Rick J van Tuijl1, Ynte M Ruigrok2, Irene C van der Schaaf1, Gabriël J. E. Rinkel2, Birgitta K Velthuis1, and Jaco J.M. Zwanenburg1
1Radiology, UMC Utrecht, Utrecht, Netherlands, 2Neurology and Neurosurgery, Rudolf Magnus Institute of Neuroscience, UMC Utrecht, Utrecht, Netherlands
1Radiology, UMC Utrecht, Utrecht, Netherlands, 2Neurology and Neurosurgery, Rudolf Magnus Institute of Neuroscience, UMC Utrecht, Utrecht, Netherlands
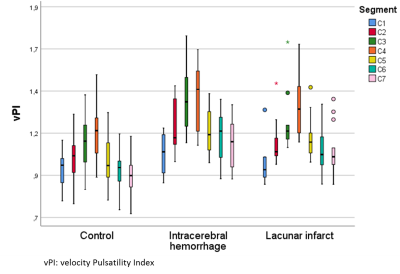
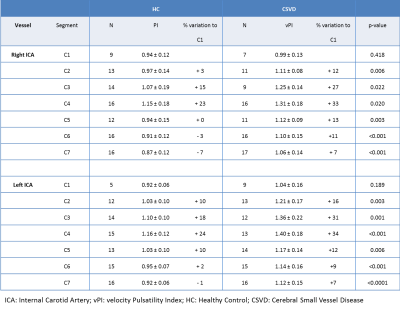
Intracranial internal carotid artery (ICA) calcification
contributes to an increased pulsatility over
the ICA in the cerebral small vessel disease group compared to healthy controls.
Pulsatility change along the ICA was influenced by calcification
volume, age, hypertension, but not by sex.