Eo-Jin Hwang 1 and Moon Hyung Choi2
1Seoul St. Mary's Hospital, College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, Seoul, Republic of Korea, 2Eunpyeong St.Mary's Hospital, College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, Seoul, Republic of Korea
1Seoul St. Mary's Hospital, College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, Seoul, Republic of Korea, 2Eunpyeong St.Mary's Hospital, College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, Seoul, Republic of Korea
The aim of this study was to differentiate prostate
cancer from benign tissues using radiomics in ADC maps that were produced by
various combinations of b-values. The ADC radiomics features with LASSO
regularization effectively discriminated prostate cancer from the benign
tissues.
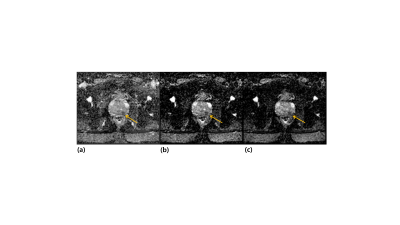
Figure1.
Representative slices of the axial, apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) maps
generated by different combinations of b-values: (a) 0 and 1000s/mm2
(ADC1), (b) 100 and 1000s/mm2 (ADC2) and (c) 100 and 1500s/mm2
(ADC3). For each map, the location of the cancer region is identified with an
orange arrow.
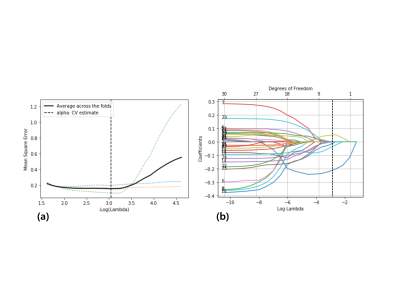
Figure2. (a)
A mean squared error plot as a function of the log of a LASSO
regularization parameter λ for
ADC2. The dotted lines illustrate each fold, and the solid line represents the
average across 5 fold cross validation. The lambda with the minimum mean
squared error was chosen as the final regularization parameter (vertical line).
(b) LASSO coefficient profiles of the radiomics features for ADC2. A coefficient
plot was produced against the log of lambda sequence. A vertical line was drawn
at the log of lambda chosen in (a), where optimal λ resulted in 4 nonzero
coefficients.