SMRT Posters
SMRT Poster Tour Part 1
S09.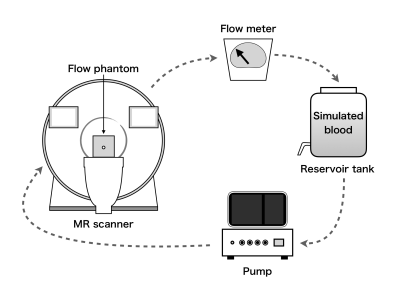 |
Accuracy of measurements of flow velocity using compressed sensing in 3D cine phase-contrast MRI - Experiments using a steady-flow pump and blood-mimicking flow phantoms -
Atsushi Fukuyama1, Katsuhiro Inoue2, Shinichi Takase2, Tsunehiro Yamahata2, Yutaka Kato3, and Shuji Koyama4
1Radiological and Medical Laboratory Sciences, Nagoya University Graduate School of Medicine, Nagoya, Japan, 2Mie University Hospital, Tsu, Japan, 3Nagoya University Hospital, Nagoya, Japan, 4Brain & Mind Sciences, Nagoya University Graduate School of Medicine, Nagoya, Japan
Compressed sensing (CS) is a technique that applies image compression theory to reconstruct an image from unusually sparse data that is used to infer the remaining data. CS is similar to parallel imaging technique, another technology that reduces imaging time. However, in case of the former, there is no reduction in the signal-to-noise ratio. In recent years, several studies have been conducted with the goal of reducing burden on patients by using the CS technique that can measure flow velocity in four dimensions (the three dimensions + time).
|
|
S03.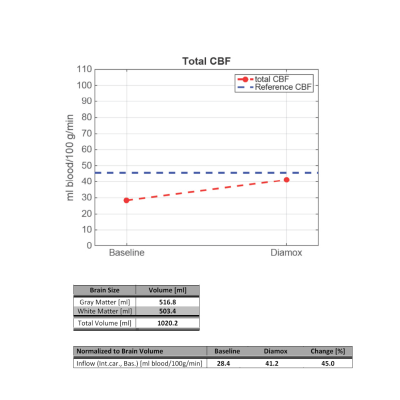 |
Clinical MRI protocol used for patients with cerebrovascular diseases
Helle Juhl Simonsen1, Ulrich Lindberg2, Karina Elin Segers3, Bente Sonne Møller3, and Henrik B.W. Larsson2
1Functional Imaging Unit Dept. of Clinical Physiology, Nuclear Medicine and PET, Rigshospitalet, Glostrup, Hvidovre, Denmark, 2Functional Imaging Unit, Dept. of Clinical Physiology, Nuclear Medicine and PET, Rigshospitalet, Glostrup, Glostrup, Denmark, 3Department of Radiology, Rigshospitalet, Glostrup, Glostrup, Denmark
To investigate the cerebral blood flow, patients with Cerebrovascular Disease have previously been referred for a single-photon-emission-computed-tomography scanning with/ maybe without Diamox (a vasodilator). If the patient has perfusion defects on the first SPECT scanning with Diamox, the patient must undergo a new SPECT scanning without Diamox to determine whether the flow defects are due to reduced flow reserve. It is time-consuming examinations in which the patient receives gamma radiation from administered radioactive drug. To prevent patients going through two long examinations and to get a more detailed examination of the cerebrovascular defects, we have set-up a clinical MRI protocol.
|
|
S06. |
How to improve your image quality when scanning young children.
Helle Juhl Simonsen1, Karina Elin Segers2, Eduardo Hansen2, Mads Rostock2, and Ulrich Lindberg1
1Functional Imaging Unit, Dept. of Clinical Physiology, Nuclear Medicine and PET, Rigshospitalet, Glostrup, Glostrup, Denmark, 2Department of Radiology, Rigshospitalet, Glostrup, Glostrup, Denmark Our research unit became in the end of 2018, involved in a major research project, where we over a period of 3 years shall MRI scan a cohort of 600, 10-year-old children. The MR scanning’s results, will be a part of a larger project, where the children have been followed with different test since birth. For the project, it will be very important that we get high image quality. Scanning children without sedation can be a bit of a challenge. We shortened our research protocol as much as possible and found a cheap solution to entertain children during the scan. |
|
| Winner: John A. Koveleski Award for Professional Development | ||
 |
S7.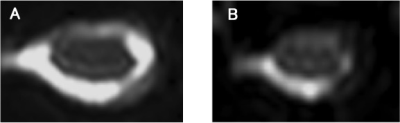 |
FA Value After 1 Week Decompressive Surgery is a Prognostic Factor in Patients with CSM
Takumi Yokohama1, Motoyuki Iwasaki2, Daisuke Oura1, Sho Furuya3, Yoshimasa Niiya2, and Tomoyuki Okuaki4
1Radiology, Otaru General Hospital, Otaru, Hokkaido, Japan, 2Neurosurgery, Otaru General Hospital, Otaru, Hokkaido, Japan, 3Nuclear of Medicine, Hokkaido University, Sapporo, Hokkaido, Japan, 4Radiology, Philips Healthcare, Tokyo, Japan
We evaluated the perioperative FA change in CSM patients using ZOOM DTI. As a result, the FA value after decompression surgery showed the proper state of the damaged cord and had a significant positive relationship with the patient’s outcome. The postsurgical FA value can become an accurate prognostic factor. Besides, the presurgical FA value did not have any relationships with the patient’s outcome, the reason why that a masking effect as an “Aligned Fibers Effect” due to strongly stenosis even using fine resolution DTI.
|
| Winner: 2nd Place, Clinical Focus Poster Award | ||
 |
S12.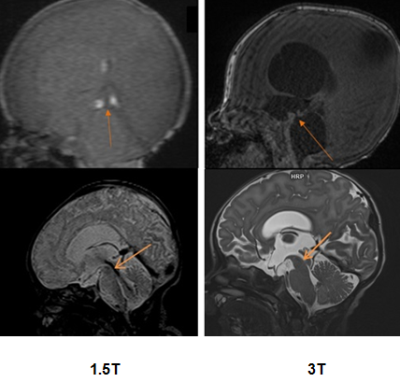 |
Advances in Neonatal Brain MRI: 1.5T to 3T
Peik Yen Teh1, Weiling Lee1, Kim Hin Lo1, and Sarat Kumar Sanamandra1
1Singapore General Hospital, Singapore, Singapore
Advances of neonatal brain imaging from 1.5T to 3T is beneficial as the additional signal gained from a greater magnetic field strength can be translated into higher spatial resolution and shorter acquisition time. This improves the depiction of intracranial structures and abnormality, hence better clinical outcome can be achieved. Nevertheless, the pitfalls with greater magnetic field strength need to be addressed to reap the benefit of higher magnetic field strength.
|
S21.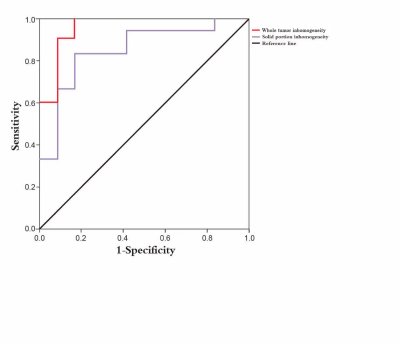 |
Texture analysis of DCE-MRI for glioma grading
zhao pengfei1, gao yang2, and qiao pengfei2
1Department of MRI, Affiliated Hospital of Inner Mongolia Medical University, Hohhot, China, 2Department of MRI, Affiliated Hospital of Inner Mongolia Medical University, Huhhot, China
The present study investigated the application of texture analysis of DCE-MRI in different ROIs in glioma grading. 50 with HGG (WHO grade III–IV) and 50 with LGG (WHO grade I–II) were included. All tumors were confirmed by pathology, and patients underwent DCE-MRI. The quantitative parameter of inhomogeneity was determined for two ROIs: whole tumor and solid portion. For both whole tumor ROI, heterogeneity was significantly different between HGG and LGG (P = 0.01). For the solid portion ROI, inhomogeneity was not significantly different between HGG and LGG (P = 0.07). Whole tumor inhomogeneity demonstrated higher diagnostic accuracy.
|
|
S16.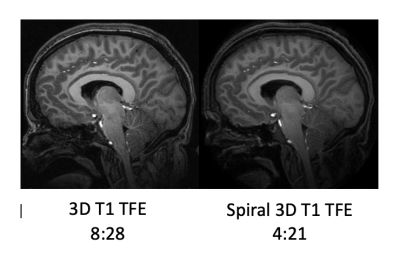 |
Benefits of Spiral MRI in routine brain imaging of pediatric patients with a VNS: prelim results
Amber Pokorney1, Jeffrey Miller1, and Ryan Robison1
1Phoenix Children's Hospital, Phoenix, AZ, United States
To compare the image quality and diagnostic utility of a spiral 3D inversion recovery gradient echo sequence versus a conventional 3D inversion recovery gradient echo sequence (i.e.TFE).
|
|
S36.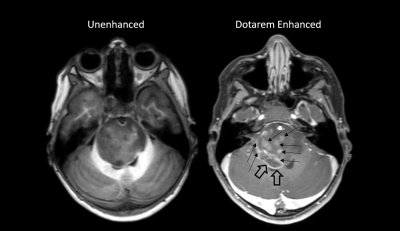 |
Intra-individual open-label, single center study to compare unenhanced MRI with Dotarem enhanced MRI in pediatric and neonatal patient population (<18years)
Amber Pokorney1, Jeffrey Miller1, and Ryan Robison1
1Phoenix Children's Hospital, Phoenix, AZ, United States
The primary objective to this study was to demonstrate superiority of lesion visualization of Dotarem enhanced MRI over unenhanced MRI along with the evaluation of safety and efficacy of Dotarem enhanced MRI in pediatric and neonate patients. Safety variables as well as the assessment of adverse events (AEs) for Dotarem enhanced MRI were collected.
|
|
| Winner: 2nd Place, Research Focus Poster Award | ||
 |
S31.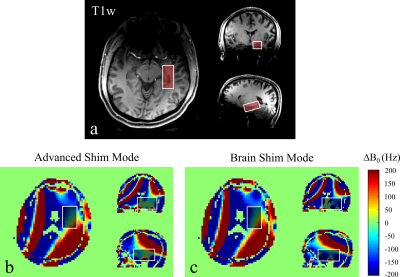 |
Performance of Automatic B0 Shim Modes for Brain MR Spectroscopy on 7T and 3T
Huijun Vicky Liao1, Eduardo Jorge Uribe Coello1, and Alexander P. Lin1
1Radiology, Brigham and Women's Hospital, Boston, MA, United States
For magnetic resonance spectroscopy, automated B0 shim mode may save scan time in a fast-paced clinical environment but is strongly dependent on performance. Two shim modes were compared in multiple brain regions at Siemens 3T and 7T. B0 maps were used to evaluate the shimming performance of each mode in the left hippocampus region. The results show that advanced shim mode is preferred on 7T (syngo MR VE12) and brain shim mode is preferred on 3T (syngo MR VE11) for brain MRS. However, more sophisticated shimming methods are still suggested for scanning more inhomogeneous regions if time permits.
|
S32.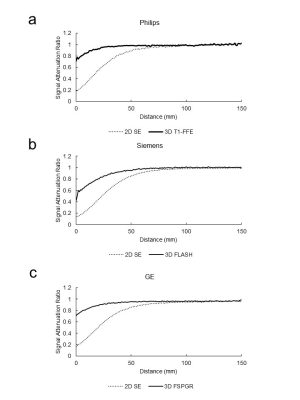 |
Useful sequence for suppressing the radiofrequency shielding effect of a titanium mesh
Yasuo Takatsu1,2, Rei Yoshida3, Kenichiro Yamamura4, Yuya Yamatani5, and Tosiaki Miyati2
1Tokushima Bunri University, Sanuki, Japan, 2Division of Health Sciences, Graduate School of Medical Sciences, Kanazawa University, Kanazawa, Japan, 3Kurihara Central Hospital, Kurihara, Japan, 4Osaka Medical College Hospital, Takatsuki, Japan, 5Nara Medical University Hospital, Kashihara, Japan
To determine which sequence for routine contrast-enhanced brain MRI (2-dimentional spin echo, 2D SE; and 3-dimentional gradient echo, 3D GRE) exhibits less RF shielding effect of the titanium mesh after cranioplasty, using a phantom in multi vendor. Every vendor had similar signal attenuation ratio and normalized absolute average deviation (NAAD) in the proximal section of phantom image. With regard to NAAD, there was a significant difference between 2D SE and 3D GRE (P < 0.05). 3D GRE shows less RF shielding effect of a titanium mesh, and it might be appropriate sequence for MRI when a titanium mesh is present.
|
|
S33.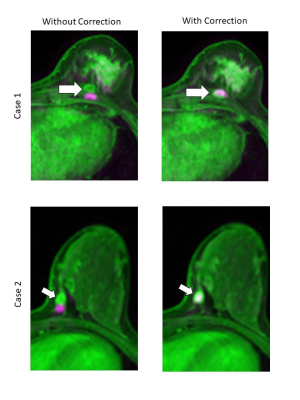 |
Effectiveness of distortion correction for diffusion-weighted imaging using clinical images
Yasuo Takatsu1,2, Hajime Sagawa3, Masafumi Nakamura4, Yuichi Suzuki5, and Tosiaki Miyati2
1Tokushima Bunri University, Sanuki, Japan, 2Division of Health Sciences, Graduate School of Medical Sciences, Kanazawa University, Kanazawa, Japan, 3Kyoto University Hospital, Kyoto, Japan, 4Otsu City Hospital, Otsu, Japan, 5The University of Tokyo Hospital, Bunkyo-ku, Japan
We investigated whether our distortion correction method could be applied practically for clinical breast MRI. The cross-correlation coefficients (CCCs) of the whole image and high-intensity regions (HIR) were calculated to assess the correlations between b0 and FS-T2WI images and b1500 and T1CE images. For all these combinations of images, the CCCs showed higher correlations with distortion correction than without the correction. This method could be adapted to any type of breast and HIR. Our method is particularly helpful as there is no additional scan and no extension in the scan time.
|
|
| S37. | 3D T2-FFE sequence—a novel 3D isotropic MR neurography technique used in the lumbosacral plexus: technical advantages over PROSET sequence
Jinglian Zhong1 and Bingjia Lai1
1Sun Yat-Sen Memorial Hospital, Sun Yat-Sen University, Guangzhou, China
3D T2-FFE sequence based neurography sequence yields images with high resolution, excellent background suppression and that enables detailed imaging of the nerves with excellent quality.Both 3D T2FFE and PROSET sequences can display the morphology of the lumbosacral plexus. However, compared with PROSET sequences, 3D T2FFE has good T2 effect, good background suppression and higher contrast. 3D T2FFE sequence can visually and clearly show the lumbosacral plexus, which has good clinical application value and is worth promoting.
|
|
| S40. | The value of magnetic resonance diffusion imaging (MRI) combined with DTT in disease evaluation of senile cerebral infarction patients was analyzed
wang chen1
1MRI, HuaDong Hospital, Shanghai, China
The value of magnetic resonance diffusion imaging (mri) combined with DTT in disease evaluation of senile cerebral infarction patients was analyzed . To observe and analyze the value of mris combined with DTT in disease evaluation of senile cerebral infarction patients. Compared with the NIHSS score predicts patients disease assessment, through magnetic resonance diffusion imaging and DTT technology evaluation in patients with disease, the accuracy is higher, so the magnetic resonance diffusion imaging joint DTT disease in elderly patients with cerebral infarction assessment has more clinical value.
|
|
S41.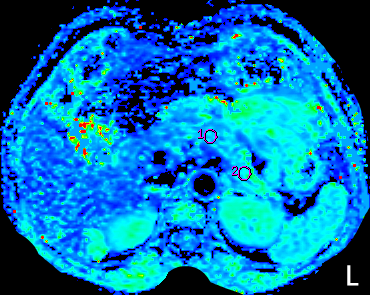 |
The Value of IVIM in the Diagnosis of Pancreatic Carcinoma
Liu ze qun1 and Sun wen ge1
1The First Affiliated Hospital of China Medical University, Shen yang, China
To evaluate the clinical application value of the monoexponential model of diffusion-weighted imaging(DWI), biexponential and stretched-exponential models of intravoxel incoherent motion(IVIM) in the diagnosis of pancreatic cancer.Retrospective collect and analyse 30 pancreatic carcinomas proven bu histopathology and/or clinical history.At the same time, 25 cases of normal pancreas were examined. In this study, multiple IVIM parameters have significant difference on the PC diagnosis from NP, and the diagnostic efficiency better than ADC value of DWI; the alpha value from IVIM sequence of the stretched exponential model is the best parameters in differential diagnosis of pancreatic carcinoma from normal tissue.
|
|
S42.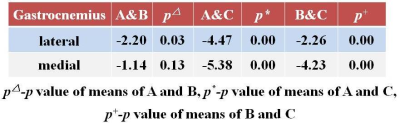 |
Evaluation gastrocnemius muscle in osteoarthritis of knee using T2 mapping
Yi Cao1, Yeda Wan2, and Binamra Gurung2
1Radiology, Tianjin hospital, Tian Jin, China, 2Radiology, Tian jin hospital, Tian jin, China
Osteoarthritis is a common chronic disease affecting the joints in older population. Knee pain or stiffness along with other specific knee joint symptoms are common entities found in future sufferers of osteoarthritis. Weight bearing joints such as the knees and hips are heavily affected. T2 mapping is a quantitative MRI technique that enables the quantification of inflammatory changes. However, most existing T2 mapping techniques are also sensitive to changes in the fat content. To evaluate lateral and medial gastrocnemius muscle in asymptomatic symptomatic individuals and patients with symptoms scheduled for knee replacement using T2 mapping.
|
|
S43.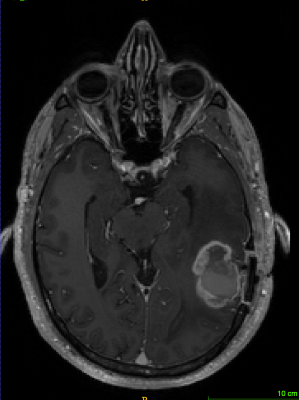 |
Assessing the reproducibility of semi-automated segmentation methods on post-operative T1 post contrast and FLAIR MRI images of GBM
Olga Fadeeva Da Costa1,2,3, Shah Islam1,3, Melanie Morrison3, Fahdi Kanavati3, Eric Aboagye3, and Adam Waldman1,4
1Imaging, Imperial College Healthcare NHS Trust, London, United Kingdom, 2Imperial Health Charity, London, United Kingdom, 3Department of Surgery & Cancer, Cancer Imaging Centre, Imperial College London, London, United Kingdom, 4Centre for Clinical Brain Sciences, University of Edinburgh, Edinburgh, United Kingdom
Glioblastomas (GBMs) are common adult primary brain tumours with high variable prognosis and a therapeutic response and outcome dominated by individual tumour biology. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) allows assessment of disease status following treatment. Accurate segmentation of GBM is the key for development of novel imaging biomarkers. A total of 35 MRI scans were analysed from patients withbiopsy confirmed GBM. Segmentation reproducibility between the two readers using semi automation was assessed and was found to be borderline. Future work is warranted using fully automated techniques to refine this ongoing work.
|
|

 Back to Program-at-a-Glance
Back to Program-at-a-Glance View the Poster
View the Poster Watch the Video
Watch the Video Back to Top
Back to Top