Digital Posters
More Psych, Metabolic, Infectious & Rare Diseases
ISMRM & SMRT Annual Meeting • 15-20 May 2021

| Concurrent 4 | 19:00 - 20:00 |
1670.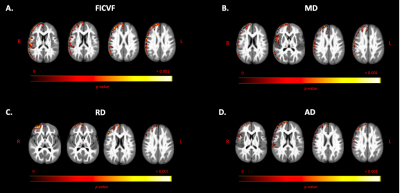 |
Gray Matter Based Spatial Statistics Shows Cortical Alterations in Individuals With Autism Spectrum Disorder
Marissa DiPiero1,2, Janet Lainhart2,3, Brittany Travers2,4, Andrew Alexander 2,3,5, and Doug Dean2,6
1Neuroscience Training Program, University of Wisconsin - Madison, Madison, WI, United States, 2Waisman Center, University of Wisconsin - Madison, Madison, WI, United States, 3Department of Psychiatry, University of Wisconsin - Madison, Madison, WI, United States, 4Department of Kinesiology, University of Wisconsin - Madison, Madison, WI, United States, 5Department of Medical Physics, University of Wisconsin - Madison, Madison, WI, United States, 6Department of Pediatrics, University of Wisconsin - Madison, Madison, WI, United States
Advanced diffusion MRI techniques, such as Neurite Orientation Dispersion and Density Imaging (NODDI), may be used to investigate cortical gray matter (GM) microstructure. In this work, we used the Gray Matter Based Spatial Statistics approach to investigate cortical GM microstructural differences in young people with autism spectrum disorder (ASD). Group differences and age by group interaction models were assessed. We observe regions of reduced neurite density and significant age-related changes of DTI and NODDI metrics in cortical GM of ASD individuals. Findings provide unique evidence of altered neurodevelopmental processes affecting microstructural development in ASD.
|
|||
1671.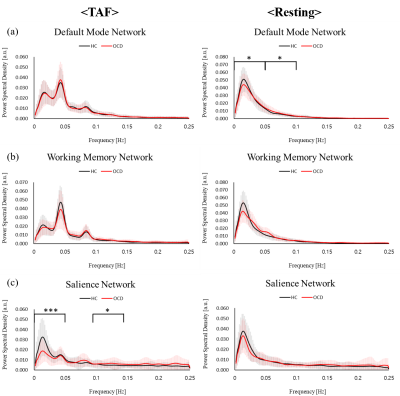 |
Power spectral density of salience network alterations in obsessive-compulsive disorder: Impact on thought-action fusion performance
Eunji Kim1, Sang Won Lee2, Hyunsil Cha1, Heajung Choi1, Seungho Kim1, Yunheung Kim3, Seung Jae Lee2, and Yongmin Chang4
1Medical & Biological Engineering, Kyungpook National University, Daegu, Korea, Republic of, 2Psychiatry, Kyungpook National University Hospital, Daegu, Korea, Republic of, 3Kyungpook National University, Daegu, Korea, Republic of, 4Radiology and Molecular Medicine, Kyungpook National University, Daegu, Korea, Republic of
Obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD) showed the functional connectivity alterations in default mode network (DMN), central executive network (CEN) and salience network (SN) 1. We investigated the difference of intrinsic networks between OCD and healthy controls (HC) from thought-action fusion (TAF) task and resting state by using fMRI. During TAF task, Power spectral density (PSD) of SN in OCD showed lower than PSD in HC in low-frequency bins. PSD of SN showed a significant correlation with TAF score and OBQ scale in OCD. Therefore when doing TAF task, OCD symptoms might have relations with alterations of PSD of SN.
|
|||
1672.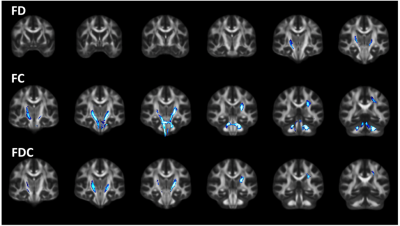 |
Evaluation of White Matter Integrity via Fixel-Based Analysis in HIV Infection
Alan Finkelstein1, Md Nasir Uddin2, Miriam Weber2, Jianhui Zhong1,3,4, and Giovanni Schifitto2,3
1Biomedical Engineering, University of Rochester, Rochester, NY, United States, 2Neurology, University of Rochester, Rochester, NY, United States, 3Imaging Sciences, University of Rochester, Rochester, NY, United States, 4Physics and Astronomy, University of Rochester, Rochester, NY, United States
Individuals with chronic HIV-infection suffer from neurocognitive impairment. These changes are thought to be mediated by atrophy and demyelination in the setting of chronic neuroinflammation. In this abstract, we used fixed-based analysis (FBA) to investigate the relationship between white matter integrity and cognitive function in the presence of HIV infection. Connectivity-based fixel ehancement and region-based statistics were performed to evaluate group differences at the fixel and tract level, respectively. Lower fixel-based metrics were observed in the HIV+ cohort. We also observed significant correlations between fixel-based metrics and cognitive scores derived from neuropsychological testing in the HIV+ cohort.
|
|||
1673.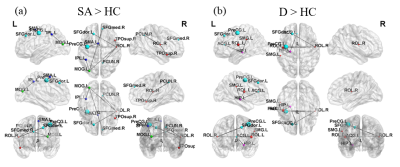 |
Assessment of brain structural connectome alterations in depressive patients with suicidal attempt using GQI
Chun-Ju Kao1, Vincent Chin-Hung Chen2,3, Yuan-Hsiung Tsai3,4, and Jun-Cheng Weng1,2,5
1Department of Medical Imaging and Radiological Sciences, and Bachelor Program in Artificial Intelligence, Chang Gung University, Taoyuan, Taiwan, 2Department of Psychiatry, Chang Gung Memorial Hospital, Chiayi, Taiwan, 3School of Medicine, Chang Gung University, Taoyuan, Taiwan, 4Department of Diagnostic Radiology, Chang Gung Memorial Hospital, Chiayi, Taiwan, 5Medical Imaging Research Center, Institute for Radiological Research, Chang Gung University and Chang Gung Memorial Hospital at Linkou, Taoyuan, Taiwan
Depression is a key factor in committing suicide. Patients with depression often accompany with brain network alterations. Three groups of participants were recruited in the study, including healthy controls (HC), depressed patients with and without suicidal attempt history (SA, D). We analyzed brain network alternations by using their GQI data. SA group showed lower global integration and higher local segregation compared to D and HC groups. Furthermore, SA and D groups had significant subnetwork connections in frontal and parietal lobes than HC group. The alternations were found in the network measurement in depressed patients with and without suicidal attempt history.
|
|||
1674.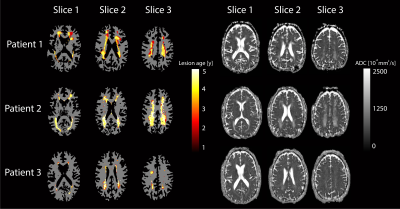 |
Longitudinal assessment of lesion volume and ADC in patients with Fabry disease: a 5 year follow up study
Koen P.A. Baas1, Simon Körver2, Bram F. Coolen3, Gustav J. Strijkers3, Carla E.M. Hollak2, and Aart J. Nederveen1
1Radiology and Nuclear Medicine, Amsterdam UMC, Amsterdam, Netherlands, 2Endocrinology and Metabolism, Amsterdam UMC, Amsterdam, Netherlands, 3Biomedical Engineering and Physics, Amsterdam UMC, Amsterdam, Netherlands
We investigated whether local ADC changes precede the formation of white matter lesions (WML) in patients with Fabry disease. A dataset was collected, containing five-year follow-up MRI data of 46 patients with Fabry disease. Within WMLs, ADC values were significantly higher compared to healthy WM and kept increasing after first detection. Moreover, ADC values were significantly higher within regions that were detected at later time points as WML on FLAIR images. These findings indicate that diffusion weighted imaging could play an important role in predicting which patients are at risk of lesion formation and require preemptive treatment.
|
|||
1675.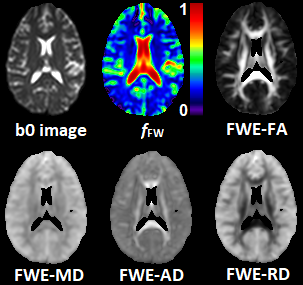 |
Free-Water Eliminated DTI Measures of Neuro-inflammation and White Matter Structural Deterioration in HIV-1 Clade C Infection
Teddy Salan1, Deepika Aggrawal2, Gaurav Garg2, Manju Mohanty2, Paramjeet Singh2, Mahendra Kumar1, Sameer Vyas2, and Varan Govind1
1University of Miami, Miami, FL, United States, 2Post Graduate Institute of Medical Education & Research, Chandigarh, India
Few neuroimaging studies have focused on HIV-1 clade C infection (HIV-1C) which comprises approximately half the global HIV population. In this work, we use a free-water eliminated diffusion tensor imaging (FWE-DTI) data processing approach to determine the extent of micro-structural brain damage in drug-naïve HIV-1C subjects. Our results show white matter (WM) structural abnormalities among HIV-1C subjects, manifested by increases in free water volume throughout the brain and reduced FWE fractional anisotropy (FWE-FA) along WM tracts. Our FWE-DTI approach provides an improved method for more accurate measures of brain abnormalities due to neuro-inflammation in HIV and other infections.
|
|||
1676.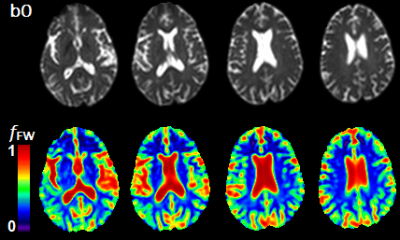 |
Mapping Increased Cerebral Free Water Volume Fraction in Hepatic Encephalopathy
Teddy Salan1, Varan Govind1, and Sameer Vyas2
1University of Miami, Miami, FL, United States, 2Post Graduate Institute of Medical Education & Research, Chandigarh, India
MRI methods have been used to measure increased brain water content in hepatic encephalopathy (HE) patients. However, these methods lack specificity to measure the increased water content from either the intracellular or extracellular compartment. In this work, we use a free-water eliminated diffusion tensor imaging (FWE-DTI) data processing approach to calculate the free water volume content fraction (fFW) in the brains of HE and healthy control subjects. This water fraction is considered as a measure of water fraction contained in the extra-axonal and sulcal spaces. We found significant fFW increases among HE patients indicating low-grade edema and glial swelling.
|
|||
1677.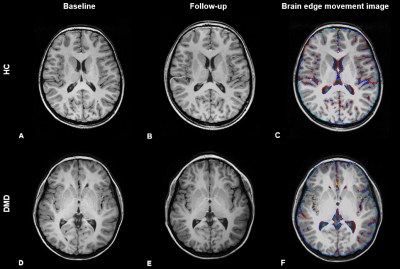 |
Preliminary results of longitudinal brain volume analyses in adolescents with Duchenne muscular dystrophy
Mariken C.R. Hoegen1,2, Nathalie Doorenweerd1,2,3, Emma M. Broek1, Kieren G. Hollingsworth4, Chiara Marini Bettolo5, Jos G.M. Hendriksen 6,7, Erik H. Niks2,8, Volker Straub3, and Hermien E. Kan1,2
1Department of Radiology, Leiden University Medical Center, Leiden, Netherlands, 2Duchenne Center Netherlands, Leiden, Netherlands, 3John Walton Muscular Dystrophy Research Centre, Newcastle upon Tyne, United Kingdom, 4Translational and Clinical Research Institute, Newcastle University, Newcastle upon Tyne, United Kingdom, 5Faculty of Medical Sciences, John Walton Muscular Dystrophy Research Centre, Newcastle upon Tyne, United Kingdom, 6Expertise Center Kempenhaeghe, Heeze, Netherlands, 7Duchenne Center Netherlands, Heeze, Netherlands, 8Department of Neurology, Leiden University Medical Center, Leiden, Netherlands
Clinical symptoms in Duchenne muscular dystrophy (DMD) not only affect the skeletal muscle but also the brain. We explored brain volume changes over a 2-4 year period in adolescents with DMD versus healthy controls (HC). Our preliminary results show no difference in growth curves between groups. We found a consistently lower total grey matter volume and no differences in white matter volume in DMD. Our data suggest that the differences in brain volume in DMD are non-progressive within the assessed age range of 8-20 years.
|
|||
1678.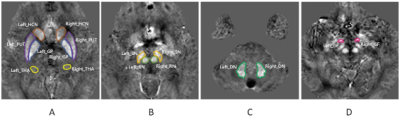 |
Cerebral iron deposition in gray nucleus in type 2 diabetes mellitus patients and the correlation with metabolic disorders
Yangyingqiu Liu1, Na Liu1, Yanwei Miao1, Ailian Liu1, Jiazheng Wang2, and Yishi Wang2
1Department of Radiology, First Affiliated Hospital of Dalian Medical University, Dalian, China, 2Philips Healthcare, Beijing, China
Iron deposition of the gray nucleus is quantitatively assessed by magnetic sensitivity value (MSV)using quantitative susceptibility mapping (QSM), and its’ correlation to metabolic disorders index is also analyzed in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM).The results show that increased MSV value of gray nucleus in T2DM patients may be associated with metabolic disorders.
|
|||
1679.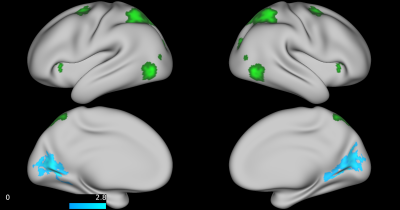 |
Examining the association between sluggish cognitive tempo and functional connectivity in children with ADHD: A pilot study
Adebayo B Braimah1, Jonathan A Dudley1, Jeffery Epstein2, Leanne Tamm2, and Stephen P Becker2
1Imaging Research Center, Cincinnati Children's Hospital Medical Center, Cincinnati, OH, United States, 2Behavioral Medicine and Clinical Psychology, Cincinnati Children's Hospital Medical Center, Cincinnati, OH, United States
Sluggish cognitive tempo (SCT) is a behavioral phenotype characterized by excessive daydreaming that is frequently present in children with ADHD. This study examined functional connectivity in children with ADHD and high SCT, children with ADHD and low SCT, and typically developing children. Resting state fMRI data were acquired and analyzed to examine group differences as well as associations with ordinal ADHD and SCT symptom scores. Three a priori seeds were generated from NeuroSynth to investigate connectivity patterns associated with default mode, attention, and orienting domains. SCT scores were negatively associated with connectivity between attentional and medial visual areas.
|
|||
1680.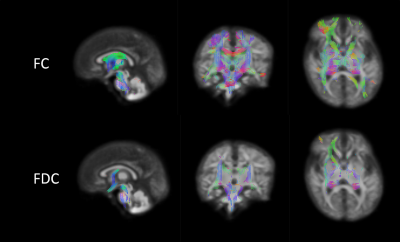 |
Fibre-specific white matter changes in neonates born to women prescribed methadone in pregnancy
Manuel Blesa Cábez1, Thijs Dhollander2, Victoria J Monnelly1, Alan J Quigley3, Scott I Semple4, Mark E Bastin4, and James P Boardman1
1MRC Centre for Reproductive Health, University of Edinburgh, Edinburgh, United Kingdom, 2Developmental Imaging, Murdoch Children's Research Institute, Melbourne, Australia, 3Department of Radiology, Royal Hospital for Sick Children, Edinburgh, United Kingdom, 4Edinburgh Imaging, University of Edinburgh, Edinburgh, United Kingdom
Methadone is often used for medication-assisted treatment of heroin addiction during pregnancy. Children with prenatal exposure to the drug are at increased risk of neurodevelopmental and behavioural impairment. We did fixel-based analysis with a group of 20 term born infants whose mothers had been prescribed methadone during pregnancy for the treatment of heroin addiction and a control group of 20 control infants. There was significant widespread reduction across the WM in fiber-bundle cross-section and fiber density and cross-section in the exposed group, this suggests that affected fibre bundles are less developed, similar to WM structures in preterm born babies.
|
|||
1681.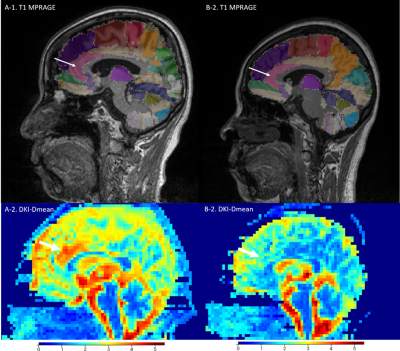 |
Correlations between microstructural changes of anterior cingulum cortex and cerebral small vascular disease induced depression : A DKI Study
Zhenyu Pan1, Kun li1, Dongtao Liu2, Xiuqin Jia1, Qiao Bu1, Rui Jia1, Tao Jiang1, Yueluan Jiang3, Qinglei Shi3, and Lichun Zhou2
1Department of Radiology, Beijing Chao-Yang Hospital, Beijing, China, 2Department of Neurology, Beijing Chao-Yang Hospital, Beijing, China, 3MR Scientific Marketing, Diagnosis Imaging, Siemens Healthineers China, Beijing, China
Diffusion kurtosis imaging (DKI) is an advanced diffusion model based on an extender b value which characterizes water diffusion process as non-gaussian distribution, accordingly parameters derived from DKI are highly sensitive to changes in the microstructural tissue organization and the complexity of anisotropic environments. This study aimed to investigate the correlation between the microstructural changes of anterior cingulum cortex (ACC) and depression in patients with cerebral small vascular disease (CSVD) by applying diffusion Kurtosis imaging.
|
|||
1682.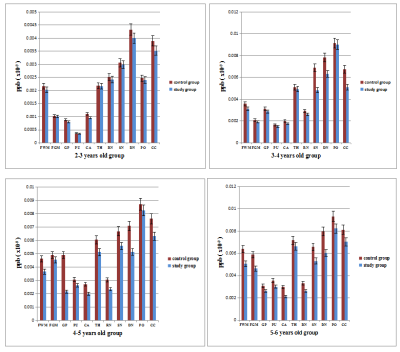 |
Application of quantitative susceptibility mapping of brain iron content in children with autism
Shilong Tang1 and Lisha Nie2
1Children's Hospital of Chongqing Medical University, Chongqing, China, 2GE Healthcare, MR Research China, Beijing, Beijing, China
ASD is caused by multiple factors,some of the pathogenic factors or possible pathogenic factors have not been clearly identified. For example, the detection of trace elements in some children with ASD found that iron content was lower than normal. Whether the lower-than-normal level of trace iron causes the lower-than-normal level of brain iron remains to be further confirmed, as does the direction of causality, i.e., whether the abnormal level of brain iron leads to the occurrence of the disease or whether the disease leads to the abnormal level of brain iron .
|
|||
1683.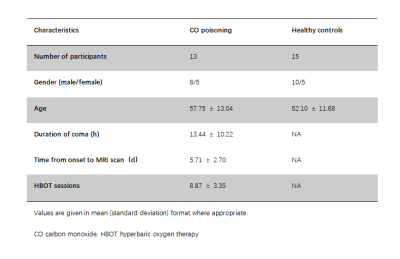 |
Preliminary Assessment of Intravoxel Incoherent Motion Diffusion-Weighted MRI Metrics in Acute Carbon Monoxide Poisoning
Shenghai Wang1, Juan Chen1, Kechao Xu1, Xiyao Zhang1, Haining Li2, and Zhengxian Zhang1
1Yan 'an People's Hospital, Yan 'an, China, 2First Affiliated Hospital of Xi 'an Jiaotong University, Xi 'an, China
The purpuse of this study was to assess microvascular perfusion and microstructural integrity using Intravoxel incoherent motion (IVIM) imaging in patients with acute CO poisoning.Thirteen patients with acute CO poisoning and 15 healthy subjects were enrolled. IVIM MRI was collected using a 3.0-T scanner.The ROIs analysis was perforemed. The IVIM perfusion fraction was significantly reduced in multiple brain regions and IVIM diffusion metirc was significantly decreased in centrum semiovale and multiple subcortical gray matter nucleis in CO poisoning. This study shows that IVIM-DWI may be a promising method to assess brain perfusion and injury in acute CO poisoning.
|
|||
1684.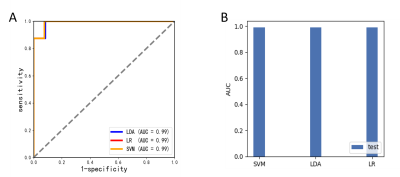 |
A radiomics method to identify non-neuropsychiatric systemic lupus erythematosus with grey matter volume
Xiangliang Tan1, Kan Deng2, Yingjie Mei2, Tianjing Zhang2, Yang Song3, Qiaoli Yao1, and Yikai Xu1
1Medical Imaging Center, Nanfang Hospital, Southern Medical University, Guangzhou, China, 2Philips Healthcare, Guangzhou, China, 3Shanghai Key Laboratory of Magnetic Resonance, East China Normal University, Shanghai, China
The present study tried to use radiomics models to find the neuroanatomical biomarkers that can improve diagnosis in distinguishing non-neuropsychiatric Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (non-NPSLE) patients from controls. The results demonstrate that the grey matter volume parameter is an effective classification feature for the radiomics models to identify non-NPSLE patients from HC subjects. This classification performance may suggest that the proposed method is a promising approach for improving the clinical diagnosis of systemic lupus erythematosus.
|
|||
1685.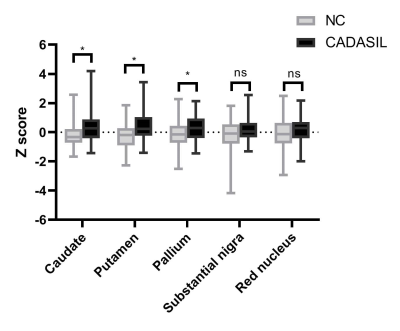 |
Demyelination is related to deep gray matter iron deposition in CADASIL patients
hui hong1, shuyue wang1, xinfeng Yu2, Yererfan Jiaerken2, Xiaojun Guan2, and minming zhang2
1radiology, Zhejiang University, hangzhou, China, 2radiology, the second affiliated hospital of zhejiang university, school of medicine, hangzhou, China
Cerebral autosomal dominant arteriopathy with subcortical infarcts and leukoencephalopathy (CADASIL) is a genetic cerebral small vessel disease. Apart from widespread white matter hyperintensities (WMHs), increased deep gray matter iron deposition was also suggested. Whether there is an association between white matter injury and deep gray matter iron deposition is undetermined. Iron deposition in deep gray matter was supposed due to the secondary degeneration followed by destroyed white matter integrity. Therefore, we investigate the iron deposition the relationship between white matter integrity and iron deposition to reveal the underlying mechanism of deep gray matter iron deposition in CADASIL patients.
|
|||
1686.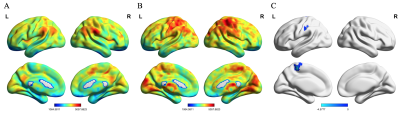 |
Altered global functional network connectivity and its relationship to cognitive dysfunction in rheumatoid arthritis
Zeyu Liu1, Bo Hou1, and Feng Feng1
1Peking Union Medical College Hospital, Beijing, China
Patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA), a systemic autoimmune disease, had cognitive dysfunction. Resting-state functional MRI wasutilized to explore the whole-brain functional network connectivity in RA patients. The whole-brain functional connectivity strength in RA patients was altered and significantly correlated to cognitive performance.
|
|||
1687.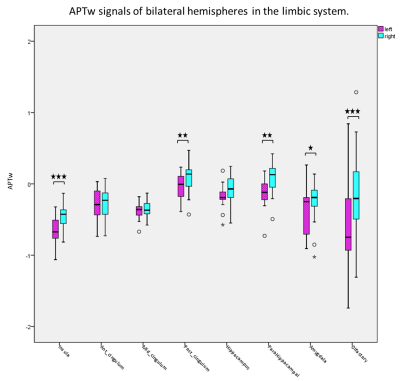 |
Limbic System Lateralization of Amide Proton Transfer Weighted Signals in Young Healthy Subjects
Yuhan Jiang1, Weiwei Wang1, Peipei Chang1, Yingqiu Liuyang1, Bingbing Gao1, Yiwei Che1, Renwang Pu1, Qingwei Song1, Ailian Liu1, Zhiwei Shen2, Jiazheng Wang2, and Yanwei Miao1
1the First Affiliated Hospital of Dalian Medical University, Dalian, China, 2Philips Healthcare, Beijing, China
Amide proton transfer weighted (APTw) imaging is a novel molecular imaging technique to acquire the proton exchanged signals from the amide in proteins or peptides to water. Previous studies discover lateralization in the brain structure and function, including limbic system. However, it is not clear whether APTw also has lateral advantage. In this prospective study, we applied the automatic brain segmentation method to quantify the APTw signal values of limbic system in young healthy subjects. Significant differences of APTw signals between left and right brain hemisphere were found, which may suppose related with right-handedness.
|
|||
1688.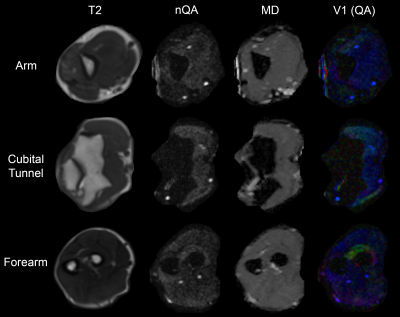 |
Diffusion Tensor Imaging in Cubital Tunnel Syndrome
Ryckie George Wade1, Timothy T Griffiths1, Robert Flather1, Irvin Teh1, Hamied A Haroon2, David Shelley3, Sven Plein1, and Grainne Bourke3
1University of Leeds, Leeds, United Kingdom, 2University of Manchester, Manchester, United Kingdom, 3Leeds Teaching Hospitals, Leeds, United Kingdom
Cubital Tunnel Syndrome (CuTS) is the 2nd most common compressive neuropathy affecting 6% of the population. Surgical decompression is the most effective treatment, but clinicians lack a reliable test to select patients for surgery. Diffusion tensor imaging (DTI) characterises tissue microstructure and so, DTI was acquired from 14 controls and 8 patients awaiting surgery in this proof-of-concept study. Patients had a significantly lower FA and higher RD than controls, throughout the length of the ulnar nerve. Therefore, DTI may add objective evidence of the ‘health’ of the ulnar nerve and aid the management of cubital tunnel syndrome.
|
|||
1689.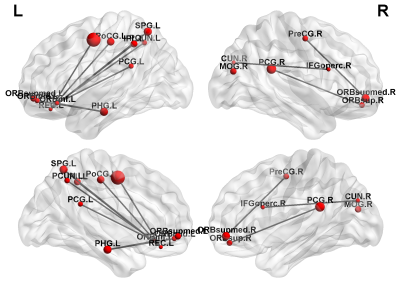 |
Resting-state functional connectivity and brain network abnormalities in depressive patients with suicidal ideation
Jun-Cheng Weng1,2,3, Yu-Syuan Chou4, Yuan-Hsiung Tsai5,6, and Vincent Chin-Hung Chen3,5
1Department of Medical Imaging and Radiological Sciences, and Bachelor Program in Artificial Intelligence, Chang Gung University, Taoyuan, Taiwan, 2Medical Imaging Research Center, Institute for Radiological Research, Chang Gung University and Chang Gung Memorial Hospital at Linkou, Taoyuan, Taiwan, 3Department of Psychiatry, Chang Gung Memorial Hospital, Chiayi, Taiwan, 4Department of Radiology, Taichung Veterans General Hospital, Taichung, Taiwan, 5School of Medicine, Chang Gung University, Taoyuan, Taiwan, 6Department of Diagnostic Radiology, Chang Gung Memorial Hospital, Chiayi, Taiwan
Our study aimed to investigate whether changes in brain function measured with functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) can be detected among individuals with depressive disorders and suicidal ideation, including amplitude of low-frequency fluctuation (ALFF), regional homogeneity (ReHo), and graph theoretical analysis (GTA). We results suggest that brain functional connectivity may be affected in depressive patients with suicidal ideation. The findings from present study can serve as the basis for further algorithm studies by machine learning method to stratify the risk population.
|
The International Society for Magnetic Resonance in Medicine is accredited by the Accreditation Council for Continuing Medical Education to provide continuing medical education for physicians.