Anna M Chen1, Teresa Gerhalter1, Seena Dehkharghani1,2, Rosemary Peralta1, Fatemeh Adlparvar1, James S Babb1, Tamara Bushnik3, Jonathan M Silver4, Brian S Im3, Stephen P Wall5, Ryan Brown1,6, Steven Baete1,6, Ivan I Kirov1,2,6, and Guillaume Madelin1
1Center for Biomedical Imaging, Department of Radiology, New York University Grossman School of Medicine, New York, NY, United States, 2Department of Neurology, New York University Grossman School of Medicine, New York, NY, United States, 3Department of Rehabilitation Medicine, New York University Grossman School of Medicine, New York, NY, United States, 4Department of Psychiatry, New York University Grossman School of Medicine, New York, NY, United States, 5Ronald O. Perelman Department of Emergency Medicine, New York University Grossman School of Medicine, New York, NY, United States, 6Center for Advanced Imaging Innovation and Research, Department of Radiology, New York University Grossman School of Medicine, New York, NY, United States
1Center for Biomedical Imaging, Department of Radiology, New York University Grossman School of Medicine, New York, NY, United States, 2Department of Neurology, New York University Grossman School of Medicine, New York, NY, United States, 3Department of Rehabilitation Medicine, New York University Grossman School of Medicine, New York, NY, United States, 4Department of Psychiatry, New York University Grossman School of Medicine, New York, NY, United States, 5Ronald O. Perelman Department of Emergency Medicine, New York University Grossman School of Medicine, New York, NY, United States, 6Center for Advanced Imaging Innovation and Research, Department of Radiology, New York University Grossman School of Medicine, New York, NY, United States
Mean TSC was lower in mild TBI than in controls across 12 brain regions, but only the caudate reached statistical significance. Significant FA differences only occurred in frontal WM, while none were detected for ADC. TSC changes existed in mild TBI and occurred with similar frequency as FA.
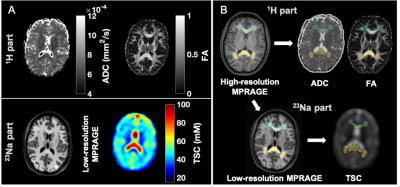
Figure 2: Example of multimodal image segmentation and registration. A) Top: During the 1H session, apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) and fractional anisotropy (FA) maps were obtained. Bottom: During the 23Na session, total sodium concentration maps (TSC) and low-resolution MPRAGE images for registration were acquired. B) ROIs were obtained from the high-resolution MPRAGE, then registered to the TSC using the low-resolution MPRAGE and to the diffusion maps using the diffusion-b0 image.
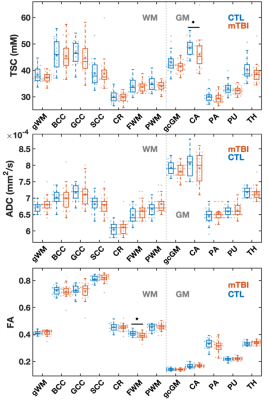
Figure 3: Boxplots of TSC, ADC, and FA distributions in mTBI and control (CTL) groups. Boxplots exclude the three oldest mTBI patients who lacked age-matched controls. FWM FA and caudate TSC were lower in mTBI patients compared to controls (MW, ♦: p<0.05). Note that nine out of 12 ROIs revealed lower median TSC values in mTBI patients compared to controls. gWM: global WM; CC: corpus callosum; BCC: body of CC; GCC: genu of CC; SCC: splenium of CC; CR: corona radiata; FWM: frontal WM; PWM: posterior WM; gcGM: global cortical GM; CA: caudate; PA: pallidus; PU: putamen; TH: thalamus.
