Yi Sui1, Jiahui Li1, Joshua D. Trzasko1, Arvin Arani1, Kevin Glaser1, Phillip J. Rossman1, Ziying Yin1, Meng Yin1, and Richard L. Ehman1
1Radiology, Mayo Clinic, Rochester, MN, United States
1Radiology, Mayo Clinic, Rochester, MN, United States
A free-breathing 3D MR elastography technique (TURBINE-MRE) was developed for liver MRE, providing motion-resolved wave images and stiffness maps in single 4-minute free breathing acquisition.
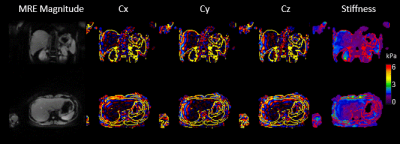
Figure
3: Results of free-breathing TURBINE-MRE from
a healthy volunteer. The animation shows the magnitude, x-, y-, z- components
of curl wave information, and stiffness maps at 5 respiratory states. The
contours on the wave images and stiffness map delineate the boundaries of the liver
and other organs. (High definition movie can be found at https://youtu.be/yw9yOhGvAi8 )
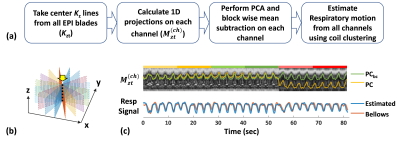
Figure 2: Respiratory motion estimation from k-space data. (a) Flow chart for respiratory motion estimation. (b) TURBINE k-space trajectory. The center Kz lines (dashed line) from all EPI blades were taken out for motion estimation. (c) Mzt: 1D z-projection of whole imaging volume along time. PC: The largest principal component of Mzt. PCbc block-wise baseline-corrected PC. Each colored ribbon marks a MRE direction as a block. The respiratory motion (blue) was estimated from all channels using a coil clustering method and was consistent with the respiratory bellows signal (orange).