Xinyue Hu1, Ruohan Feng2, Lianqing Zhang1, Yang Li3, Xinyu Hu1, Shi Tang1, Yingxue Gao1, Lihua Zhuo2, Guoping Huang3, and Xiaoqi Huang1
1Huaxi MR Research Center (HMRRC), Functional and molecular imaging Key Laboratory of Sichuan Province, Department of Radiology, West China Hospital, Sichuan University, Chengdu 610041, China, Chengdu, China, 2Department of Radiology, the third hospital of Mianyang, Mianyang, China, Mianyang, China, 3Department of Psychiatry, the third hospital of Mianyang, Mianyang, China, Mianyang, China
1Huaxi MR Research Center (HMRRC), Functional and molecular imaging Key Laboratory of Sichuan Province, Department of Radiology, West China Hospital, Sichuan University, Chengdu 610041, China, Chengdu, China, 2Department of Radiology, the third hospital of Mianyang, Mianyang, China, Mianyang, China, 3Department of Psychiatry, the third hospital of Mianyang, Mianyang, China, Mianyang, China
The volume reduction of the right precentral
gyrus will contribute to the affective and cognitive abnormities in adolescents
with MDD.
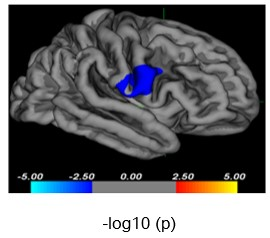
Figure
1. Diminished cortical volume in the right precentral gyrus in patients with
first-episode drug-naïve MDD compared to HC (cluster level; x=58.7,
y=6.5,
z=18.2,
vertex=19, cluster size= 979.27mm2, -log10(p)= -2.04, Monte-Carlo
corrected). Negative values for -log10(p) represent a decreased cortical volume
in patients with MDD.
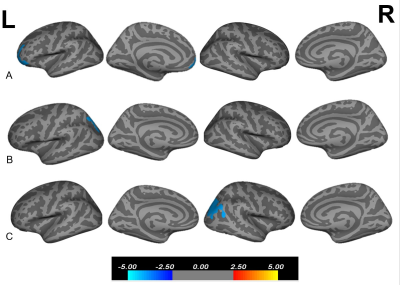
Figure 3. (A)Volume correlations
with HAMD scores in MDD patients. (B) Thickness correlations with HAMA scores
in MDD patients. (C).Surface area correlations with PSQI scores in MDD patients.
“L” indicates the left hemisphere. “R” indicates the right hemisphere. The
color bar represents the -log10(p) values from −5 to −2.5 and 2.5 to 5.