Ziyu Li1, Qiyuan Tian2, Chanon Ngamsombat2,3, Samuel Cartmell4, John Conklin2,4, Augusto Lio M. Gonçalves Filho2,4, Wei-Ching Lo5, Guangzhi Wang1, Kui Ying6, Kawin Setsompop7,8, Qiuyun Fan2, Berkin Bilgic2, Stephen Cauley2, and Susie Y Huang2,4
1Department of Biomedical Engineering, Tsinghua University, Beijing, China, 2Athinoula A. Martinos Center for Biomedical Imaging, Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, MA, United States, 3Department of Radiology, Siriraj Hospital, Mahidol University, Bangkok, Thailand, 4Department of Radiology, Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, MA, United States, 5Siemens Medical Solutions, Boston, MA, United States, 6Department of Engineering Physics, Tsinghua University, Beijing, China, 7Department of Radiology, Stanford University, Stanford, CA, United States, 8Department of Electrical Engineering, Stanford University, Stanford, CA, United States
1Department of Biomedical Engineering, Tsinghua University, Beijing, China, 2Athinoula A. Martinos Center for Biomedical Imaging, Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, MA, United States, 3Department of Radiology, Siriraj Hospital, Mahidol University, Bangkok, Thailand, 4Department of Radiology, Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, MA, United States, 5Siemens Medical Solutions, Boston, MA, United States, 6Department of Engineering Physics, Tsinghua University, Beijing, China, 7Department of Radiology, Stanford University, Stanford, CA, United States, 8Department of Electrical Engineering, Stanford University, Stanford, CA, United States
Novel generative adversarial network with a 3D generator and 2D discriminator entitled HDnGAN.
Control over image sharpness by adjusting adversarial loss contributions.
Results similar to standard images with longer scan time and superior to those from state-of-the-art denoising methods.
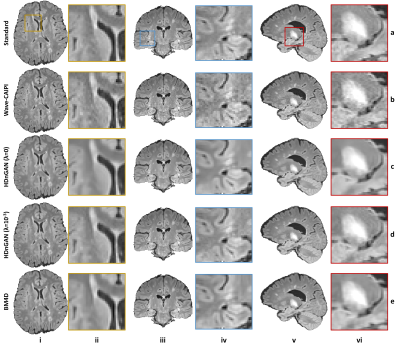
Figure 4. Results
along different directions. Representative axial (column i),
coronal (column iii), and sagittal (column v) image slices and enlarged regions
(columns ii, iv and vi) from different methods including standard (row a),
Wave-CAIPI (row b), HDnGAN (λ=0) (row c), HDnGAN (λ=10-3) (row d) of
3 evaluation subjects.
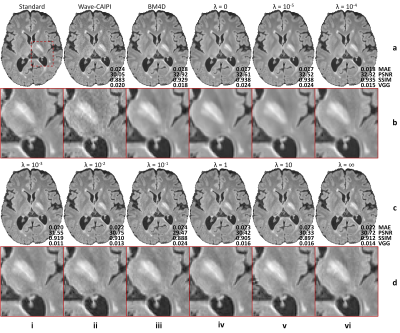
Figure 2. Effects
of the adversarial loss on image quality. Representative axial image slices
(rows a and c) and enlarged regions (rows b and d) from different methods and
weights (λ) of the adversarial loss of a multiple sclerosis patient. Metrics
including the mean absolute error (MAE), peak signal-to-noise ratio (PSNR),
structural similarity index (SSIM), and VGG perceptual loss are listed to
quantify the similarity between images from different methods and the standard
FLAIR image.