Scientific Session
Spinal Cord, Head and Neck
Session Topic: Spinal Cord, Head and Neck
Session Sub-Topic: Head & Neck
Oral
Neuro
| Thursday Parallel 2 Live Q&A | Thursday, 13 August 2020, 15:05 - 15:50 UTC | Moderators: Kirk Welker |
Session Number: O-05
1186.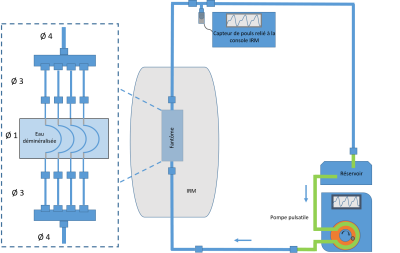 |
2D ungated PC-MRI for the exploration of small vessels in head and neck vascularisation
Agnès Paasche1, Jérémie Bettoni1, Stéphanie Dakpé1, and Olivier Balédent1
1CHU AMIENS-PICARDIE, AMIENS, France
2D ungated PC-MRI could be accurate enough to assess cervicofacial vascularization where vessels are often less than 4 mm in diameter but hey are sensitive to the pulsatile flow and their accuracy and precision should be evaluate. We have designed a phantom model to determine the better MRI parameters for pulsatile flow in pipes of one millimeter of diameter. 108 sequences have been tested and 2 were selected as accurate and precise even in case of high pulsatility. The duration of the acquisition was 15 second. 2D ungated sequences should be suitable for daily clinical practice in small vessels evaluation.
|
|
1187.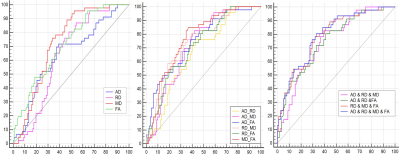 |
Multi-parametric diffusion tensor imaging for early detection of dysthyroid optic neuropathy during thyroid-associated ophthalmopathy
Ping Liu1, Gui-hua Jiang1, and Jing Zhang2
1Radiology, Guangdong Second Provincial General Hospital, Guangzhou, China, 2Radiology, The Affiliated Tongji Hospital, Tongji Medical College, Huazhong University of Science & Technology, Wuhan, China
Dysthyroid optic neuropathy (DON) is the most serious complication of Thyroid-Associated Ophthalmopathy(TAO). Untimely and ineffective treatment of could lead to permanent blindness. Early detection is the principle factor for timely intervention. Diffusion tensor imaging(DTI) is a noninvasive tool to reveal microstructural or non-overt damage and quantify pathological processes of nerve fiber bundle. We applied the multi-parametric of optic nerve to identify the DON from TAO. The result reveals that DTI can be considered a useful and noninvasive tool to differentiate DON from TAO with higher accuracy.
|
|
 |
1188.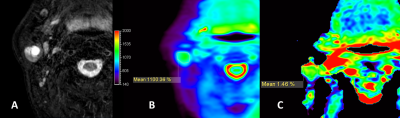 |
Evaluation of APT imaging in parotid glands and strategy in clinical usage
Yu Chen1, Tong Su1, Zhuhua Zhang1, Zhentan Xu1, Xiaoqi Wang2, Huadan Xue1, and Zhengyu Jin1
1Peking Union Medical College Hospital, Beijing, China, 2Philips HealthCare, Beijing, China, Beijing, China
This study was to prospectively evaluate APT imaging for the parotid glands and lesions. 32 patients, confirmed cancer in parotid glands, underwent 3D TSE APTw imaging. Scores for integrity and for hyperintensity artifacts of both tumor lesions and normal parotid glands were evaluated. Tumor lesions had better integrity score than normal parotid glands. Scores for hyperintensity artifacts in APTw images showed no significant difference between tumor lesions and normal parotid glands. Most APTw images of parotid glands lesions were scored with good integrity and had acceptable image quality, while challenges still exist in some cases.
|
 |
1189.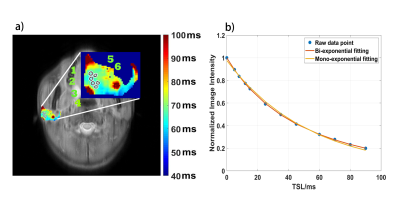 |
Bi-exponential T1ρ relaxation calculation of parotid glands in vivo at 3T
Huimin Zhang1, Qiyong Ai1, Queenie Chan2, Ann D. King1, and Weitian Chen1
1Department of Imaging and Interventional Radiology, The Chinese University of Hong Kong, Hong Kong, Hong Kong, 2Philips Healthcare, Hong Kong, Hong Kong
T1ρ relaxation, known as the spin‐lattice relaxation time in the rotating frame, is sensitive to molecular interactions including dipolar interactions, chemical exchange, and diffusion. T1ρ is often measured by mono-exponential relaxation models. Bi-exponential T1ρ relaxation have been previously observed in muscle, cartilage, menisci and brain. We report our observation of bi-exponential T1ρ relaxation in parotid glands.
|
1190.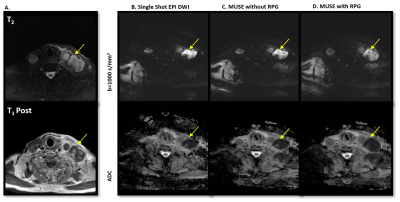 |
DW-EPI distortion reduction using Multi-shot EPI (MUSE) and Reverse Polarity Gradient (RPG) in Head & Neck Region
Maggie M Fung1, Amaresha Konar Shridhar2, Arnaud Guidon3, Amita Shukla-Dave2,4, and Vaios Hatzoglou4
1MR Apps & Workflow, GE Healthcare, New York City, NY, United States, 2Department of Medical Physics, Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center, New York City, NY, United States, 3MR Apps & Workflow, GE Healthcare, Boston, MA, United States, 4Department of Radiology, Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center, New York City, NY, United States
The purpose of this study is to investigate the distortion correction performance and ADC value consistency of the single shot EPI (SSEPI), multi-shot EPI (MUSE) and reverse polarity gradient (RPG) method in phantom, and head & neck cancer patients. We observed improved distortion correction performance in MUSE, and best distortion correction in MUSE plus RPG method. Improved anatomical details, reduced artifacts and improved perceived clinical utility were also observed in MUSE (with and without RPG) as compare to SSEPI. ADC values remained consistent between these techniques.
|
|
1191.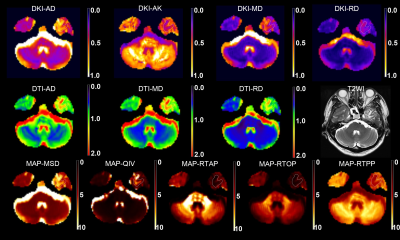 |
Detection of radiation brain injury in patients with nasopharyngeal carcinoma: A comparative study of DTI, DKI and MAP-MRI
Weike Zeng1, Mengzhu Wang2, Yaxuan Pi3, Yi Li3, Xu Yan4, Guang Yang5, and Jun Shen6
1Deptpartment of Radiology, SUN YAT-SEN Memorial Hospital, SUN YAT-SEN University, Guangzhou, China, 2MR Scientific Marketing, Siemens Healthcare, Guangzhou, China, 3department of NEUROLOGY, Sun Yat-sen Memorial Hospital, Sun Yat-sen University, Guangzhou, China, 4MR Scientific Marketing, Siemens Healthineers, Shanghai, China, 5Shanghai Key Laboratory of Magnetic Resonance, East China Normal University, Shanghai, China, 6Sun Yat-sen Memorial Hospital, Sun Yat-sen University, Guangzhou, China
Mean apparent propagator (MAP)-MRI, which builds a powerful analytical framework based on the random motion distribution of real water molecules, can more accurately and comprehensively characterize microstructure features of brain tissues than conventional diffusion imaging. This study investigated the application of MAP-MRI in the early diagnosis of radiation-induced brain injury in patients with nasopharyngeal carcinoma, compared with diffusion tensor imaging (DTI) and diffusion kurtosis imaging (DKI).
|
|
 |
1192.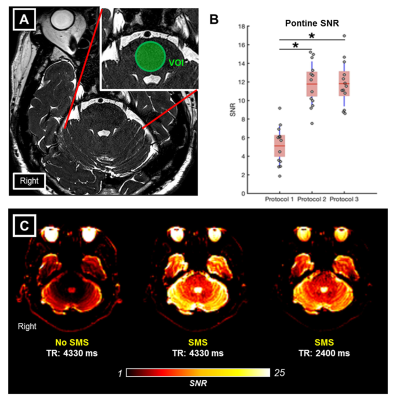 |
Trigeminal nerve tractography with accelerated simultaneous multislice readout-segmented echo planar diffusion tensor imaging
Yao Chia Shih1, Yeow Hoay Koh2, Soo Lee Lim1, Yen San Kiew1, Ee Wei Lim2, See Mui Ng1, Leon Qi Rong Ooi2, Wen Qi Tan1,3, Helmut Rumpel1, Eng King Tan2,3, and Ling Ling Chan1,3
1Department of Diagnostic Radiology, Singapore General Hospital, Singapore, Singapore, 2Department of Neurology, National Neuroscience Institute – Outram Campus, Singapore, Singapore, 3Duke-NUS Medical School, Singapore, Singapore
The impact of simultaneous multi-slice imaging (SMS) with short repetition time (TR) accelerated acquisition on diffusion tensor imaging (DTI) combined with readout-segmented echo planar imaging (RESOLVE) on the intra-cranial nerves is unexplored. Compared to non-SMS RESOLVE-DTI, two SMS RESOLVE-DTI protocols showed higher pontine signal-to-noise ratio (SNR). Consistent measures of different DTI metrics of cisternal trigeminal nerves across the three RESOLVE-DTI protocols and significant positive correlations of mean DTI metrics in pairwise comparison across these suggest that SMS RESOLVE-DTI allows fast and reliable evaluation of the microstructural integrity of the cisternal trigeminal nerve, with possible utility in trigeminal neuralgia.
|
1193.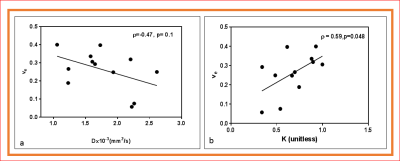 |
Predicting tumor aggressiveness in papillary thyroid cancers using multiparametric quantitative imaging metrics
Ramesh Paudyal1, Jung Hun Oh1, Vaios Hatzoglou2, Andre L. Moreira 3, Ashok shaha4, R. Michael Tuttle5, and Amita Shukla-Dave1,2
1Medical Physics, Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center, New York, NY, United States, 2Radiology, Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center, New York, NY, United States, 3Pathology, NYU Langone Medical Center, New York, NY, United States, 4Surgery, Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center, New York, NY, United States, 5Medicine, Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center, New, NY, United States
Accurate risk stratification and predicting tumor aggressiveness is critically important for the management of papillary thyroid cancer. The results from the present study predict tumor aggressiveness in papillary thyroid cancer using noninvasive multi-parametric MRI (i.e. non-Gaussian intravoxel incoherent motion (NG-IVIM) diffusion weighted (DW) and dynamic contrast-enhanced (DCE)-MRI). The surrogate biomarkers of tumor vascularity (Ktrans) and tumor cellularity (D) were negatively correlated. The kurtosis coefficient (K) reflecting tissue microstructure showed a moderate and significant correlation with the contrast agent leakage space (ve). DWI and DCE-MRI derived metrics can predict tumor aggressiveness in PTC.
|

 Back to Program-at-a-Glance
Back to Program-at-a-Glance Watch the Video
Watch the Video Back to Top
Back to Top