Chathura Kumaragamage1, Anastasia Coppoli1, Peter B Brown1, Scott McIntyre1, Terence W Nixon1, Henk M De Feyter1, Graeme Mason1, and Robin A de Graaf1
1Department of Radiology and Biomedical Imaging, Magnetic Resonance Research Center, Yale University, New Haven, CT, United States
1Department of Radiology and Biomedical Imaging, Magnetic Resonance Research Center, Yale University, New Haven, CT, United States
An ECLIPSE-IVS
method with a TE = 22.2 ms utilizing GOIA-WURST RF pulses (Tp = 3ms,
BW = 15 kHz) was developed for macromolecule-nulled MRSI acquisitions. Results demonstrate
robust extracranial lipid suppression with artifact-free metabolic maps.
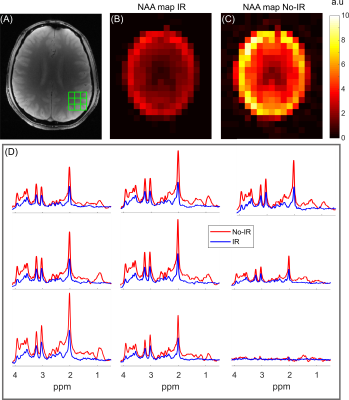
Figure 4. MRSI data acquired (TE/TR = 22.2/2500 ms, 10.2 min acquisition time, 1 x 1 cm2
grid) with IR and no-IR methods. (A) The axial slice imaged, with the nine
voxel regions overlaid. (B-C) NAA maps from both methods. (D) Voxel locations
from the grid illustrated in (A). Both methods demonstrate high quality spectra,
despite the overall reduced amplitude with the IR method. The IR data
demonstrate minimal macromolecular resonances evident by the flat baseline,
compared to the No-IR data.
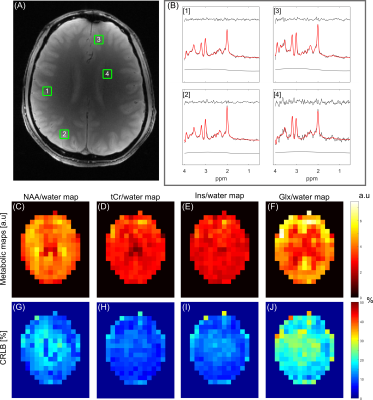
Figure 5. Summary of MRSI (TE/TR = 22.2/2500 ms) data in Figure 4 with LCModel
fitting of the IR data. (A) The corresponding axial slice image, with four
voxel locations marked. (B) LCModel fitting of spectral locations in (A). In
each panel the residual, fitted spectra overlaid on the measured spectra, and
the baseline are illustrated. (C-F) Metabolic maps referenced to water for NAA,
tCr, Ins, and Glx. (G-J) illustrate corresponding CRLB maps for the metabolic
maps in (C-F).
