Julio A. Oscanoa1,2, Frank Ong3, Zhitao Li2,3, Christopher M. Sandino3, Daniel B. Ennis2,4, Mert Pilanci3, and Shreyas S. Vasanawala2
1Department of Bioengineering, Stanford University, Stanford, CA, United States, 2Department of Radiology, Stanford University, Stanford, CA, United States, 3Department of Electrical Engineering, Stanford University, Stanford, CA, United States, 4Cardiovascular Institute, Stanford, CA, United States
1Department of Bioengineering, Stanford University, Stanford, CA, United States, 2Department of Radiology, Stanford University, Stanford, CA, United States, 3Department of Electrical Engineering, Stanford University, Stanford, CA, United States, 4Cardiovascular Institute, Stanford, CA, United States
Our Coil Sketching approach can be used to accelerate and improve memory efficiency of iterative reconstruction with virtually no penalty on reconstruction accuracy.
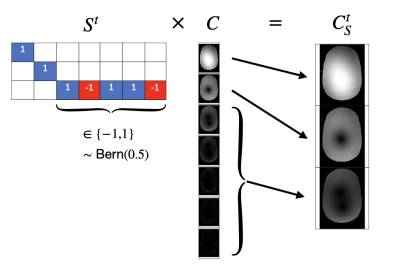
Figure 1. Structure of Eigen-Sketching matrix $$$S^t$$$. Effectively, matrix $$$S^t$$$ sketches the sensitivity map operator $$$C$$$, yielding a reduced sensitivity map operator $$$C^t_S$$$ with less coils. Similar to coil compression4-7(CC) the Eigen-Sketching matrix considers the high-energy virtual coils; but unlike CC, the matrix also considers a sketched coil. This sketched coil is formed by multiplying the remaining coils by “-1” or “+1” with probability 50% each and then summing them together. In sketching literature, this scheme is denoted as CountSketch.10-12
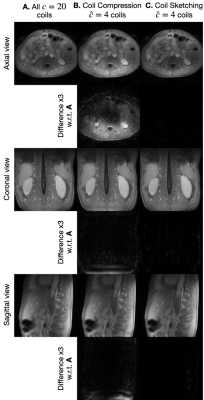
Figure 5. Image comparison of 3D Cones reconstruction for (A) reconstruction with all $$$c=20$$$ coils, (B) coil compression with $$$\hat{c}=4$$$ coils, (C) our proposed Coil Sketching with $$$\hat{c}=4$$$ coils. Coil compression with $$$\hat{c}=4$$$ presents significantly lower image quality and shading artifacts, specially towards the lower borders of the volume. Coil Sketching yields virtually the same image as reconstruction with all $$$c=20$$$ coils.