Bhumi Bhusal1, Ehsan Kazemivalipour2, Jasmine Vu1, Stella LIn1, Bach Thanh Nguyen1, John Kirsch3, Elizabeth Nowac4, Julie Pilitsis5, Joshua Rosenow1, Ergin Atalar2, and Laleh Golestanirad1
1Northwestern University, Chicago, IL, United States, 2Bilkent University, Ankara, Turkey, 3Massachusetts General Hospital, Charlestown, MA, United States, 4Illinois Bone and Joint Institute, Wilmette, IL, United States, 5Albany Medical College, Albany, NY, United States
1Northwestern University, Chicago, IL, United States, 2Bilkent University, Ankara, Turkey, 3Massachusetts General Hospital, Charlestown, MA, United States, 4Illinois Bone and Joint Institute, Wilmette, IL, United States, 5Albany Medical College, Albany, NY, United States
The RF induced heating of patients with deep brain stimulation implants
during MRI can be significantly reduced using 1.2T vertical MRI scanner
compared to 1.5T horizontal scanner.
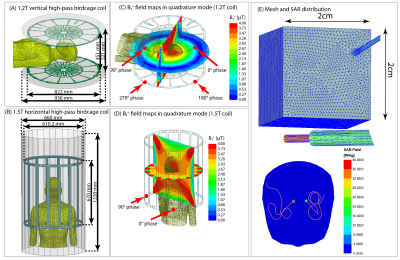
Figure
1: Geometry of (A) 1.2 T high-pass radial planar
birdcage coil and (B) 1.5 T high-pass birdcage coil. (C-D) B1+
field maps on the central coronal and axial planes passing through the human
body model with no implants. The input power of the coils is adjusted to
generate a mean B1+
= 4 μT on a circular axial plane passing through coil’s iso-center. (E) Example
of mesh distribution in the lead, insulation and SAR box. The distribution of
0.1g-SAR in a plane passing through the lead tip has also been shown for a
patient with bilateral leads.
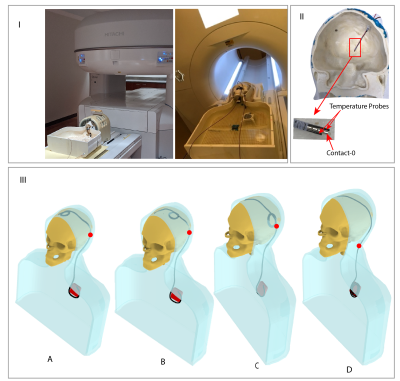
Figure
3: I Picture showing anthropomorphic
phantom in 1.2T vertical scanner (left)
an in 1.5T horizontal scanner (right). II DBS lead attached to temperature probes
implanted into the skull. III Schematic of phantom setup showing different
trajectories (A, B, C and D) with different loop position. The red dot represents the 40cm mark measured
from intracranial end, representing the end-point for 40 cm wire.
