Robert J Holtackers1,2,3, Suzanne Gommers1,2, Caroline M van de Heyning3,4, Jouke Smink5, Amedeo Chiribiri3, Joachim E Wildberger1,2, and Rachel ter Bekke2,6
1Department of Radiology & Nuclear Medicine, Maastricht University Medical Centre, Maastricht, Netherlands, 2CARIM School of Cardiovascular Diseases, Maastricht University, Maastricht, Netherlands, 3School of Biomedical Engineering and Imaging Sciences, King’s College London, London, United Kingdom, 4Department of Cardiology, Antwerp University Hospital, Antwerp, Belgium, 5Philips Healthcare, Best, Netherlands, 6Department of Cardiology, Maastricht University Medical Centre, Maastricht, Netherlands
1Department of Radiology & Nuclear Medicine, Maastricht University Medical Centre, Maastricht, Netherlands, 2CARIM School of Cardiovascular Diseases, Maastricht University, Maastricht, Netherlands, 3School of Biomedical Engineering and Imaging Sciences, King’s College London, London, United Kingdom, 4Department of Cardiology, Antwerp University Hospital, Antwerp, Belgium, 5Philips Healthcare, Best, Netherlands, 6Department of Cardiology, Maastricht University Medical Centre, Maastricht, Netherlands
The use of a time-varying dynamic inversion time leads to significantly improved and more consistent blood-pool suppression compared to a conventional fixed inversion time when used in high-resolution isotropic 3D whole-heart dark-blood LGE without additional magnetization preparation.
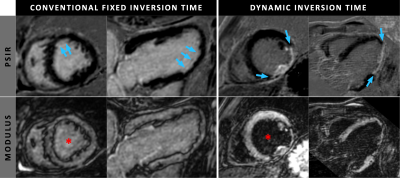
Modulus and PSIR images acquired in two patients, one with a conventional, fixed inversion time (TI) and one with the proposed dynamic TI. The blue arrows indicate areas of myocardial infarction. Note that the blood-pool in the modulus images (marked by a *) is accurately nulled with the dynamic TI, which is not achieved with the conventional fixed TI. The PSIR images with the dynamic TI therefore show excellent dark-blood contrast and scar visibility, while the PSIR images with the conventional TI have poor scar-to-blood contrast with greatly reduced subendocardial scar conspicuity.
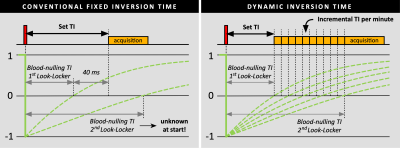
Overview of an inversion-recovery sequence with a conventional fixed inversion time (TI) and proposed dynamic TI. For the conventional method, a Look-Locker (LL) is used to obtain the actual blood-nulling TI, which is increased by 40 ms to compensate for contrast washout. This resulting TI is set. The second LL was only used to calculate the average increase in blood-nulling TI. For the dynamic TI, a LL scan is performed to obtain the actual blood-nulling TI, which is set and automatically increased every minute during acquisition with the average increment value found in the first group.
