Jan Martin1, Alexis Reymbaut2, Michael Uder3, Frederik Bernd Laun3, and Daniel Topgaard1
1Lund University, Lund, Sweden, 2Random Walk Imaging AB, Lund, Sweden, 3Institute of Radiology, University Hospital Erlangen, Friedrich-Alexander-Universität Erlangen-Nürnberg (FAU), Erlangen, Germany
1Lund University, Lund, Sweden, 2Random Walk Imaging AB, Lund, Sweden, 3Institute of Radiology, University Hospital Erlangen, Friedrich-Alexander-Universität Erlangen-Nürnberg (FAU), Erlangen, Germany
We here implement D-R1-R2 distribution imaging using a 20-min acquisition protocol with tensor-valued diffusion encoding and varying TR and TE. Monte Carlo data inversion yields nonparametric distributions,
statistical descriptors, and orientation-resolved properties of white matter.
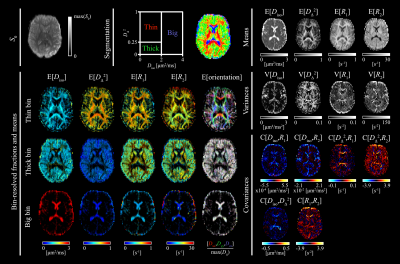
Statistical descriptors derived from the 6D $$$\bf D$$$-$$$R_1$$$-$$$R_2$$$ distributions shown for a representative axial slice. Displayed are the median values of 100 per-bootstrap means $$$\mathrm{E}$$$, variances $$$\mathrm{V}$$$, and covariances $$$\mathrm{C}$$$. Bin-resolved fractions and means obtained by binning the parameter space to isolate WM ("thin"), GM ("thick"), and CSF ("big"). $$$\bf D$$$ is characterized in terms of the isotropic diffusivity $$$D_{iso} = (D_{||} + 2 D_\bot)/3$$$ and normalized anisotropy $$$D_\Delta = (D_{||} - D_\bot)/D_{iso}$$$.
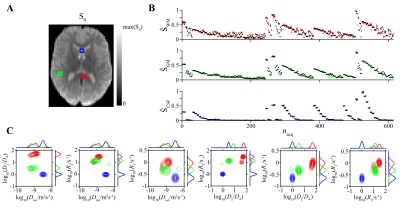
Experimental data in three representative voxels. (A) $$$S_0$$$ map with labeled voxels: WM in the corpus callosum (red), cortical GM (green), and CSF in the frontal ventricle (blue). (B) Normalized signal $$$S$$$ versus acquisition index $$$n_{acq}$$$ (measured: black, fitted: colors correspond to the selected voxels). (C) Selected 2D projections of the 6D $$$\bf{D}$$$-$$$R_1$$$-$$$R_2$$$ nonparametric distributions obtained by the Monte Carlo inversion.
