Hongyan Liu1,2, Oscar van der Heide1,2, Cornelis A.T. van den Berg1,2, and Alessandro Sbrizzi1,2
1Computational Imaging Group for MR Diagnostics and Therapy, Center for Image Sciences, University Medical Center Utrecht, Utrecht, Netherlands, 2Department of Radiology, Division of Imaging and Oncology, University Medical Center Utrecht, Utrecht, Netherlands
1Computational Imaging Group for MR Diagnostics and Therapy, Center for Image Sciences, University Medical Center Utrecht, Utrecht, Netherlands, 2Department of Radiology, Division of Imaging and Oncology, University Medical Center Utrecht, Utrecht, Netherlands
In the current
work, we develop an accelerated MR-STAT algorithm.
High-resolution 2D quantitative maps can be reconstructed within 10 minutes on
a desktop PC thereby drastically facilitating the application of
MR-STAT in the clinical work-flow.
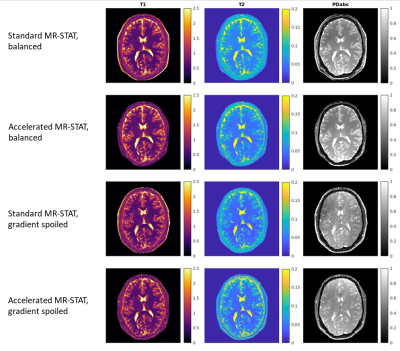
Figure
5: Comparison between standard and accelerated
MR-STAT reconstructions. Quantitative maps including $$$T_1$$$, $$$T_2$$$ and
PD from both balanced (scan time 10.3s) and gradient spoiled (scan
time 9.8s) sequences
are
shown. The image size is 224x224 with resolution of 1.0x1.0x3.0mm$$$^3$$$. Four
SVD compressed virtual-coil data are used for reconstruction.
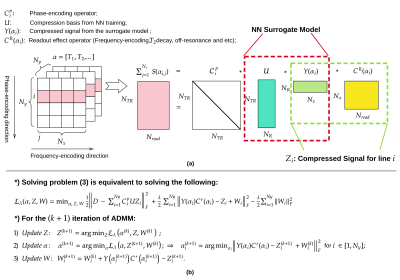
Figure
2: Model factorization and the corresponding ADMM algorithm. (a): Graphic illustration of the new problem Eq. (2). Four operators
are introduced to generate the full model: $$$C_i^p$$$,
$$$U$$$, $$$Y(\alpha_i)$$$ and $$$C^r(\alpha_i)$$$ (definition
given in the figure). (b): The ADMM algorithm with data $$$d$$$ formatted as a matrix $$$D$$$. In step (1), the compressed signals $$$Z_i$$$ are computed by solving a linear problem. In step (2),
quantitative maps are obtained by solving separate nonlinear problems
using a trust-region method.