Kagayaki Kuroda1, Satoshi Yatsushiro1, Yuta Hiranobu1, Takuya Watanabe1, Toru Niwa2, and Yutaka Imai2
1Department of Human and Information Sciences, School of Information Science and Technology, Tokai University, Hiratsuka, Japan, 2Department of Radiology, School of Medicine, Tokai University, Isehara, Japan
1Department of Human and Information Sciences, School of Information Science and Technology, Tokai University, Hiratsuka, Japan, 2Department of Radiology, School of Medicine, Tokai University, Isehara, Japan
Fatty tissue temperature was quantified by T2 synthesized from T2’s of methylene chain and terminal methyl obtained by chemical shift suppression of water and surrounding fatty acid components. While the aqueous tissue temperature was estimated by PRF shift of water proton.
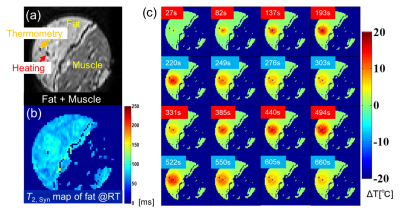
Fig. 3 Non-suppressed T1W image of the sample showing the locations of the heating and thermometry fibers (a), T2, synmap of fat (b), and temperature elevation maps (c) during laser irradiation in fat based on T2, Syn of methylene chain and terminal methyl signals.
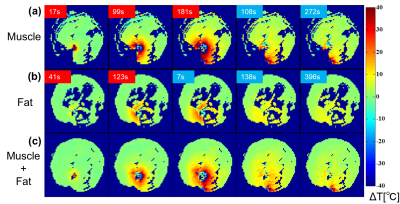
Fig. 5 Temperature elevation maps during laser irradiation. Temperature elevation in muscle (a) was obtained from PRF shift, while that in fat (b) was obtained by T2, syn. The combined temperature elevation map was obtained by the weighted sum of the muscle and fat temperature elevation maps based on their content ratio in each voxel.
