Anastasia Fotaki1,2, Karl Kunze1, Harith Alam2, Yasodhara Emmanuel2, Alessandra Frigiola2, Kuberan Pushparajah1,2, René Botnar1, and Claudia Prieto1
1School of Biomedical Engineering and Imaging Sciences, King's College London, London, United Kingdom, 2Adult Congenital Heart Disease Department, Guy’s and St Thomas’s Hospital, London, United Kingdom
1School of Biomedical Engineering and Imaging Sciences, King's College London, London, United Kingdom, 2Adult Congenital Heart Disease Department, Guy’s and St Thomas’s Hospital, London, United Kingdom
A free-breathing contrast-free 3D whole-heart sequence, MTC-BOOST, for simultaneous bright- and black-blood visualisation has been validated in a cohort of 35 patients with CHD, demonstrating improved image quality and promising potential integration in clinical settings
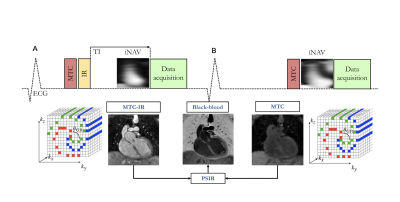
Magnetization transfer with an inversion pulse is used in odd heartbeats (A), magnetization transfer solely is exploited in even heartbeats (B). A short TI is used for fat saturation in odd heartbeats, spectral presaturation (Fat Sat) is used in even heartbeats. Data acquisition is performed using a 3D Cartesian trajectory with spiral profile order . A low‐resolution 2D iNAV is acquired in each heartbeat. The bright‐blood MTC‐IR BOOST and MTC BOOST volumes are non‐rigidly motion corrected and combined in a PSIR‐like reconstruction to generate a complementary black‐blood volume
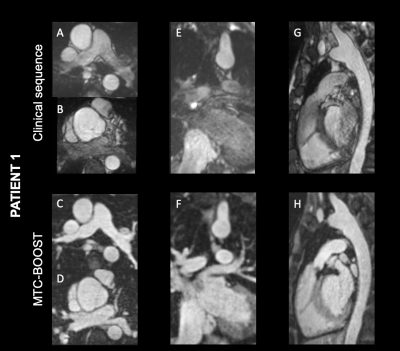
Bright blood images for a patient with congenital aortic stenosis, post Ross procedure with moderate regurgitation along the pulmonary homograft. Luminal signal loss in the pulmonary arteries due to turbulent flow and in the pulmonary veins and left atrium due to off resonance effects is observed with the clinical 3D sequence. MTC-BOOST demonstrates uniform signal in all cardiac and vascular structures.
