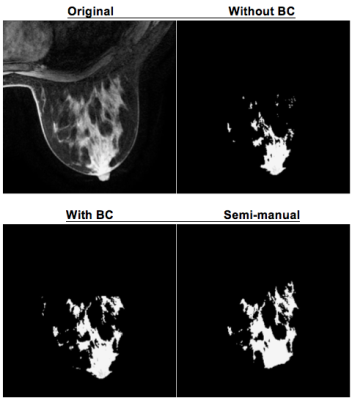 |
85 | Bias Correction for Improved Segmentation and Background Parenchymal Enhancement Calculation in Multi-Center Breast MRI Trials
Alex Anh-Tu Nguyen, Fredrik Strand, Nola Hylton, David Newitt
The presence of bias field inhomogeneity can negatively impact segmentation of breast fibroglandular tissue on MRI and subsequent quantification of background parenchymal enhancement. This can be particularly problematic in multi-center trials utilizing multiple imaging platforms. We have implemented the N4ITK algorithm for bias correction and evaluated the agreement between semi-automatic and semi-manual segmentation methods. Our results show that bias correction produces tissue segmentations and BPE estimates with better agreement with a reference manual segmentation method than non-corrected images.
|
|
1863. 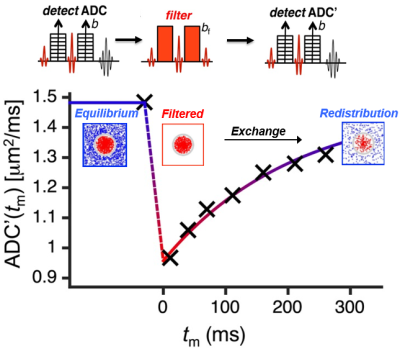 |
86 | Apparent Exchange Rate Mapping with Diffusion MRI: A Novel Marker For In Vivo Breast Cancer Characterization
Neal Shekar, Debosmita Biswas, Adrienne Kim, Mara Rendi, Markus Nilsson, Karin Bryskhe, Samo Lasic, Savannah Partridge
Filter exchange MR imaging (FEXI) offers potential to measure the diffusional exchange rate of water between intra- and extra-cellular spaces, which may provide unique insights to alterations in cell physiology. We investigated the feasibility of implementing FEXI for in vivo measurement of breast tumor apparent exchange rates (AXR) and association with pathologic factors. Our findings showed reduced AXR in breast tumors and suggested association with aquaporin five (AQP5) concentration, previously shown to correlate with tumor aggressiveness and metastatic risk. Further investigation is warranted to evaluate FEXI as a new prognostic marker and early marker of response to therapy.
|
|
1864. 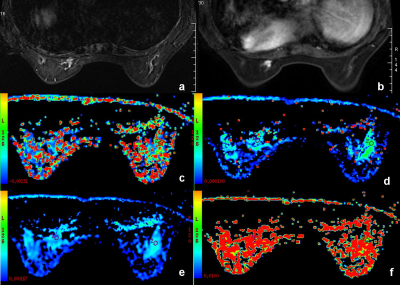 |
87 | Intravoxel incoherent motion imaging in the prediction of aggressiveness of T1 breast carcinoma patients
Lina Zhang, Jianyun Kang, Qingwei Song, Shiyun Tian, Ailian Liu, Lizhi Xie
Intravoxel incoherent motion (IVIM) imaging provides quantitative measurement of ADCslow for cellularity and ADCfast and ffast for vascularity. It is helpful for the differentiation between benign and malignant breast lesions. This study concerned perfusion as well as diffusion parameters of T1 breast carcinoma lesions using IVIM imaging based on the biexponential analysis and then compared these parameters from T1-weighted, T2-weighted and contrast-enhanced MR images on the classification of high and low aggressiveness of T1 breast carcinomas.
|
|
1865 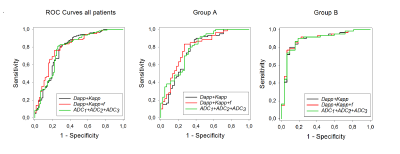 |
88 | Diffusion kurtosis imaging and intravoxel incoherent motion analysis in comparison to a combination of multi-level diffusion coefficients in MR mammography of suspicious breast lesions Video Permission Withheld
Anna Mlynarska-Bujny, Sebastian Bickelhaupt, Franziska König, Frederik Laun, Wolfgang Lederer, Heidi Daniel, Stefan Delorme, Heinz-Peter Schlemmer, Tristan Kuder
Diffusion-weighted imaging (DWI) is increasingly used in MR mammography for assessing malignancy of breast lesions. In particular, quantitative analysis of DWI data acquired with several b-values is gaining importance. Common data evaluation approaches include intravoxel incoherence motion (IVIM) and kurtosis imaging. The aim of this work was to evaluate the performance of kurtosis and IVIM based parameters in comparison to an approach combining several conventional diffusion coefficients measured with different b-values. The dataset comprised 198 examinations of patients with suspicious mammography findings. The simple approach using several ADCs showed a similar performance as the combination of kurtosis and IVIM.
|
|
1866. 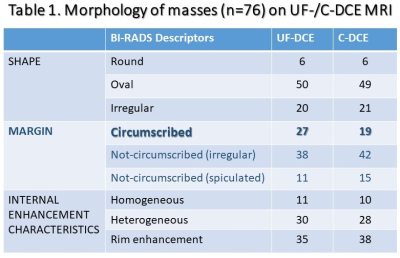 |
89 | Morphology of Breast lesions on Ultrafast Dynamic Contrast Enhanced MRI using Compressed Sensing Reconstruction
MASAKO KATAOKA, Maya Honda, Natsuko Onishi, Mami Iima, Akane Ohashi, Ayami Kishimoto, Rie Ota, Marcel Nickel , Masakazu Toi, Kaori Togashi
Using ultrafast DCE (UF-DCE) MRI with compressed sensing reconstruction, size and morphology of breast lesions on very early phase images within 1 minutes post contrast injection were compared to those on conventional DCE (C-DCE) MRI. The size of the lesions was slightly smaller on UF-DCE but within-2mm difference in approximately 80 % of the lesions. Morphological evaluations were the same in approximately 80% of the lesions yet irregular margin and clustered ring on C-DCE MRI may not be reflected to the appearance on UF-DCE, which should be noted in interpreting lesions using UF-DCE.
|
|
1867. 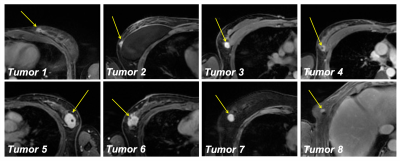 |
90 | Preoperative Supine Breast MRI for Surgical Planning: Comparison of Dynamic Contrast Enhancement Curves to Prone Diagnostic MRIs
Stephanie Perkins, Brian Hargreaves, Bruce Daniel
Dynamic contrast-enhanced breast imaging is typically performed in the prone position, but supine breast MRI is desirable for patient comfort and better correspondence to the surgical position. We have developed a breath-held multiphase supine bilateral DCE breast imaging protocol with Dixon fat-water separation. In this work, we compare the DCE curves to those from the prone diagnostic MRIs in 6 tumors. The shape of the curves is generally preserved, demonstrating that our supine scans are limited primarily by resolution, as opposed to SNR or motion.
|
|
1868.  |
91 | Kaplan-Meier survival curves in breast cancer patients: contributions of nodal volume, tumor volume, residual disease, and response to chemotherapy
Renee Cattell, Pauline Huang, James Kang, Thomas Ren, Ashima Muttreja, Haifang Li, Jules Cohen, Lea Baer, Cliff Bernstein, Roxanne Palermo, Sean Clouston, Timothy Duong
The goal of our study was to evaluate whether pre- and post-chemotherapy nodal volume affects the survival profiles of breast cancer patients. In addition, we also evaluated these effects with respect to responders and non-responders to neoadjuvant chemotherapy. Comparison was made by analyzing the effects of tumor volume on survival profiles. We concluded that recurrence-free survival profile is dependent on axillary lymph node volume, and that non-responder patients with large nodes may need more vigorous treatment and follow up as they were associated with worse recurrence-free survival.
|
|
1869. 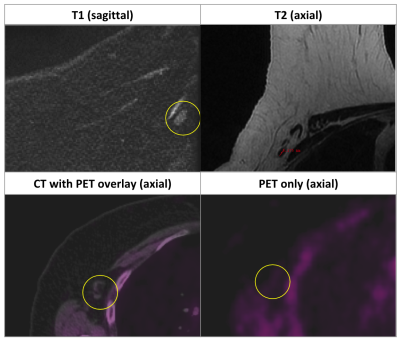 |
92 | Pre-chemo MRI staging of axillary lymph node metastasis in breast cancer: validation with PET
Pauline Huang, Renee Cattell, Julie Leong, Meghan Italo, Jason Ha, Dinko Franceschi, Jules Cohen, Haifang Li, Lea Baer, Cliff Bernstein, Roxanne Palermo, Timothy Duong
This study evaluated the use of pre-chemo MRI of axillary lymph nodes (aLNs) to detect metastasis in breast cancer with PET and pathology as reference standards. PET versus pathology reports agreed 87% for presence of disease in the aLNs, while PET and MRI reports agreed 93%. We found good agreement between MRI and PET scores (Cohen’s Kappa ??= 0.39, p=10-5). The MRI sensitivity, specificity, NPV and accuracy were 66.1%, 72.1%, 73.1% and 69.9%, respectively. Although improvement is needed, MRI staging of aLN is possible and practical. This approach may prove helpful in diagnosis and treatment planning of breast cancer patients.
|
|
1870. 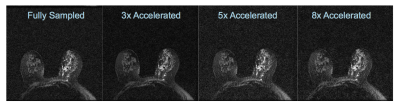 |
93 | Accelerated T2 Mapping of Breast Cancer Using Compressed Sensing
Meredith Sadinski, Ricardo Otazo, Elizabeth Morris, Li Feng
The use of T2 mapping in the breast is currently limited by prohibitively long acquisition times. We present here a compressed sensing approach and show that we are able to acquire T2 mapping breast images with 5-fold acceleration relative to a fully sampled, multi spin echo sequence. This reduction in acquisition time may make T2 mapping a feasible option for quantitative imaging of the breast, particularly for longitudinal studies such as those evaluating treatment efficacy and response.
|
|
1871.  |
94 | Tumor sphericity as a predictor of response in patients undergoing neoadjuvant chemotherapy treatment for invasive breast cancer
David Newitt, Wen Li, Bo Yun, Laura Esserman, I-SPY 2 Consortium, Nola Hylton
In the realm of personalized and precision medicine, quantitative metrics are needed for predicting treatment outcomes during neoadjuvant chemotherapy for breast cancer. We evaluated an automated tumor sphericity measurement as an addition to standard functional tumor volume for prediction of treatment response in a cohort of 220 patients with invasive breast cancer. Tumor sphericity captured some similar information to a visually assessed morphologic pattern score. Pre-treatment sphericity showed comparable prediction of pathologic complete response to pre-treatment volume, and added benefit in a logistic regression model. Sphericity may be useful in combination with tumor size to improve prediction of outcome.
|
|
1872.  |
95 | A dual-slab 3D gradient echo spectroscopic imaging sequence with correction of respiration- and hardware-related frequency variations for bilateral evaluation of lipid composition in the breast
Pippa Storey, Linda Moy, Sungheon Kim
To enable rapid bilateral evaluation of lipid composition in the breast with high spatial resolution and easy integration into clinical workflow, we have developed a gradient echo spectroscopic imaging sequence, which consists of a simultaneous dual-slab 3D gradient echo imaging acquisition with 128 monopolar echoes. To correct for the frequency drift of the scanner over the course of the acquisition, as well as frequency fluctuations due to respiration, the sequence includes a quick frequency navigator every TR period. The navigator was found to improve spectral quality in all subjects.
|
|
1873. 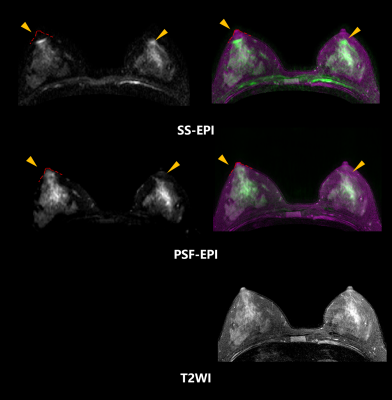 |
96 | Distortion correction in diffusion-weighted MRI of the breast: using point spread function (PSF) encoding
Ziyi Pan, Yishi Wang, Hua Guo
Diffusion-weighted MRI of the breast is a promising technique that can detect and characterize breast cancer sensitively and safely. However, geometric distortions of echo-planar imaging (EPI) due to field inhomogeneity and eddy currents has limited its clinical application. Conventional correction methods in breast DWI need additional B0 field maps that are either measured or estimated, and achieve limited effects at tissue interfaces. In this work, we attempted the feasibility of the distortion-free breast DWI using a point spread function (PSF) encoded method. The results showed higher fidelity and better image quality on breast DWI, which could facilitate the anatomical/DWI image registration and improve the quantitative measurements of the breast.
|
|
1874 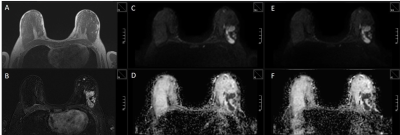 |
97 | Simultaneous multi-slice echo planar imaging for accelerated diffusion-weighted imaging of malignant and benign breast lesions Video Permission Withheld
Sabine Ohlmeyer, Frederik Laun, Theresa Palm, Rolf Janka, Elisabeth Weiland, Michael Uder, Evelyn Wenkel
The diagnostic accuracy of breast MRI can be increased by performing an additional diffusion sequence (EPI), however, further extending the examination time. Aim of our study was to investigate simultaneous multi-slice (SMS) accelerated EPI (TA 1:37 min) compared to the standard sequence (TA 2:57 min) in a clinical study. Image quality, artifacts and the apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) of 72 breast lesions were determined. SMS-EPI achieved the same ADC values in benign and malignant breast lesions compared to the standard sequence, image quality did not differ. This indicates that SMS acceleration can be used for diffusion imaging in breast MRI.
|
|
1875. 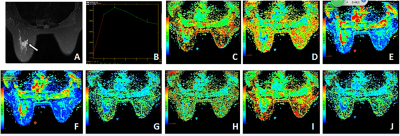 |
98 | Preliminary study of diffusion kurtosis imaging in differential diagnosis of benign and malignant breast lesions Presentation Not Submitted
Aodan Zhang, Jie Bian , Jiawen Luo , Chuanwen Yu, Lizhi Xie
Objective to investigate the diagnostic value of diffusion kurtosis imaging (DKI) in benign and malignant breast lesions. At present, Imaging diagnosis of benign and malignant breast nodules mainly focuses on morphology and hemodynamics to reflect the characteristics of lesions. This study intends to reflect the characteristics and changes of microstructure in breast tissues at molecular level by quantitative parameters of DKI, which provides an effective basis for early detection and accurate diagnosis of breast cancer.
|
|
1876. 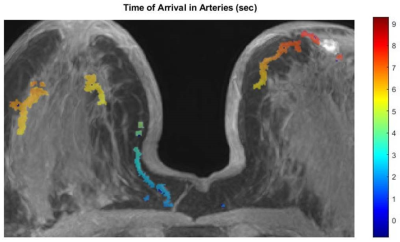 |
99 | A new approach to quantitative measurement of breast tumor blood flow, capillary permeability, and interstitial pressure.
Ty Easley, Federico Pineda, Byol Kim, Rina Foygel-Barber, Chengyue Wu, Thomas Yankeelov, Xiaobing Fan, Deepa Sheth, David Schacht, Hiro Abe, Gregory Karczmar
Ultrafast DCE-MRI detects sparse enhancement during the early phase of contrast media uptake [8]. This facilitates reconstruction of arteries and lesions using partial k-space data to obtain even higher temporal resolution. In addition, new approaches to tracking blood vessels in breast [10] identify arteries feeding suspicious lesions and possibly also draining veins. As a result, tumor blood flow can be accurately measured from propagation of the contrast media bolus along arteries that supply tumors. This approach avoids assumptions and artifacts that are inherent in pharmacokinetic analysis, and facilitates measurement of important biomarkers, e.g. capillary permeability and interstitial pressure.
|
Digital Poster
| Exhibition Hall | 14:45 - 15:45 |
| Computer # | |||
1877.  |
101 | Comparison of algorithms to determine Ventilated Volume Fraction from Oxygen-Enhanced MRI in Cystic Fibrosis
Marta Tibiletti, Josephine Naish, Katharina Martini, Thomas Frauenfelder , Geoff Parker
We have compared four different algorithms to determine the ventilated volume fraction (VVF) in a population of 4 healthy volunteers and 21 cystic fibrosis adult patients who underwent volumetric dynamic oxygen-enhanced MRI at 1.5T. Results were compared with pulmonary function tests and a CT-based scoring system (Brody score). All considered methods present significant correlation between VVF and FEV1 (R2>0.5), FVC (R2>0.4), FEV1/FVC (R2>0.4). Weaker correlation was found between VVF and the Brody score (R2 ~0.2).
|
|
1878. 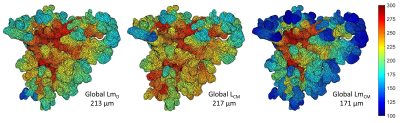 |
102 | Validation of theoretical models of hyperpolarized gas diffusion MRI with finite element simulation in geometrical and realistic models of lung acinar airways from micro-CT
Ho-Fung Chan, Guilhem Collier, Jim Wild
In this work, the stretched exponential (SEM) and cylindrical airway (CM) theoretical models for hyperpolarized gas diffusion MRI are validated with finite element (FE) simulations in two different acinar airway geometries. Simulations of 3He multiple b-value diffusion experiments were performed in a theoretical cylindrical acinar airway geometry and a micro-CT derived realistic acinus model. The simulated MRI diffusion signal was fitted to the CM and SEM. In FE simulations of both models, derived acinar airway parameters from CM and SEM demonstrated strong correlation and good agreement with the underlying model.
|
|
1879. 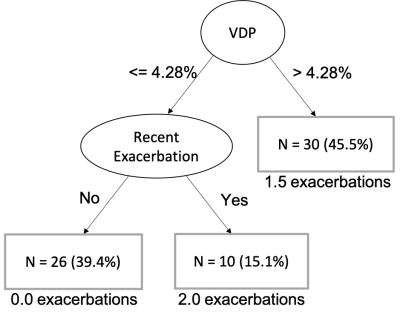 |
103 | Ventilation defects on hyperpolarized helium-3 MRI are predictive of 2-year exacerbation frequency in asthma
David Mummy, Katherine Carey, Michael Evans, Wei Zha, Ronald Sorkness, Mark Schiebler, Loren Denlinger, Nizar Jarjour, Sean Fain
Ventilation defects on hyperpolarized 3He MRI in asthma are predictive of exacerbation frequency in the two years following imaging. Incorporating VDP and exacerbation history into a single model allows for a decision-tree based approach to assessing propensity for asthma exacerbation.
|
|
1880.  |
104 | Comparison of quantified pulmonary blood flow using phase-resolved functional lung (PREFUL) MRI and dynamic contrast enhanced MRI in COPD, CF and CTEPH patients
Lea Behrendt, Andreas Voskrebenzev, Filip Klimes, Marcel Gutberlet, Till Kaireit, Tawfik Moher Alsady, Frank Wacker, Jens Vogel-Claussen
Phase-resolved functional lung (PREFUL) MRI is a very promising method for contrast agent free pulmonary perfusion measurement in free breathing. Still a large-scale validation of quantified pulmonary blood flow (PBFPREFUL) with the current gold standard PBFDCE derived by dynamic contrast enhanced (DCE) MRI is missing. Therefore, 52 patients with COPD, CF and CTEPH were included in this study and the correlations for PBFPREFUL and PBFDCE were assessed. Except for CTEPH, strong and moderate correlations were found. Low or no correlation can be explained by respiratory motion (DCE) and perfusion delay (PREFUL).
|
|
1881. 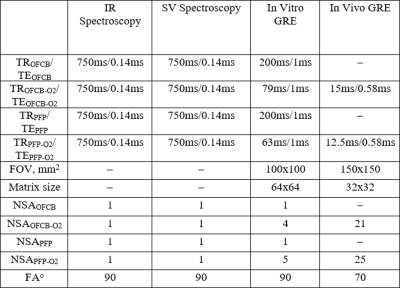 |
105 | Octafluorocyclobutane as a novel 19F MRI gas agent for significant lung image quality improvement
Yurii Shepelytskyi, Tao Li, Francis Hane, Alanna Wade, Vira Grynko, Camryn Newman, Mitchell Albert
Two different MRI gas techniques are presently being employed for lung imaging: hyperpolarized noble gas MRI and fluorinated inert gas MRI. Perfluoropropane (PFP) is the most widely used 19F gas for imaging purposes. In this work, we demonstrate the feasibility of using an octafluorocyclobutane (OFCB) as a novel gas contrast agent for 19F lung MRI. Furthermore, the direct comparison between OFCB and PFP was performed In Vivo and In Vitro. OFCB, due to its chemical structure and relaxation properties, demonstrated a higher SNR. Therefore, usage of OFCB can significantly improve the image quality of 19F lung MRI.
|
|
1882. 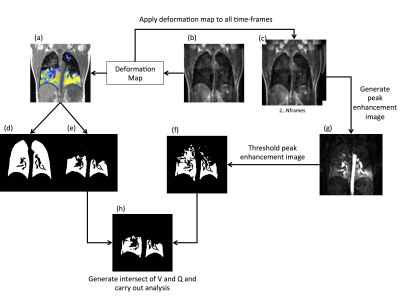 |
106 | Ventilation perfusion matching in patients with Cystic Fibrosis assessed via co-registered hyperpolarised gas and dynamic contrast enhanced lung MRI
Paul Hughes, Laurie Smith, Jody Bray, Oliver Rodgers, Martin Wildman, Noreen West, Alexander Horsley, Helen Marshall, Jim Wild
Assessment of regional ventilation and perfusion is of clinical interest for better understanding of disease mechanisms and lung pathophysiology, as the primary function of the lung is gas exchange. This work aimed to assess ventilation and perfusion in patients with Cystic Fibrosis using co-registered hyperpolarised gas and dynamic contrast enhanced lung MRI.
|
|
1883.  |
107 | Integration of HP 3He MRI with In Silico Models to Predict Gas Flows in Severe Asthma Subjects
Kamran Poorbahrami, David Mummy, Ben Piperno, Stephen Paik, Ellesse Cooper, Michaiah Parker, Sean Fain, Jessica Oakes
Hyperpolarized 3He MRI, CT data, and patient-specific computational modeling methods are combined to predict airflow distributions, pressure maps, and central and peripheral resistances in three severe asthma subjects. Simulation results indicate variations in gas flows between the subjects and show a correlation between SVDP and peripheral respiratory resistances.
|
|
1884. 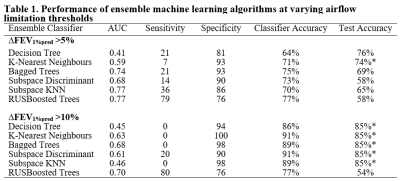 |
108 | Hyperpolarized Ventilation MRI and Ensemble Machine Learning Predict Airflow Limitation Worsening in Ex-smokers Presentation Not Submitted
Cathy Ong-Ly, Andrew Westcott, Inderdeep Dhaliwal, Aaron Fenster, Miranda Kirby, Grace Parraga
Hyperpolarized noble-gas pulmonary imaging provides a way to measure ventilation and perfusion in patients. The potential of highly sensitive MRI biomarkers of lung function has not yet been exploited using machine-learning. Ensemble machine-learning merges diverse classifiers to improve classification accuracy and reduce the potential for misclassification. Our aim was to evaluate the performance of ensemble machine-learning algorithms and hyperpolarized gas MRI features for predicting worsening airflow measured using spirometry. This proof-of-concept study revealed that MRI ventilation combined with ensemble machine-learning predicted small changes in airflow limitation (?FEV1%pred=5%) over relatively short time period (2.5 yr) in ex-smokers with and without COPD.
|
|
1885. 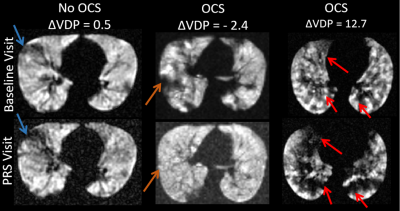 |
109 | Ventilation Defect Percent from Hyperpolarized Helium-3 MRI as a predictor of Asthma Exacerbation Severity
Katherine Carey, David Mummy, Wei Zha, Michael Evans, Chase Hall, Mark Schiebler, Ronald Sorkness, James Quirk, Dimitriy Yablonskiy, Jason Woods, Loren Denlinger, Nizar Jarjour, Mario Castro, Sean Fain
We assessed ventilation defect percent (VDP) on hyperpolarized (HP) 3He MRI in 28 asthmatics at baseline and recovery visits following an exacerbation (10 ± 7 months apart). We found that pre-bronchodilator VDP at baseline was a stronger predictor of severe exacerbations than conventional asthma control indices, and subjects that underwent a severe exacerbation had highly variable VDP changes after recovery. These findings suggest that VDP is a potential biomarker of asthma instability.
|
|
1886. 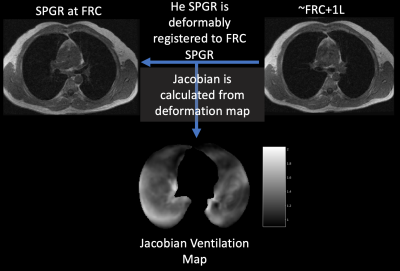 |
110 | Jacobian-based Ventilation Derived from Lung Proton MRI: Correlation with Ventilation Defects on Hyperpolarized Gas MRI
Katherine Carey, David Mummy, Wei Zha, Michael Evans, Mark Schiebler, Ronald Sorkness, Nizar Jarjour, Loren Denlinger, Sean Fain
We used deformable registration between 1H MRI at two lung volumes to create a Jacobian based ventilation map for quantification of ventilation heterogeneity. We compared values derived from the Jacobian ventilation map to the ventilation defect percent (VDP) from hyperpolarized Helium-3 MRI (HP 3He MRI) and to spirometry measures and found that the Jacobian minimum was associated with both VDP and FEV1/FVC %. These findings suggest that ventilation quantified using Jacobian maps of deformable registration on 1H MRI is a potential alternative to HP MRI ventilation imaging.
|
|
1887.  |
111 | Comparing Hyperpolarized 3He MRI Fractional Ventilation to CT-Derived Fractional Ventilation
Ryan Baron, Faraz Amzajerdian, Stephen Kadlecek, Hooman Hamedani, Ian Duncan, Yi Xin, Mehrdad Pourfathi, Francisca Bermudez, Maurizio Cereda, Rahim Rizi
Although hyperpolarized helium-3 (HP 3He) MRI has been viewed as the gold-standard for ventilation imaging of the lungs, validating fractional ventilation (FV) measurements obtained with HP 3He MRI has proven challenging, as no other technique delivers qualitatively comparable information regarding gas distribution throughout the lungs. In this work, we assessed the feasibility of deriving CT-based FV assessments from end-inspiratory (EI) and end-expiratory (EE) images obtained from subjects in the national COPDGene study, to be used for validation of FV measurements obtained during HP 3He MRI.
|
|
1888. 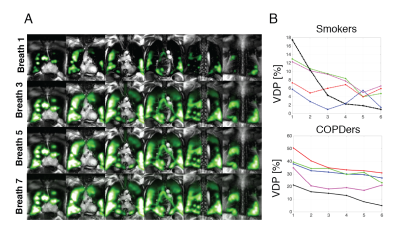 |
112 | Hyperpolarized Gas MR Imaging of Regional Ventilation; Dissimilarities of Single- and Multi-breath Imaging
Hooman Hamedani, Francisca Bermudez, Ryan Baron, Stephen Kadlecek, Kai Ruppert, Ian Duncan, Yi Xin, Sarmad Siddiqui, Mehrdad Pourfathi, Faraz Amzajerdian, Luis Loza, Tahmina Achekzai, Federico Sertic, Rahim Rizi
Single and Multi-breath Hyperpolarized Gas MR Imaging Provides Different Measures of Lung Ventilation
|
|
1889. 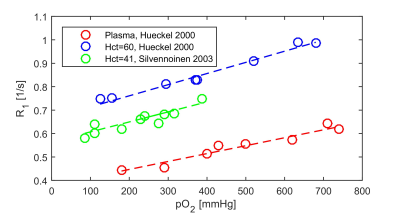 |
113 | Common misconceptions about pulmonary oxygen enhanced MRI
Simon Kindvall, Lars Olsson
There are several common misconceptions about pulmonary oxygen enhanced MRI. Most importantly, the relaxivity of molecular oxygen is, like other contrast agents, macromolecule dependent and not static. Moreover, the signal from the lung results from both oxygenated and non-oxygenated blood, where the oxygen enhancement effect will work to both shorten and elongate blood T1. The resultant relaxation enhancement primarily reflect blood partitioning. Finally, oxygen enhanced MRI has been shown to correlate with diffusing capacity in the lung, but this is only in severe disease. Rather, pulmonary shunt is the main determinant of arterial oxygenation and will affect the relaxation enhancement.
|
|
1890. 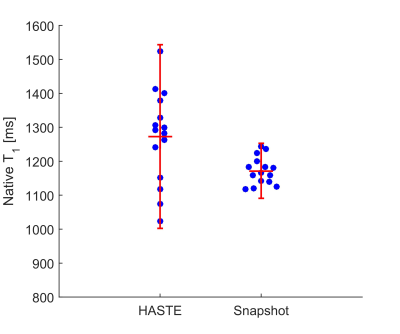 |
114 | Spin echo and gradient echo quantification in oxygen enhanced MRI may yield different results
Simon Kindvall, Lars Olsson
Pulmonary oxygen enhanced MRI is currently performed with a variety of pulse sequences. This abstract provides evidence that the oxygen enhancement, quantified as the change in longitudinal relaxation rate, ΔR1, assessed with a spin-echo or gradient-echo sequence may yield different values. Indeed, a standard IR-HASTE quantification yielded group mean ΔR1 10% higher than the Snapshot-FLASH quantification in 15 healthy volunteers. Although studies employing different quantification schemes are likely comparable, caution is warranted since the mean ΔR1 quantified with HASTE-type sequences is likely higher.
|
|
1891. 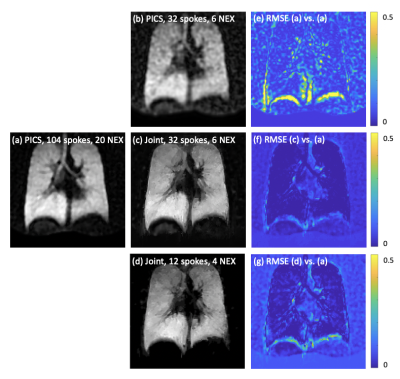 |
115 | Joint Reconstruction of 1H and 19F gas MRI in the Human Lung
Arnd Obert, Marcel Gutberlet, Andreas Voskrebenzev, Gesa Pöhler, Robert Grimm, Frank Wacker, Jens Vogel-Claussen
Due to its low costs, high inertness and applicability at thermal polarization, ?uorinated gases are promising tracers for imaging lung ventilation using fluorine magnetic resonance imaging. In this work, the joint reconstruction of proton density and 19F ventilation images in the human lung is shown. To exploit the structural similarity of both imaging modalities, a regularized reconstruction is used, minimizing the parallel level sets. Quantitative analysis of the reconstruction performance could be achieved by retrospective undersampling of data collected during a 2.5-minute breath hold. Furthermore, computation of VDP maps has been analyzed using joint reconstruction in three COPD patients.
|
|
1892 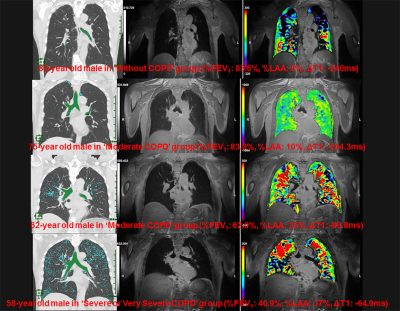 |
116 | Comparison of Capabilities for Pulmonary Functional Loss Evaluation and Clinical Stage Classification between 3D Oxygen-Enhanced MRI at 3T System and Thin-Section CT in Smokers Video Permission Withheld
Yoshiharu Ohno, Masao Yui, Takeshi Yoshikawa, Shinichiro Seki, Katsusuke Kyotani, Takamichi Murakami
Recently, 3D O2-enhanced MRI at 3T system is recently developed by Cannon Medical Systems Corporation. On the other hands, no one directly compare this technique with quantitatively assessed CT for smoking-related COPD assessment. We hypothesized that 3D O2-enhanced MRI has a potential for quantitative assessment of morphological changes due to smoking-related COPD as well as quantitatively assessed thin-section CT. The purpose of this study was to prospectively and directly compare the quantitative capability for pulmonary functional loss assessment and clinical stage classification between 3D O2-enhanced MRI and thin-section CT in smokers.
|
|
1893.  |
117 | In Vivo 19F-Isoflurane Chemical Shift Imaging in mouse lung
Gang Zheng, Michael Veer, Gary Egan
Proton MRI of lungs has challenges because of the available signal and high susceptibility of the air and tissue interface. Isoflurane is a commonly used fluorinated anesthetic with an excellent safety record in preclinical studies, which contains small amounts of the stable fluorine isotope 19F. This abstract demonstrates that Isoflurane can be used as both an anesthetic and as 19F contrast agent simultaneously. Inhaled isoflurane provides 19F signals in the gas and the dissolved phases which offers potentials for functional MR imaging of lungs.
|
|
1894. 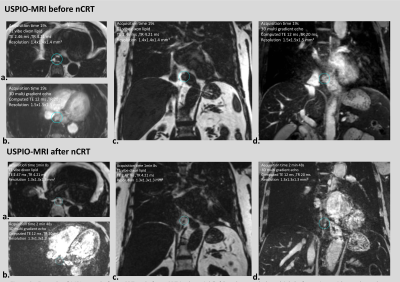 |
118 | USPIO-enhanced MRI for pre-operative lymph node staging after neoadjuvant chemoradiotherapy: feasibility and validation framework
Didi de Gouw, Bastiaan Klarenbeek, Marnix Maas, Rutger Stijns, Maroeska Rovers, Cor Slagt, Jörg Mühling, John Hermans, Tom Scheenen, Camiel Rosman
Extensive lymph node dissections during esophagectomy may be omitted in patients with esophageal cancer without lymph node metastases, reducing associated morbidity. A promising technique to detect lymph node metastases is MRI with ultrasmall superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles (USPIO, ferumoxtran-10). To validate USPIO-enhanced MRI in patients with esophageal cancer, a framework is designed to compare lymph nodes of the MRI scans with histopathology data on a node-to-node level.
|
|
1895.  |
119 | Shortening scan times for functional lung imaging using matrix pencil decomposition
Grzegorz Bauman, Orso Pusterla, Sylvia Nyilas, Philipp Latzin, Oliver Bieri
This study examines the performance of functional lung MRI using matrix pencil (MP) decomposition for the estimation of regional fractional ventilation and perfusion by exploring the relationship between the scanning time and the quantitative outcomes. Our results show excellent promise that the overall scan time for functional lung imaging using MP decomposition can be considerably shortened, which can allow for easier integration of MP MRI in clinical routine protocols.
|
|
1896. 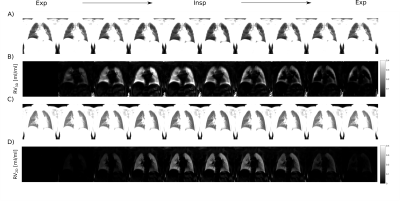 |
120 | Feasibility of 3D PREFUL: 3D dynamic lung ventilation imaging, initial comparison to 2D PREFUL in healthy volunteers
Filip Klimeš, Andreas Voskrebenzev, Marcel Gutberlet, Grzegorz Bauman, Oliver Bieri, Robert Grimm, Tawfik Moher Alsady, Frank Wacker, Jens Vogel-Claussen
Pulmonary ventilation assessed by Fourier Decomposition (FD) is limited by its 2D acquisition and does not consider dynamics of ventilation. In this work, a method to assess dynamic lung ventilation in 3D using self-gating and phase-resolved functional lung imaging (PREFUL) is presented. The full respiratory cycle was reconstructed and dynamic regional ventilation (RV) maps were generated. Mean slice correlation and anterior-posterior gradient of ventilation values were compared between the 3D and the 2D PREFUL approaches. 3D PREFUL imaging was able to reconstruct dynamic imaging of the respiratory cycle, generate dynamic RV maps and provide good agreement with the 2D approach.
|
|
1897. 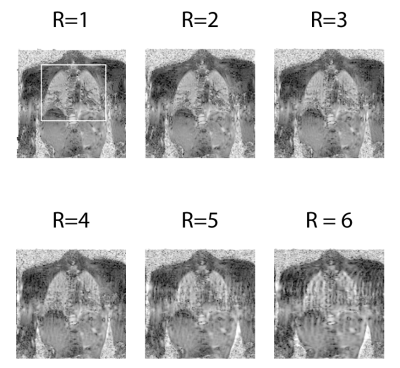 |
121 | Compressed Sensing reconstruction in non-contrast-enhanced functional lung MRI using Fourier Decomposition: An initial study
Efe Ilicak, Jorge Chacon-Caldera, Jascha Zapp, Lothar Schad, Frank Zoellner
Ventilation and perfusion functions have significant clinical value for the diagnosis of pulmonary diseases. Fourier Decomposition is a non-contrast-enhanced method for assessing regional ventilation and perfusion information from time-resolved images. However, its robustness suffers from poor temporal resolution. Here we propose a compressed sensing reconstruction of undersampled acquisitions to improve temporal resolution of dynamic images. Retrospective demonstrations on in vivo acquisitions indicate that the proposed reconstruction scheme achieves similar image quality to conventional acquisitions while improving scan efficiency.
|
|
1898. 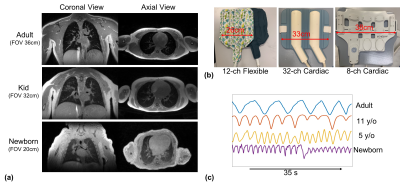 |
122 | 5-minute non-sedated neonatal and pediatric pulmonary UTE based MRI studies
Xucheng Zhu, Marilynn Chan, John Mackenzie, Scott Nagle, Joseph Cheng, Shreyas Vasanawala , Michael Lustig, Kevin Johnson, Peder Larson
Pulmonary MRI is free of ionizing radiation, which is beneficial for screening and longitudinal imaging in radio-sensitive populations, like newborns and children. However, practical considerations make pediatric pulmonary MRI challenging, including smaller body size, increased respiration rate, and increased motion from inability to hold still. In this work, we propose an optimized 5-minute non-sedated neonatal and pediatric pulmonary UTE, applied on seven patients.
|
|
1899. 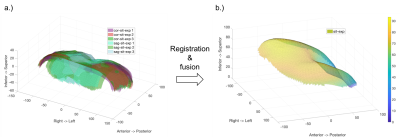 |
123 | Impact assessment of posture and breath hold state on diaphragm shape
Christoph Arthofer, Shahideh Safavi, Andrew Cooper, James Harkin, Saleh Alenazi, Penny Gowland, Charlotte Bolton, Ian Hall
The diaphragm plays a crucial role in respiratory mechanics. However, commonly used image acquisition methods are limited by position and breath hold duration. We developed a novel MR protocol for scanning the diaphragm in an upright low-field MR scanner and analysis tools to investigate the impact of posture and breath hold state on its morphology.
|
|
1900. 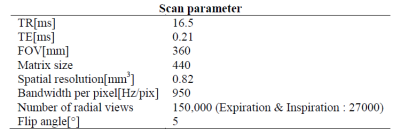 |
124 | Any Correlation between Pulmonary Function Test and Lung UTE-MRI?
Seokwon Lee, Jinil Park, Ho Yun Lee, Jang-Yeon Park
Although PFT is widely used for diagnosis pulmonary disease, there has been continuing interest in the possibility of using MRI to detect the pulmonary function value such as FEV1, FVC and FEV/FVC. However, previous works acquired distribution of lung lesions and ventilation defect region. Here, we proposed a new method to evaluate lung function by MRI. We demonstrated its feasibility with six healthy subjects. Despite the number of subject was too small, the results show a correlation with the results of the PFT.
|
Digital Poster
| Exhibition Hall | 14:45 - 15:45 |
| Computer # | |||
1901. 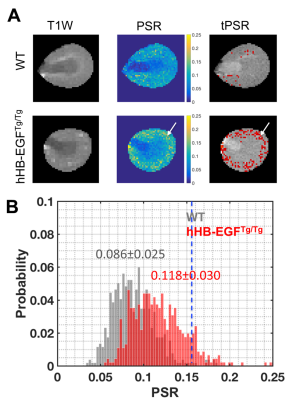 |
126 | Noninvasive Assessment of Tubulointerstitial Fibrosis in a Murine Fibrosis Model by Quantitative Magnetization Transfer MRI
Feng Wang, Suwan Wang, Ke Li, Raymond Harris, John Gore, Ming-Zhi Zhang
Renal fibrosis is a hallmark of chronic kidney disease, which drives further kidney injury and leads to renal failure. It is critical to assess the spatiotemporal extent of fibrosis in kidney. However, currently there are no reliable non-invasive means for assessing the severity and progression of fibrosis in individual kidney. Therefore, here we evaluate the utility of MT imaging for measuring renal fibrosis in kidney using hHB-EGFTg/Tg mouse model, in which progressive fibrosis is the predominant event. In this study, we compare and assess the utility of MTR and PSR for detecting tubulointerstitial fibrosis in OSOM of kidney.
|
|
1902. 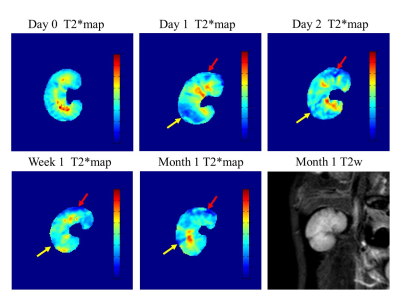 |
127 | A longitudinal study of lesion evolution in atheroembolic renal disease using BOLD MRI
Hanjing Kong, Chengyan Wang, Fei Gao, Xiaodong Zhang, Min Yang, Jue Zhang, Xiaoying Wang
Atheroembolic renal disease (AERD) is part of a multisystemic disease caused by showers of cholesterol emboli from the atherosclerotic aorta to many organs and is usually associated with poor renal and patient survival. The specific evolution of renal tissue properties remains unclear because of the lack of sensitive imaging biomarkers to detect subtle AERD lesions. Once the embolus enters the blood circulation, it will cause tissue ischemia, endothelial inflammation and even renal function damage. Therefore, the level of blood oxygen is a perfect pointcut for AERD development. In this study, we aim to use blood oxygenation level dependent (BOLD) MRI to evaluate longitudinal changes in kidney properties before and after AERD appearance.
|
|
1903. 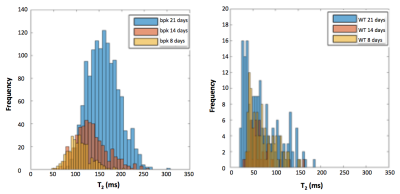 |
128 | Multi-parametric MRI of Kidney Disease Progression in a Mouse Model of Autosomal Recessive Polycystic Kidney Disease (ARPKD)
Christina MacAskill, Bernadette Erokwu, Yifan Zhang, Samantha Rodriguez, Christian Anderson, Suraj Serai, Erum Hartung, Oliver Wessely, Katherine Dell, Chris Flask
There are currently no sensitive measures for kidney disease progression in Autosomal Recessive Polycystic Kidney Disease (ARPKD). In this study, T1 and T2 relaxation times and Apparent Diffusion Coefficient (ADC)) were evaluated for their sensitivity to detect ARPKD progression in the bpk mouse model of ARPKD, which closely mimics human ARPKD kidney disease. Mean kidney T2 showed a significant correlation with both age and kidney volume. T1 and ADC showed no significant correlations. These results suggest that renal T2 relaxometry may be a viable marker for ARPKD kidney disease progression in vivo.
|
|
1904. 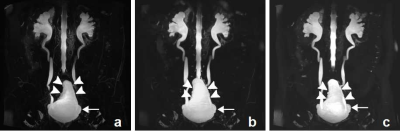 |
129 | The value of three-dimensional, compressed sensing magnetic resonance urography, with and without breath-holding: comparison of acquisition time, image quality, and diagnostic performance with conventional magnetic resonance urography Presentation Not Submitted
Xiaoge Liu, Jingliang Cheng, Jinxia Zhu, Bernd Kühn, Elisabeth Weiland, Xiangtian Zhao, Yingyu Che, Xuemei Gao, Mengyue Huang
This study aimed to prospectively evaluate the feasibility of three-dimensional (3D), compressed sensing (CS) magnetic resonance urography (MRU), with and without breath-holding (BH), for shortening the acquisition time, with better image quality and diagnostic performance. Forty-five patients were enrolled. BH-CS MRU, navigator-triggered (NT) CS MRU, and conventional NT MRU were performed. Comparisons of acquisition time, image quality (sharpness of urinary tract and background suppression), and diagnostic performance were made among these three protocols. BH-CS MRU was superior to the other MRU protocols, with the shortest acquisition time and better image quality with comparable diagnostic performance.
|
|
1905. 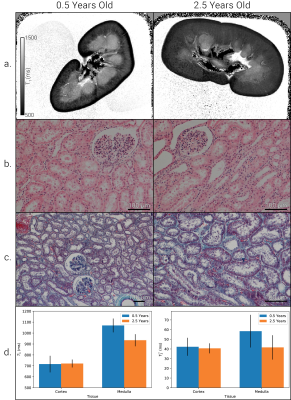 |
130 | The Effects of Fixation and Age on Relaxometry Measurements of Ex-Vivo Kidneys
Alexander Daniel, Charlotte Buchanan, Isma Kazmi, Eleanor Cox, Nicholas Selby, David Gardner, Susan Francis
The study of post-mortem brain tissue using MRI has been shown to provide a tool to assess whole organ microstructure and pathology with high spatial resolution. However, few studies have been performed on other organs in the body, here we perform ex-vivo imaging of whole kidneys. T1 and T2* of ex-vivo porcine kidneys are monitored over a ten-week period to study how T1 and T2* of the renal cortex and medulla vary over time from fixation. A clear understanding of the effects of fixation on tissue MRI parameters is crucial for interpreting ex-vivo MRI studies.
|
|
1906. 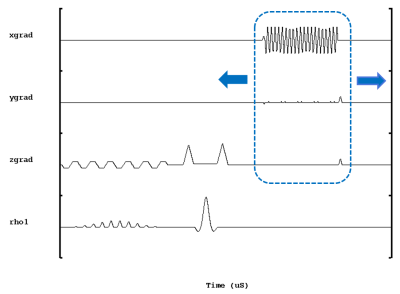 |
131 | Optimization of an asymmetric spin echo EPI approach for oxygen extraction fraction measurement in the healthy kidney
Yong Zhang, Bing Wu
The noninvasive assessment of renal oxygenation is of great clinical interest. Some recent studies used a single shot asymmetric spin echo (ASE) EPI approach to measure oxygen extraction fraction (OEF) in the brain. Compared to the brain, the abdomen suffers much larger field inhomogeneity and respiration induced motion artifacts. The ASE EPI sequence was optimized by shifting the readout position rather than the 180° RF pulse to reduce TE and hence susceptibility artifacts for better OEF measurement in the kidney. OEF results were in good agreement with the normal range of about 30%, as reported in the previous literature.
|
|
1907. 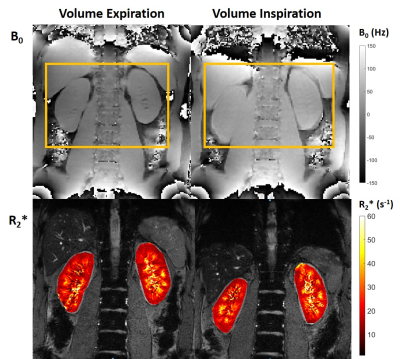 |
132 | Effect of B0 shimming method and breath-holding position on the quantification of renal BOLD R2* in healthy volunteers
Charlotte Buchanan, Benjamin Prestwich, Eleanor Cox, Susan Francis
Tissue hypoxia is thought to play a key role in the development and progression of kidney disease. Blood oxygenation level-dependent (BOLD) MRI based on the absolute transverse relaxation rate (R2*) is widely used to assess renal tissue oxygenation. This study shows that breath-hold location (inspiration/expiration) and B0 shimming method (default/volume) can influence the quantification of renal R2* mapping. By using associated B0 mapping data it is possible to determine outliers in R2* arising from significant left-right B0 gradients/B0 offsets/large B0 FWHM, thus reducing the variance in quantified renal R2* values across a subject group.
|
|
1908. 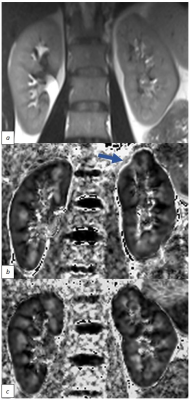 |
133 | Small field of view 2D spatially selective RF excitation diffusion tensor (DTI) imaging of the kidneys: initial experience in healthy controls and patients with Type 2 diabetes
Julia Williams, Yuliya Perchyonok, Leonid Churilov, Emma Hornsey, Lucy McKenna, Niloufar Torkamani, Daniel Staeb, Julie Smith, Elif Ekinci, Artem Mikheev, Henry Rusinek, Ruth Lim
Fractional anisotropy (FA) and mean diffusivity (MD) derived from diffusion tensor imaging (DTI) are promising for assessing subclinical changes in diabetic kidney disease (DKD). However, renal echo planar DTI can be challenging due to susceptibility artefacts, which can be mitigated by a small field of view (FOV) 2D spatially selective RF excitation. We report initial experience at 3T in 9 controls and 4 diabetic patients, finding high inter-reader agreement for cortical and medullary FA and MD, and significantly lower medullary and cortical FA in patients compared to controls. Small FOV DTI is a feasible non-invasive method of DKD assessment/ monitoring.
|
|
1909. 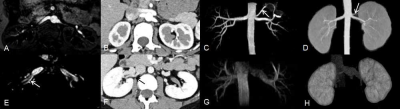 |
134 | Evaluation of renal vascular in living donors before transplantation using non-contrast enhanced magnetic resonance angiography Presentation Not Submitted
Xiaotian Li, Lihua Chen, Zhizheng Zhuo, Wen Shen
Previous studies showed that contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance angiography can be used for preoperative renal transplantation donor vascular evaluation, but requires exogenous contrast agent. Non-contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance angiography (NCE-MRA) can describe vascular anatomy without contrast agent. Thus, the purpose of this study was to evaluate NCE-MRA for the preoperative evaluation of potential living kidney donors.
|
|
1910. 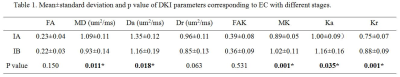 |
135 | Feasibility of DKI in distinguishing stage IA and IB of endometrial carcinoma
Meng-yao Wang, Mei-yu Sun, Xu Han, Rui Fan, Lizhi Xie
Preoperative information about depth of myometrial invasion is therefore essential in tailoring the surgical approach for patients in stage I. Consequently, we investigate the feasibility of diffusion-kurtosis imaging(DKI) in distinguishing the stage IA and IB of EC.
|
|
1911. 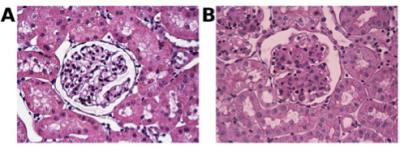 |
136 | Glomerular fibrosis in rat kidneys assessed with a clinical 3T MR scanner
Jeff L Zhang, Christopher C Conlin, Xiaowan Li, Bin Wang, Yufeng Huang, Vivian S Lee
Glomerular fibrosis develops in multiple types of chronic kidney diseases. This study aims to explore the promising MRI methods for quantifying glomerular fibrosis, and to evaluate the feasibility of performing the measurements for rat kidneys using clinical MRI scanner. Four healthy and 4 fibrotic rats were included in the experiment. With fibrosis, significant changes were found in cortical and medullary T1 and T2. Measurement of T2* suffered from susceptibility artifact. This study verified that clinical MRI scanners can be used to monitor the development of renal fibrosis in rat kidneys.
|
|
1912. 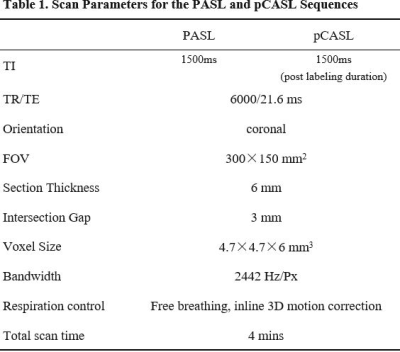 |
137 | Use of 3D Arterial Spin Labeling to Evaluate Renal Perfusion in Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease
Shuohui Yang, Fang Lu, Jing Yang, Songhua Zhan, Kuehn Bernd, Caixia Fu, Mengxiao Liu, Zhongshuai Zhang
The purpose of this study is to evaluate the effectiveness of 3D PASL and 3D pCASL in assessing RBF in both the renal cortex and medulla of CKD patients and healthy volunteers. The results showed that RBF maps derived from 3D pCASL had significantly better image quality than RBF maps derived from 3D PASL. 3D pCASL has the potential to become a novel non-invasive and non-contrast MRI technique to assess renal cortical and medullary perfusion.
|
|
1913. 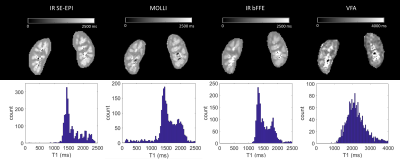 |
138 | Accuracy of renal T1 mapping schemes: a comparison of four T1 mapping methods.
Eleanor Cox, Charlotte Buchanan, Susan Francis
T1 methods - inversion recovery (IR) spin-echo EPI, IR balanced fast field echo (bFFE), MOLLI 5(3)3, and variable flip angle mapping - are compared for the assessment of renal cortex and medulla T1. IR SE-EPI and IR bFFE allow multi-slice assessment using respiratory triggering, whilst MOLLI and VFA are collected in breath-holds. Compared with IR SE-EPI, MOLLI is in agreement (bias -53ms), IR bFFE is lower (bias -177ms) and VFA significantly overestimates T1 (bias +350ms). MOLLI T1 is shown to vary with simulated heart rate. Histogram analysis for the IR SE-EPI T1 map allows differential regions within the medulla to be separated.
|
|
1914. 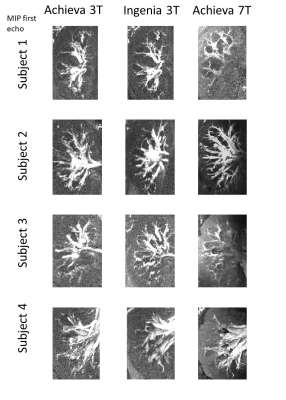 |
139 | High resolution multi-echo time-of-flight angiography of the kidney at 3 and 7T
Joshua McAteer, Emma Doran, Christopher Mirfin, Paul Glover, Susan Francis, Penny Gowland
We have used a multi-echo time-of-flight angiography sequence to provide increased signal-to-noise ratio, by summing the echoes, to image the kidney at 0.75 mm in-plane resolution and visualize the small distal vessels without the use of contrast agent. Clear images could be obtained at 7T, but results at 7T were not consistently good across all subjects due to limitations in RF power and shimming. |
|
1915. 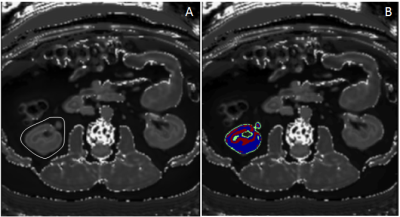 |
140 | Segmentation of the Cortex and Medulla in Multiparametric Magnetic Resonance Images of the Kidney using K-Means Clustering
David Morris, Mhairi Donnelly, Fiona Gifford, Philip Dunne, Peter Hayes, Kenneth Simpson, Jonathan Fallowfield, Scott Semple
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI), including T1, T2*, Apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) and Arterial Spin Labelling (ASL) perfusion, represents a powerful tool for renal investigations. This allows for simultaneous assessment of structure and function in pathologies from Acute Kidney Injury (AKI) to Chronic Kidney Dysfunction (CKD). Differentiation of the medulla and cortex is essential as these tissues have different biomarker distributions. Currently, segmentation of the biomarker histograms is carried out with manual definition of thresholds. Here, we applied K-means clustering to segment the maps and showed that this produced physiologically meaningful results while improving biomarker precision compared with whole kidney regions.
|
|
| 1916. |
141 | The value of diffusion kurtosis imaging in evaluation of the pathological grade and correlation with angiogenesis and proliferative activity in clear cell renal cell carcinoma Presentation Not Submitted
qiang feng
To investigate if the mean diffusivity (MD) and mean kurtosis (MK) allows assessment of renal clinical pathology. MK were better than MD values in identifying the grade of nuclear grade. A significant difference between high and low grade in MVD, MVA, and ki-67 was found.l DKI may predict angiogenesis and proliferative activity in CCRCC and make a plan for preoperative assessment.
|
|
1917. 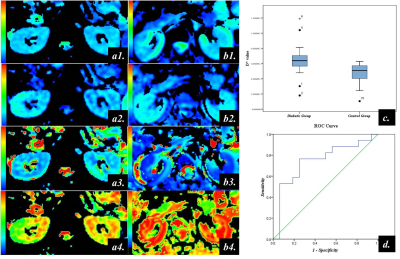 |
142 | Intravoxel incoherent motion MR imaging for diffusion and perfusion assessment of renal function of diabetes mellitus with normal serum creatinine
Ye Ju, Ailian Liu
Comparing the parameters of IVIM-MRI between diabetes mellitus with normal creatinine and healthy controls, we found that they may provide more useful information to assess renal function. IVIM-MRI can evaluating renal function of diabetes mellitus with normal creatinine noninvasively in order to diabetic nephropathy early detection and early prevention.
|
|
1918. 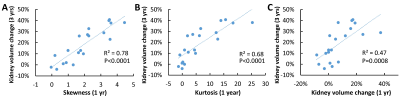 |
143 | Dynamic changes in cyst growth rates in early autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease
Harrison Kim, Allan Yu, Vicente Torres, Arlene Chapman, Frederic Rahbari-Oskoui, Kyongtae Bae, Peter Harris, William Bennett, Douglas Landsittel, Michal Mrug
The best method for the identification of high-risk patients with rapidly progressive autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease (ADPKD) is based on height and age-adjusted total kidney volume (TKV). We sought to improve this assessment by exploring individual renal cyst growth rates over time. MRI data revealed that ADPKD cysts grow, remain stable or disappear. The individual cyst volume distribution over the first year (e.g., skewness or kurtosis) correlated strongly with TKV change over 3 years (better than TKV change over the first year). It remains to be determined whether these indices outperform TKV in the prediction of renal function outcomes.
|
|
1919. 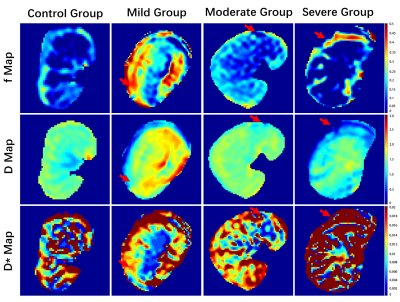 |
144 | Use of Intravoxel incoherent motion imaging in assessment of different degrees of renal lesions: alterations in diffusion and perfusion in animal study with renal lesions
Zhiheng Feng, Hanjing Kong, Chengyan Wang, Xiaodong Zhang, Min Yang, Jue Zhang, Xiaoying Wang
IVIM DWI (intravoxel incoherent motion diffusion-weighted image) is a noninvasive imaging technology capable of simultaneously detecting diffusion and perfusion characteristics of renal tissue . This study investigates the feasibility of IVIM DWI in evaluating different degree of renal lesions. IVIM DWI was performed on sixteen rabbits with different degree of renal lesions, which were confirmed by the corresponding pathological results. A noticeable change of renal diffusion and perfusion can be clearly observed in different degrees of renal lesions. There exists significant difference in f values among four groups with different severity in renal lesions.
|
|
1920. 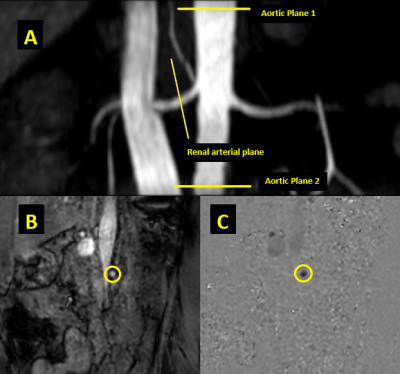 |
145 | MRI based Renal Resistivity Index in Chronic Kidney Disease
Muditha S. Bandara, Hasith E. Perera, Chirath Sulalith, Aruna Pallewatte, Janaka P. Wansapura
We show, for the first time, the feasibility of using MRI based renal resistivity index (RRI) to differentiate patients with chronic kidney disease from healthy subjects. RRI and the Pulse Wave Velocity (PWV) of the abdominal aorta were calculated using quantitative phase contrast imaging. The RRI was significantly higher in CKD patients (0.71 ± 0.07) than in the healthy subjects (0.65 ± 0.04). The mean PWV was also significantly higher in CKD patient indicating hypertension and arterial stiffness in CKD. The high RRI in CKD indicates restriction to perfusion, probably due to of tubulointerstitial fibrosis in the kidney.
|
|
1921 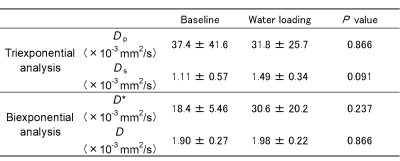 |
146 | The Effect of Water Loading on Renal Diffusion Parameters with Triexponential Analysis Video Permission Withheld
Yuki Koshino, Naoki Ohno, Tosiaki Miyati, Kotaro Yoshida, Satoshi Kobayashi, Naoki Hori, Yukihiro Matsuura, Toshifumi Gabata
To assess the response of water loading on diffusion parameters in the renal tissue, we evaluated renal diffusion coefficients with tri- and biexponential analyses before and after water loading. Our results showed that slow-restricted diffusion coefficient with triexponential analysis in the renal medulla was significantly increased after water loading, whereas none of the diffusion parameters with biexponential analysis significantly changed. Diffusion analysis with triexponential function could enable us to obtain more detailed information on renal function.
|
|
1922. 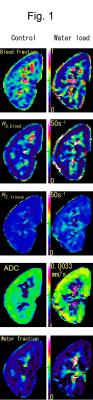 |
147 | Renal intravoxel-incoherent-motion analysis with a three-compartment model taking into account the renal tubules
Hajime Tamura, Hideki Ota, Tatsuo Nagasaka
We were able to estimate diffusion and relaxation parameters of the renal parenchyma, flowing blood and tubular water by intravoxel incoherent motion (IVIM) analysis with a three-compartment model and SE+FLAIR diffusion imaging. The reactive change of three parameters (apparent diffusion coefficient of parenchyma, transverse relaxation rate of blood, and fraction of flowing blood in the renal cortex) were observed.
|
|
1923. 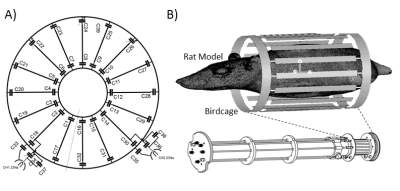 |
148 | Whole Body Quadrature Birdcage RF Coil for 23Na MRI of Small Rodents at 9.4T and Its Application in Sodium Imaging of the Eye and Kidneys
Laura Boehmert, Helmar Waiczies, Daniel Wenz, Celal Oezerdem, Andre Kuehne, Paula Ramos Delgado, Erdmann Seeliger, Andreas Pohlmann, Thoralf Niendorf
Sodium ions play a major role in the physiology of the human organism. The kidneys and eyes both have a high sodium concentration, and we suggest that probing tissue sodium concentration in these organs using 23Na MRI can add a very useful dimension to our understanding of renal and ocular disorders. Changes in the sodium concentration might be indicative of early pathophysiological changes in such diseases. Therefore we present a quadrature birdcage coil tailored for sodium imaging of small rodents at 9.4T, along with the RF coil design, EMF simulations and in vivo 23Na MRI of the eye and kidney.
|
|
1924. 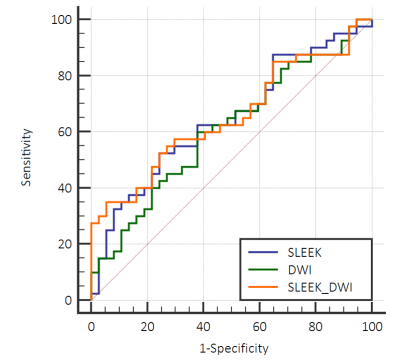 |
149 | Assessment of Renal Function Using noncontrast-enhanced MRI: 3D-FIESTA with spatial labeling with multiple inversion pulses and Diffusion-weighted imaging
Ping Liang, Chuou Xu, Jiali Li, Anqin Li, Daoyu Hu, Zhen Li
Previous researchs had proved that corticomedullary differentiation contrast ratio obtained from SLEEK was significantly positively correlated with eGFR. But they did not quantitatively analyze the diagnostic performance of SLEEK and did not compare it to other imaging methods. We obtained the area under the curve (AUC) by making the ROC curve to compare the diagnostic performance between SLEEK and DWI. DWI, previous reports have shown that ADC values are positively correlated with eGFR, may be an effective methods to evalaute renal function. Therefor we compared SLEEK with DWI to assess the diagnostic value of SLEEK.
|
|
 |
1925. 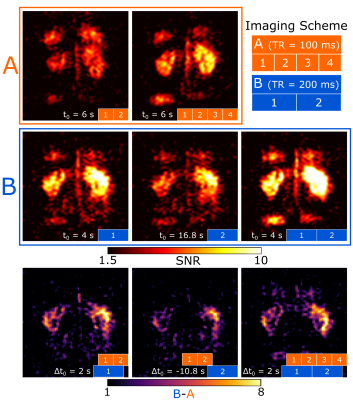 |
150 | Perfusion-Weighted Imaging in Human Kidneys using Hyperpolarized Xenon-129
Jorge Chacon-Caldera, Adam Maunder, Madhwesha Rao, Graham Norquay, Oliver Rodgers, Lothar Schad, Jim Wild
Cortical perfusion is an important biomarker that could reflect pathophysiological changes in kidney disease. Novel methods to assess kidney perfusion could be complementary to DCE and ASL techniques. In this work, we demonstrate a proof-of-concept to obtain perfusion-weighted kidney images using time-resolved dissolved hyperpolarized 129Xe MRI. Subtraction of images acquired with different TR showed high contrast within the kidneys that qualitatively match those seen on ASL perfusion maps and indicate higher xenon uptake in the cortex when compared to the medulla. This work demonstrates the potential of hyperpolarized 129Xe as injection free means of assessment of renal perfusion imaging.
|
Digital Poster
| Exhibition Hall | 14:45 - 15:45 |
| Computer # | |||
1926. 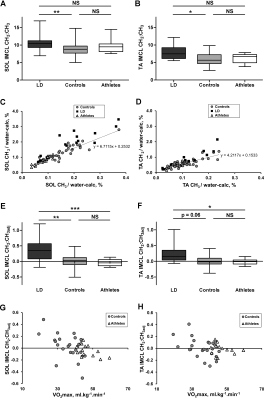 |
151 | Accumulation of saturated IMCL is associated with insulin resistance
David Savage, Laura Watson, Katie Carr, Claire Adams, Soren Brage, Krishna Chatterjee, Leanne Hodson, Chris Boesch, Graham Kemp, Alison Sleigh
Use of a recently validated 1H MRS approach to determine both the intramyocellular lipid composition, and concentration independent of composition, within the soleus and tibialis anterior muscles of female individuals covering a wide range of insulin sensitivities, has revealed that accumulation of saturated intramyocellular lipid is more strongly associated with whole-body insulin resistance than concentration alone.
|
|
1927. 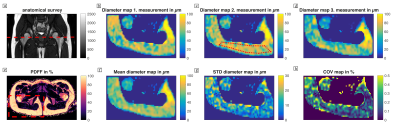 |
152 | Spatially resolved measurement of lipid droplet size in white adipose tissue with high b-value stimulated echo-prepared diffusion-weighted 2D single shot TSE
Dominik Weidlich, MingMing Wu, Stefan Ruschke, Daniela Franz, Julius Honecker, Oliver Gmach, Thomas Skurk, Hans Hauner, Ulrich Kulozik, Dimitrios Karampinos
Despite its strong relevance in metabolic dysfunction, non-invasive measurement of fat microstructure remains an unmet need. In white adipose tissue, enlarged adipocyte size is linked to the obese phenotype. DW-MRS has been previously applied to probe diffusion restriction effects of intramyocellular lipids or brown adipocytes using preclinical systems. However, probing diffusion restriction in large lipid droplets remains a major challenge and DW-MRS can only measure spatially averaged effects. This work proposes a method that probes lipid droplet sizes with high b-value stimulated-echo prepared DW 2D single shot TSE, validates the methods in water-fat phantoms and applies it in the gluteal fat depot in vivo.
|
|
1928. 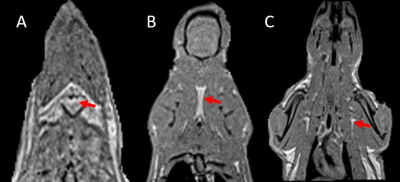 |
153 | Metabolic Imaging of Brown Adipose Tissue in Aging Rodent Model
Rengaraj Anantharaj, Jadegoud Yaligar, Sanjay Kumar Verma, Giang Le Thi Thu, Kavita Kaur, Venkatesh Gopalan, Adaikalavan Ramasamy, Karthik Mallilankaraman, S Sendhil Velan
Loss of BAT function and activity is associated with aging. Understanding the metabolic and phenotypic changes in aging brown adipose tissue is important for healthy aging. In this study, we have characterized various brown adipose tissue depots including interscapular BAT(iBAT), cervical BAT(cBAT), and axillary BAT(aBAT) ) in aging rodent model. Fat content in all BAT depots increased with aging and reduced with β3 agonist treatment. The iBAT was more responsive to β3 intervention compared to other BAT depots. Functional genes PRDM16, PPARg, PGC1α were upregulated in BAT tissues of 3 months old animals with β3 agonist due to high metabolic activity and improved quality of BAT compared to older animals.
|
|
1929. 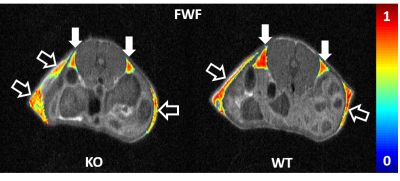 |
154 | White fat browning in a murine model detected by Z-Spectrum Imaging
Alessandro Scotti, Victoria Gil, Weiguo Li, Chong Wee Liew, Kejia Cai
"Browning" of visceral fat is of particular interest to human health due to its association to high risk of metabolic disease and its resistance to conventional browning stimuli. Developing a strategy to stimulate and monitor visceral fat browning could be extremely beneficial in combating epidemic metabolic diseases. Here we report the successful detection of white visceral fat browning in a treated transgenic mouse model by longitudinal Z-Spectrum Imaging. The fat-water fraction measured by ZSI and the fat depots volume were reduced over time compared to the control group. Being noninvasive and with no radiation, the protocol is suitable for longitudinal studies.
|
|
1930. 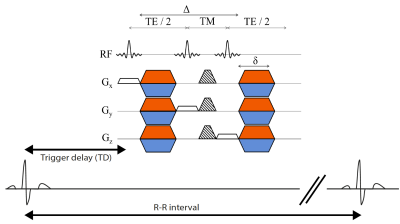 |
155 | On the Technical Challenges of Diffusion-Weighted MR Spectroscopy for Water ADC Quantification in Human Supraclavicular Fat
Mingming Wu, Dominik Weidlich, Stefan Ruschke, Daniela Franz, Dimitrios Karampinos
The study of brown adipose tissue (BAT) has attracted many researchers in the context of human metabolism. In adult humans, BAT is mostly present in the supraclavicular fossa as a heterogeneous mixture of white and brown adipose tissue. DW MR is a powerful technique to detect microstructural differences which could potentially help to differentiate BAT from surrounding tissue. However, physiological motion in close proximity to the soft adipose tissue in the supraclavicular fossa could lead to signal cancelations and quantification errors. In this work we investigate the feasibility of human BAT DW-MRS for the ADC quantification of the water component in vivo.
|
|
1931. 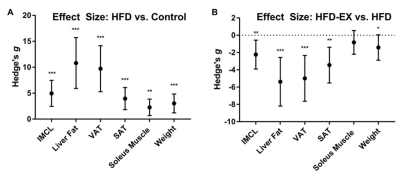 |
156 | Evaluation of long-term exercise intervention on ectopic fat accumulation in high fat diet fed rats
Venkatesh Gopalan, Navin Michael, Kavita Kaur, Anantharaj Rengaraj, Jadegoud Yaligar, Sanjay Verma, Giang Le, Adaikalavan Ramasamy, Suresh Sadananthan, Karthik Babu Mallilankaraman, S Sendhil Velan
In this study, we evaluated the effect of long-term exercise in reversing the effects of an obesogenic environment on pathogenic fat accumulation and insulin sensitivity in high fat diet fed rats. Bias-corrected effect size (Hedge’s g, 95% CI), of IHL, IMCL, triglycerides, cholesterol, leptin and Matsuda Index after 12 weeks intervention was determined between high fat diet (HFD), Control, HFD + Exercise groups. The long term exercise intervention improved the insulin sensitivity in high fat diet fed rats by reducing all fat depots, triglycerides, and leptin.
|
|
1932. 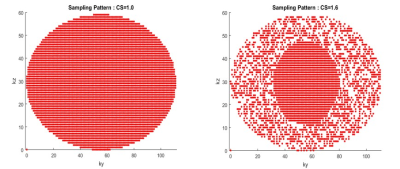 |
157 | Quantitative assessment of body composition parameters with CS accelerated Dixon method
Vijay Nimbargi, Thobias Romu, Patrik Tunon, Olof Dahlqvist Leinhard, Ty Cashen, Kang Wang, Ersin Bayram, Magnus Borga
MRI provides accurate and high-precision body composition measurements. Routinely, data acquisition is performed using system’s integrated body coil, which creates a challenge in terms of scan time and breath-hold duration. This work utilized Compressed Sensing with 2pt Dixon to reduce the acquisition time by 40% without impacting the quantitation of body composition measurements. Variations were found to be small compared to test-retest precision. This provides an opportunity to add MRI based body composition analysis to most MRI examinations with minimal scan time impact without a change in coil or patient setup
|
|
1933. 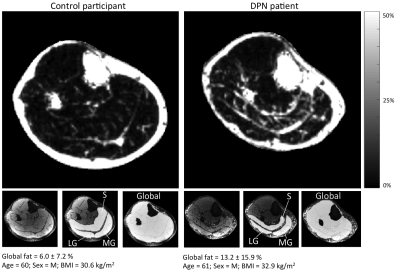 |
158 | Skeletal Muscle Adipose Tissue Quantification in Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy
Amanda Ho, Shannon Haas, Antonio Convit, Kenneth Mroczek, Jill Slade, Prodromos Parasoglou, Ryan Brown
Diabetic peripheral neuropathy (DPN) is a common and serious complication of diabetes, where persistent hyperglycemia impairs metabolic and microvascular function, ultimately resulting in fatty infiltration. Quantitative adipose measurements using MRI may provide a useful tool to evaluate the effects of therapeutic intervention. We tested a chemical-shift based technique to measure skeletal muscle fatty infiltration in a cohort with DPN. Fatty infiltration was found to be increased in the ankle plantar flexors of DPN patients, with significant elevation detected in the medial gastrocnemius muscle.
|
|
1934. 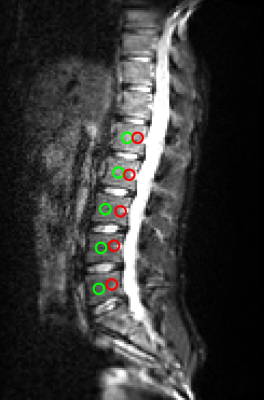 |
159 | Regional differences of IVIM-measured perfusion fraction in vertebral bone marrow at 1.5 T.
Louis Marage, Jérémy Lasbleiz, Mathieu Lederlin, Hervé Saint-Jalmes, Giulio Gambarota
The purpose of this study was to assess regional differences of IVIM (Intra-Voxel Incoherent Motion) parameters in vertebral bone marrow. A RESOLVE Diffusion sequence with SPAIR fat suppression was acquired on healthy volunteers. The current study shows a significant difference in perfusion fraction f between the anterior and posterior regions in lumbar vertebrae L1 to L5.
|
|
1935. 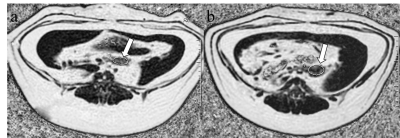 |
160 | 3.0T MRI with IDEAL-IQ sequence for Assessment of pancreatic fatty infiltration During Progression of T2DM Animal Model
Yidi Chen, Liling Long
This study was undertaken to determine the accuracy of pancreatic MR imaging by proton density fat fraction measurements with the iterative decomposition of water and fat with the echo asymmetry and least-squares estimation quantitation (IDEAL-IQ) sequences, and to explore changes of pancreatic fat content in a diabetic animal model. We found that estimation of pancreatic fat content by pulse sequence imaging is accurate and reproducible across readers. Further, greater pancreatic fat infiltration was observed in diabetic animals and it is related to the level of fasting blood glucose, which supports its use as a biomarker for diabetes risk.
|
|
1936 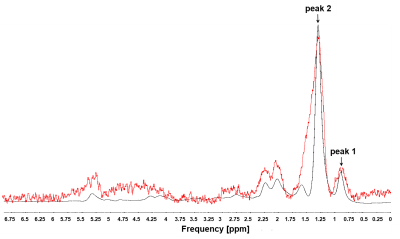 |
161 | Towards MR-based interrogation of adipose tissue pO2. Video Permission Withheld
Darya Morozov, James D. Quirk, Scott C. Beeman
There is a significant body of evidence suggesting that adipose hypoxia triggers systematic insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes. Non-invasive and longitudinal characterization of adipose tissue oxygenation during adipose tissue expansion would provide critical insight into the pathogenesis of type 2 diabetes. The major purpose of this study is to develop a non-invasive and quantitative measures of adipose oxygenation by MR. Our approach is based on exploiting the paramagnetic nature of O2 which can directly affect the lipid 1H longitudinal relaxation. We show that simple inversion recovery MR method can be potentially used for non-invasive quantification of adipose tissue hypoxia.
|
|
1937. 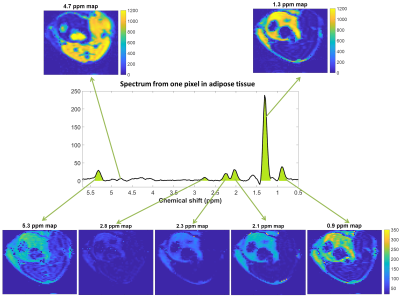 |
162 | Pre-clinical fatty acid composition estimate of adipose tissue using echo planar spectroscopic imaging (EPSI) at 4.7T
Angeline Nemeth, Sophie Gaillard, Olivier Beuf, Hélène Ratiney
This pilot study performed on a preclinical system at 4.7T shows the feasibility of using the echo planar spectroscopic imaging sequence (EPSI with a spin echo) to quantify the fatty acid composition. This sequence permitted to image separately each resonating component of fat spectrum. The signal of the EPSI sequence was compared with more standard spectroscopic sequence used for the fatty acid quantification (PRESS). The quantification results from the EPSI sequence on calibrated phantom were consistent with gas chromatography theoretical values. The in vivo acquisition showed a significant difference of the fatty acid composition between the subcutaneous and the visceral adipose tissue, consistent with published monovoxel results.
|
|
1938. 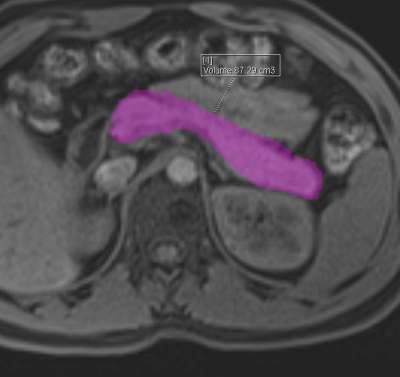 |
163 | Can MRI Determined ectopic pancreatic fat and volume be used as a discriminant marker to screen for diabetics.
Sonal Krishan
By identifying
|
|
1939  |
164 | Non-invasive assessment of early stage diabetic nephropathy by BOLD and DTI MRI Video Permission Withheld
Youzhen Feng, Zhongyuan Cheng, Xiangran Cai, Qian Long
Although the specific pathogenesis of diabetic nephropathy (DN) has not yet been clearly elucidated, it has been acknowledged that the development of kidney hypoxia is an early manifestation of the diabetic kidney. In past decades, blood oxygenation level dependent (BOLD) imaging was extensively applied to assess the tissue oxygenation levels, and diffusion imaging was demonstrated the capacity of detecting the tissue damage induced by acute or chronic hypoxia. Hence, to test whether the early DN patients can be detected using both BOLD and diffusion tensor imaging, in current study, patients with diabetes mellitus, diabetic nephropathy and Health volunteers were analyzed.
|
|
1940. 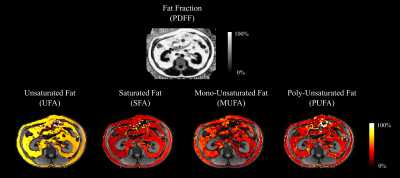 |
165 | Assessing variability in MRI-based quantitative measurements of body fat in patients with NASH
Erin Shropshire, Manuel Schneider, Bohui Zhang, Alaattin Erkanli, Dominik Nickel, Mustafa Bashir
NASH is a common cause of chronic liver disease, and is closely associated with other metabolic derangements; quantifying types of fat (saturated, mono-unsaturated, poly-unsaturated) in the body may provide insights into metabolism. We assessed a chemical-shift encoded MRI technique for quantifying types of fat in various depots. Inter-reader repeatability in the subcutaneous tissues and retroperitoneum was high (mean 0.86-0.90), and similar to PDFF (mean 0.89). Correlation between fat types was moderate to strong between non-liver fat depots, and weaker and inconsistent between liver and non-liver fat depots.
|
|
1941. 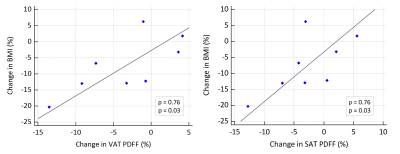 |
166 | Proton density fat fraction mapping for tracking tissue changes under weight loss in cancer cachexia
Daniela Franz, Jan Syväri, Christoph Zöllner, Rickmer Braren, Ulrich Nitsche, Ernst Rummeny, Dimitrios Karampinos
Cancer cachexia, a multifactorial wasting syndrome, affects up to 50% of cancer patients and is a major cause of morbidity and mortality. Proton density fat fraction (PDFF) mapping based on a multi-echo gradient echo acquisition enables spatially-resolved fat quantification and can help characterize tissue changes during the course of cancer cachexia. This study investigates changes in volume and PDFF metrics of adipose tissue induced by weight loss in cancer cachexia.
|
|
1942. 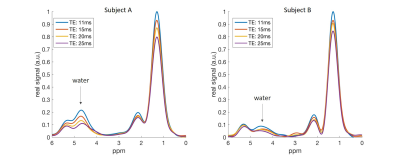 |
167 | MRS-based water T2 relaxation time in the supraclavicular fossa relates to anthropometric and imaging obesity markers
Daniela Franz, Dominik Weidlich, Jan Syväri, Stefan Ruschke, Mingming Wu, Christina Holzapfel, Theresa Drabsch, Ernst Rummeny, Hans Hauner, Dimitrios Karampinos
The development of non-invasive imaging biomarkers for the detection and quantification of brown adipose tissue (BAT) remains an active research field thanks to the potential implications of BAT activation in treatment of metabolic dysfunction. BAT is known to be characterized by the presence of iron-rich mitochondria, increased oxygenation and denser vasculature compared to white adipose tissue. All above BAT characteristics would be expected to affect the T2 relaxation time of water within BAT. The present work aims to show the feasibility of measuring water-only T2 relaxation times using single-voxel MRS in the human supraclavicular fossa and to characterize the relationship of water T2 values to other metabolic and imaging parameters.
|
|
1943. 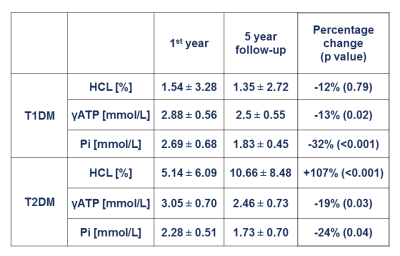 |
168 | Changes of hepatocellular lipids and phosphorus metabolite content in diabetes patients over 5 years after diagnosis
Yuliya Kupriyanova, Oana-Patricia Zaharia, Volker Burkart, Karsten Müssig, Julia Szendroedi, Michael Roden, Jong-Hee Hwang
This study aimed at monitoring possible changes in hepatocellular lipids, γ-adenosine triphosphate and inorganic phosphate contents using 1H- and 31P-MRS in patients with type 1 or type 2 diabetes mellitus in the 1st year and at 5 years after diagnosis. Hepatocellular lipids content was higher at the 5-year follow-up in type 2, but not in type 1 diabetes patients. Diabetes patients generally exhibited decreases of phosphorus metabolites during the first 5 years of the disease.
|
|
1944 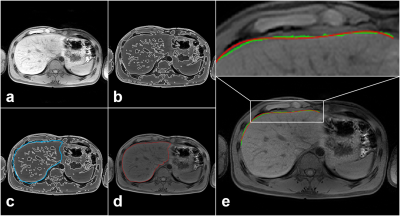 |
169 | Development of liver surface nodularity quantification program and its clinical application in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease Video Permission Withheld
Tae-Hoon Kim, Ji Eon Kim, Jong-Hyun Ryu, Chang-Won Jeong
Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) is the most common liver disease in the United States and its prevalence is reported to between 10% and 30%. NAFLD comprises a wide spectrum of liver damage, ranging from macrovesicular steatosis, inflammation, fibrosis, and cirrhosis. Liver biopsy has been regarded as the reference standard for diagnosing hepatic inflammation, fibrosis and cirrhosis in NAFLD. There is an unmet need for widely applicable non-invasive methods to diagnose advanced liver fibrosis and cirrhosis. Recently, liver surface nodularity (LSN) based on CT images is used to diagnose and stage a variety of liver disease in chronic liver disease, and is predictive of cirrhosis decompensation and death. The liver morphological changes in relation to fibrosis stage in NAFLD have not yet been clearly identified. Our study developed a MRI-suitable LSN quantification program and compared the fibrosis grades in NAFLD.
|
|
1945 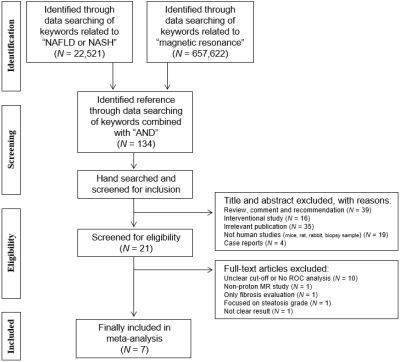 |
170 | Accuracy of proton magnetic resonance technique for diagnosing non-alcoholic steatohepatitis: a meta-analysis Video Permission Withheld
Tae-Hoon Kim, Chang-Won Jeong, Hong Young Jun, ChungSub Lee, SiHyung Noh, Ji Eon Kim, SeungJin Kim, Kwon-Ha Yoon
Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) is a rapidly increasing health problem in world wide. NAFLD comprises a wide spectrum of liver damage, ranging from simple macrovesicular steatosis, liver inflammation, fibrosis, and cirrhosis. Liver biopsy has been regarded as the reference standard for diagnosing hepatic inflammation, fibrosis and cirrhosis in NAFLD. A subset non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) is the early stage of progression that develops to cirrhosis in 15-25% of patients and can lead to the development of hepatocellular carcinoma. Thus, non-invasive diagnostics of NASH are clinically important issue and are warranted. Recently, considerable effort is underway to identify screening strategies that non-invasively diagnose NASH using a variety of techniques such as laboratory tests and imaging techniques. Up to date, there are several published studies using serum biochemical tests, ultrasound and CT, however there was no strong evidence in clinical practice. In this study, the diagnostic accuracy in NAFLD using 1H MR modality have not yet been clearly identified. Our meta-analysis study was estimated the accuracy of 1H MRI on this topic, non-invasively diagnosing NASH.
|
|
1946. 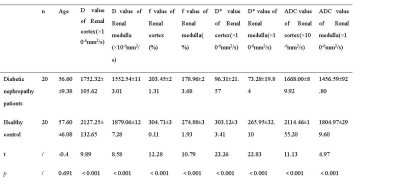 |
171 | Intravoxel incoherent motion (IVIM) diffusion weighted imaging in Renal Function Assessment of Diabetic Nephropathy – A Preliminary Study Presentation Not Submitted
Jing Chen, Xirong Zhang, Nan Yu, Qi Yang, Yong Yu, Robert Grimm, Shaoyu Wang
The aim of this study is to evaluate the renal microstructural changes in patients with diabetic nephropathy using intravoxel incoherent motion (IVIM) imaging. IVIM could be used to indicate the changes of renal function of diabetic nephropathy patients, especially in renal cortex. The changes of renal function were found to be positively correlated with the glomerular filtration rate. Thus IVIM could deliver useful information for the early diagnosis of diabetic nephropathy.
|
|
1947.  |
172 | 3D hepatocyte fraction index using 3D look locker
Yu Ueda, Minori Onoda, Naoki Ohno, Makoto Obara, Masami Yoneyama, Yuta Akamine, Satoshi Kobayashi, Tosiaki Miyati, Marc Van Cauteren
The Hepatocyte Fraction index (HeFra), which is based on a simple pharmacokinetic model, can quantitatively estimate the fraction of hepatocytes. It is calculated from R1 change between pre contrast and hepatobiliary phases. 2D look locker (LL) has been used to calculate T1 value in HeFra studies, but covers only a single slice in one breath hold. Clinically 3D scanning is preferable to get a wider coverage of the liver. Therefore, we optimized the imaging parameters of 3D LL. T1 value and HeFra using the optimized 3D LL were the same as those of 2D LL in subjects under T1 1400ms.
|
|
1948. 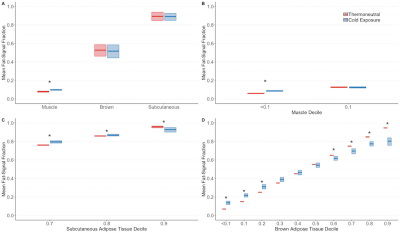 |
173 | Fat-Water Magnetic Resonance Imaging Reveals Dynamic Alterations in Brown Adipose Tissue Lipid Content During Cold Exposure
Crystal Coolbaugh, Bruce Damon, Emily Bush, E Welch, Theodore Towse
Fat-water MRI (FWMRI) provides a powerful means of exploring changes in the lipid content of brown adipose tissue (BAT) in response to cold exposure. Most previous FWMRI studies of changes in BAT's fat signal fraction (FSF) have done so only before and after cold exposure, however, and studies have used different FSF thresholds for defining BAT. Here, we show that in healthy young men, cold exposure elicits varied responses in BAT FSF, with areas of higher initial lipid content undergoing a net lipid depletion and areas of lower initial lipid content undergoing a net lipid accumulation.
|
|
1949. 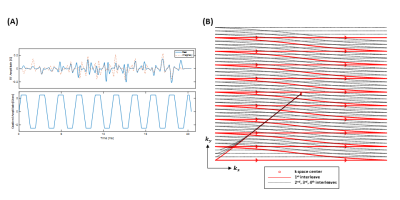 |
174 | Simultaneous Assessment of Hyperpolarized [1-13C]Lactate and [13C]Bicarbonate with Fly-Back Echo Planar Imaging
Junjie Ma, Edward Hackett, Rolf Schulte, Jae Mo Park
In this study, we designed a spectral-spatial radiofrequency pulse that excites hyperpolarized [13C]bicarbonate and [1-13C]lactate peaks simultaneously while suppressing [1-13C]alanine, [1-13C]pyruvate and [1-13C]pyruvate hydrate signal. In combination with multi-shot fly-back echo planar imaging readout, the excited bicarbonate and lactate images can be spatially separated with an appropriate echo-spacing. The proposed method was validated by a phantom study, and tested in vivo using healthy Wistar rats with hyperpolarized [1-13C]pyruvate.
|
|
1950 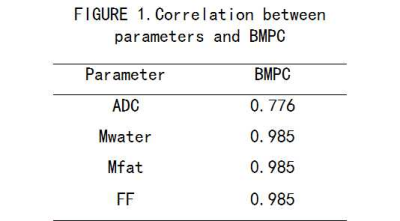 |
175 | Correlation between multi-parameters and the proportion of bone marrow plasma cells in focal lesions of multiple myeloma in whole body DWI combined with T1-Dixon Video Permission Withheld
Xiaodong JI, Huzheng Dong, Shuang Xia, Yu Guo, Zhizheng Zhuo, Wen Shen
Purpose: To investigate the correlation between multi-parameters of focal lesions and the ratio of bone marrow plasma cells (BMPC) by using whole body DWI and T1-mDIXON imaging in patients with multiple myeloma. Materials and Method:41 patients were collected with pathologically confirmed multiple myeloma from February 2015 to June 2018 including 21 males of aged 46-66 years (55.6+10.1 years) and 20 females of aged 42-66 years old (49.1±9.9 years). All patients underwent whole body DWI and T1-mDIXON examination before treatment based on a 3T MR scanner (Ingenia, Philips, Best, The Netherland). The ratio of bone marrow plasma cells (BMPC) was examined by bone marrow smear. The focal lesions of the Anterior superior iliac spine were detected and the corresponding ADC value, fat signal intensity (Mfat) and water signal intensity (Mwater) were extracted. The fat fraction (FF) was also calculated by dividing the signal intensity in the fat image by the corresponding in-phase mDIXON image. The Spearman correlation test was performed to evaluate the correlation between the above parameters of focal lesions with the ratio of BMPC. Result: There was high positive correlations between ADC value and BMPC ratio (r=0.776) as well as between the Mwater and BMPC ratio (r=0.985). And there was high negative correlations between Mfat and BMPC ratio (r=-0.985) as well as the FF and the BMPC ratio (r=-0.985). Discussion:DWI help to increase the lesion detection through qualitative assessment and can furtherly increase the diagnostic confidence of focal lesions by using ADC measurements. After multiple myeloma cells invading the bone marrow, the normal structure of the bone marrow is destroyed and osteolytic changes are formed. The increase in the number of tumor cells leads to an increase in normal bone marrow destruction, which leads to a decrease in extracellular space and a severe osteolytic change, which could be represented by ADC values. Due the increasing of
water content and the destruction of normal fat cells in the bone marrow, Mfat and FF decreased as the bone marrow invasion developed. Conclusion:There is a high correlation between Mfat, Mwater, FF value, ADC value and the ratio of bone marrow plasma cells, which is beneficial for assessing the degree of bone marrow invasion.
|
 Back to Program-at-a-Glance |
Back to Program-at-a-Glance |  Back to Top
Back to Top