Breast
Breast
Oral
Oral
Body: Breast, Chest, Abdomen, Pelvis
Monday, 13 May 2019
| Room 513D-F | 16:00 - 18:00 | Moderators: Rebecca Rakow-Penner, Savannah Partridge |
16:00 |
0277. 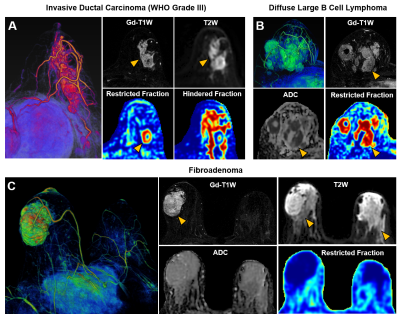 |
Quantification of Benign and Malignant Breast Tumor Cellularity
Zezhong Ye, Na Zhao, Joshua Lin, Sam Gary, Jeffrey Viox, Chunyu Song, Ruimeng Yang, Peng Sun, Jie Zhan, Qingsong Yang, Jianping Lu, Sheng-Kwei Song
Recent consensus suggested that breast MRI lacks the needed sensitivity or specificity to detect breast cancer. Breast cancer over-diagnosis may result in over-treatments. We recently modified diffusion basis spectrum imaging (DBSI) to accurately localize breast cancer lesion and quantify cancer cellularity. Results revealed that modified-DBSI afforded greater diagnostic sensitivity and specificity than ADC in distinguishing between tumor and benign tissues.
|
16:12 |
0278. 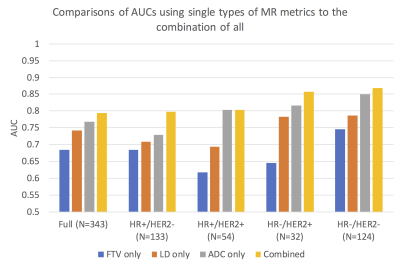 |
Combination of MRI quantitative measures improves prediction of residual disease following neoadjuvant chemotherapy (NAC) for breast cancer in the I-SPY 2 TRIAL
Wen Li, David Newitt, Lisa Wilmes, Ella Jones, Jessica Gibbs, Elizabeth Li, Bo La Yun, John Kornak, Bonnie Joe, Christina Yau, On behalf of the I-SPY 2 Consortium, Laura Esserman, Nola Hylton
This abstract presents the work of combining different MR measures to predict primary tumor residual after patients with breast cancer went through neoadjuvant chemotherapy. Three types of MR measures are investigated in this study: longest diameter, functional tumor volume, and apparent diffusion coefficient. Results showed that when all three types of MR measures are combined in the logistic regression model, it yielded the highest AUC compared to the model with only one of the MR measures. Results also suggested that measures taken at various treatment time points, not just pre-surgery, should be included in the prediction of the residual disease.
|
| 16:24 |
0279. 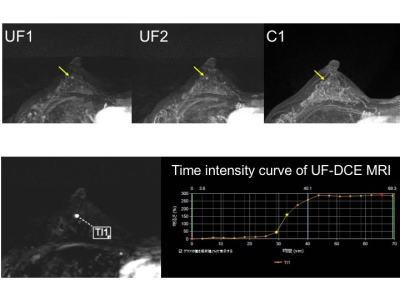 |
Improved lesion conspicuity and confidence level through suppressed background parenchymal enhancement in ultrafast breast dynamic contrast enhanced MRI
Maya Honda, Masako Kataoka, Mami Iima, Akane Ohashi, Ayami Kishimoto, Rie Ota, Marcel Nickel, Masakazu Toi, Kaori Togashi
Ultrafast dynamic contrast enhanced (UF-DCE) MRI is known for its reduced background parenchymal enhancement (BPE), but the evidence is limited. We evaluated BPE, lesion conspicuity and confidence level of UF-DCE MRI compared with those of conventional DCE (C-DCE) MRI. BPE was reduced, and lesion conspicuity and confidence level were improved on UF-DCE MRI compared to C-DCE MRI, indicating another advantage of UF-DCE MRI when applied to younger women and for high-risk screening.
|
| 16:36 |
0280. 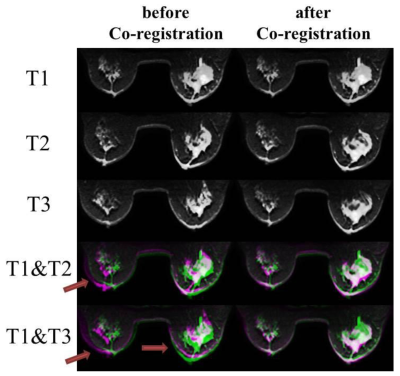 |
Co-registration of Breast Diffusion MR Images Across Multiple Time Points in a Longitudinal Study to Evaluate the Response to Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy
Guangyu Dan, Muge Karaman, Shunan Che, Zheng Zhong, Han Ouyang, Xiaohong Zhou
Breast cancer is one of the most common cancers among women. Recently, several diffusion models have been proposed to characterize breast cancer. To extend these models for the assessment or prediction of treatment response of breast cancer, image co-registration throughout the time course of treatment is a significant challenge, particularly considering the vulnerability to deformation of the breast tissue. In this study, we demonstrate a 3D non-rigid co-registration method, and apply it to diffusion weighted (DW) images acquired in a longitudinal study during neoadjuvant chemotherapy.
|
| 16:48 |
0281. 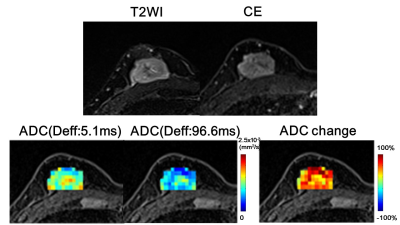 |
Time-Varying Diffusion Patterns in Breast Cancer Linked to Prognostic Factors
Mami Iima, Masako Kataoka, Maya Honda, Ayami Kishimoto Ohno, Rie Ota, Akane Ohashi, Yuta Urushibata, Thorsten Feiweier, Masakazu Toi, Kaori Togashi
We investigated the utility of diffusion time-dependence of ADC measurements for the differentiation of prognostic biomarkers in human breast tumors using OGSE and PGSE sequences. Malignant tumors had significantly lower ADC values with longer diffusion times. ADC change significantly correlated with Ki-67 expression. Significant association was found between ADC value (at the effective diffusion time of 5.1ms) and PgR expression. These associations indicate the potential of the diffusion-time-dependent ADC values as a tool to differentiate these prognostic biomarkers and highlight tumor heterogeneity without the need of contrast agents.
|
| 17:00 |
0282. 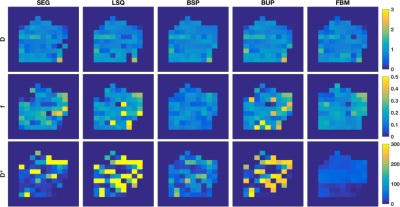 |
Breast lesion classification accuracy using intravoxel incoherent motion diffusion modelling is improved by incorporating all parameters and informative Bayesian priors
Neil Jerome, Igor Vidic, Tone Bathen, Pål Goa, Peter While
Strategies for intravoxel incoherent motion (IVIM) diffusion imaging acquisition and analysis are often framed in terms of curve-matching, whereas for breast lesions, classification accuracy against histopathologic assessment is a true metric of functional imaging performance. In this study, we show that IVIM diffusion modelling is best able to discriminate breast lesions (23 benign, 29 malignant) when using all parameters, and when derived from Bayesian methods employing either Gaussian shrinkage or local homogeneity priors, with ROC AUC values increasing from 0.83 (D, conventional least-squares) to 0.92 (D+f+D*, shrinkage prior).
|
| 17:12 |
0283. 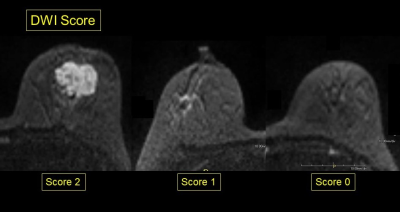 |
Pre-surgical evaluation of residual cancer by breast MRI after neoadjuvant systemic treatment: DWI-based algorism
Rie Ota, Masako Kataoka, Maya Honda, Shotaro Kanao, Mami Iima, Kanae Kawai, Akane Ohashi, Ayami Kishimoto, Takaki Sakurai, Tatsuki Kataoka, Masakazu Toi, Kaori Togashi
We aimed to re-evaluate DWI of pre-surgical MRI as a clue to diagnose pCR or non-pCR. DCE-MRI including kinetic information were also evaluated for comparison. DWI-based evaluation of residual disease in pre-surgical MRI demonstrate excellent diagnostic performance. On the other hand, residual disease is difficult to evaluate based on kinetic information. DWI-based evaluation of residual disease is a useful approach in pre-surgical evaluation of breast cancer following neoadjuvant systemic treatment.
|
| 17:24 |
0284. 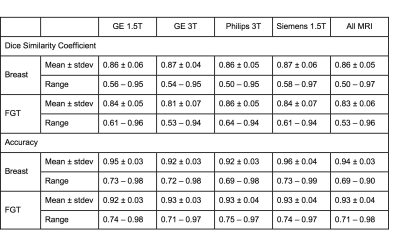 |
Independent Validation of U-Net Based Breast and Fibroglandular Tissue Segmentation Method on MRI Datasets Acquired Using Different Scanners
Yang Zhang, Jeon-Hor Chen, Kai-Ting Chang, Vivian Park, Min Kim, Siwa Chan, Peter Chang, Daniel Chow, Alex Luk, Tiffany Kwong, Min-Ying Su
Segmentation of breast and fibroglandular tissue (FGT) using the U-net architecture was implemented using training MRI from 286 patients, and the developed model was tested in independent validation datasets from 28 healthy women acquired using 4 different MR scanners. The dice similarity coefficient was 0.86 for breast, 0.83 for FGT; and the accuracy was 0.94 for breast and 0.93 for FGT. The results on MRI acquired using different MR scanners were similar. U-net provides a fully automatic, efficient, segmentation method in large MRI datasets for evaluating its role on breast cancer risk assessment and hormonal therapy response prediction.
|
| 17:36 |
0285. 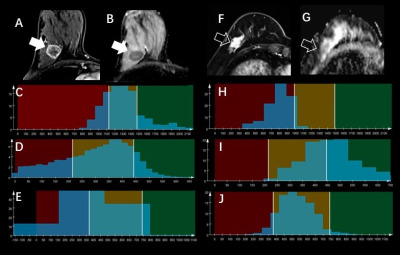 |
Can Machine-Learning-based Radiomics of Whole Tumor on MR Multiparametric Maps Predict the Ki-67 index of Breast Cancer?
Tianwen Xie, Qiufeng Zhao, Caixia Fu, Robert Grimm, Yajia Gu, Weijun Peng
There has recently been increased interest in quantitative MR parameters for assessing tumor proliferation. A total of 134 consecutive patients with pathologically-proven invasive ductal carcinoma were retrospectively evaluated. We extracted the whole-tumor histogram and textural features from an ADC map and DCE-MRI semi-quantitative maps. The LASSO for feature selection and the KNN algorithm for classification were performed. Classifications performed between Ki-67-positive and Ki-67-negative groups resulted in an accuracy of 75.4% using three texture features, whereas classification with only the entropy of ADC yielded an accuracy of 74.6%.
|
| 17:48 |
0286. 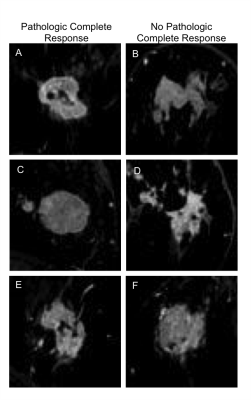 |
Convolutional neural network uses pre-chemotherapy breast MRI data to predict which tumors will exhibit a pathologic complete response post-chemotherapy
Sarah Eskreis-Winkler, Harini Veeraraghavan, Natsuko Onishi, Shreena Shah, Meredith Sadinski, Danny Martinez, Yi Wang, Elizabeth Morris, Elizabeth Sutton
In this study, we evaluate the performance of a convolutional neural network (CNN) to predict pathologic complete response based on pre-treatment breast MRI images. We achieved moderate accuracy in this initial feasibility study. Future work with larger patient datasets will improve CNN performance.
|
 Back to Program-at-a-Glance |
Back to Program-at-a-Glance |  Back to Top
Back to Top