Tom Bruijnen1,2, Osman Akdag1,2,3, Charlotte VM Bruel1,2,3, Bjorn Stemkens1,2, Tim Schakel1, Jan JW Lagendijk1, Cornelis AT van den Berg1,2, and Rob HN Tijssen1
1Department of Radiotherapy, University Medical Center Utrecht, Utrecht, Netherlands, 2Computational Imaging Group for MRI diagnostics and therapy, Centre for Image Sciences, University Medical Center Utrecht, Utrecht, Netherlands, 3Department of Biomedical Engineering, Eindhoven University of Technology, Eindhoven, Netherlands
1Department of Radiotherapy, University Medical Center Utrecht, Utrecht, Netherlands, 2Computational Imaging Group for MRI diagnostics and therapy, Centre for Image Sciences, University Medical Center Utrecht, Utrecht, Netherlands, 3Department of Biomedical Engineering, Eindhoven University of Technology, Eindhoven, Netherlands
Cartesian acquisitions with rewinded spiral profilering ordering with motion compensated image reconstruction enables high quality free-breathing T2-weighted TSE with similar contrast to conventional imaging while quantifying the respiratory motion.
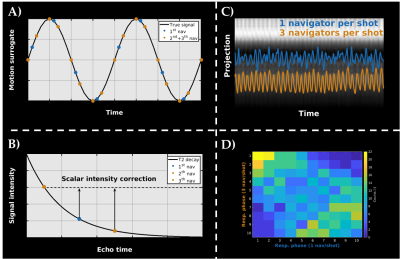
Figure 2: TSE self navigation acquisition. A) Three navigators (nav) are acquired per TSE shot to improve the temporal resolution of the self-navigation signal. The orange points indicate the extra points gained with rCASPR. B) The different navigators along the echo train are aligned using a scalar factor to compensate for T2 relaxation. C) Using 3 nav/shot instead of one improves the quality of the self-navigation signal. D) Confusion matrix counts the number of phase assignments using 1 or 3 nav/shot. For example, entry [1,1] shows how many times both methods assigned data to phase 1.
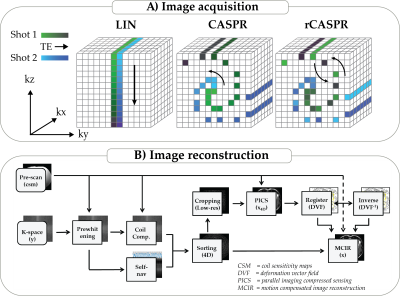
Figure 1: A): CASPR samples phase encodes along one spiral interleaf for each TSE shot and subsequent spirals are rotated with the golden ratio (137 deg). CASPR samples the spiral out, while rCASPR samples the spiral in-out. B): Overview of the reconstruction algorithm. First, a pre-scan is acquired to estimate the coil sensitivity maps (CSM), which is used to pre-whiten and compress the k-space data. Second, low resolution 4D images are reconstructed and registered to obtain the DVF. Then in a final step, the motion compensated image is reconstructed using the DVFs.
