Mohammed Salman Shazeeb1, Elizabeth Degrush2,3, Zeynep Vardar1, Clifford Lindsay1, Matthew Gounis1, and Nils Henninger2,3
1Department of Radiology, University of Massachusetts Medical School, Worcester, MA, United States, 2Department of Neurology, University of Massachusetts Medical School, Worcester, MA, United States, 3Department of Psychiatry, University of Massachusetts Medical School, Worcester, MA, United States
1Department of Radiology, University of Massachusetts Medical School, Worcester, MA, United States, 2Department of Neurology, University of Massachusetts Medical School, Worcester, MA, United States, 3Department of Psychiatry, University of Massachusetts Medical School, Worcester, MA, United States
The multidrug treatment therapy with the statin
cocktail (simvastatin, L-Arginine, and tetrahydrobiopterin) that targets
augmentation of the endothelial nitric
oxide synthase pathway may improve cerebral blood flow and cognitive
function in patients with Alzheimer’s Disease.
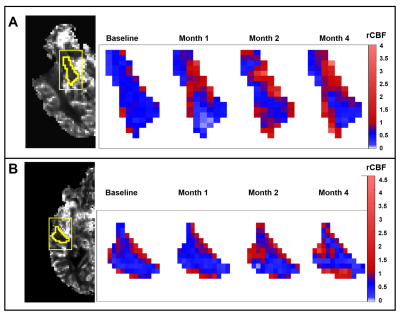
Time-series
cerebral blood flow rCBF images are shown for the right
hippocampus (A) and right middle temporal lobe (B) of Patient 1
from Group 1. With the progression of time, the rCBF values show an increased
signal for structures in the limbic system and the cortical area for all
patients in Group 1.
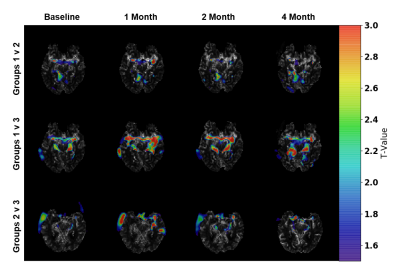
T-value maps generated
using the SPM12 software results are shown for the MCA region of the brain
comparing all the patient groups at each time-point. A single patient rCBF map
is shown with intensity overlays, which show the regional differences for each
group comparison. Higher T-values indicate greater differences compared to the
lower T-values. Groups 1 and 3 show the greatest difference between each other
compared to the other group comparisons particularly at the 1-month and 2-month
time-points. By 4 months, groups 1 and 3 showed more differences compared to
the others.