Digital Posters
Female Pelvis, Placenta & Fetal
ISMRM & SMRT Annual Meeting • 15-20 May 2021

| Concurrent 5 | 15:00 - 16:00 |
3871.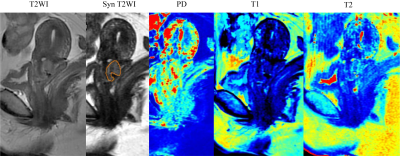 |
Grading of Cervical Cancer by Quantitative Maps from Synthetic MRI
Xiao-Li Song1, Jialiang Ren2, Kaiyu Wang3, and Bing Wu3
1The Second Hospital of Shanxi Medical School, Taiyuan, China, 2GE Healthcare, Beijing, China, 3GE Healthcare, MR Research China, Beijing, China
Cervical cancer remains the most common gynecological cancers. Histological subtype and grade of differentiation determines the course of the disease, the therapeutic outcome and survival of patient. Low-grade cervical cancers are associated with more favorable outcomes and lower tumor recurrence rates when compared to the high-grade cervical cancers.The multiple quantitative maps derived from synthetic magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) might have potential applications in describing the characteristics of cervical cancer.
|
|||
3872.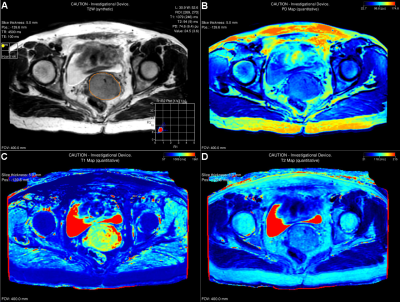 |
Quantitative Synthetic T1 and T2 Mapping in the Characterization of Cervical Squamous Cell Carcinoma
Mandi Wang1, Yiang Wang1, Chia-Wei Lee2, Chien-Yuan Lin2, and Elaine Y.P. Lee1
1The University of Hong Kong, Hong Kong, Hong Kong, 2GE Healthcare, Taipei, Taiwan
T1 and T2 relaxation mapping of tissues could provide valuable information for pathologic characterization but is limited by long scan time and consequently hampered routine clinical integration. This study aimed to investigate the ability of T1 and T2 values derived from synthetic technique dubbed MAGnetic resonance image Compilation (MAGiC) in the characterization of cervical squamous cell carcinoma (SCC). Mean T2 value was significantly higher in FIGO stage III~IV than FIGO stage I~II which demonstrated that T2 value could be a potential imaging biomarker for FIGO staging in SCC.
|
|||
3873.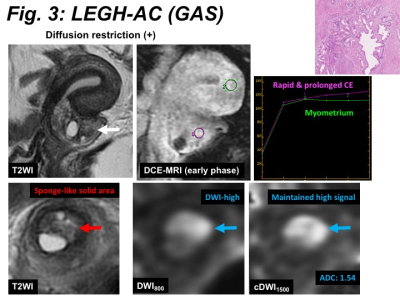 |
Uterine cervical adenocarcinomas associated with lobular endocervical glandular hyperplasia: MR imaging manifestations
Mayumi Takeuchi1, Kenji Matsuzaki2, and Masafumi Harada1
1Department of Radiology, Tokushima University, Tokushima, Japan, 2Department of Radiological Technology, Tokushima Bunri University, Sanuki, Japan
Lobular endocervical glandular hyperplasia (LEGH) is considered as a precursor lesion of cervical adenocarcinomas with poor prognosis, and early diagnosis on MRI is important. MRI of 9 LEGH-associated adenocarcinomas (LEGH-ACs) and 10 LEGHs were retrospectively evaluated. Both LEGH-AC and LEGH appeared as multicystic masses with solid components. 4 of 9 LEGH-ACs (44%) showed diffusion restriction, whereas 5 of 9 LEGH-ACs (56%) and all LEGHs showed no diffusion restriction. On DCE-MRI, 4 of 4 LEGH-ACs (100%) and 2 of 6 LEGHs (33%) showed rapid and prolonged contrast-enhancement pattern, whereas 4 of 6 LEGHs (66%) showed gradual contrast-enhancement pattern suggesting their benignity.
|
|||
3874.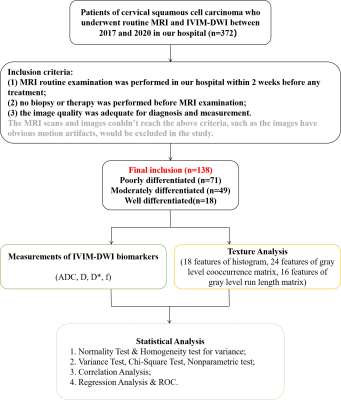 |
A combination analysis of IVIM-DWI biomarkers and T2WI-based texture features for tumor differentiation of cervical squamous cell carcinoma
Bin Shi1 and Jiang-Ning Dong1
1The First Affiliated Hospital of USTC, Anhui Provincial Cancer Hospital, Hefei, China The study aimed to explore the diagnostic value of IVIM-DWI and texture analysis on T2WI for the tumor differentiation grade of cervical squamous cell carcinoma. Finally, we carried out a combined analysis of IVIM-DWI and T2WI-based texture analysis for four compared groups, the AUC of these regression model for four comparison was 0.797, 0.954, 0.795, 0.952, respectively; better than each parameters of IVIM-DWI and texture features alone (0.503~0.684, 0.547~0.805, 0.511~0.712, 0.636~0.792, respectively). Thus, the combination of IVIM-DWI biomarkers and texture features based on tumorous heterogeneity could develop a novel predictive paradigm for the formulation of operation or radiation therapy. |
|||
3875.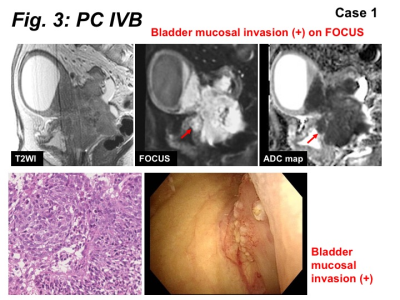 |
The feasibility of reduced field-of-view DWI in evaluating bladder invasion of uterine cervical cancer
Mayumi Takeuchi1, Kenji Matsuzaki2, and Masafumi Harada1
1Department of Radiology, Tokushima University, Tokushima, Japan, 2Department of Radiological Technology, Tokushima Bunri University, Sanuki, Japan
Uterine cervical cancer with urinary bladder invasion is classified as stage IVA with poor prognosis. Cystoscopy is a diagnostic procedure but relatively invasive examination. MRI can rule out the bladder invasion and skipping cystoscopy may be possible, however, high false positive rate may be problematic. The bladder mucosal invasion in 14 cases was evaluated with reduced FOV DWI (rFOV-DWI) and compared with cystoscopic findings. The diagnosis of invasion had a sensitivity of 100%, specificity of 50%, accuracy of 93%, PPV of 92%, and NPV of 100%. Addition of rFOV-DWI may improve the staging accuracy in assessing the bladder mucosal invasion.
|
|||
3876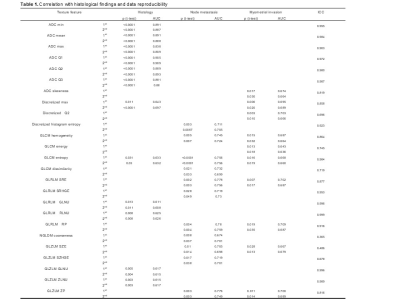 |
Some texture features from ADC map show both significance with histological findings and good reproducibility in uterine endometrial lesions Video Permission Withheld
Masamitsu Hatakenaka1, Makoto Nozaki1, and Koichi Onodera1
1Diagnostic Radiology, Sapporo Medical University, Sapporo, Japan
Some texture features from ADC map show both significant correlation with histology (benign vs. malignant), lymph node metastasis and myometrial invasion (<1/2 vs. >1/2), acceptable AUC (>0.7) and high data reproducibility (ICC>0.8) in uterine endometrial lesions.
|
|||
3877.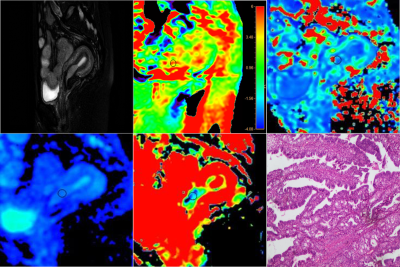 |
Improved accuracy of differential diagnosis of endometrial carcinoma and endometrial polyp combined with APTw and IVIM MR imaging
Xing Meng1, Ailian Liu1, Shifeng Tian1, Qinhe Zhang1, Qingwei Song1, and Jiazheng Wang2
1Department of Radiology, the First Affiliated Hospital of Dalian Medical University, Dalian, China, 2Philips Healthcare, Beijing, China
Accurate differential diagnosis of endometrial carcinoma (EC) and endometrial polyp (EP) determines the choice of surgical methods. Recent studies have separately applied Amide proton transfer (APT) and Intra-voxel-incoherent-motion (IVIM) imaging in diagnosing female pelvic system diseases including cervical carcinoma (CC) and EC. In this study, we investigated the combination of APTw and IVIM for differential diagnosis of EC and EP. The Results suggested that the combination of APTw and IVIM effectively aids in differentiating EC from EP.
|
|||
3878.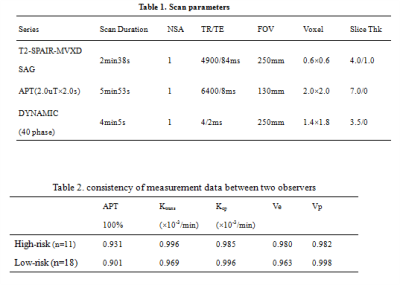 |
The feasibility of the combination of APT and DCE in preoperative risk assessment of endometrial carcinoma
Ye Li1, Shifeng Tian1, Ailian Liu1, Jiazheng Wang2, and Peng Sun2
1The First Affiliated Hospital of Dalian Medical University, Dalian, China, 2Philips Healthcare, Beijin, China
Preoperative risk assessment of endometrial carcinoma (EC) is crucial to therapy planning. The present study explores the feasibility of the combination of APT and DCE in preoperative risk assessment of endometrial carcinoma. Compared with low-risk EC, the APT values and volume transfer constant (Ktrans) derived from DCE in high-risk EC increased significantly. Our results suggest that both APT and Ktrans can differentiate high-risk EC and low-risk EC. However, a combination of APT and DCE does not improve the AUC statistically significantly.
|
|||
3879.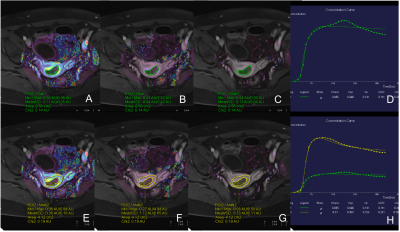 |
The value of GRASP DCE-MRI for the differentiation between benign and malignant endometrium lesions
yaling wang1, Zhongshuai Zhang2, Yuancheng Wang1, and Shenghong Ju1
1Zhongda Hospital,School of Medicine,Southeast University, NanJing, China, 2SIEMENS Healthcare, Shanghai, China
This prospective study aimed to investigate the value of GRASP(Golden-angle RAdial Sparse Parallel)on dynamic gadolinium-enhanced T1-weighted MRI (DCE-MRI) for the differentiation between benign and malignant lesions of endometrium on 88 patients. The results showed that the quantitative parameters include Kep and Ve of DCE-MRI have statistically significant difference between the benign and malignant endometrium lesions
|
|||
 |
3880.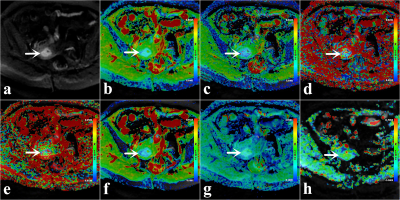 |
Prediction Model for Histological Grade of Endometrioid Adenocarcinoma: Based on Amide Proton Transfer-weighted Imaging and Multimodel DWI
Nan Meng1, Zhun Huang2, Pengyang Feng2, Ting Fang1, Fangfang Fu1, Yaping Wu1, Wei Wei1, Xuejia Wang3, Kaiyu Wang4, and Meiyun Wang*1
1Department of Radiology, Zhengzhou University People’s Hospital & Henan Provincial People’s Hospital, Zhengzhou, China, 2Department of Radiology, Henan University People’s Hospital & Henan Provincial People’s Hospital, Zhengzhou, China, 3Department of MRI, The First Affiliated Hospital of Xinxiang Medical University,, Weihui, China, 4GE Healthcare, MR Research China, BeiJing, China
Our results showed that both multimodel DWI and APTWI can estimate the histological grade and Ki-67 index of endometrial adenocarcinoma (EA), and the combination of a high MTRasym(3.5 ppm) and low D may be an effective imaging marker for predicting the grade of EA.
|
||
3881.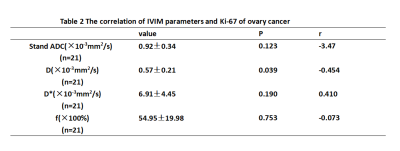 |
Correlation between Ki67 expression and Intraventricular incoherent motion (IVIM) in ovarian cancer
Xinliu He1, Yulin Chen1, Li Liu1, Ye Li1, Qingwei Song1, and Ailian Liu1
1The First Affiliated Hospital of Dalian Medical University, Dalian, China
Ki-67 is one of the prognostic marker which determines the growth fraction of a tumour and its over expression is associated with malignancy, tumour aggression, reserved prognosis and metastasis. This worked aimed at exploring the correlation of Intravoxel incoherent motion (IVIM) quantitative parameters with ki-67 expression level in ovarian cancer. The results proved that there are correlation between D value and Ki-67 gene expression in ovarian cancer, P value is 0.039 and the r value is -0.454.
|
|||
3882.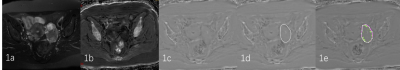 |
Evaluation of R2* and automatically quantitative ITSS in diagnosis of malignant ovarian tumor.
Wenjun JUN Hu1, Ailian Liu1, Ye Li1, Hongkai Wang2, Mingrui Zhuang2, and Qingwei Song1
1The First Affiliated Hospital of Dalian Medical University, Dalian, China, 2Dalian University of Technology, Dalian, China
Malignant ovarian tumor is characterized of high incidence, poor treatment outcomes and high treatment costs. The aim of this study was to explore the value of R2* and automatically quantitative ITSS in differentiating malignant ovarian tumor (MOTs) from other ovarian tumors (OOTs). Results of this study indicate the ITSS and R2* values of MOTs were significantly higher than those of OOTs. The combination of the two parameters can improve the differential diagnosis efficiency.
|
|||
3883.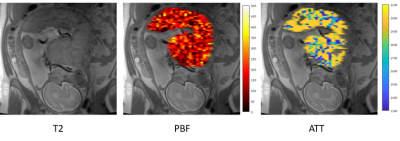 |
Multi-parametric functional and structural assessment of the placenta at late gestational ages using MRI
Daphna Link1, Netanell Avisdris1,2, Xingfeng Shao3, Liat Ben-Sira4,5, Leo Joskowicz2, Ilan Gull6, Danny J.J Wang3, and Dafna Ben-Bashat1,5
1Sagol Brain Institute, Tel Aviv Sourasky Medical Center, Tel Aviv, Israel, 2School of Computer Science and Engineering, The Hebrew University of Jerusalem, Jerusalem, Israel, 3Laboratory of FMRI Technology (LOFT), USC Stevens Neuroimaging and Informatics Institute, Keck School of Medicine, University of Southern California, Los Angeles, CA, United States, 4Division of Pediatric Radiology, Tel Aviv Sourasky Medical Center, Tel Aviv, Israel, 5Sackler Faculty of Medicine & Sagol School of Neuroscience, Tel Aviv University, Tel Aviv, Israel, 6Ultrasound Unit, Lis Maternity Hospital, Tel Aviv Sourasky Medical Center, Tel Aviv, Israel
Early and accurate placental insufficiency assessment is of a great importance. Here we comprehensively assessed placental perfusion and structure, and fetal brain and body volumes, in normal fetuses and in cases with fetal growth restriction (FGR) caused by placental insufficiency, at late gestational ages (GA=31-34 weeks). Increased Placental Blood Flow and Arterial Transit Time were detected in normal cases compared to earlier GA reported previously. Significant differences were found in several placental and fetal characteristics between normal and FGR cases. This study emphasizes the importance of multi-parametric assessment of fetuses to enable identification of high risks for FGR.
|
|||
3884.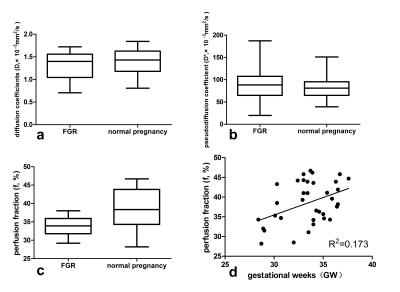 |
Use of intravoxel incoherent motion MRI to assess placental perfusion in normal and Fetal Growth Restricted pregnancies on their third trimester
liu xilong1, Feng jie1, Huang chantao1, Mei Yingjie2, and xu yikai1
1Department of Medical Imaging Center, Nanfang Hospital, Southern Medical University, Guang Zhou, China, 2Clinical science, Philips Healthcare, Guangzhou, China
Early diagnosis of FGR is vitally important for the management of pregnancy and delivery planned accordingly. IVIM MRI is a non-invasive, in vivo techniques which can assess placental perfusion quantitatively, and be useful for evaluating placental microcirculation. In this study, the IVIM parameters of placental was measured and to investigate whether FGR pregnancies have different placental perfusion compared with normal pergnancies. The results show that perfusion fraction (f) have a significantly lower in FGR group. And f value moderately incresased with increasing gestational age in normal pregnancies.
|
|||
3885.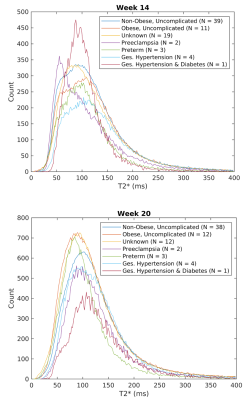 |
Longitudinal Study on Early Gestation T2*-based BOLD effect in Human Placenta
Ruiming Chen1, Ante Zhu2, Jitka Starekova3, Daniel Seiter1, Kevin M. Johnson1,3, Scott B. Reeder1,3,4,5,6, Dinesh M. Shah7, Oliver Wieben1,3, and Diego Hernando1,3,4,8
1Medical Physics, University of Wisconsin - Madison, Madison, WI, United States, 2GE Global Research, Niskayuna, NY, United States, 3Radiology, University of Wisconsin - Madison, Madison, WI, United States, 4Biomedical Engineering, University of Wisconsin - Madison, Madison, WI, United States, 5Medicine, University of Wisconsin - Madison, Madison, WI, United States, 6Emergency Medicine, University of Wisconsin - Madison, Madison, WI, United States, 7Obstetrics and Gynecology, University of Wisconsin - Madison, Madison, WI, United States, 8Electrical and Computer Engineering, University of Wisconsin - Madison, Madison, WI, United States
Maternal obesity is associated with negative pregnancy outcomes, potentially due to insufficient placental flow and oxygen delivery. Blood oxygen level-dependent (BOLD) based T2* measurements are associated with oxygenation and have shown to provide assessment of placental function. Here, we report placental T2* values in a cohort of 70 obese and non-obese subjects with normal and adverse gestational outcomes. Results show variation of T2* histograms between normal subjects and subjects with pregnancy complications at both 14 and 20 weeks, whereas no significant median T2* value differences were observed in between non-obese and obese groups.
|
|||
3886.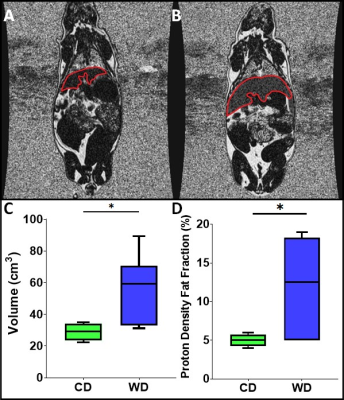 |
Effects of Life-Long Western Diet Consumption on Fetal and Maternal Guinea Pig Body Composition at Mid-Gestation
Lindsay E Morris1, Flavien Delhaes2, Lanette Friesen Waldner1, Trevor Wade1, Lauren M Smith1, Mary-Ellen ET Empey1, Simran Sethi1, Timothy RH Regnault2,3,4, and Charles A McKenzie1,4
1Medical Biophysics, Western University, London, ON, Canada, 2Physiology and Pharmacology, Western University, London, ON, Canada, 3Obstetrics and Gynaecology, Western University, London, ON, Canada, 4Division of Maternal, Fetal and Newborn Health, Children's Health Research Institute, London, ON, Canada
Effects of a life-long high fat and high sugar diet (Western diet: WD) in ~38-day gestation guinea pigs. Pregnant life-long WD or control diet (CD) fed sows underwent T1-weighted and IDEAL water-fat images on a 3T MRI at mid gestation. Regions of interest were segmented around key volumes. The maternal liver volume and median fat fraction were significantly higher in WD relative to CD sows while measures of other fat depots were unaltered between diet groups. The fetal and placental volumes were not significantly different between the diet groups. This research expands our understanding of metabolically unhealthy pregnancies.
|
|||
3887.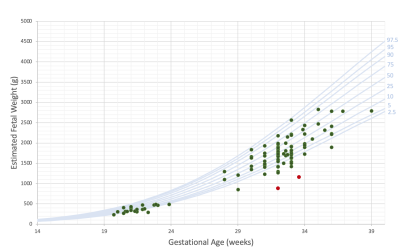 |
Automatic Segmentation and Normal Dataset of Fetal Body from Magnetic Resonance Imaging
Bella Fadida-Specktor1, Dafna Ben Bashat2,3, Daphna Link Sourani2, Netanell Avisdris1,2, Elka Miller4, Liat Ben Sira3,5, and Leo Joskowicz1
1School of Computer Science and Engineering, The Hebrew University of Jerusalem, Haifa, Israel, 2Sagol Brain Institute, Tel Aviv Sourasky Medical Center, Tel Aviv, Israel, 3Sackler Faculty of Medicine & Sagol School of Neuroscience, Tel Aviv University, Tel Aviv, Israel, 4Medical Imaging, Children’s Hospital of Eastern Ontario, University of Ottawa, Ottawa, ON, Canada, 5Division of Pediatric Radiology, Tel Aviv Sourasky Medical Center, Tel Aviv, Israel
Weight estimation is of great importance in assessing fetal development, yet unavailable in routine fetal MRI. The aim of this study was to develop an automatic fetal body segmentation method and to create a large dataset of volumetric body measurements of normal fetuses. Automatic fetal body segmentation was performed on data obtained from two clinical sites, three MRI systems and two sequences. Using a neural network trained for each sequence, high performance was achieved for both of them. A database of normal fetal volumes with a wide range of gestational age was created and was consistent with ultrasound growth chart.
|
The International Society for Magnetic Resonance in Medicine is accredited by the Accreditation Council for Continuing Medical Education to provide continuing medical education for physicians.