Lydia M. Le Page1, Jayson Ball2, Linda Watkins2, and Myriam Chaumeil1
1Physical Therapy and Rehabilitation Science, Radiology and Biomedical Imaging, UCSF, San Francisco, CA, United States, 2Department of Psychology & Neuroscience & the Center for Neuroscience, University of Colorado, Boulder, CO, United States
1Physical Therapy and Rehabilitation Science, Radiology and Biomedical Imaging, UCSF, San Francisco, CA, United States, 2Department of Psychology & Neuroscience & the Center for Neuroscience, University of Colorado, Boulder, CO, United States
We have optimized a protocol for NMR analysis of metabolites from freshly isolated adult rat brain microglia, and can distinguish creatine, creatine phosphate, o-phosphoethanolamine, taurine, glutamate and aspartate. We will apply this protocol to neuroinflammatory disease models.
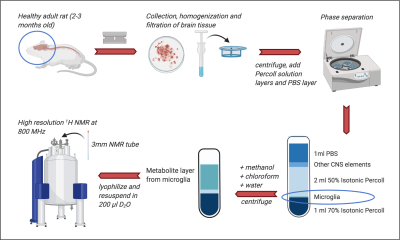
Microglial isolation protocol followed by metabolite extraction for NMR. Brains were removed from healthy rats, minced with a razor blade and homogenized before straining and centrifugation. Layers of 70% and 50% Percoll solution and PBS were added. Centrifugation separated microglia from the other CNS elements. Microglia was added to ice-cold methanol, chloroform and water. The metabolite layer was then lyophilized before resuspension in 200μl D2O and acquisition of NMR spectra at 800MHz. Created in BioRender.com
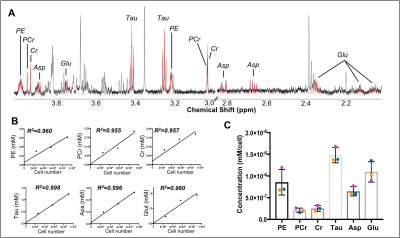
(A) Spectral fitting of six microglia-specific metabolites shown on spectrum from 3 rats combined, using Chenomx software: PE = o-phosphoethanolamine, PCr = creatine phosphate, Asp = apartate, Glu = glutamate, Tau = taurine (B) Total concentration of the six microglia-specific metabolites in all brain samples, expressed in mM. These graphs show that the levels of metabolites are linearly increasing with cell number, with good reproducibility. (C) Concentration of the six microglia specific metabolites expressed as mM/cell.
