Mark Velasquez1, Laurel Nelson1, Bonnie Lam1, Kevin Godines1, Soo Hyun Shin1, and Moriel Vandsburger1
1Department of Bioengineering, University of California, Berkeley, Berkeley, CA, United States
1Department of Bioengineering, University of California, Berkeley, Berkeley, CA, United States
Adeno-associated virus generates endogenous CEST contrast that can be quantified.
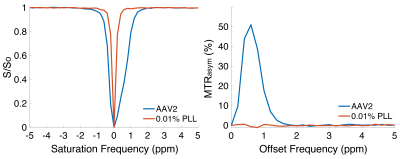
Figure 1. (Left) Representative Z-spectrum from AAV2 (5.25 x 108 viral genomes/μL) acquired at 800MHz using 5s continuous wave saturation at saturation power of 5.7μT demonstrates significant variation between 0 – 2ppm compared to background poly-L-Lysine (PLL) CEST contrast. (Right) CEST contrast derived from Z-spectra was quantified via MTRasym and showed substantial contrast between 0.6-0.8ppm in AAV2. The source is exchangeable hydroxyl protons on the capsid surface.
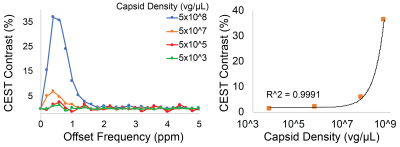
Figure 4. (Left) MTRasym spectra generated from Z-spectra acquired in phantoms containing varying capsid densities of AAV2, expressed as viral genomes per microliter, at pH 6.0 using saturation power of 6.3μT. (Right) CEST contrast demonstrated a correlation (contrast = 7*10-8* viral concentration + 1.9%) with capsid density.