Julian A. Luetkens1, Marilia Voigt1, Anton Faron1, Alexander Isaak1, Darius Dabir1, Alois M. Sprinkart1, Daniel Kuetting1, Ulrike Attenberger1, and Daniel Thomas1
1Radiology, Universityhospital Bonn, Bonn, Germany
1Radiology, Universityhospital Bonn, Bonn, Germany
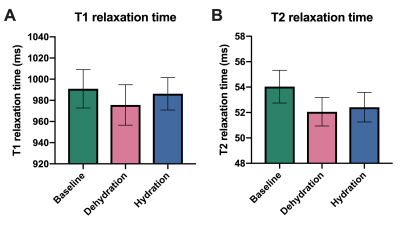
In
an intra-individual, interventional, parametric, cardiac MRI study, T1 and T2 relaxation times were reduced compared to
baseline after dehydration indicating a detectable effect of the hydration
status on relaxation time assessment.