SMRT Posters
SMRT Poster Tour Part 2
Session Sub-Topic: SMRT Poster Tour Part 2
SMRT Poster Presentations
S44.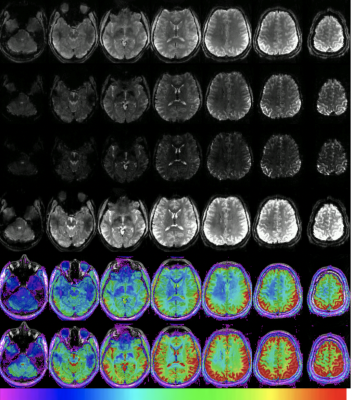 |
Multiband and Multi-echo EPI – the good, the bad and the future of fMRI at ultra-high field
Rebecca Glarin1,2, Yasmin Blunck1, and Bradford Moffat1
1MBCIU, The University of Melbourne, Parkville, Australia, 2Royal Melbourne Hospital, Melbourne, Australia
Functional MRI is a dominant tool in both neuroscience research and neurosurgical planning. Multiband EPI can not be ignored as a staple acquisition tool for fMRI. It has the ability to assist in improving temporal resolution, spatial resolution and signal to noise. When using this highly effective and efficient technique there are considerations in order to gain the most for the sequence without producing detrimental imaging artefacts. Once the technique is understood there is a future application of Multiecho Multiband EPI which can potentially be used with great success to increase sensitivity and specificity of BOLD signal and fMRI.
|
|
S46.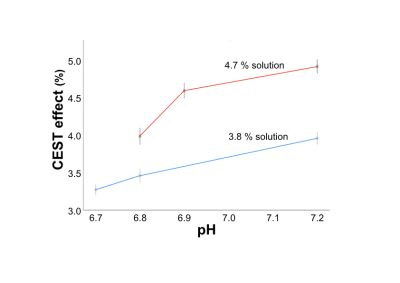 |
APT-CEST for pH imaging; a phantom study using egg white powder
Yoshihiro Akatsuka1, Hiroyuki Takashima1, Rui Imamura1, Hiroshi Nagahama1, and Mitsuhiro Nakanishi1
1Division of Radiology and Nuclear Medicine, Sapporo Medical University Hospital, Sapporo, Japan
We examined whether APT-CEST can reflect the difference of pH in solutions using egg white powder (EWP) using a 3-Tesla MRI. EWP was dissolved in distilled water to various concentrations, and their pH levels were subsequently titrated to 6.7-7.2. CEST effect (%)/ pH in 3.8 % solution were 3.27 ± 0.11/ 6.7, 3.46 ± 0.14/ 6.8 and 3.95 ± 0.11/ 7.2. CEST effect (%)/ pH in 4.7 % solution were 3.97 ± 0.17/ 6.8, 4.56 ± 0.15/ 6.9 and 4.88 ± 0.14/ 7.2. The solution using EWP can be used as a phantom reflecting the difference of pH in APT-CEST.
|
|
S50.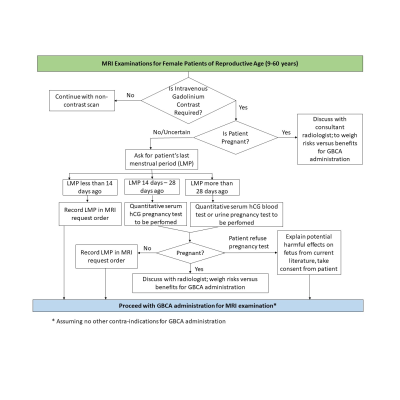 |
Plugging the gap: A reassessment of gadolinium administration policy in patients of unknown pregnancy status
Dejian Qiu1, Bertwin Chen1, Peik Yen Teh1, and Tee Meng Tan1
1Radiological Sciences, Singapore General Hospital, Singapore, Singapore
The administration of gadolinium-based contrast agents in magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is traditionally avoided during pregnancy, due to safety concerns over gadolinium exposure to the fetus. In our institution, female patients of reproductive age are required to undergo a urine pregnancy test (UPT), should contrast-enhanced MRI be required. However, this policy is not sufficiently comprehensive in safeguarding patients in the early stages of pregnancy as a UPT can be inaccurate between days 14 to 28 of the menstrual cycle. This presentation will reassess and propose changes to the gadolinium administration policy in patients of unknown pregnancy status in our institution.
|
|
| Winner: 1st Place, Research Focus Poster Award | ||
 |
S51.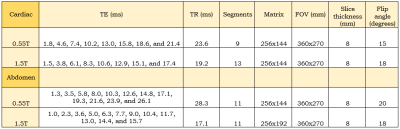 |
Iron overload detection in extra-hepatic organs on a high-performance 0.55T scanner
Christine Mancini1, W. Patricia Bandettini1, Peter Kellman1, Hui Xue1, Anna Conrey1, Swee Lay Thein1, and Adrienne E. Campbell-Washburn1
1Division of Intramural Research, National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute, National Institutes of Health, Bethesda, MD, United States
Normal iron storage can be found in the liver. When the liver becomes saturated with iron due to a primary or secondary disease process, the iron will deposit in targeted extra-hepatic organs. T2*-based imaging is a non-invasive tool for quantifying iron in an individual organ. This study compared the T2* imaging of extra-hepatic organs on a 1.5T and a prototype low field 0.55T. These results were then compared to blood ferritin levels and found to have a modest correlation.
|
S52.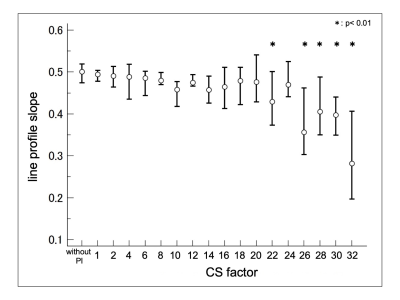 |
The upper limit of accelerating on three-dimensional (3D) -TSE using compressed sensing MRI (CS)
Rui Imamura1, Hiroyuki Takashima1, Mitsuhiro Nakanishi1, Hiroshi Nagahama1, and Yoshihiro Akatsuka1
1Division of Radiology and Nuclear Medicine, Sapporo Medical University Hospital, Sapporo, Japan
The CS technique has been applied to various sequence of MRI, which helped reduce the acquisition time while showing minimal effect on image quality. The aim of this study was to investigate the change of image quality and resolution with increase of acceleration factor, and reveal the upper limit of the number of acceleration factor of CS with 3D MRI. The line profile slope was significantly different with acceleration factor higher than 22 compared to without PI. Our results suggested that the upper limit of acceleration factor on T2WI with 3D-TSE was 22 because of decrease of resolution.
|
|
S53.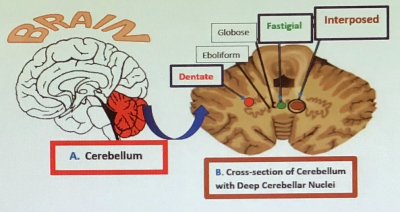 |
Multiple Targets for Drug Infusion Using Real-Time Convection-Enhanced Delivery in NHP Model for Therapies of Neurodegenerative Disorders
Anna M Borkon1, Michael J DiBalsi2, Megan Keiser3, and Timothy H Lucas4
1Research, University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, PA, United States, 2ClearPoint, ClearPoint, MRI Interventions, INC., Irvine, CA, United States, 3The Center for Cellular and Molecular Therapy, The Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia, Philadelphia, PA, United States, 4Department of Neurosurgery, University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, PA, United States
The current technological advances of the intracranial Convection-Enhanced Delivery (CED) open a novel possibility for infusing therapeutics directly into multiple targets located in the same cerebellar hemisphere with high precision and safety. The presented experiment is based on the AAV1 infusion into the Deep Cerebellar Nuclei (DCN), namely the dentate, interposed and fastigial in NHPs using the real-time CED approach. In retrospect, the conclusion of this experiment is that multiple targets located close to each other in the brain can be successfully infused during the same MRI session with no or minimal reflux visualized on the post-infusion images.
|
|
S55.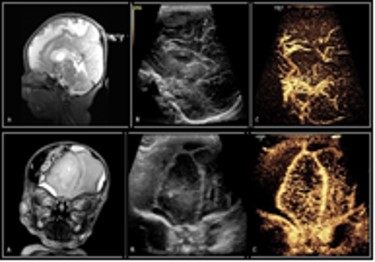 |
Tiny Bubbles versus Spinning Protons: Can Contrast-Enhanced Transfontanelle Ultrasound (ce-TUS) Compete with MRI in Neonatal Brain Imaging?
Nancy Hill Beluk1, Morie Kephart2, Ashok Panigrahy1, and Judy H. Squires1
1Radiology, University of Pittsburgh, Pittsburgh, PA, United States, 2Aureus Medical Group, Omaha, NE, United States
MRI is considered to be the current gold standard for neonatal brain imaging. However, there are often challenges when transporting critically ill neonates for diagnostic imaging studies including clinical instability, safety related to patient transport, the possible need for sedation, and MR incompatibility of patient monitoring equipment. Our study retrospectively examined standard brain MRI to contrast-enhanced transfontanelle ultrasound (ce-TUS) in neonates.
|
|
S76.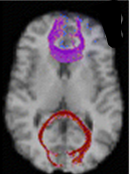 |
What Information Can Diffusion Tensor Fractional Anisotropy Provide Relative to Environmental Enrichment in Children with Congenital Heart Defects?
Nancy Hill Beluk1, Tracy Baust2, Vincent Kyu Lee1, Benjamin Meyers1, Julia Wallace1, Lauren Lorenzi3, Alexandra Mikulis2, Maddie Chrisman4, Yulia Domnina2, and Ashok Panigrahy1
1Radiology, University of Pittsburgh Medical Center, Pittsburgh, PA, United States, 2Critical Care Medicine, University of Pittsburgh Medical Center, Pittsburgh, PA, United States, 3Behavioral Health Sciences, University of Pittsburgh Medical Center, Pittsburgh, PA, United States, 4Physical and Occupational Therapies, University of Pittsburgh Medical Center, Pittsburgh, PA, United States
Children with Congenital Heart Defects (CHD) are at an increased risk for neurological deficits and neurodevelopmental delays with the most common anomaly being white matter injury (WMI). Diffusion tensor imaging (DTI), uses water’s diffusivity to characterize microstructural changes in WM. One DTI metric, fractional anisotropy (FA), increases with myelination and decreases in the presence of demyelination. We examined the association between early developmental therapies (such as OT, PT, and SLP) and WMI in infants with CHD using FA as a quantitative imaging metric for white matter integrity.
|
|
S57.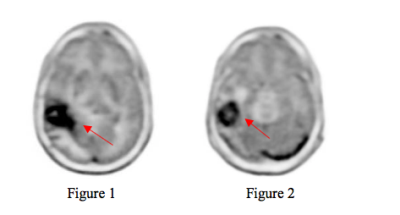 |
Impact of Reformatting Brain PET Images to the AC-PC line of MR images
Vahid Ravanfar1, Mohammad Mehdi Khalighi2, Chad Bobb3, Namasvi Jariwala1, Edgar Castellanos Diaz1, Emma Bahroos1, and Javier Villanueva-Meyer1
1Radiology, UCSF, San Francisco, CA, United States, 2Stanford University, Palo Alto, CA, United States, 3PET/MR Engineering, GE Healthcare, Waukesha, WI, United States
When PET images are fused to MR images which are aligned to the Talairach anterior commissure (AC) – posterior commissure(PC) line, the PET images are reformatted to the AC-PC plane. The reformatting of the PET images may change the visual appearance of a tumor based on the axial slice angle of the fused images. When reading PET/MR images, one must note the displayed plane of PET images as compared to the MR images. Cross-referencing between PET and MR should be performed on images displayed in the same plane.
|
|
| S58. | Application of super-fast and high resolution magnetic resonance imaging with pathology in the diagnosis of fetal central nervous system abnormalities
LI MING1
1radiology departmengt, NANJING DRUM TOWER HOSPITAL, NANJING, China
To investigate the role of super-fast and high-resolution MRI in vivo and in vitro fetus confirmed by pathological autopsy. The fetuses were scanned with 1.5T, Philips, Balance-Fast Field Echo(B-FFE) and half-fourier acquisition singo-shot T2W-DRIVE, in vivo. Ten of them took MRI scans in vitro within 2 hours after induced labor then autopsy. The post-mortem MRI sequences were susceptibility weighted imaging(SWI)。Two fetus were confirmed abnormalities in brain and 8 were body malformation after autopsy. The findings of ultrasound, prenatal and post-mortem MRI were contrasted with autopsy as a retrospective study.
|
|
S59.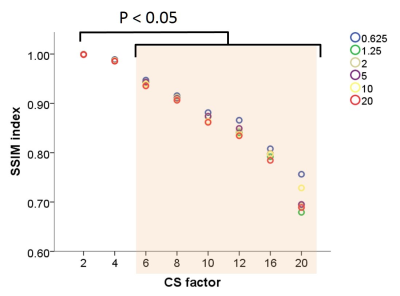 |
What is the appropriate number of acceleration factor of compressed sensing with diffusion weighted image?
Hiroyuki Takashima1, Mitsuhiro Nakanishi1, Hiroshi Nagahama1, Rui Imamura1, and Yoshihiro Akatsuka1
1Division of Radiology and Nuclear Medicine, Sapporo Medical University Hospital, Sapporo, Japan
In several recent studies, the compressed sensing (CS) technique has been applied to various sequence, which helped reduce the scan time while showing minimal effect on image quality. However, the appropriate number of acceleration factor of CS is unclear. We aimed to reveal the appropriate number of acceleration factor of CS with TSE-DWI. We calculated %CV from the image of ADC, the similarity between images of the control and the accelerated sequences was evaluated using structural similarity index (SSIM). From results of this research, the appropriate number of acceleration factor of CS with TSE-DWI was revealed as up to 4.
|
|
S60.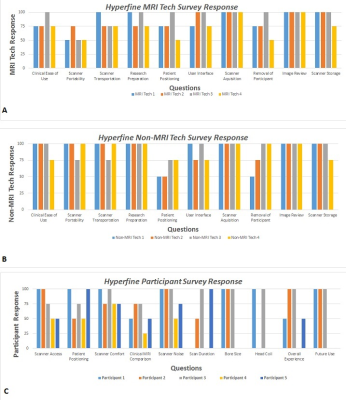 |
Usability Comparison of a Portable Low-Field, Point-of-Care MRI Scanner with High-Field MRI
Lisa M Desiderio1, Danielle Urban1, Lauren Karpf1, Leeanne Lezotte1, Sabrina Williams1, Samantha By2, Brian Welch2, Jacqui Meeks1, Bridget Pomponio1, Andrea Pogozelski1, and Joel M Stein1
1Radiology, University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, PA, United States, 2Hyperfine Research Inc, Guiford, CT, United States
The purpose of this study is to evaluate the usability and acceptability of a newly developed low-field (64 mT), portable, point-of-care (POC) MRI scanner in comparison to standard clinical high-field (1.5 and 3T) imaging from both a patient and operator perspective. Standard MRI units are expensive and technically challenging to install, maintain, and operate and can be difficult for some patients with sensitivity to noise or claustrophobia. Based on our early experience, we find that the experience of POC MRI can be acceptable and preferable to patients as well as operators, including personnel without a technical background in MRI.
|
|
S62.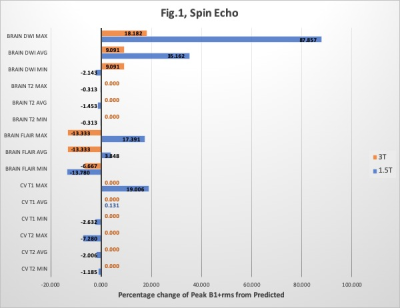 |
Is B1+rms as reliable as we think? A quantitative review.
Jennifer Croll1 and Gemma Stoddart1
1Royal Melbourne Hospital, Melbourne, Australia
Specific Absorption Rate (SAR) and B1+rms are two radiofrequency (RF) exposure metrics used in MRI. The monitoring of RF exposure in patients with implants is crucial for ensuring compliance with specific implant scanning conditions. As SAR can be highly variable many implants now state a B1+rms value to allow scanning of conditional implants. However, more recently several scanner manufacturers have stated that the actual B1+rms value recorded during scanning may be higher than the predicted value. This could impact the scanning of patients with conditional implants and potentially compromise patient safety.
|
|
S65.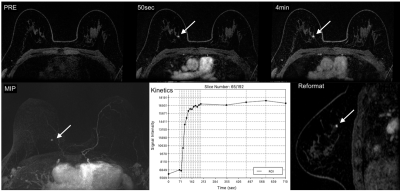 |
High spatial and temporal resolution dynamic contrast enhanced MRI of the breast for improved breast cancer detection: Differential Subsampling with Cartesian Ordering (DISCO) Versus LAVA VIBRANT-Flex Breast MRI
Larowin Toni1, Olga Smelianskaia1, Sunitha Thakur1, and Katja Pinker-Domenig1
1Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center, New York, NY, United States
MRI of the breast is the most sensitive test for breast lesion detection. The backbone of any breast MRI protocol is a high-resolution T1-weighted contrast enhanced sequence, which allows the assessment of high-resolution breast tumor and enhancement kinetics to depict angiogenesis as a tumor-specific feature. DISCO and LAVA VIBRANT-Flex MRI provide similar excellent image quality while allowing faster acquisition time and high spatial and temporal resolution. In comparison DISCO provides excellent fat suppression at 3T where conventional fat saturation techniques are often suboptimal, reduces motion artifacts and it provides better and higher spatial resolution.
|
|
S75.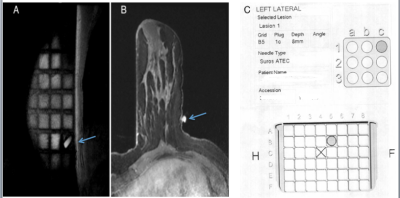 |
Does computer-aided localization of a breast lesion impact Breast MRI-guided biopsies compared with manual localization?
Larowin Toni1, Olga Smelianskaia1, Elizabeth Morris1, and Yolanda Bryce1
1Radiology, Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center, New York, NY, United States
An MRI-guided breast biopsy can be lengthy and uncomfortable for the patient, which potentially can be mitigated by computer-aided software that helps localize the lesion, compared with manual localization. We performed a retrospective trial to see if a computer-aided software system reduces procedure length, increases accuracy, and increases confidence of the clinician performing the procedure. Our study demonstrates that computer-aided software can significantly decrease length of time of the procedure but does not impact accuracy of the biopsy or confidence of the clinician performing the procedure.
|
|
S111.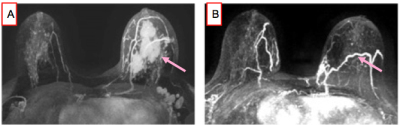 |
Accuracy of Non-Contrast MRI Biopsy in Diagnosing a Breast Cancer Pathologic Complete Response Following Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy
Larowin Toni1, Olga Smelianskaia1, Elizabeth Morris1, and Elizabeth Sutton1
1Radiology, Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center, New York, NY, United States
Non-contrast MRI-guided biopsy is a promising minimally-invasive approach with high accuracy in diagnosing a breast cancer pathologic complete response post-neoadjuvant chemotherapy which could potentially obviate surgery in this subset of patients.
|
|

 Back to Program-at-a-Glance
Back to Program-at-a-Glance Watch the Video
Watch the Video View the Poster
View the Poster Back to Top
Back to Top