Prostate MR: Bench to Bedside
Prostate MR: Bench to Bedside
Oral
Oral
Body: Breast, Chest, Abdomen, Pelvis
Wednesday, 15 May 2019
| Room 518A-C | 15:45 - 17:45 | Moderators: Silvia Chang, KyungHyun Sung |
15:45 |
0986. 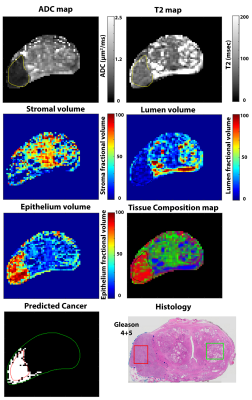 |
Validation of prostate tissue composition measurement using Hybrid Multidimensional MRI: Correlation with quantitative histology
Aritrick Chatterjee, Crystal Mercado, Roger Bourne, Ambereen Yousuf, Brittany Hess, Tatjana Antic, Gregory Karczmar, Aytekin Oto
This study validates prostate tissue composition measured non-invasively using Hybrid Multidimensional MRI (HM-MRI) with ground truth reference standard quantitative histology results from whole mount prostatectomy. There was no significant difference in prostate tissue composition measured using HM-MRI and quantitative histology with excellent correlation (0.89) and agreement on Bland-Altman analysis (bias <5%). There is significant difference in epithelium and lumen volume between cancer and normal tissue with high area under the ROC curve (0.87-0.95). This study demonstrates that the tissue composition measured using HM-MRI matches very closely with ground truth quantitative histology measures and can be used for non-invasive prostate cancer diagnosis.
|
15:57 |
0987. 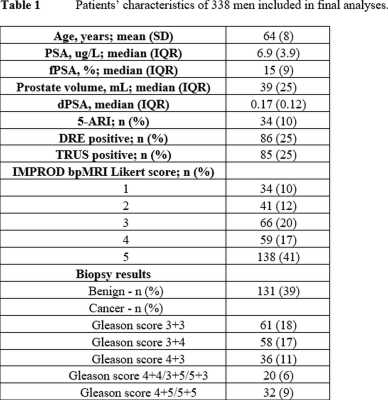 |
Prospective multi-institutional validation of IMPROD biparametric MRI in men with a clinical suspicion of prostate cancer (MULTI-IMPROD trial)
Ivan Jambor, Janne Verho, Otto Ettala, Juha Knaapila, Pekka Taimen, Kari Syvänen, Aida Kiviniemi, Esa Kähkönen, Ileana Montoya Perez, Marjo Seppänen, Antti Rannikko, Outi Oksanen, Jarno Riikonen, Sanna-Mari Vimpeli, Tommi Kauko, Harri Merisaari, Tarja Lamminen, Markku Kallajoki, Tuomas Mirtti, Jani Saunavaara, Hannu Aronen, Peter Boström
In this prospective multicenter trial, a prior developed unique MRI acquisition and reporting protocol, IMPROD bpMRI (NCT01864135), enabled the detection of 97% (143/146) of men with Gleason score ≥3+4. IMPROD bpMRI consists of T2-weighted imaging and three separate diffusion weighted imaging acquisitions with acquisition time <15 minutes. IMPROD bpMRI appears to be a powerful tool for improved prostate cancer risk stratification in men with a clinical suspicion of prostate cancer based on elevated PSA and/or digital rectal examination. Public access to all data is provided at the following addresses: http://petiv.utu.fi/improd and http://petiv.utu.fi/multiimprod
|
| 16:09 |
0988. 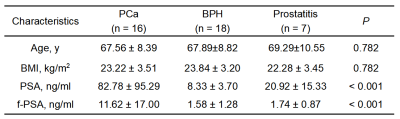 |
Preliminary application of Three-Dimensional Multifrequency MR Elastography for the Prostate Disease
Tianhui Zhang, Ying Deng, Sichi Kuang, Bingjun He, Jingbiao Chen, Bing Wu, Phillip Rossman, Kevin J Glaser, Sudhakar K Venkatesh, Richard L Ehman, Jin Wang
Prostate cancer (PCa) is the second leading cause of cancer deaths among males in the in the United States. Early detection of clinically significant PCa is a major challenge. MR elastography (MRE) is a noninvasive technique capable of quantifying the mechanical properties of tissue and has shown promising results in the detection and localization of PCa. Our results show that transpelvic three-dimensional (3D) MRE using a pelvic wall driver could be successful performed in the prostate at the frequencies of 60 Hz and 90 Hz and can provide a potential quantitative biomarker to evaluate prostate diseases.
|
16:21 |
0989. 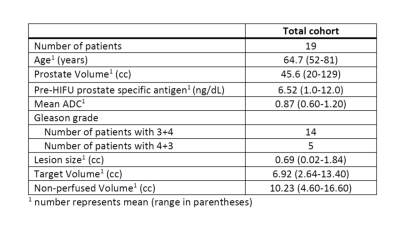 |
Post-treatment diffusion weighted imaging predicts ablation zone margins following MRI-guided high intensity focused ultrasound of the prostate.
Ryan Brunsing, Signy Holmes, Rachelle Bitton, Bruce Daniel, Geoffrey Sonn, Pejman Ghanouni
The efficacy and safety of magnetic resonance imaging-guided high intensity focused ultrasound (MRg-HIFU) treatment of intermediate risk prostate cancer is being assessed as part of a clinical trial. Non-perfused volume (NPV) on post-treatment contrast-enhanced imaging defines the zone of ablation, however contrast administration precludes further treatment due to concern for gadolinium dissociation. Thus, pre-contrast imaging tools which can predict NPV are of value. From a cohort of 19 men who underwent MFg-HIFU for treatment of prostate cancer, we show that post-treatment DWI can predict NPV, with the potential to increase confidence in predicting the ablation zone prior to contrast administration.
|
| 16:33 |
0990. 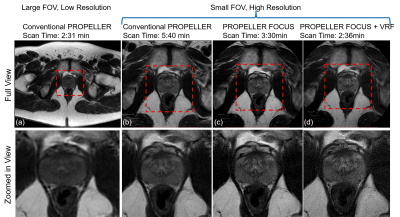 |
High Resolution T2W imaging using Multi-shot Reduced Field-of-View PROPELLER
Xinzeng Wang, Daniel Litwiller, Lloyd Estkowski, Kang Wang, Arnaud Guidon, Jason Stafford, Ersin Bayram
Multi-shot fast-spin-echo based PROPELLER (FSE-PROPELLER) combines the robustness to off-resonance and bulk motion and has been increasingly used in body imaging. However, FSE-PROPELLER methods require longer acquisition times compared with conventional FSE methods, especially in high resolution imaging with small FOV, since the oversampling is not confined to a single axis. Outer volume suppression alone can provide a modest reduction in scan time. In this work, we optimized the rotating outer volume suppression method and combined it with variable refocusing flip angles to further reduce scan time for high resolution T2W imaging.
|
16:45 |
0991. 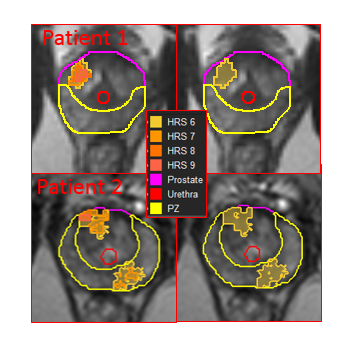 |
Clinical-genomic Risk Group Classification of Suspicions Lesions on Prostate mpMRI
Olmo Zavala-Romero, Alan Pollack, Deukwoo Kwon, Adrian Breto, Mattew Abramowitz, Alan Dal Pra, Sanoj Punnen, Radka Stoyanova
The applications of prostate mpMRI in clinical decisions, related to the need for prostate biopsy and which areas to biopsy, have rapidly increased over the past few years. After the biopsy, clinicians also have series of methods to determine the aggressiveness of the prostate cancer. The National Comprehensive Cancer Network [NCCN]1 risk groups is one of the most commonly used system. The primary intent of the NCCN is to predict biochemical recurrance rather than survival outcomes such as distant metastasis (DM). Recently, NCCN was integrated with a genomic classifier, Decipher,2 optimized to predict the risk of DM. The resultant new 3-tier risk clinical-genomic classification (CGC) system grouped the patients in low-, intermidiate- and high-risk.3 Here we present radiomics-based approach to predict the low risk group based on the novel CGC.
|
16:57 |
0992. 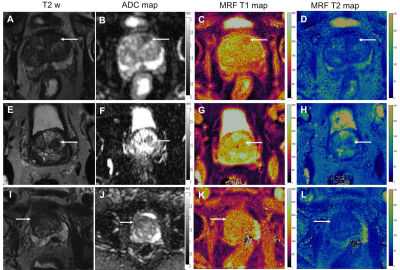 |
Utility of Quantitative Exam with MR Fingerprinting and Diffusion Mapping for Characterization of Cancer Suspicious Lesions in the Transition Zone of Prostate
Ananya Panda, Verena Obmann, Seunghee Margevicius, Wei-Ching Lo, Mark Schluchter, Gregory O'Connor, Yun Jiang, Gregory MacLennan, Irina Jaegar, Lee Ponsky, Vikas Gulani
This study presents the utility and two-reader reliability of a quantitative protocol comprising of MRF-relaxometry and diffusion-based ADC mapping in differentiating transition zone (TZ) prostate cancers from non- cancers. Two-reader agreement was good to excellent for T1, T2 and ADC. T1, T2 and ADC values were significantly lower in targeted biopsy-proven cancers versus non-cancers. T1+ADC combination could differentiate all cancers from non-cancers with an AUC of 0.95. For indeterminate PIRADS category 3 TZ lesions, non-cancers had significantly higher T1 and ADC than cancers and T1 may be the best property for further characterization of indeterminate TZ lesions (AUCT: 0.87 versus AUCADC: 0.84).
|
| 17:09 |
0993. 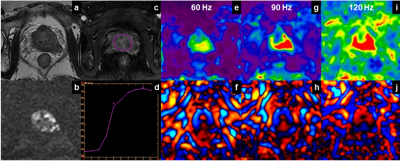 |
Feasibility of Using Combined PI-RADS Version 2 and Three-Dimensional Multifrequency Prostate MRE in Diagnosing Clinically Significant Prostate Cancer.
Ying Deng, Tianhui Zhang, Sichi Kuang, Bingjun He, Yuanqiang Xiao, Kritisha Rajlawot, Bing Wu, Phillip Rossman, Kevin J Glaser, Sudhakar K Venkatesh, Richard L Ehman, Jin Wang
PI-RADS v2 can be used as a valuable scoring system in clinically significant PCa detection. MRE is expected to add a new method to routine clinical practice. In this study, we combined PI-RADS v2 and MRE at 60, 90 and 120Hz and compared the diagnostic performance for differentiating PCa from prostatitis lesions. Our results showed that the diagnostic accuracy of combined PI-RADS v2+MRE approach at 90 and 120Hz were improved compared with PI-RADS v2. In conclusion, the combined PI-RADS v2+MRE approach, especially at 90 and 120Hz, may have the potential to improve PCa diagnosis.
|
| 17:21 |
0994. 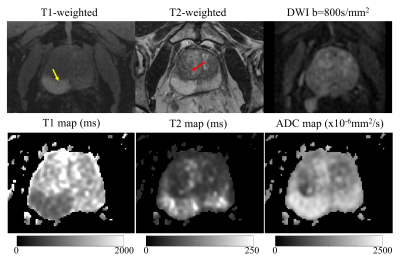 |
Simultaneous T1, T2 and ADC Mapping in Prostate Cancer and BPH using STimulated-Echo based Mapping (STEM)
Yuxin Zhang, Shane Wells, Alejandro Roldán-Alzate, Diego Hernando
A method for simultaneous T1, T2 and Apparent Diffusion Coefficient (ADC) mapping, STimulated-Echo based Mapping (STEM), has been proposed to achieve rapid and co-registered multi-slice T1, T2 and ADC maps within a moderate scan time. In this study, the STEM method is optimized for prostate imaging and evaluated in 16 patients with suspected prostate cancer (PCa) or benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH). T1, T2 and ADC maps were successfully estimated and compared among BPH, PCa and healthy prostate tissues.
|
 Back to Program-at-a-Glance |
Back to Program-at-a-Glance |  Back to Top
Back to Top