XIAODAN ZHAO1, LIWEI HU2, RONG ZHEN OUYANG2, RU SAN TAN1,3, PING CHAI4, MARIELLE FORTIER3,5, SHUO ZHANG6, WEN RUAN1, SHUANG LENG1, JUN-MEI ZHANG1,3, BRYANT JENNIFER1, LYNETTE LS TEO4, ROB VAN DER GEEST7, TENG HONG TAN3,5, JAMES YIP4, JU LE TAN1,3, YUMIN ZHONG2, and LIANG ZHONG1,3
1National Heart Centre Singapore, Singapore, Singapore, 2Shanghai Children’s Medical Centre, Shanghai Jiaotong University School of Medicine, ShangHai, China, 3Duke-NUS Medical School, Singapore, Singapore, 4National University Hospital Singapore, Singapore, Singapore, 5KK Women’s and Children’s Hospital, Singapore, Singapore, 6Philips Germany, Humburg, Germany, 7Department of Radiology, Leiden University Medical Center, Leiden, Netherlands
1National Heart Centre Singapore, Singapore, Singapore, 2Shanghai Children’s Medical Centre, Shanghai Jiaotong University School of Medicine, ShangHai, China, 3Duke-NUS Medical School, Singapore, Singapore, 4National University Hospital Singapore, Singapore, Singapore, 5KK Women’s and Children’s Hospital, Singapore, Singapore, 6Philips Germany, Humburg, Germany, 7Department of Radiology, Leiden University Medical Center, Leiden, Netherlands
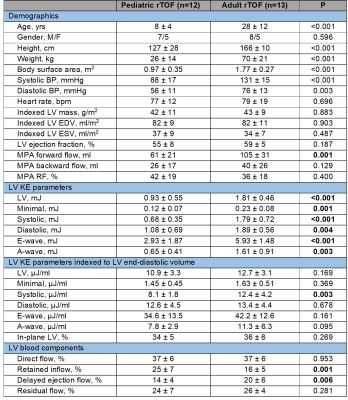
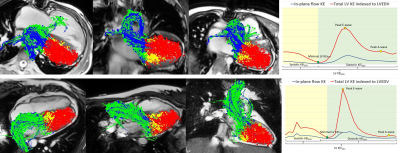
CMR 4D flow with left ventricle
(LV) kinetic energy (KE) and flow component analyses showed lower LV systolic
KE (indexed to end-diastolic volume), retained inflow and higher delayed
ejection flow in pediatric vs. adult repaired Tetralogy of Fallot.