Nan Wang1,2, Yibin Xie1, Zhaoyang Fan1,2, Sen Ma1,2, Rola Saouaf3, Yu Guo1,4, Stephen L. Shiao5,6, Anthony G. Christodoulou1,2, and Debiao Li1,2
1Biomedical Imaging Research Institute, Cedars Sinai Medical Center, Los Angeles, CA, United States, 2Department of Bioengineering, University of California, Los Angeles, Los Angeles, CA, United States, 3Department of Imaging, Cedars Sinai Medical Center, Los Angeles, CA, United States, 4Department of Radiology, Tianjin First Central Hospital, Tianjin, China, 5Department of Radiation Oncology, Cedars-Sinai Medical Center, Los Angeles, CA, United States, 6Biomedical Sciences, Division of Immunology, Cedars-Sinai Medical Center, Los Angeles, CA, United States
1Biomedical Imaging Research Institute, Cedars Sinai Medical Center, Los Angeles, CA, United States, 2Department of Bioengineering, University of California, Los Angeles, Los Angeles, CA, United States, 3Department of Imaging, Cedars Sinai Medical Center, Los Angeles, CA, United States, 4Department of Radiology, Tianjin First Central Hospital, Tianjin, China, 5Department of Radiation Oncology, Cedars-Sinai Medical Center, Los Angeles, CA, United States, 6Biomedical Sciences, Division of Immunology, Cedars-Sinai Medical Center, Los Angeles, CA, United States
The
low-dose Multitasking DCE was proposed for DCE quantification with whole-breast
coverage and high spatiotemporal resolution at 20% dose. The technique showed excellent
image quality and repeatability, and matched diagnosis from clinical standard.
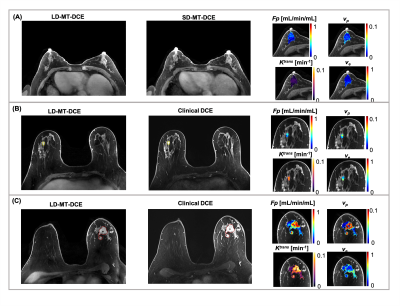
Figure
2: Representative maps of kinetic parameters showing normal breast tissue from
a 52-year-old healthy volunteer (A), a benign tumor (marked by a yellow solid
boundary) from a 49-year-old patient (B), and a malignant tumor (marked by a
red dashed boundary) from a 65-year-old patient (C). The gray-scale images
display peak-enhanced LD-MT-DCE images and the standard-dose images at the same
slice. The overlaid colormaps represents Fp, vp, Ktrans,
and ve, respectively.
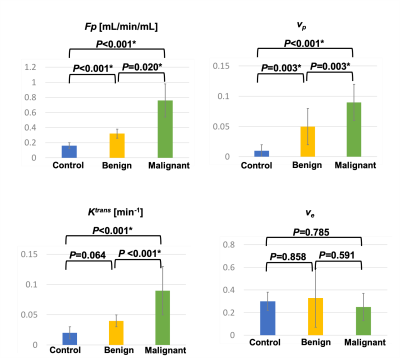
Figure
4: Mean and standard deviation measurements of Fp, vp, Ktrans,
and ve for control group, and benign and malignant tumors in patient
group. The P value of each pair by one-way ANOVA with Tukey test are marked on
top of the bar graphs. Fp, vp, and Ktrans were
significantly different between control and malignant tumor, and between benign
and malignant tumors; Fp, and vp were significantly
different between control and benign tumors. * indicates statistically
significant difference.