Jinrong Qu1, Hongkai Zhang2, Mingzhe Xu1, Xu Yan3, Shaoyu Wang4, and Fei Han5
1Radiology, the Affiliated Cancer Hospital of Zhengzhou University & Henan Cancer Hospital, Zhengzhou, China, 2Radiology, the Affiliated Cancer Hospital of Zhengzhou University, Zhengzhou, China, 3MR Scientific Marketing, Siemens Healthcare, Shanghai, China, 4MR Scientific Marketing, Siemens Healthcare, Xi'an, China, 5MR R&D Collaboration, Siemens Medical Solutions, Los Angeles, CA, United States
1Radiology, the Affiliated Cancer Hospital of Zhengzhou University & Henan Cancer Hospital, Zhengzhou, China, 2Radiology, the Affiliated Cancer Hospital of Zhengzhou University, Zhengzhou, China, 3MR Scientific Marketing, Siemens Healthcare, Shanghai, China, 4MR Scientific Marketing, Siemens Healthcare, Xi'an, China, 5MR R&D Collaboration, Siemens Medical Solutions, Los Angeles, CA, United States
To improve the ability to differentially diagnose
malignant liver tumors, quantitative ADCs and T2 values were evaluated in 117
patients. The results showed combining quantitative ADC and T2 values could make
the differential diagnosis of various malignant liver tumors easier.
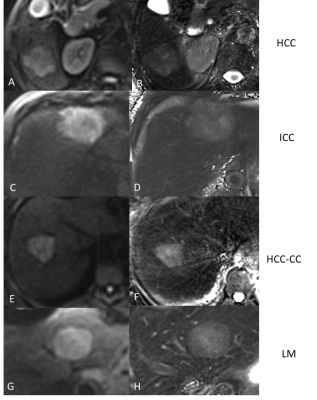
Figure 1. Diffusion-weighted
images (DWI) (A,C,E,G) and T2-mapping images (B,D,F,H) of different malignant
liver cancer groups. A, B, Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), C,D, Intrahepatic
cholangiocarcinoma (ICC), E,F, combined hepatocellular and cholangiocarcinoma
(HCC-CC), and G,H, metastatic liver disease (LM). The DWI data is presented with
a b-value = 700 s/mm2.
