Zepeng Wang1,2 and Fan Lam1,2
1Department of Bioengineering, University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign, Urbana, IL, United States, 2Beckman Institute for Advanced Science and Technology, Urbana, IL, United States
1Department of Bioengineering, University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign, Urbana, IL, United States, 2Beckman Institute for Advanced Science and Technology, Urbana, IL, United States
We propose a novel method to achieve fast high-resolution 3D DW-MRSI. In vivo experimental results have been obtained, which demonstrated that the proposed method can provide high-SNR DW-MRSI of the brain and metabolite-specific ADC maps with the highest ever resolution (3.4×3.4×5.3 mm3).
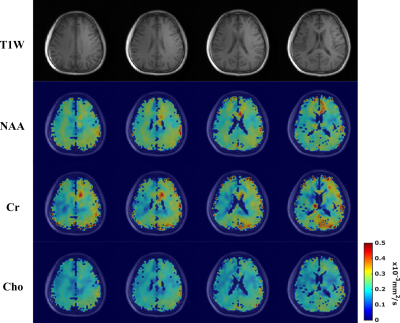
Figure 5. Estimated metabolite ADC maps from the 64x64x12
data at a nominal resolution of 3.4×3.4×5.3 mm3. Row 1 shows the
T1-weighted images for several slices from the 3D imaging volume. Rows 2-4
display the ADC maps of NAA, Cr, and Cho (from Gdir1) for the corresponding
slices, respectively. Patterns of white matter and gray matter diffusion
property differences (white matter having larger metabolite ADCs than gray matter)
can be visualized due to the high resolution. To the best of our knowledge, these
are the highest resolution metabolite ADC maps ever produced.
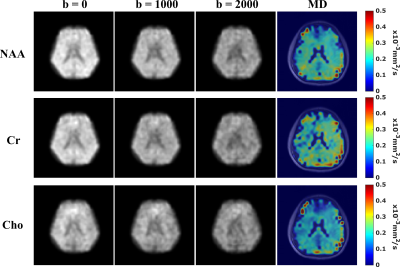
Figure 4. Reconstructed DW metabolite and MD maps from the
32x32x8 data. Columns 1-3 present the metabolite maps at 3 b-values from Gdir1.
Column 4 shows the MD maps of the matched slice for NAA, Cr, and Cho
respectively (Rows 1-3). The MD maps are generated by averaging the registered
ADC maps fitted from 3 orthogonal diffusion encoding directions and then
overlaid on aligned anatomical images. DW contrast can be observed and
the ranges and values of the MD for each metabolite are consistent with reported
values7-9,17.
