Gustavo Chau Loo Kung1, Juliet Knowles2, Lijun Ni2, John Huguenard2, Michelle Monje2, and Jennifer McNab3
1Bioengineering Department, Stanford University, Stanford, CA, United States, 2Neurology Department, Stanford University, Stanford, CA, United States, 3Radiology Department, Stanford University, Stanford, CA, United States
1Bioengineering Department, Stanford University, Stanford, CA, United States, 2Neurology Department, Stanford University, Stanford, CA, United States, 3Radiology Department, Stanford University, Stanford, CA, United States
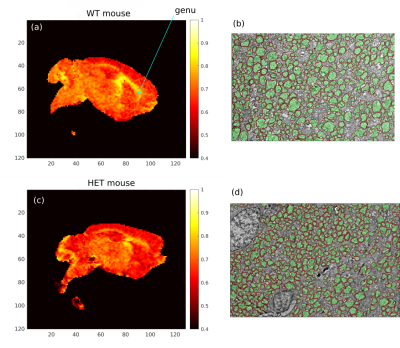
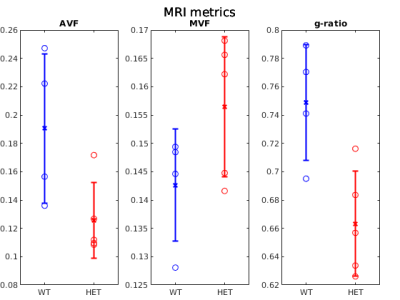
Our results on ex vivo mouse brains suggest a decrease in MRI derived g-ratios in the genu of the corpus callosum of a mouse model of absence epilepsy, in accordance with a similar decrease on ground truth EM measurements.