Hong-Hsi Lee1, Els Fieremans1, Jiangyang Zhang1, and Dmitry S Novikov1
1New York University School of Medicine, New York, NY, United States
1New York University School of Medicine, New York, NY, United States
We propose a universal denoising pipeline for non Cartesian MRI. After sampling non Cartesian data in a Cartesian grid, we unwrap the noise correlation in Cartesian k space, identify and remove the noise using well established denoising method. The applicability is demonstrated in brain data.
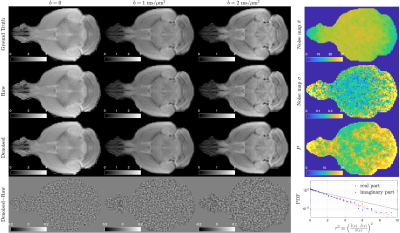
Fig. 3. Demonstrate of noise removal pipeline (USD) on dMRI data in an ex vivo mouse brain (4b=0 images + 60 DWIs). The noise level in DWIs of b = [1, 2] ms/µm2 was reduced dramatically after denoising, and the image residual maps have no anatomical structures. Further, the noise maps before and after re-normalization ($$$\hat{\sigma}$$$ and σ) are both smooth, and the number P of signal components in PCA domain is low. Finally, the histogram of image residual r is normally distributed and below the reference line of slop -1/2 in semi-log scale, indicating that USD only removes the noise.
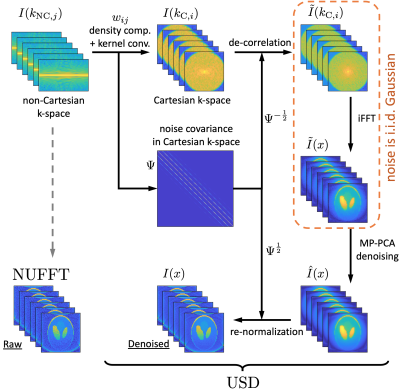
Fig. 1. The pipeline of Universal Sampling Denoising (USD) for non-Cartesian k-space data, as detailed in Theory section. Here we take the radial trajectory as an example. The key idea in USD is to de-correlate the noise statistics in gridded/Cartesian k-space before applying any denoising algorithm in the image space. The noise covariance matrix in Cartesian k-space is determined by coefficients of density compensation and convolution with interpolation kernel. After denoising using MP-PCA algorithm, re-normalization of the denoised image recovers the original image contrast.