Stroke
Stroke
Oral
Oral
Neuro
Wednesday, 15 May 2019
| Room 516C-E | 08:15 - 10:15 | Moderators: Qiyong Gong, John Huston |
| 08:15 |
0736. 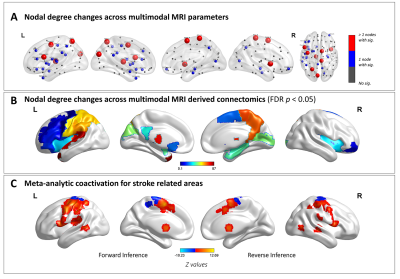 |
On the nodal degree configuration of multimodal brain connectomics in severe asymptomatic carotid stenosis Did Not Present
Lei Gao, Tao Wang, Sirui Li, Ying Liu, Yawen Ao, Junjian Zhang, Haibo Xu
Patients with severe asymptomatic carotid stenosis (SACS) are at high risk of cognitive impairment and future strokes. The basis of remote brain consequences is less well known. We investigated nodal configuration (centrality, hubs, efficiency, resilience, and wiring cost) of multimodal MRI brain connectomics in twenty-four patients with SACS and 24 comorbidities-matched controls. Our results suggest that patients with SACS is predominantly characterized by hub pathology and maladaptive pattern of network efficiency and wiring cost, following primary sensorimotor-transmodal cortical gradient. These results will contribute to a better understanding of the cognitive impairment and future cerebrovascular events in these patients with SACS.
|
08:27 |
0737. 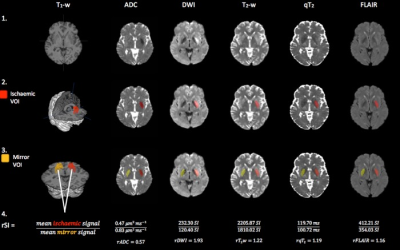 |
T2 relaxation times identify acute ischaemic stroke patients within the thrombolysis treatment window with higher accuracy than T2-weighted signal intensities
Bryony McGarry, Isabel Chew, Robin Damion, Michael Knight, Rose Bosnell, Peter Jezzard, George Harston , Davide Carone , James Kennedy , Salwa El-Tawil , Jennifer Elliot, Keith Muir, Philip Clatworthy, Risto Kauppinen
Unknown symptom onset time is a common contraindication for thrombolysis of hyperacute ischaemic stroke. MRI may identify patients within the 4.5-hour thrombolysis treatment window, but it is unclear which parameter is most accurate. We compared the ability of hemispheric differences in quantitative T2 (qT2), ADC, and signal intensities of DWI, T2-weighted and T2-weighted FLAIR images at distinguishing between patients scanned within and beyond 4.5-hours. qT2 correlated significantly with time from onset (r = .491, p =.003) and had the highest and only significant AUC (0.77, p = .007). These data point to qT2 as a stroke timer.
|
08:39 |
0738. 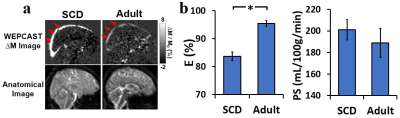 |
Impaired blood-brain barrier function in pediatric sickle cell disease
Zixuan Lin, Eboni Lance, Yang Li, Pan Su, Peiying Liu, Alicia Cannon, James Casella, Hanzhang Lu
Sickle cell disease (SCD) is associated with endothelium dysfunction, but the role of the blood-brain barrier (BBB) in SCD has not been evaluated. We evaluated BBB function in pediatric SCD using a novel non-invasive method, water-extraction-with-phase-contrast-arterial-spin-tagging (WEPCAST) MRI. Children with SCD showed lower water extraction compared with healthy individuals. Higher permeability-surface-area-product (PS), i.e. leaky BBB, was associated with a number of known abnormalities in SCD, including lower hematocrit, lower hemoglobin, higher HbS fraction, impaired cognition, and a higher risk for silent cerebral infarction. Collectively, these findings support a potential role for BBB dysfunction in SCD pathogenesis.
|
08:51 |
0739. 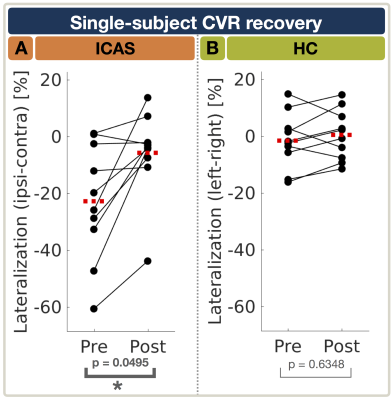 |
Recovery of cerebrovascular reactivity after asymptomatic carotid artery stenosis treatment is assessable by Breathhold-fMRI within global watershed areas
Stephan Kaczmarz, Jens Goettler, Nico Sollmann, Jan Kufer, Mikkel Hansen, Andreas Hock, Christian Sorg, Claus Zimmer, Kim Mouridsen, Fahmeed Hyder, Christine Preibisch, Jan Petr
Asymptomatic unilateral internal carotid-artery stenosis (ICAS) causes complex and currently poorly understood hemodynamic impairments which could possibly improve treatment decisions. Cerebrovascular reactivity (CVR) is an important biomarker of vascular health and can potentially serve to evaluate ICAS-treatment efficacy. We present perfusion MRI-data from a longitudinal study in 16 asymptomatic ICAS-patients before and after treatment plus 17 age-matched healthy controls. We hypothesize that CVR impairments in ICAS and their recovery after treatment can be assessed by Breathhold-fMRI analyzed by a data-driven approach. Our results demonstrate statistically significant CVR impairments within global watershed areas before treatment and significant CVR recovery after treatment.
|
09:03 |
0740. 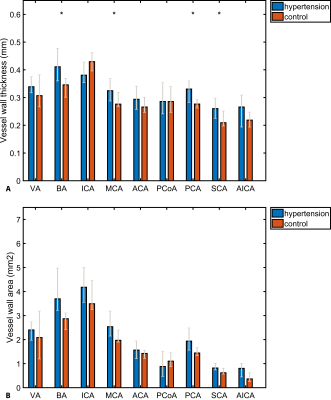 |
Intracranial vessel wall thickness measurements: A post-mortem comparison between hypertensive patients and controls
K. van Hespen, H. Kuijf, P. Luijten, J. Hendrikse, J. Zwanenburg
For the intracranial arteries, only a few studies have investigated arterial wall thickening. In this post-mortem, explorative study we investigated the effect of hypertension on vascular remodeling in the Circle of Willis in male and female groups using 7T MRI. Circle of Willis specimens were scanned at ultra-high resolution(0.11mm isotropic). Vessel wall thickness and vessel wall area were measured at 21 locations across the major arterial branches. Results showed a larger vessel wall thickness and area in the female hypertension subgroup in four different arteries as compared to the control group(p<0.05). Male hypertension and control groups showed no significant difference.
|
09:15 |
0741. 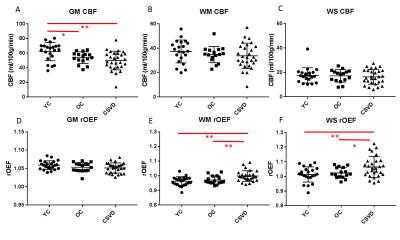 |
Elevated oxygen extraction fraction is a tissue biomarker of chronic ischemia for cerebral small vessel disease
Chunwei Ying, Andria Ford, Peter Kang, Alla Al-Habib, Slim Fellah, Yasheng Chen, Jin-Moo Lee, Hongyu An
Cerebral small vessel disease (CSVD) increases stroke risk and often leads to vascular cognitive impairment. We hypothesized that elevated oxygen extraction fraction (OEF) is a tissue biomarker of chronic ischemia in patients with CSVD. We found that reduction of cerebral blood flow (CBF) in gray matter depends on age, but not on CSVD. In contrast, OEF is increased in watershed and white matter in patients with CSVD and watershed OEF is significantly associated with white matter hyperintensities (WMH) lesion volumes after adjusting for age.
|
| 09:27 |
0742. 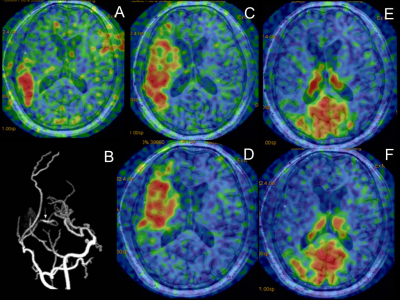 |
Cerebral Perfusion Territory Changes after Direct Revascularization Surgery in Moyamoya Disease: A Super Selective Arterial Spin Labeling Study
Jing Yuan, Jianxun Qu, Peiyi Gao
The super selective arterial spin labeling (ssASL) was used in the early postoperative period to evaluate the revascularization area (RA) obtained by a bypass from the superficial temporal artery to the middle cerebral artery in Moyamoya disease, and the perfusion territory changes of the major cerebral arteries were evaluated. The results indicated the postoperative perfusion territory changes of the major cerebral arteries differed between the RA-positive group and the RA-negative group. The incidence of preoperative external carotid artery compensation was significantly higher in the RA-negative group than the RA-positive group. There was good intermodality agreement between ssASL and CT angiography.
|
| 09:39 |
0743. 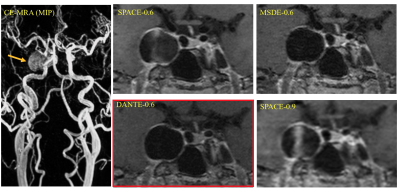 |
Comparison of Four 3D Black Blood MRI Sequences for the Characterization of Unruptured Intracranial Aneurysm Wall Enhancement
Chengcheng Zhu, Bing Tian, Laura Eisenmenger, Qi Liu, Jianping Lu, Christopher Hess, David Saloner
Aneurysm wall enhancement (AWE) post Gadolinium contrast on high-resolution black blood MRI has been studied as a marker of unstable intracranial aneurysms. However, a recent study showed slow flow could mimic AWE. This study evaluated four black blood sequences with high- and low-resolution fast-spin-echo (SPACE), with and without MSDE/DANTE blood suppression modules. In 30 unruptured saccular aneurysms, we found low-resolution SPACE significantly overestimated AWE (20/30 enhanced) compared to high-resolution SPACE (16 enhanced) and sequences with MSDE/DANTE (14 and 13 enhanced). High-resolution DANTE-SPACE has the best blood suppression and image quality, which is a preferred method for AWE assessment.
|
09:51 |
0744. 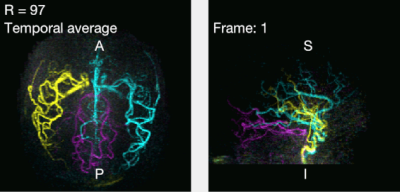 |
Highly Accelerated Dynamic 2D and 3D Vessel-Encoded Arterial Spin Labelling Angiography
S. Schauman, Mark Chiew, Thomas Okell
Vessel-encoded ASL can produce vessel-selective cerebral angiograms, but to separate blood from multiple arteries more images are needed than for standard ASL angiography, which increases scan time. Angiograms are however well suited for under-sampling and compressed sensing reconstruction because of their high intrinsic sparsity. In this work we demonstrate in-vivo that vessel-selective angiograms allow for higher acceleration factors, yielding comparable image quality to conventional angiography with matched scan time using 2D and 3D time-resolved golden angle radial acquisitions. With this optimised acquisition and reconstruction method, scan time of the 3D case can be reduced from 8:35 hours to ~5 minutes.
|
| 10:03 |
0745. 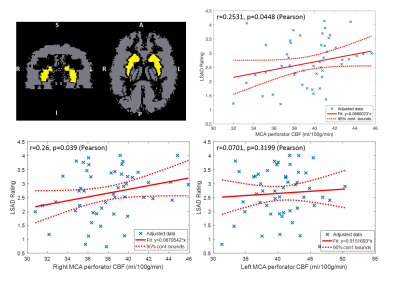 |
Characterization of Lenticulostriate Arteries using High-resolution 3D Black Blood MRI and Subcortical CBF using 3D pCASL as a Biomarker in Vascular Cognitive Impairment and Dementia
Samantha Ma, Kay Jann, Giuseppe Barisano, Xingfeng Shao, Lirong Yan, Marlene Casey, Lina D'Orazio, John Ringman, Danny Wang
Lenticulostriate arteries (LSAs) with small diameters of 280-510 µm take origin directly from the high flow middle cerebral artery (MCA), making them especially susceptible to damage by small vessel disease (SVD). In this study, we characterized the morphology of LSAs using High-resolution 3D Black Blood MRI and measured CBF in the MCA perforator territory (MCAperf) using 3D pCASL in a cohort of elderly Latino subjects. Our results show that the product of LSA delineation rating and MCAperf CBF are positively correlated with cognitive functions, and are reduced in subjects with mild cognitive impairment and hyperlipidemia.
|
 Back to Program-at-a-Glance |
Back to Program-at-a-Glance |  Back to Top
Back to Top