Maurizio Bergamino1, Ashley Nespodzany1, Leslie C Baxter1,2, Anna Burke3, Richard Caselli2, Marwan N Sabbagh4, Ryan R Walsh5, and Ashley M Stokes1
1Division of Neuroimaging Research, Barrow Neurological Institute, Phoenix, AZ, United States, 2Mayo Clinic Arizona, Phoenix, AZ, United States, 3Department of Neuropsychiatry, Barrow Neurological Institute, Phoenix, AZ, United States, 4Lou Ruvo Center for Brain Health, Cleveland Clinic, Las Vegas, NV, United States, 5The Muhammad Ali Parkinson Center, Barrow Neurological Institute, Phoenix, AZ, United States
1Division of Neuroimaging Research, Barrow Neurological Institute, Phoenix, AZ, United States, 2Mayo Clinic Arizona, Phoenix, AZ, United States, 3Department of Neuropsychiatry, Barrow Neurological Institute, Phoenix, AZ, United States, 4Lou Ruvo Center for Brain Health, Cleveland Clinic, Las Vegas, NV, United States, 5The Muhammad Ali Parkinson Center, Barrow Neurological Institute, Phoenix, AZ, United States
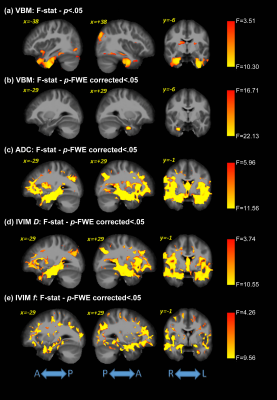
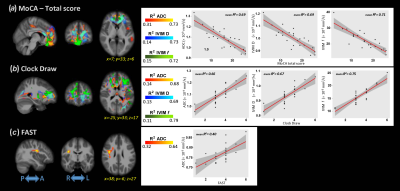
IVIM-DWI was used to investigate early
AD-related microstructural and functional changes. Significant differences were
observed using IVIM biomarkers between healthy controls, MCI, and AD groups,
while VBM showed differences only in later AD stages.