Ali Caglar Özen1,2, Simon Reiss1, Thomas Lottner1, Dursun Korel Yildirim3,4, Ozgur Kocaturk3,5, and Michael Bock1
1Deptartment of Radiology, Medical Physics, University Medical Center Freiburg, University of Freiburg, Freiburg, Germany, 2German Consortium for Translational Cancer Research Partner Site Freiburg, German Cancer Research Center (DKFZ), Heidelberg, Germany, 3Institute of Biomedical Engineering, Bogazici University, Istanbul, Turkey, 4Cardiovascular Branch, Division of Intramural Research, National Heart Lung and Blood Institute, National Institutes of Health, Bethesda, MD, United States, 5Transmural Systems, Andover, MA, United States
1Deptartment of Radiology, Medical Physics, University Medical Center Freiburg, University of Freiburg, Freiburg, Germany, 2German Consortium for Translational Cancer Research Partner Site Freiburg, German Cancer Research Center (DKFZ), Heidelberg, Germany, 3Institute of Biomedical Engineering, Bogazici University, Istanbul, Turkey, 4Cardiovascular Branch, Division of Intramural Research, National Heart Lung and Blood Institute, National Institutes of Health, Bethesda, MD, United States, 5Transmural Systems, Andover, MA, United States
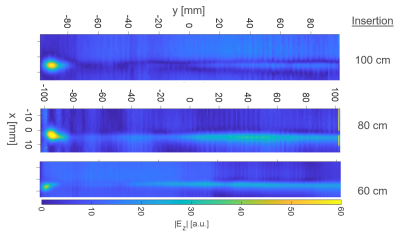
MR-safety of an actively visualized guidewire was evaluated at three different field strengths, for three different insertion lengths using a single setup that consists of an electrooptic sensor, local excitor, and dipole antennae.
Figure
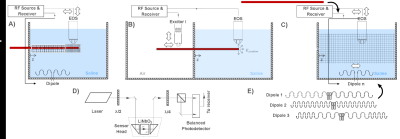
1: Schematic of the TF evaluation approach for AICs and AIGWs. A) Hot spot
detection with high resolution E field mapping during continuous RF excitation
with a dipole antenna. B) TF measurement. C) TF validation by E field mapping
with and without the AIGW. D) A detailed schematic of the electrooptical
sensor. E) Dipole antennae used for generating uncorrelated incident fields.