Jieying Zhang1, Chunjie Guo2, Xinrui Liu3, Yishi Wang1,4, Huimao Zhang2, and Hua Guo1
1Center for Biomedical Imaging Research, Department of Biomedical Engineering, School of Medicine, Tsinghua University, Beijing, China, 2Department of Radiology, the First Hospital of Jilin University, Changchun, China, 3Department of Neurosurgery, the First Hospital of Jilin University, Changchun, China, 4Philips Healthcare, Beijing, China
1Center for Biomedical Imaging Research, Department of Biomedical Engineering, School of Medicine, Tsinghua University, Beijing, China, 2Department of Radiology, the First Hospital of Jilin University, Changchun, China, 3Department of Neurosurgery, the First Hospital of Jilin University, Changchun, China, 4Philips Healthcare, Beijing, China
PSF-EPI can
achieve high-resolution distortion-free DWI in the pituitary, in which two
kinds of lesions show different features. PSE-EPI may help with the preoperative
differentiation of pituitary lesions without contrast agent.
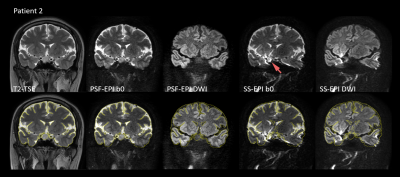
Figure 1: Images
of patient 2 (female, 41-year-old) with an RCC in coronal view.
The
upper row shows the images of T2-TSE, non-DW PSF-EPI, mean DW PSF-EPI, non-DW
SS-EPI and mean DW SS-EPI from left to right.
In
PSF-EPI, resolution = 1 x 1 x 2 mm3 and b-value = 800 mm/s2 were used.
The
bottom row shows the same images as those of upper but overlaid with the edges
extracted from T2-TSE.
Image
distortion and signal piling up exist in SS-EPI (red arrow).
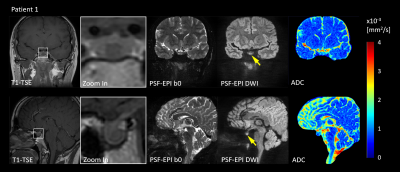
Figure 2: Images
of patient 1 (female, 36-year-old) with microadenomas (8.3 mm) in coronal
(upper) and sagittal view (bottom).
From
left to Right: T1-TSE, zoom-in T1-TSE, non-DW PSF-EPI, mean DWI(1 x 1 x 2 mm3, b=800 mm/s2) and ADC maps.
The
lesion shows hypointense in T1-TSE and hyperintense in distortion-free DWI
(yellow arrows).
