Zhangxuan Hu1, Zhe Zhang2, Yishi Wang3, Yajing Zhang4, and Hua Guo1
1Center for Biomedical Imaging Research, Department of Biomedical Engineering, School of Medicine, Tsinghua University, Beijing, China, 2China National Research Center for Neurological Diseases, Beijing Tiantan Hospital, Capital Medical University, Beijing, China, 3Philips Healthcare, Beijing, China, 4MR Clinical Science, Philips Healthcare (Suzhou), Suzhou, China
1Center for Biomedical Imaging Research, Department of Biomedical Engineering, School of Medicine, Tsinghua University, Beijing, China, 2China National Research Center for Neurological Diseases, Beijing Tiantan Hospital, Capital Medical University, Beijing, China, 3Philips Healthcare, Beijing, China, 4MR Clinical Science, Philips Healthcare (Suzhou), Suzhou, China
Point-spread-function
(PSF) encoded EPI (PSF-EPI) DWI and T2-weighted images were used to generate
T2w-FLAIR images by taking the advantages of high-resolution and
distortion-free of PSF-EPI. This method has the potential to improve the
acquisition efficiency of MRI.
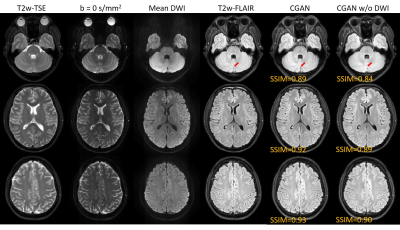
Fig.
3 Generated T2w-FLAIR images using the proposed method with or without PSF-DWI
(denoted by CGAN and CGAN w/o DWI, respectively) and their counterpart of the
acquired T2w-FLAIR. SSIM values between the generated and acquired T2w-FLAIR
were shown on each image. The input T2W-TSE, b = 0 s/mm2
and mean DWI images acquired by PSF-EPI were also provided.
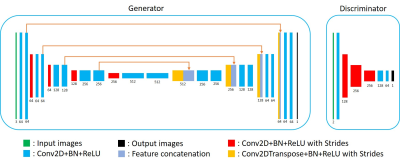
Fig.
2 Network architecture of the generator and the discriminator. Generator: a 2D U-net
was designed with 19 convolutional layers (kernel size =3×3),
4 convolutional layers with strides for downsampling (kernel size = 2×2,
strides = 2×1),
4 deconvolutional layers with strides for upsampling (kernel size = 2×2,
strides = 2×2),
and 4 feature contracting paths. Discriminator: 4 convolutional layers (kernel
size =3×3)
and 4 convolutional layers with strides for downsampling (kernel size = 3×3,
strides = 2×2).
Batch-normalization (BN) and ReLU were used for each layer.
