Multinuclear Imaging & Spectroscopy: Exploration of Fluorine-19 & Oxygen-17
Multinuclear Imaging & Spectroscopy: Exploration of Fluorine-19 & Oxygen-17
Sunrise Session
Sunrise Session
ORGANIZERS: Malgorzata Marjanska, Gregory Metzger
Thursday, 16 May 2019
| Room 512A-H | 07:00 - 08:00 | Moderators: Eric Ahrens, Wei Chen |
Skill Level: Basic to Advanced
Session Number: S-TH-05
Overview
This is the fourth course of a four-part sunrise educational series on multi-nuclear imaging and spectroscopy. The potential to further interrogate biological systems is made possible through using other nuclei beyond protons. In the first lecture we will investigate unique properties of 19F as an exogenous contrast for cell tracking and oximetry while in the second we will investigate the potential and methods of using 17O to assess metabolic rates.
Target Audience
MR physicists and clinicians looking for sensitive methods beyond proton imaging and spectroscopy to non-invasively track cells, evaluate oxygenation, and measure metabolic rates.
Educational Objectives
As a result of attending this course, participants should be able to:
- Explain the potential applications of 19F studies for performing cell tracking and assessing hypoxia;
- Evaluate advantages and disadvantages of using 17O versus PET to assess metabolic rates; and
- Describe the technical limitations and hardware necessary to image both nuclei in animals and humans.
Overview
This is the fourth course of a four-part sunrise educational series on multi-nuclear imaging and spectroscopy. The potential to further interrogate biological systems is made possible through using other nuclei beyond protons. In the first lecture we will investigate unique properties of 19F as an exogenous contrast for cell tracking and oximetry while in the second we will investigate the potential and methods of using 17O to assess metabolic rates.
Target Audience
MR physicists and clinicians looking for sensitive methods beyond proton imaging and spectroscopy to non-invasively track cells, evaluate oxygenation, and measure metabolic rates.
Educational Objectives
As a result of attending this course, participants should be able to:
- Explain the potential applications of 19F studies for performing cell tracking and assessing hypoxia;
- Evaluate advantages and disadvantages of using 17O versus PET to assess metabolic rates; and
- Describe the technical limitations and hardware necessary to image both nuclei in animals and humans.
| 07:00 |
The Role of 19F in Cell Tracking
Paula Foster
This presentation will describe the methods and applications for fluorine-19 based cell tracking with MRI. 19F MRI has emerged as a promising tool for in vivo cell tracking because it addresses some of the shortcomings of, the more widely used, iron-based cell tracking. Specifically, direct quantification of cell number and issues related to low specificity. The main limitation of 19F cell tracking is sensitivity. Current detection limits on preclinical imaging systems is thousands of cells/voxel. 19F cell tracking has been applied to the detection and quantification of therapeutic immune cells in cancer patients. Strategies for improving cell detection by 19F MRI will be discussed.
|
|
| 07:30 |
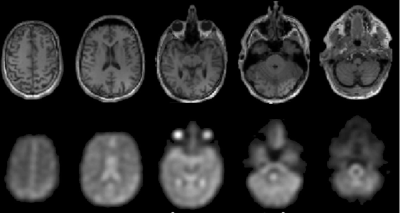 |
Measuring Metabolic Rate with 17O: MR vs. PET
Michael Bock
17O MRI can be used to quantify metabolic rates of oxygen consumption. The use of 17O methods is currently still complicated as the SNR of 17O is very low, and the spatial resolution is limited. Nevertheless, reliable measurements of the cerebral metabolic rate of oxygen consumption have been performed that are in good agreement with values from 15O PET.
|
| 08:00 |
Adjournment |
 Back to Program-at-a-Glance |
Back to Program-at-a-Glance |  Back to Top
Back to Top