Rita Alves1, Rafael Neto Henriques1, Sune Nørhøj Jespersen2,3, and Noam Shemesh1
1Champalimaud Research, Champalimaud Centre for the Unknown, Lisbon, Portugal, 2Center of Functionally Integrative Neuroscience (CFIN) and MINDLab, Department of Clinical Medicine, Aarhus University, Aarhus, Denmark, 3Department of Physics and Astronomy, Aarhus University, Aarhus, Denmark
1Champalimaud Research, Champalimaud Centre for the Unknown, Lisbon, Portugal, 2Center of Functionally Integrative Neuroscience (CFIN) and MINDLab, Department of Clinical Medicine, Aarhus University, Aarhus, Denmark, 3Department of Physics and Astronomy, Aarhus University, Aarhus, Denmark
We provide
a first characterization of non-Gaussian kurtosis sources in stroke via correlation
tensor imaging (CTI). The CTI contrasts enhanced the sensitivity and
specificity of the underlying ischemic alterations at 3 h post onset.
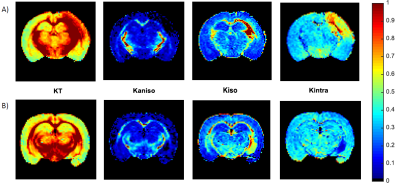
Fig.2 – Ex vivo CTI kurtosis measures for a representative slice of brain
specimens from the 3 h post-stroke (A) and sham (B) animal groups. From left to
right: panels A and B show the total kurtosis (KT), anisotropic kurtosis (Kaniso), isotropic kurtosis (Kiso) and intracompartmental
kurtosis (Kintra). KT and Kintra
reveal to have elevated contribution in both white and gray
matter in the ipsilesional hemisphere, where the infarct core is located.
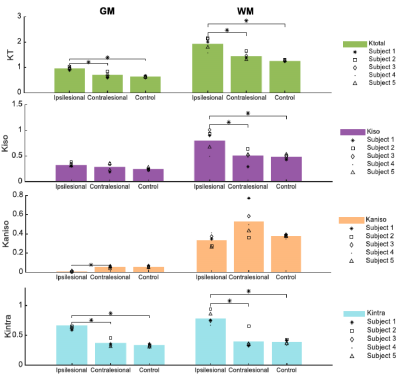
Fig.3 – Specificity analysis after
ANOVA (multiple comparisons) across different regions of interest (ROIs).
Different kurtosis sources are plotted along rows and each plot contains the
respective kurtosis source measure for the L1, R1 and counter control animal group
ipsilateral hemisphere, consecutively. Each column refers to only GM and only
WM, respectively (p < 0.05).
