Jingjing Liu1, Jingliang Cheng1, and Jinxia Zhu2
1Department of MR Imaging, the First Affiliated Hospital of Zhengzhou University, Zhengzhou, China, 2MR Collaboration, Siemens Healthcare Ltd, Beijing, China
1Department of MR Imaging, the First Affiliated Hospital of Zhengzhou University, Zhengzhou, China, 2MR Collaboration, Siemens Healthcare Ltd, Beijing, China
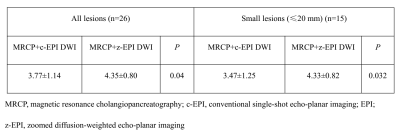
Compared with c-EPI DWI, z-EPI DWI showed remarkable improvements in overall image quality for assessing periampullary carcinoma lesions. Combined with MRCP, the diagnostic accuracy scores were also increased when z-EPI DWI was used.
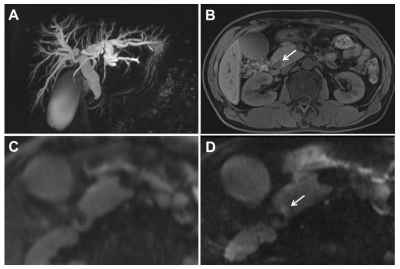
Fig. 2. A 49-year-old man with a distal common bile duct carcinoma. A. Magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography shows marked bile ductular dilatation with distal common bile duct stenosis. Primary pancreatic duct dilatation was not noted. B. A T1-weighted MR image shows a hypointense nodule (arrow) in the periampullary region. C. Conventional single-shot echo-planar imaging (c-EPI) shows no abnormalities in the periampullary region. D. Zoomed diffusion-weighted EPI (z-EPI) shows increased lesion signal intensity with better delineation compared with C.