A comparison of RESOLVE DWI with delayed gadolinium-enhanced T1-weighted MRI in detecting cholesteatoma based on 531 patients’ data
Yaru Sheng1, Yan Sha1, Rujian Hong1, Zhongshuai Zhang2, and Wenhu Huang1
1Radiology, EENT Hospital of Fudan University, Shanghai, China, 2Siemens Healthcare, Shanghai, China
The comparison between readout-segmented echo-planar imaging (RESOLVE) DWI and delayed gadolinium-enhanced T1-weighted MRI diagnosis of 531 patients with cholesteatoma shows that DWI is a good tool for detecting cholesteatoma.
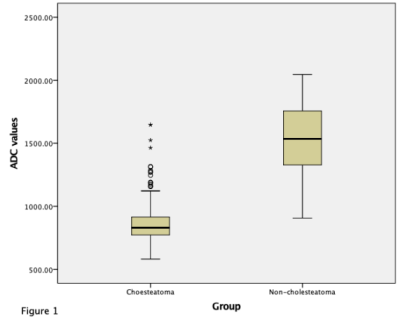
Figure 1. The ADC distribution of cholesteatoma and non-cholesteatoma. The mean ADC values of these two sets of statistical measurements are: cholesteatoma: 860.77×10-6 mm2/s and non-cholesteatoma: 1529.78×10-6 mm2/s (Wilcoxon rank-sum test, p<0.01).
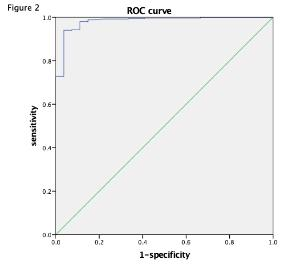
Figure 2. The area under the ROC curve of the mean ADC value is 0.98, which indicates that the ADC values have very good predictive ability for the detection and differentiation of cholesteatoma and non-cholesteatoma (granulation tissue or cholesterol granulation).

