Chung-Man Moon1, Amritha Nayak1,2, M. Okan Irfanoglu1, and Carlo Pierpaoli 1
1National Institute of Biomedical Imaging and Bioengineering, National Institutes of Health, Bethesda, MD, United States, 2Henry M. Jackson Foundation for the Advancement of Military Medicine, Rockville, MD, United States
1National Institute of Biomedical Imaging and Bioengineering, National Institutes of Health, Bethesda, MD, United States, 2Henry M. Jackson Foundation for the Advancement of Military Medicine, Rockville, MD, United States
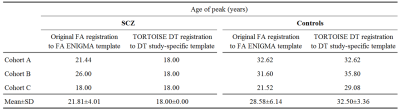
Some diffusion
MRI processing methods introduce significant bias in the results, creating an
apparent lack of inter-site harmonization that disappears using other methods. The
approach chosen for spatial normalization seem to play a key role in quality of population analysis of DTI results.
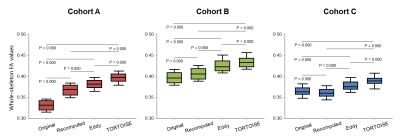
Figure 1. Mean whole-skeleton FA values obtained in
the controls of three cohorts with the correction method used in the original ENIGMA
processing with eddy_correct, compared with the three methods
we tested: recomputed with eddy_correct, eddy, and TORTOISE. P-values were obtained
from paired-t test analysis.