Hamza Raki1,2, Kevin Tse Ve Koon1, Isabelle Saniour1, Henri Souchay2, Simon A Lambert1, Fraser Robb3, and Olivier Beuf1
1Univ Lyon, INSA-Lyon, Université Claude Bernard Lyon 1, UJM-Saint Etienne, CNRS, Inserm, CREATIS UMR 5220, U1206, F-69100, Lyon, France, 2GE Healthcare, Buc, France, 3GE Healthcare, Aurora, OH, United States
1Univ Lyon, INSA-Lyon, Université Claude Bernard Lyon 1, UJM-Saint Etienne, CNRS, Inserm, CREATIS UMR 5220, U1206, F-69100, Lyon, France, 2GE Healthcare, Buc, France, 3GE Healthcare, Aurora, OH, United States
The
performance of an endoluminal receiver coil including a serial MEMS switch for
active decoupling is compared to a similar coil with a conventional decoupling
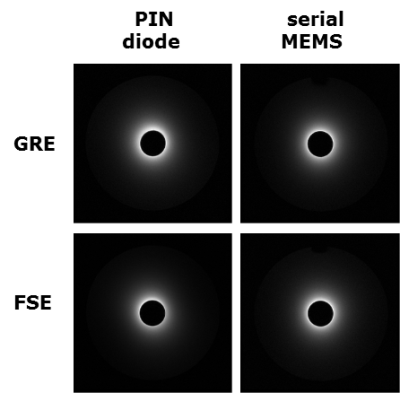
circuit using a PIN diode. Acceptable bench and image results of MEMS were
obtained. MEMS can ensure efficient and fast decoupling.
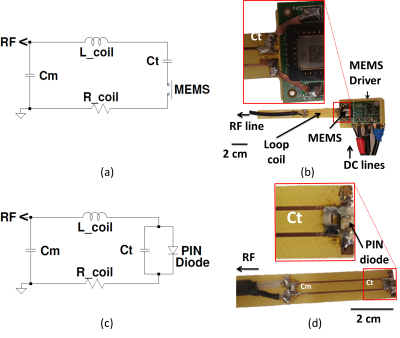
Fig. 1. Electrical schematics
(left) and associated built prototypes (right) of RECs using a MEMS switch
integrated in series (a,b) or a PIN-diode in parallel (c,d) to the loop (47x5.1x0.8 mm)
to ensure an active detuning during RF transmission. Ct, Cm, R_coil and L_coil
were tuning capacitor, matching capacitor, coil resistance and coil-inductance,
respectively. MEMS was biased and controlled directly by the connector of MRI
system.